Arrays are important concepts in programming or scripting. Arrays allow us to store and retrieve elements in a list form which can be used for certain tasks. In bash, we also have arrays that help us in creating scripts in the command line for storing data in a list format. In this article, we will understand the basics of arrays in bash scripting.
Creating Arrays
To create a basic array in a bash script, we can use the declare -a command followed by the name of the array variable you would like to give.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
OR
#!/bin/usr/env bash
sport[0]=football
sport[1]=cricket
sport[2]=hockey
sport[3]=basketball
The value of the elements can be any integer or strings or any other form of data as desired. We can see that the array is declared in a bash script in two ways the former seems more convenient and less hectic to declare. If we want to declare the array in one go, the former is the optimum choice but if the elements are to be added in bits and pieces the latter is a good choice.
Printing the Arrays
After declaring the array, if we wanted to display all the elements in the array we can use the @ symbol.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
echo "${sport[@]}"

echo "${array_name[@]}"
We use the [@] as an index to the array to display all the elements. All the elements are printed with space-separated, The quotes around the variable expands and print all the elements in the array.
Iterating over the Array
To iterate over an array one element at a time, we can use loops and perform any operations within the body of it.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
for i in ${nums[@]}
do
echo -e "$i \n"
done

As we can see we have used a for loop to print the element from the array one by one. We have used the trick in the previous section of getting all the elements of the array and iterating over it one by one in the for a loop. The "${array_name[@]}" expands into all the elements in the array and the for loop iterates over them one by one with the iterator in the example it is the variable i, inside the body of the for loop we print the variable/iterator i and thus iterate over the array.
Get the number of elements in the Array
To fetch the number of the elements array we can use the # operator before the array name in the s in "${array_name[@]}".
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
echo "${#sport[@]}"

We thus return the size of the array by using the command "${#sport[@]}", the # is used to get the size of the variable next to it, using the double quotes the value of the command is evaluated and we get the number of the elements in the array as desired.
Inserting an element into Array
To insert an element is quite straightforward, we need to set the element's appropriate index followed by the value of the element you liked to give.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
echo "${sport[@]}"
sport[4]="dodgeball"
sport[2]="golf"
echo "${sport[@]}"
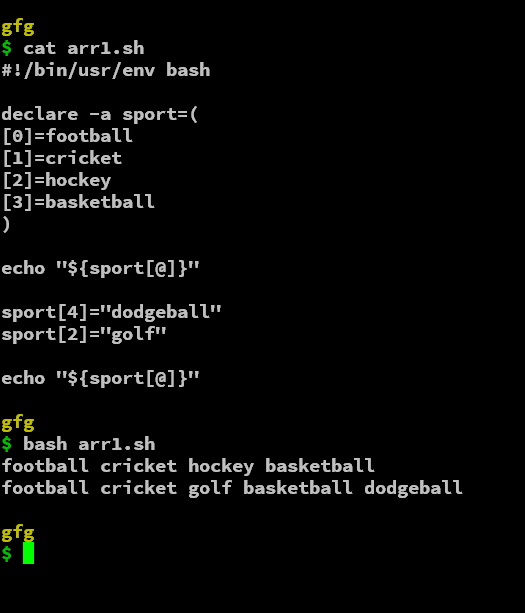
We have added the 5th element (4th index) into the array and also modified/edited the array's 3rd element(2nd index). The arrayname[index]=value is all the tricks to add, modify or initialize the elements of the array.
We can also add elements to an array using the += operator.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
echo "${sport[@]}"
sport+=("golf" "baseball")
echo "${sport[@]}"
echo "Size : ${#sport[@]}"

As seen in the example, we can add multiple elements to the array with minimal code. We use the array_name+=(elements) to append elements to the array.
Deleting an element from Array
To delete an element from the array, we can use the command unset. The command takes in the name of the variable in our case the array name and the index of that element. The index can also be relative i.e. -1 indicating the last element and -2 to second last and so on.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
unset sport[1]
echo "${sport[@]}"
echo "${#sport[@]}"

As we can see unset arrayname[index] will delete the element at index from the array. Also, the size of the array has been reduced to 3 from 4 which indicates that the element is entirely removed and not just replaced with whitespace.
Using relative indices
If we use indices like -1,-2, and so on, the elements are referenced from the last element, and hence we can delete or modify them with relative ordering from the back as well.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport=(
[0]=football
[1]=cricket
[2]=hockey
[3]=basketball
)
unset sport[-3]
echo "${sport[@]}"

As we can see index 1 is also referenced as -3 from the back and hence it becomes relatively easier to reference certain elements in a large array.
Splice an Array
We can splice(take out a potion) an array to take assign or print it to another variable/array.
#!/bin/usr/env bash
declare -a sport
sport+=("football" "cricket" "hockey" "basketball")
sport+=("golf" "baseball")
echo "sport = ${sport[@]}"
arr="${sport[@]:1:3}"
echo "arr = ${arr[@]}"

We have taken out a chunk from the sport array i.e. the element between index 1 and 3 inclusive and assigned it to the arr variable which is also an array. The @ operator gets all the elements from the array and then we can splice the array between indices 1 and 3 so that we have the elements at 1,2and 3 (cricket, hockey, and baseball) from the sport array.
Define a static array and print the elements of the array
#To declare static Array
programmingArray=(Java Python Ruby Perl)
#In below 2 ways we can print the elements of the static array
echo "Way 1 of printing static values by using <array>[@]:0 - " ${programmingarray[@]$
echo "Way 2 of printing static values by using <array>[*]:0 - " ${programmingarray[*]$ In 2ways we can print elements of static array
In 2ways we can print elements of static array
Program execution
sh <filename>
So, we can give as
sh arraycheck2.sh # arraycheck2.sh is the name of the script file here

Passing the command line arguments in a script file
#All the array elements are stored in an array called programmingArray
programmingArray=("$@")
#Index values start from 0
#If we do not specify the index, it will take up the size of first index value
echo "Size of programmingArray at 0th location..:" $(#programmingArray[0]}
echo "Size of programmingArray at 1st location..:" $(#programmingArray[1]}

The above script can be executed as
# Here Java, Python and Ruby are command line arguments
sh arrayCheck.sh Java Python Ruby
Script execution steps :
programmingArray=(Java Python Ruby)
#Java will be present at the 0th index, its size can be computed in the below way
${#programmingArray[0]}
Similarly, Python will be present at the 1st index, its size can be computed in the below way
${#programmingArray[1]}
Output:

Iterating the array values using for loop
$@ will give all the values that got passed via command-line arguments and it is stored in an array.
It can be iterated by using the "for" loop
declare -a programmingArray=("$@")
i=0
for programming in "$@"
do
echo "Array value at index " $i " : " $programming
i=$((i+1));
done

Output:

Let us take a quick look of what each and every symbol represent
|
Syntax
| Output |
| arr=() |
arr[0]=3 Overwrite 1st element
arr+=(4) Append value(s)
str=$(ls) Save ls output as a string
arr=( $(ls) ) Save ls output as an array of files
${arr[@]:s:n} Retrieve n elements starting at index
|
|
#We can provide set of values
like this
arr=(one two three)
| To initialize an array |
| ${arr[0]} | To retrieve the first element. Always index starts with 0 |
| ${arr[@]} | To retrieve all elements and thereupon we can iterate in a loop |
| ${!arr[@]} | To retrieve array indices alone |
| ${#arr[@]} | To calculate the size of an array |
| arr[2]=3 | To overwrite 3rd element we need to use it this way. As the index starts at 0, arr[2] is correct. |
| arr+=(40) | To append value(s), we can use + and then assign with = and hence += is used. |
| str=$(ls) | To save "ls" command output as a string(Example 4 is shown for this output) |
| arr=( $(ls) ) | To save "ls" output as an array of files(Example 5 is shown for this output) |
| ${arr[@]:s:n} | To retrieve "n" elements starting at index "s" |
Similar Reads
Linux/Unix Tutorial Linux is one of the most widely used open-source operating systems. It's fast, secure, stable, and powers everything from smartphones and servers to cloud platforms and IoT devices. Linux is especially popular among developers, system administrators, and DevOps professionals.Linux is:A Unix-like OS
10 min read
Getting Started with Linux
What is Linux Operating SystemLinux is based on the UNIX operating system. UNIX is a powerful, multi-user, multitasking operating system originally developed in the 1970s at AT&T Bell Labs. It laid the foundation for many modern operating systems, including Linux.Linux is free and open-source, accessible to everyone.Its sour
10 min read
LINUX Full Form - Lovable Intellect Not Using XPLINUX stands for Lovable Intellect Not Using XP. Linux was developed by Linus Torvalds and named after him. Linux is an open-source and community-developed operating system for computers, servers, mainframes, mobile devices, and embedded devices. Linux receives requests from system programs and it r
2 min read
Difference between Linux and WindowsLinux: Linux could be a free and open supply OS supported operating system standards. It provides programming interface still as programme compatible with operating system primarily based systems and provides giant selection applications. A UNIX operating system additionally contains several several
7 min read
What are Linux Distributions ?A Linux distribution, often shortened to “distro,†is a packaged version of Linux that comes with the Linux kernel plus a collection of software and utilities that make the OS functional and user-friendly. Some distros are optimized for business environments, offering tools for productivity and ente
8 min read
Difference between Unix and LinuxUnix was created in the 1970s by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs. Dennis Ritchie was also the creator of the C programming language. Originally a command-line operating system, Unix has evolved to support graphical interfaces (GUI) as well. It became popular in universities, enterprises
5 min read
Installation with Linux
How to Install Arch Linux in VirtualBox?Installing Arch Linux on a virtual machine is an excellent way to experience this powerful and flexible Linux distribution without affecting your main system. If you're looking to install Arch Linux in VirtualBox, this guide will take you through the process step-by-step. Arch Linux is known for its
7 min read
Fedora Linux Operating SystemFedora Linux is a free and open-source operating system based on the Linux kernel and was developed by the community-supported Fedora Project. It is known for its fast release cycle, which keeps the operating system up to date with the latest software and technologies.What is the Fedora Linux Operat
12 min read
How to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox?Installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox is a great way to experience the powerful features of this popular Linux distribution without altering your main operating system. Whether you’re a developer, a student, or simply curious about Linux, setting up Ubuntu on VirtualBox allows you to test and explore in a
6 min read
How to Install Linux Mint?Linux Mint is the second-largest Linux-based distro used in the world. Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu which itself is based on Debian and bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications. So here we discuss the installation of Linux mint. Installation
3 min read
How to Install Kali Linux on Windows?Kali Linux is an open-source Linux distribution based on Debian, designed for sophisticated penetration testing and security auditing. Kali Linux includes hundreds of tools for diverse information security activities such as penetration testing, security research, computer forensics, and reverse eng
2 min read
How to Install Linux on Windows PowerShell Subsystem?There are several ways to Install a Linux subsystem on your Windows PC Powershell Environment. It is good for learners, but it is recommended using original Linux OS if you are a developer as the Subsystem lacks the pre-installed Linux tools. Before we begin installing a Linux subsystem, we need to
2 min read
How to Find openSUSE Linux Version?openSUSE is well known for its GNU/Linux-based operating systems, mainly Tumbleweed, a tested rolling release, and Leap, a distribution with Long-Term-Support(LTS). MicroOS and Kubic are new transactional, self-contained distributions for use as desktop or container runtime. Here we figure out which
2 min read
How to Install CentOSCentOS is a popular open-source Linux distribution aimed at servers and provides compatibility with Red Hat's RPM package manager. It is built with the goal of providing a stable operating system that provided great compatibility with the upstream RHEL (Red hat enterprise Linux) CentOS is therefore
2 min read
Linux Commands
Linux CommandsLinux commands are essential for controlling and managing the system through the terminal. This terminal is similar to the command prompt in Windows. It’s important to note that Linux/Unix commands are case-sensitive. These commands are used for tasks like file handling, process management, user adm
15+ min read
Essential Unix CommandsUnix commands are a set of commands that are used to interact with the Unix operating system. Unix is a powerful, multi-user, multi-tasking operating system that was developed in the 1960s by Bell Labs. Unix commands are entered at the command prompt in a terminal window, and they allow users to per
7 min read
How to Find a File in Linux | Find CommandThe find command in Linux is used to search for files and directories based on name, type, size, date, or other conditions. It scans the specified directory and its sub directories to locate files matching the given criteria.find command uses are:Search based on modification time (e.g., files edited
9 min read
Linux File System
Linux File SystemA file system is a structured method of storing and managing data—including files, directories, and metadata—on your machine. Think of it like a library. If thousands of books were scattered around, finding one would be hard. But in an organized structure, like labeled shelves, locating a book becom
12 min read
Linux File Hierarchy StructureThe Linux File Hierarchy Structure or the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) defines the directory structure and directory contents in Unix-like operating systems. It is maintained by the Linux Foundation. In the FHS, all files and directories appear under the root directory /, even if they are sto
6 min read
Linux Directory StructureIn Linux, everything is treated as a file even if it is a normal file, a directory, or even a device such as a printer or keyboard. All the directories and files are stored under one root directory which is represented by a forward slash /. The Linux directory layout follows the Filesystem Hierarchy
6 min read
Linux Kernel
Linux KernelLinux Kernel is the heart of Linux operating systems. It is an open-source (source code that can be used by anyone freely) software that is most popular and widely used in the industry as well as on a personal use basis. Who created Linux and why? Linux was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 as a hob
4 min read
Kernel in Operating SystemA kernel is the core part of an operating system. It acts as a bridge between software applications and the hardware of a computer. The kernel manages system resources, such as the CPU, memory and devices, ensuring everything works together smoothly and efficiently. It handles tasks like running pro
9 min read
How Linux Kernel Boots?Many processes are running in the background when we press the system's power button. It is very important to learn the Linux boot process to understand the workings of any operating system. Knowing how the kernel boots is a must to solve the booting error. It is a very interesting topic to learn, l
11 min read
Difference between Operating System and KernelIn the world of computing, two terms that are frequently mentioned are Operating System (OS) and Kernel. In this article, we will explore the key differences between the OS and the Kernel, their functions, and how they work together to manage hardware and software.What is an Operating System?An Oper
3 min read
Linux Kernel Module Programming: Hello World ProgramKernel modules are pieces of code that can be loaded and unloaded into the kernel upon demand. They extend the functionality of the kernel without the need to reboot the system. Custom codes can be added to Linux kernels via two methods. The basic way is to add the code to the kernel source tree and
7 min read
Linux Loadable Kernel ModuleIf you want to add code to a Linux kit, the basic way to do that is to add source files to the kernel source tree and assemble the kernel. In fact, the process of setting up the kernel consists mainly of selecting which files to upload to the kernel will be merged. But you can also add code to the L
7 min read
Loadable Kernel Module - Linux Device Driver DevelopmentFor Linux device drivers, we can use only two languages: Assembler and C. Assembler implements the main parts of the Linux kernel, while C implements the architecture-dependent parts. Uploaded kernel modules are often referred to as kernel modules or modules, but those are misleading names because t
4 min read
Linux Networking Tools
Network configuration and troubleshooting commands in LinuxComputers are often connected to each other on a network. They send requests to each other in the form of packets that travel from the host to the destination. Linux provides various commands from network configuration and troubleshooting. Network Configuration and Troubleshooting Commands in Linux
5 min read
How to configure network interfaces in CentOS?A network interface is a link between a computer and another network(Private or Public). The network interface is basically a card which is known as NIC or Network Interface Card, this does not necessarily have to be in a physical form instead, it can be inbuilt into the software. If we take the exa
5 min read
Command-Line Tools and Utilities For Network Management in LinuxIf you are thinking of becoming a system administrator, or you are already a system admin, then this article is for you.As a system admin, your daily routine will include configuring, maintaining, troubleshooting, monitoring, securing networks, and managing servers within data centers. Network confi
8 min read
Linux - Network Monitoring ToolsNetwork monitoring is using a system (hardware or software) that continuously observes your network and the data flows through it, depending on how the monitoring solution actually functions and informs the network administrator. We can keep a check on all the activities of our network easily. While
4 min read
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting
Introduction to Linux Shell and Shell ScriptingWhenever we use any modern operating system like Linux, macOS, or Windows we are indirectly interacting with a shell, the program that interprets and executes our commands. While running Ubuntu, Linux Mint, or any other Linux distribution, we are interacting with the shell by using the terminal. In
8 min read
What is Terminal, Console, Shell and Kernel?Understanding the terms terminal, console, shell, and kernel is crucial for anyone working with computers or learning about operating systems. These concepts are key components of how we interact with our devices and software. The terminal is a text-based interface used to interact with the computer
5 min read
How to Create a Shell Script in linuxShell is an interface of the operating system. It accepts commands from users and interprets them to the operating system. If you want to run a bunch of commands together, you can do so by creating a shell script. Shell scripts are very useful if you need to do a task routinely, like taking a backup
7 min read
Shell Scripting - Different types of VariablesThe shell is a command-line interpreter for Linux and Unix systems. It provides an interface between the user and the kernel and executes commands. A sequence of commands can be written in a file for execution in the shell. It is called shell scripting. It helps to automate tasks in Linux. Scripting
4 min read
Bash Scripting - Introduction to Bash and Bash ScriptingBash is a command-line interpreter or Unix Shell and it is widely used in GNU/Linux Operating System. It is written by Brian Jhan Fox. It is used as a default login shell for most Linux distributions. Scripting is used to automate the execution of the tasks so that humans do not need to perform them
12 min read
Bash Script - Define Bash Variables and its typesVariables are an important aspect of any programming language. Without variables, you will not be able to store any required data. With the help of variables, data is stored at a particular memory address and then it can be accessed as well as modified when required. In other words, variables let yo
12 min read
Shell Scripting - Shell VariablesA shell variable is a character string in a shell that stores some value. It could be an integer, filename, string, or some shell command itself. Basically, it is a pointer to the actual data stored in memory. We have a few rules that have to be followed while writing variables in the script (which
6 min read
Bash Script - Difference between Bash Script and Shell ScriptIn computer programming, a script is defined as a sequence of instructions that is executed by another program. A shell is a command-line interpreter of Linux which provides an interface between the user and the kernel system and executes a sequence of instructions called commands. A shell is capabl
4 min read
Shell Scripting - Difference between Korn Shell and Bash shellKorn Shell: Korn Shell or KSH was developed by a person named David Korn, which attempts to integrate the features of other shells like C shell, Bourne Shell, etc. Korn Shell allows developers to generate and create new shell commands whenever it is required. Korn shell was developed a long year bac
3 min read
Shell Scripting - Interactive and Non-Interactive ShellA shell gives us an interface to the Unix system. While using an operating system, we indirectly interact with the shell. On Linux distribution systems, each time we use a terminal, we interact with the shell. The job of the shell is to interpret or analyze the Unix commands given by users. A shell
3 min read
Shell Script to Show the Difference Between echo “$SHELL†and echo ‘$SHELL’In shell scripting and Linux, the echo command is used to display text on the terminal or console. When used with the $SHELL variable, which contains the path of the current user's shell program, the output of the echo command can be different depending on whether the variable is enclosed in single
4 min read