Spring Boot - Creating docker image using Gradle
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Spring boot is a backed-end framework used for developing stand-alone Java applications rapidly. It minimizes configuration so developers can focus only on developing business logic.
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform designed for developing, transporting, and strolling applications. Docker has containers that's a standalone, executable packages that include everything that has to run a chunk of software program, along with the code, runtime, libraries, and gadget tools. A docker image is a blueprint for creating packing containers. It consists of the software code and all its dependencies, as well as the runtime, machine equipment, and libraries.
In this article, we can learn how to dockerize our Spring boot software built on Gradle.
Prerequisite
If you need to learn how to create a Spring boot application or need to research extra about Docker check below articles:
Steps for creating a docker image using Gradle in Spring Boot
Step 1: Create Spring Boot Application
In your web browser visit start.spring.io and create a Spring Boot project with the following configurations,
- Project: Gradle - Groovy
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 3.2.1
- Packaging: Jar
- Java: 17
- Dependencies: Spring Web
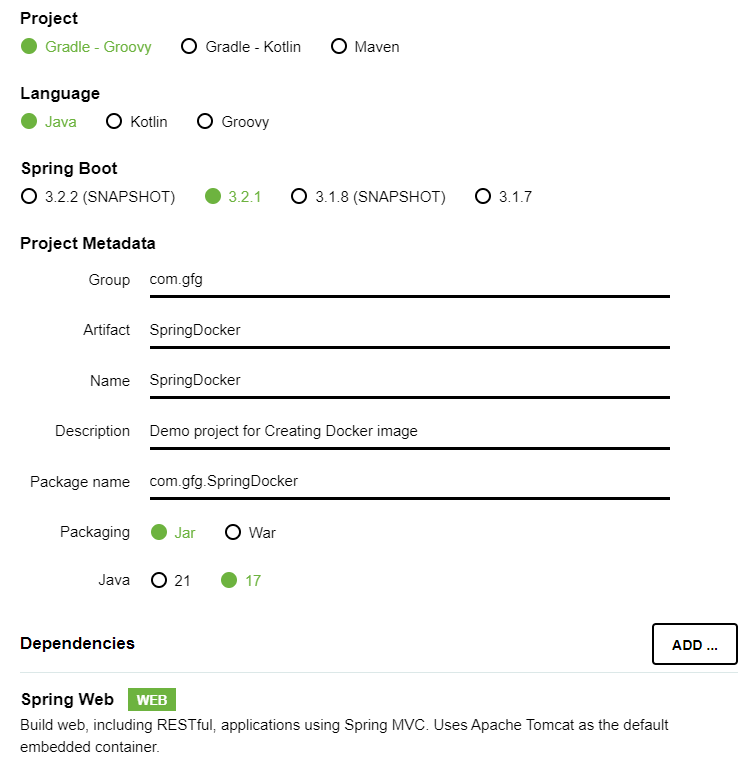
Click on Generate and download the project, after it finishes download, Open with any IDE of your choice and wait for some time untill it finishes the configuration and indexing.
Here is the gradle.build file for reference:
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.1'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.4'
}
group = 'com.gfg'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
java {
sourceCompatibility = '17'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}Step 2: Create a Controller
Now for the time being, create a REST controller just to display "Hello World" when requested.

Inside com.gfg.SpringDocker let's create a new class name HelloController
HelloController.java:
Java
package com.gfg.SpringDocker;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello") public String getMessage()
{
return "Hello World!";
}
}
Let's quickly run this and check if it's working.
.png)
On the web browser type localhost:8080/hello and check if we are getting the output from the REST controller.

Step 3: Create and Configure Docker File
In your project create a file and name it as "Dockerfile" where we will write docker configurations. Right click on the SpringDocker package and select New, then click on File and name it.

Check the folder structure now,

Inside your Dockerfile write,
FROM openjdk:17
ARG JAR_FILE=build/libs/*.jar
COPY ${JAR_FILE} app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]
FROM openjdk:17: This line specifies the base picture for the Docker image. In this case, it's using the OpenJDK 17 base image.
ARG JAR_FILE=construct/libs/*.Jar: This argument is used to specify the direction to the JAR report so as to be copied into the Docker image. The *.Jar suggests that any JAR file in the particular listing might be taken into consideration.
COPY $JAR_FILE app.Jar: This line copies the JAR file distinct with the aid of the JAR_FILE argument from the construct context into the Docker image.
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.Jar"]: This line sets the default command to be carried out whilst the Docker field starts off evolved. It specifies that the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) have to run the JAR report (app.Jar) the use of the -jar option.
If you have no .Jar document in buid/libs folder attempt executing the subsequent command on Terminal.
./gradlew build

Below is the build folder:

Step 4: Create Docker image
Get the Docker desktop installed from docker.com/products/docker-desktop if you don't have it installed in your computer.
Open terminal in your project directory and execute the following commands.
docker image build -t app .
This command will initiate the docker image build. The -t flag allows you to specify a name and optionally a tag for the image. The dot at the end specifies that the Dockerfile and other necessary files for building the image are located in the current directory.

Now to check the docker image created and its details run the following command:
docker images
This will help you get the IMAGE ID.

Otherwise, you can use the Docker Desktop Application to check and run your application.

Step 5: Run Docker Container
Now, to run the docker image enter the following command, otherwise use the start button on the Docker Desktop.
docker run -d IMAGE_ID
docker run command is used to run a Docker container and -d stands for "detach." It runs the container in the background, and the terminal is freed up for in addition commands. Update the IMAGE_ID with your docker image identification from that you want to run the container.

Below we can see the docker desktop:

Let's check the log in Docker Desktop App if it's running on the default port no 8080.

Step 6: Check Output
Let's go to port no 8080 on our local host without running the Spring Boot aplication through IDE, You should be able to see the "Hello World" text which is coming from the application running on the Docker Container.

Now you can build your Spring boot application and create a Docker image of the same and send it out or run efficiently with simple commands or using Docker Desktop. This simplifies the deployment process, as containers can be easily distributed and executed on any platform supporting Docker.
Similar Reads
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
Spring Boot Basics and Prerequisites
Introduction to Spring BootSpring is one of the most popular frameworks for building enterprise applications, but traditional Spring projects require heavy XML configuration, making them complex for beginners.Spring Boot solves this problem by providing a ready-to-use, production-grade framework on top of Spring. It eliminate
4 min read
Difference between Spring and Spring BootSpring Spring is an open-source lightweight framework that allows Java developers to build simple, reliable, and scalable enterprise applications. This framework mainly focuses on providing various ways to help you manage your business objects. It made the development of Web applications much easier
4 min read
Spring - Understanding Inversion of Control with ExampleSpring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container is the core of the Spring Framework. It creates and manages objects (beans), injects dependencies and manages their life cycles. It uses Dependency Injection (DI), based on configurations from XML files, Java-based configuration, annotations or POJOs. Sinc
6 min read
Spring - IoC ContainerThe Spring framework is a powerful framework for building Java applications. It can be considered a collection of sub-frameworks, also referred to as layers, such as Spring AOP, Spring ORM, Spring Web Flow, and Spring Web MVC. We can use any of these modules separately while constructing a Web appli
2 min read
BeanFactory vs ApplicationContext in SpringThe Spring Framework provides two core packages that enable Inversion of Control (IoC) and Dependency Injection (DI):org.springframework.beansorg.springframework.contextThese packages define Spring containers that manage the lifecycle and dependencies of beans.Spring offers two main containers1. Bea
6 min read
Spring Boot Core
Spring Boot - ArchitectureSpring Boot is built on top of the Spring Framework and follows a layered architecture. Its primary goal is to simplify application development by providing auto-configuration, embedded servers and a production-ready environment out of the box.The architecture of Spring Boot can be divided into seve
2 min read
Spring Boot - AnnotationsAnnotations in Spring Boot are metadata that simplify configuration and development. Instead of XML, annotations are used to define beans, inject dependencies and create REST endpoints. They reduce boilerplate code and make building applications faster and easier. Core Spring Boot Annotations 1. @Sp
5 min read
Spring Boot ActuatorDeveloping and managing an application are the two most important aspects of the application’s life cycle. It is very important to know what is going on beneath the application. Also, when we push the application into production, managing it gradually becomes critically important. Therefore, it is a
5 min read
How to create a basic application in Java Spring BootSpring Boot is the most popular Java framework that is used for developing RESTful web applications. In this article, we will see how to create a basic Spring Boot application.Spring Initializr is a web-based tool using which we can easily generate the structure of the Spring Boot project. It also p
3 min read
Spring Boot - Code StructureThere is no specific layout or code structure for Spring Boot Projects. However, there are some best practices followed by developers that will help us too. You can divide your project into layers like service layer, entity layer, repository layer,, etc. You can also divide the project into modules.
3 min read
Spring Boot - SchedulingSpring Boot provides the ability to schedule tasks for execution at a given time period with the help of @Scheduled annotation. This article provides a step by step guideline on how we can schedule tasks to run in a spring boot application Implementation:It is depicted below stepwise as follows:Â St
4 min read
Spring Boot - LoggingLogging in Spring Boot plays a vital role in Spring Boot applications for recording information, actions, and events within the app. It is also used for monitoring the performance of an application, understanding the behavior of the application, and recognizing the issues within the application. Spr
8 min read
Exception Handling in Spring BootException handling in Spring Boot helps deal with errors and exceptions present in APIs, delivering a robust enterprise application. This article covers various ways in which exceptions can be handled and how to return meaningful error responses to the client in a Spring Boot Project. Key Approaches
8 min read
Spring Boot with REST API
Spring Boot - Introduction to RESTful Web ServicesRESTful Web Services REST stands for REpresentational State Transfer. It was developed by Roy Thomas Fielding, one of the principal authors of the web protocol HTTP. Consequently, REST was an architectural approach designed to make the optimum use of the HTTP protocol. It uses the concepts and verbs
5 min read
Spring Boot - REST ExampleIn modern web development, most applications follow the Client-Server Architecture. The Client (frontend) interacts with the server (backend) to fetch or save data. This communication happens using the HTTP protocol. On the server, we expose a bunch of services that are accessible via the HTTP proto
4 min read
How to Create a REST API using Java Spring Boot?Representational State Transfer (REST) is a software architectural style that defines a set of constraints for creating web services. RESTful web services allow systems to access and manipulate web resources through a uniform and predefined set of stateless operations. Unlike SOAP, which exposes its
4 min read
How to Make a Simple RestController in Spring Boot?A RestController in Spring Boot is a specialized controller that is used to develop RESTful web services. It is marked with the @RestController annotation, which combines @Controller and @ResponseBody. This ensures that the response is automatically converted into JSON or XML, eliminating the need f
2 min read
JSON using Jackson in REST API Implementation with Spring BootWhen we build REST APIs with Spring Boot, we need to exclude NULL values from the JSON responses. This is useful when we want to optimize the data being transferred, making the response more compact and easier to process for the client.In this article, we are going to learn the approach that is used
4 min read
Spring Boot with Database and Data JPA
Spring Boot with Kafka
Spring Boot Kafka Producer ExampleSpring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Spring Boot Kafka Consumer ExampleSpring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to consume JSON messages using Apache KafkaApache Kafka is a stream processing system that lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to publish JSON messages on the console of a Spring boot application using Apache Kafka. In order to learn how to create a Spring Boot project, refer
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to consume string messages using Apache KafkaApache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging queue used for real-time streams of data. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article we will see how to send string messages from apache kafka to the console of a spring boot application. Appro
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to publish String messages on Apache KafkaApache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to send string messages to Apache Kafka in a spring boot application. In order to learn how to create a spring boot project, r
2 min read
Spring Boot | How to publish JSON messages on Apache KafkaApache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to send JSON messages to Apache Kafka in a spring boot application. In order to learn how to create a spring boot project, ref
4 min read
Spring Boot with AOP
Spring Boot - AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)The Java applications are developed in multiple layers, to increase security, separate business logic, persistence logic, etc. A typical Java application has three layers namely they are Web layer, the Business layer, and the Data layer. Web layer: This layer is used to provide the services to the e
4 min read
How to Implement AOP in Spring Boot Application?AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) breaks the full program into different smaller units. In numerous situations, we need to log, and audit the details as well as need to pay importance to declarative transactions, security, caching, etc., Let us see the key terminologies of AOP Aspect: It has a set of
10 min read
Spring Boot - Difference Between AOP and OOPAOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming) complements OOP by enabling modularity of cross-cutting concerns. The Key unit of Modularity(breaking of code into different modules) in Aspect-Oriented Programming is Aspect. one of the major advantages of AOP is that it allows developers to concentrate on business
3 min read
Spring Boot - Difference Between AOP and AspectJSpring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read
Spring Boot - Cache ProviderThe Spring Framework provides support for transparently adding caching to an application. The Cache provider gives authorization to programmers to configure cache explicitly in an application. It incorporates various cache providers such as EhCache, Redis, Guava, Caffeine, etc. It keeps frequently a
6 min read