Basics of pointer, pointer expressions, pointer to pointer and pointer in functions
- 1. Introduction to Pointers • A Pointer is a derived data type in ‘C’ . • It is built from one of the fundamental data types available in ‘C’ . • Pointers contain the memory addresses as their values . • Memory addresses, being the location of computer memory, can be accessed & used to store data via pointers .
- 2. Understanding Pointers • During the whole program execution the variable num is associated with the address 6843. This value of address, being a simple integer, can bee stored in another variable which is called pointer. • Pointer, again, is stored in some another memory location 6894 which too is accessible. • The link between address & value of variable can be visualized with the help of pointer in figure.
- 3. The term instructs the system to find a location for integer variable ‘a’ and assign 100 value in that location. Pointers, on the other side, spot the address or location area of the variable and not directly on the intermediate value of that variable. The coding… …reflects how to declare a pointer variable. 1. Using asterisk ‘*’ with the data type before the variable name declares it as a ‘pointer’ . 2. The address operator ‘&’ assigns the address of the specified variable to the pointer variable. 3. Variable that hasn’t been assigned any value may contain garbage and make the pointer point to unknown locations.
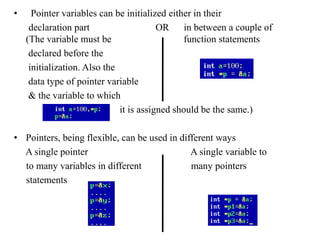
- 4. • Pointer variables can be initialized either in their declaration part OR in between a couple of (The variable must be function statements declared before the initialization. Also the data type of pointer variable & the variable to which it is assigned should be the same.) • Pointers, being flexible, can be used in different ways A single pointer A single variable to to many variables in different many pointers statements
- 5. • Pointers may be used to assign a value to a variable based on the other one like… …assigns 223 to ‘n’ in two ways 1. By using the pointer to extract the value stored in ‘a’ . 2. By directly using the address of ‘a’ . NOTE : A value stored in address 4243 or any other can’t be accessed by ‘ *4243 ‘ .
- 6. 6 Understanding Pointers by Examples x : 4892 ip : 4904 int x = 70, y = 80, z[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40 }; int *ip; // int pointer ip ip = &x; // ip is assigned to address of x *ip = 200; // content of ip is assigned to 200 y = *ip; // y is assigned to content of ip ip = &z[2]; *ip = *ip + 20; // same as *ip += 20; y = *ip+1; y : 4894 Z, Z[0] : 4896 Z[1] : 4898 Z[2] : 4900 Z[3] : 4902 200 70 200 80 51 10 20 30 50 40 ???? 4892 4900
- 7. Pointer to Pointer • Pointer itself are variables whose locations are specifies on memory and their storage address too can be known by assigning a pointer. • We can access a target value indirectly pointed to by a pointer by applying the indirection operator or the asterisk mark twice. … ‘a’ is assigned a value ‘100’ and it’s location stored in ‘p1’ whose location in turn is stored in ‘p2’ . ‘*p1’ refers to ‘100’ so does ‘**p2’ . • REMEMBER to assign similar data types to chain pointing variables.
- 8. Pointer Expressions • Arithmetic operations between two or more pointer is not possible. • But pointers can be used to perform arithmetic operations on the value they point to. e.g.: …same as ((*p1) * (*p2)) / (*p3) …same as (10 * (-(*p3))) / (*p2) Note to keep a space between / and * to not to make compiler interpret it to be a comment. • Pointer incrementation is valid in ‘C’ . e.g.: p++; OR p=p1+2; are valid statements . • A pointer, when incremented, it increases it’s value by the length of the data type it points to. 1. characters – 1 byte 3. Float – 4 bytes 2. integer – 2 bytes 4. double – 8 bytes
- 9. Illustration Of ‘Pointer to Pointer’ + ‘Expressions using Pointer’ 1. int a,b,c,*p,**q; 2. a=10; 3. b=20; 4. c=30; 5. printf(“%d %d %d”,a,b,c); 6. p=&a; 7. q=&p; 8. b=b/ (( *p * **q ) / 10); 9. c=c+ ( 2 * *p) - **q; 10. printf(“n%d %d %d”,a,b,c); Output: 10 20 30 10 2 40 b= 20/ ( ( ( value indicated by pointer p) * ( value indicated by chain pointer q ) ) / 10 ) c=30 + (2 * (value indicated by pointer p) ) - ( value indicated by chain pointer q )
- 10. Pointer & Arrays • The compiler, by default, allocates sufficient amount of storage to contain all elements when an array is declared. • These memory locations are contiguous as shown below. Elements Value Address a[0] a[1] a[2] a[3] a[4] 31 24 43 6 13 1030 1032 1034 1036 1038 • The memory address increases by the bits of data the data type of the variable occupies.
- 11. • These memory locations, being contiguous, can be used by pointers to access the exact locations of any specific variable of an array. E.g. :- int a[5],*p; p=a; /* by default p is the address of a[0] */ p+1=4; /* assigning ‘4’ to a[1], shown by ‘p+1’ */ p+2=12; /* assigning ‘12’ to a[3], shown by ‘p+2’ */ p+3=10; /* assigning ‘10’ to a[2], shown by ‘p+3’ */ • Also a[1], a[2],etc. can be directly referred by using *(p+1), *(p+2), etc. Pointer & Arrays
- 12. Examples of ‘Arithmetic Operation On Pointer’ as well as ‘Pointers & Arrays’ float a[4]; float *ptr; ptr = &(a[2]); *ptr = 3.14; ptr++; *ptr = 9.0; ptr = ptr - 3; *ptr = 6.0; ptr += 2; *ptr = 7.0; Data Table Name Type Description Value a[0] float float array element (variable) ? a[1] float float array element (variable) ? a[2] float float array element (variable) ? a[3] float float array element (variable) ? ptr float * float pointer variable *ptr float de-reference of float pointer variable 3.14 7.0 address of a[2] 3.14 ? 3] 9.0 9.0 0] 6.0 6.0 7.0
- 13. Pointer & Functions : Pointer as function arguments • By using pointer as parameter, addresses of variables is passed to the called function. This process of calling a function to pass address of variables is called ‘Call By Reference’ OR ‘Pass By Pointers’ . • The function called by ‘reference’ can change the value of the variable used in the call. • E.g. :- The function value() receives the address of variable a & not the value. Inside value(), a is pointer & therefore it increments the value of variable a by 50. OUTPUT : 70
- 14. Pointer & Functions : Function Returning • As pointers are a data type in ‘C’ , a function can return a pointer to the calling function. • E.g. :- The coding aside shows the function addvalue() receiving address of a as a parameter. It increments the value stored in the address of a & then returns that specific address to the calling function, which is then assigned to pointer variable p. OUTPUT :- 40 Pointers
- 15. Pointer & Functions : Pointers to Functions • Function too has an address location as well as a type in the memory. So, it is thereby possible to use pointer to point to a specific function, which can then be used as argument in another function. • The declaration of pointer to a function takes place as follows: data_type (*pointer_name) (data); Here, the data type specifies must be the same the function, which the pointer points to, is going to return. Moreover a pointer can be assigned to a function by simply equating the pointer name to the name of the function. e.g. :- float add(int, int); float (*p) (int, int); p=add; A function can also be called using pointer like :- (*p)(a,b); /* equivalent to [ add(x,y); ] */
- 16. Pointer & Functions : Pointers to Functions • An Illustration to add two integral numbers :- #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<stdlib.h> int (*p)(int, int); /*declaration of function pointer ‘p’ which points function ‘add ‘*/ void print(int (*p)(int, int)); /* declaration of function ‘print’ */ int add(int, int); /* declaration of function ‘add’ */ void main() { p=add; /* initializing pointer */ print(p); /* calling function ‘print’ which receives the address of function ‘add’ through pointer ‘p’ */ } /* Continued */
- 17. Pointer & Functions : Pointers to Functions • An Illustration to add two integral numbers (continued) :- OUTPUT void printf(int (*p)(int, int)) { int a,b; scanf(“%d %d”,&a,&b); printf(“n%d”,(*p)(a,b)); /* passes values of ‘a’ & ‘b’ to ‘add’ through ‘p’ */ } int add(int a, int b) { return(a+b); /* adds ‘a’ & ‘b’ */ } /* program over */ 30 50 80
- 18. Uses of Pointers i. Pointers can be used to return multiple values from a function via function arguments . ii. They prove to be an efficient tool for manipulating dynamic data structures such as Linked Lists, Queens, Stacks & Trees. iii. They reduce the program execution speed as well as their altitude of complexity . iv. Pointers save a lot of data storage space in memory when used with character strings
- 19. Pitfalls Of Pointer • Since Pointer holds addresses of memory location, it must never be used without proper initialization. • An uninitialized pointer may hold addresses of some memory location that is protected by the Operating System. In such cases, de-referencing a pointer may crash the program. • Pointer can’t track the boundaries of an array.





![6
Understanding Pointers by Examples
x : 4892
ip : 4904
int x = 70, y = 80, z[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40 };
int *ip; // int pointer ip
ip = &x; // ip is assigned to address of x
*ip = 200; // content of ip is assigned to 200
y = *ip; // y is assigned to content of ip
ip = &z[2];
*ip = *ip + 20; // same as *ip += 20;
y = *ip+1;
y : 4894
Z, Z[0] : 4896
Z[1] : 4898
Z[2] : 4900
Z[3] : 4902
200
70
200
80
51
10
20
30
50
40
????
4892
4900](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofpointerpointerexpressionspointertopointerandpointerinfunctions-141103051914-conversion-gate01/85/Basics-of-pointer-pointer-expressions-pointer-to-pointer-and-pointer-in-functions-6-320.jpg)



![Pointer & Arrays
• The compiler, by default, allocates sufficient amount of storage to
contain all elements when an array is declared.
• These memory locations are contiguous as shown below.
Elements
Value
Address
a[0] a[1] a[2] a[3] a[4]
31 24 43 6 13
1030 1032 1034 1036 1038
• The memory address increases by the bits of data the data type of
the variable occupies.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofpointerpointerexpressionspointertopointerandpointerinfunctions-141103051914-conversion-gate01/85/Basics-of-pointer-pointer-expressions-pointer-to-pointer-and-pointer-in-functions-10-320.jpg)
![• These memory locations, being contiguous, can be used by pointers
to access the exact locations of any specific variable of an array.
E.g. :-
int a[5],*p;
p=a; /* by default p is the address of a[0] */
p+1=4; /* assigning ‘4’ to a[1], shown by ‘p+1’ */
p+2=12; /* assigning ‘12’ to a[3], shown by ‘p+2’ */
p+3=10; /* assigning ‘10’ to a[2], shown by ‘p+3’ */
• Also a[1], a[2],etc. can be directly referred by using *(p+1), *(p+2),
etc.
Pointer & Arrays](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofpointerpointerexpressionspointertopointerandpointerinfunctions-141103051914-conversion-gate01/85/Basics-of-pointer-pointer-expressions-pointer-to-pointer-and-pointer-in-functions-11-320.jpg)
![Examples of ‘Arithmetic Operation On Pointer’
as well as ‘Pointers & Arrays’
float a[4];
float *ptr;
ptr = &(a[2]);
*ptr = 3.14;
ptr++;
*ptr = 9.0;
ptr = ptr - 3;
*ptr = 6.0;
ptr += 2;
*ptr = 7.0;
Data Table
Name Type Description Value
a[0] float float array element (variable) ?
a[1] float float array element (variable) ?
a[2] float float array element (variable) ?
a[3] float float array element (variable) ?
ptr float * float pointer variable
*ptr float de-reference of float pointer
variable
3.14
7.0
address of a[2]
3.14
?
3]
9.0
9.0
0]
6.0
6.0
7.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofpointerpointerexpressionspointertopointerandpointerinfunctions-141103051914-conversion-gate01/85/Basics-of-pointer-pointer-expressions-pointer-to-pointer-and-pointer-in-functions-12-320.jpg)


![Pointer & Functions : Pointers to Functions
• Function too has an address location as well as a type in the memory. So, it
is thereby possible to use pointer to point to a specific function, which can
then be used as argument in another function.
• The declaration of pointer to a function takes place as follows:
data_type (*pointer_name) (data);
Here, the data type specifies must be the same the function, which the
pointer points to, is going to return.
Moreover a pointer can be assigned to a function by simply equating the
pointer name to the name of the function.
e.g. :-
float add(int, int);
float (*p) (int, int);
p=add;
A function can also be called using pointer like :-
(*p)(a,b); /* equivalent to [ add(x,y); ] */](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofpointerpointerexpressionspointertopointerandpointerinfunctions-141103051914-conversion-gate01/85/Basics-of-pointer-pointer-expressions-pointer-to-pointer-and-pointer-in-functions-15-320.jpg)



