Introduction to programming using c
- 1. Introduction to programming using C# Eng. Reham M. El-Safarini
- 2. •Outline: 2 History. About C# Language. .NET Framework Platform Architecture. C# built-In types. Namespace & Nested Namespace. Object Oriented. Visual Studio installation. Hello world – First application. Lab work.
- 3. •History In concurrence with the success of java programming language, the idea of new programming language starts to be under construction and it’s called C#. C# is simple managed C (SMC) compiler system unlike the C/C++ unmanaged language. C# means musical note such as C/C++. C# is an object oriented programming language which means it’s class based and developer can apply relations such as Inheritance , Encapsulation and Polymorphism. It was released in 2000 and the project called .NET framework 3
- 4. •About C# Language 4 C# syntax is highly expressive, yet it is also simple and easy to learn. The curly-brace syntax of C# will be instantly recognizable to anyone familiar with C, C++ or Java. Developers who know any of these languages are typically able to begin to work productively in C# within a very short time. C# syntax simplifies many of the complexities of C++ and provides powerful features such as nullable value types, enumerations, delegates, lambda expressions and direct memory access, which are not found in Java. C# supports generic methods and types, which provide increased type safety and performance, and iterators, which enable implementers of collection classes to define custom iteration behaviors that are simple to use by client code.
- 5. •About C# Language-Cont. 5 Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) expressions make the strongly-typed query a first-class language construct. As an object-oriented language, C# supports the concepts of encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. All variables and methods, including the Main method, the application's entry point, are encapsulated within class definitions. A class may inherit directly from one parent class, but it may implement any number of interfaces. Methods that override virtual methods in a parent class require the override keyword as a way to avoid accidental redefinition. In C#, a struct is like a lightweight class; it is a stack-allocated type that can implement interfaces but does not support inheritance. In addition to these basic object-oriented principles, C# makes it easy to develop software components through several innovative language constructs, including the following:
- 6. •About C# Language-Cont. 6 Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) which provides built-in query capabilities across a variety of data sources. If you have to interact with other Windows software such as COM objects or native Win32 DLLs, you can do this in C# through a process called "Interop." Interop enables C# programs to do almost anything that a native C++ application can do. C# even supports pointers and the concept of "unsafe" code for those cases in which direct memory access is absolutely critical. The C# build process is simple compared to C and C++ and more flexible than in Java. There are no separate header files, and no requirement that methods and types be declared in a particular order. A C# source file may define any number of classes, structs, interfaces, and events.
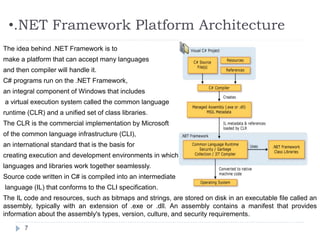
- 7. •.NET Framework Platform Architecture 7 The idea behind .NET Framework is to make a platform that can accept many languages and then compiler will handle it. C# programs run on the .NET Framework, an integral component of Windows that includes a virtual execution system called the common language runtime (CLR) and a unified set of class libraries. The CLR is the commercial implementation by Microsoft of the common language infrastructure (CLI), an international standard that is the basis for creating execution and development environments in which languages and libraries work together seamlessly. Source code written in C# is compiled into an intermediate language (IL) that conforms to the CLI specification. The IL code and resources, such as bitmaps and strings, are stored on disk in an executable file called an assembly, typically with an extension of .exe or .dll. An assembly contains a manifest that provides information about the assembly's types, version, culture, and security requirements.
- 8. •.NET Framework Platform Architecture-Cont 8 When the C# program is executed, the assembly is loaded into the CLR, which might take various actions based on the information in the manifest. Then, if the security requirements are met, the CLR performs just in time (JIT) compilation to convert the IL code to native machine instructions. The CLR also provides other services related to automatic garbage collection, exception handling, and resource management. Code that is executed by the CLR is sometimes referred to as "managed code," in contrast to "unmanaged code" which is compiled into native machine language that targets a specific system. The following diagram illustrates the compile-time and run-time relationships of C# source code files, the .NET Framework class libraries, assemblies, and the CLR.
- 9. •.NET Framework Platform Architecture-Cont 9
- 10. •C# built-In types: 10 In order to define variables, developer needs to decide which type to choose for example if you want to define a number you need to declare a variable using int, for example: int number = 0; And so on. Type variable Assig n Initial value semicolon Left hand-side Right hand- side
- 11. •C# built-In types – Cont.: 11 It is used to declare variables to store the Boolean values, true and false. The byte keyword denotes an integral type that stores values that ranges between 0-255, allocate size Unsigned 8-bit integer The char keyword is used to declare an instance of the System.Char structure that the .NET Framework uses to represent a Unicode character. The value of a Char object is a 16-bit numeric (ordinal) value. The byte keyword denotes an integral type that stores values that ranges between -128 to 127, allocate size signed 8-bit integer The decimal keyword indicates a 128-bit data type. Compared to floating-point types, the decimal type has more precision and a smaller range, which makes it appropriate for financial and monetary calculations. The approximate range is (-7.9 x 1028 to 7.9 x 1028) / (100 to 28) and precision for the decimal type is 28-29 significant digits The double keyword signifies a simple type that stores 64-bit floating-point values. The precision is ±5.0 × 10−324 to ±1.7 × 10308 and approximate range for the double type is 15-16 digits. The float keyword signifies a simple type that stores 32-bit floating-point values. The precision is 7 digits and approximate range for the float type is -3.4 × 1038to +3.4 × 1038. The int keyword denotes an integral type that stores values within Signed 32-bit integer size and within - 2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 range The uint keyword signifies an integral type that stores values within Unsigned 32-bit integer size and within 0 to 4,294,967,295 range The long keyword denotes an integral type that stores values within Signed 64-bit integer size and within 9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 range The ulong keyword denotes an integral type that stores values within Unsigned 64-bit integer size and within 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 The object type is an alias for Object in the .NET Framework. In the unified type system of C#, all types, predefined and user-defined, reference types and value types, inherit directly or indirectly from Object. You can assign values of any type to variables of type object The short keyword denotes an integral data type that stores values within -32,768 to 32,767 size and within Signed 16-bit integer range . The ushort keyword indicates an integral data type that stores values within Unsigned 16-bit integer size and within 0 to 65,535 range . The string type represents a sequence of zero or more Unicode characters. string is an alias for String in the .NET Framework.
- 12. •Namespace: 12 Namespaces are used to provide a "named space" in which your application resides. They're used especially to provide the C# compiler a context for all the named information in your program, such as variable names. Without namespaces, for example, you wouldn't be able to make a class named Console, as .NET already uses one in its System namespace. The purpose of namespaces is to solve this problem, and release thousands of names defined in the .NET Framework for your applications to use, along with making it so your application doesn't occupy names for other applications, if your application is intended to be used in conjunction with another. So namespaces exist to resolve ambiguities a compiler wouldn't otherwise be able to do.
- 13. •Nested Namespace: 13 Normally, your entire application resides under its own special namespace, often named after your application or project name. Sometimes, companies with an entire product series decide to use nested namespaces though, where the "root" namespace can share the name of the company, and the nested namespaces the respective project names. This can be especially convenient, if you're a developer who has made a library with some usual functionality that can be shared across programs. If both the library and your program shared a parent namespace, that one would then not have to be explicitly declared with the using keyword, and still not have to be completely typed out. If your code was open for others to use, third party developers that may use your code would additionally then see that the same company had developed the library and the program. The developer of the library and program would finally also separate all the named information in their product source codes, for fewer headaches especially, if common names are used.
- 14. •Object Oriented: 14 Object Oriented is a very important concept that every developer to be needs to know. The simple type int lets you declare integer variables as shown previously in slide 10 , and in the same way, you can create your own classes, which contain not only data like the simple types, but methods as well. Just as you create integer variables with the int type, so you create objects from classes. An integer variable is an instance of the int type, just like an object is an instance of a class. Classes are types, but are far more powerful than the simple types like int and float. Not only can you customize your data storage using classes, but you can also add methods to classes. That kind of compartmentalization—where data and methods are rolled up into a single class—is the entire reason that OOP was introduced in the first place. It enables the programmers to deal with larger programs. The process of wrapping related data and methods into a class (and so preventing them from cluttering up the rest of the program) to create a single entity is called encapsulation.
- 15. •Object Oriented-Cont.: 15 You create classes in C# with the class statement: [attributes] [modifiers] class identifier [:base-list] { class-body }[;] Here are the parts of this statement: attributes (Optional)—Attributes hold additional declarative information. modifiers (Optional)—The allowed modifiers are new, static, virtual, abstract, override, and a valid combination of the four access modifiers. identifier—The class name. n base-list (Optional)—A list that contains the base class and any implemented interfaces, separated by commas. class-body—Declarations of the class members.
- 16. •Object Oriented-Cont.: 16 Creating Objects To create an object, also called an instance, of a class, you use the new keyword. We’ve seen how this process works; you can see how we create a new object of the Calculator in exercise at last slide, AddItem method to add numbers. Note the parentheses after Calculator -highlighted with blue- in the statement Calculator obj = new Calculator();. These parentheses are necessary when you use the new keyword. They let you pass data to a class’s constructor, the special method that lets you initialize the data in a class.
- 17. •Visual Studio installation 17 Definition : Visual studio is a Microsoft IDE(Integrated Development Environment) where a developer can install and use to create programs. To install VS you need to visit visualstudio and then select one of these products as shown in figure below
- 18. •Visual Studio installation – Cont. 18 Once you click on the link, the execution file will automatically be downloaded. As shown in figure below,
- 19. •Visual Studio installation – Cont. 19 A wizard will launch , press continue A waiting dialogue will start
- 20. •Visual Studio installation – Cont. 20 Check the boxes and then press install
- 21. •Visual Studio installation – Cont. 21 The installer will start acquiring to finally install the VS.
- 22. •Visual Studio installation – Cont. 22 Now the installer has finished , press launch.
- 23. •Visual Studio installation – Cont. 23 Sign in with your account, and if you don’t have one sign up for one, or you can press Not now , maybe later. Choose your color and then press start visual studio
- 24. •Hello world 24 After successfully installing Visual studio now it’s time to create your first application. Select File -> New -> Project as shown in figure below,
- 25. •Hello world – Cont. 25 Now select console application, and then type “Hello World” application. Then press Ok
- 26. •Hello world – Cont. 26 Inside the main class type Console.WriteLine("Hello World"); . Press Ctrl+F5
- 27. •Hello world – Cont. 27 Output:
- 28. •Lab work: 28 Description: 1.Launch VS, and then create new project. 2.The project will be building a calculator that will add, subtract, divide and multiply numbers. 3.Apply Object oriented to the project. Challenge : try to create windows form application. Note: I will provide the solution next week.
- 29. •References: https://classes.soe.ucsc.edu/cmps020/Winter08/lectures /intro-csharp.pdf https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/z1zx9t92.aspx https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ya5y69ds.aspx https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/C_Sharp_Programming/Na mespaces http://catalogue.pearsoned.co.uk/samplechapter/067232 5470.pdf 29














![•Object Oriented-Cont.:
15
You create classes in C# with the class statement:
[attributes] [modifiers] class identifier [:base-list] { class-body }[;]
Here are the parts of this statement:
attributes (Optional)—Attributes hold additional declarative information.
modifiers (Optional)—The allowed modifiers are new, static, virtual, abstract,
override, and a valid combination of the four access modifiers.
identifier—The class name. n base-list (Optional)—A list that contains the base class
and any implemented interfaces, separated by commas.
class-body—Declarations of the class members.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoprogrammingusingc-170422203811/85/Introduction-to-programming-using-c-15-320.jpg)













