Programming in Python
- 1. Programming in Python Tiji Thomas HOD Department of Computer Applications MACFAST
- 2. Jointly organized by Dept. of Computer Applications, MACFAST KSCSTE & UNAI , Computer Society of India (CSI) MAR ATHANASIOS COLLEGE FOR ADVANCED STUDIES TIRUVALLA (MACFAST) UNAI-MACFAST-ASPIRE Taliparamba Arts & Science College Accredited by NAAC with A grade
- 3. Introduction Python is a general-purpose interpreted, object- oriented, and high-level programming language. What can we do with Python –Web Development , , Desktop Applications, Data Science , Machine Learning , Computer Games , NLP etc. Python supports many databases (SQLite, Sqlite, Oracle, Sybase, PostgreSQL etc.) Python is an open source software Google, Instagram, YouTube , Quora etc
- 4. Executing a Python Program a) Command Prompt • print “Hello World” • b)IDLE 1. Run IDLE. ... 2. Click File, New Window. ... 3. Enter your script and save file with . Python files have a file extension of ".py" 4. Select Run, Run Module (or press F5) to run your script. 5. The "Python Shell" window will display the output of your script.
- 5. Reading Keyboard Input • Python provides two built-in functions to read a line of text from standard input, which by default comes from the keyboard. These functions are − • raw_input • input • The raw_input Function • The raw_input([prompt]) function reads one line from standard input and returns it as a string (removing the trailing newline). str = raw_input("Enter your input: "); print "Received input is : ", str
- 6. • The input Function • The input([prompt]) function is equivalent to raw_input, except that it assumes the input is a valid Python expression and returns the evaluated result to you. str = input("Enter your input: "); print "Received input is : ", str
- 7. Python Decision Making Statement Description if statements An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. if...else statements An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is FALSE. If .. elif You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s).
- 8. Indentation • Python provides no braces to indicate blocks of code for class and function definitions or flow control. Blocks of code are denoted by line indentation if True: print "True" else: print "False"
- 9. Python Loops • while - loops through a block of code if and as long as a specified condition is true • for - loops through a block of code a specified number of times
- 10. Example - while #Display first n numbers n=input("Enter value for n ") i=1 while i<=n: print i i= i + 1
- 11. Example for #for loop example str= “Python” for letter in str: print 'Current Letter :', letter
- 12. Standard Data Types • Python has five standard data types − • Numbers • String • List • Tuple • Dictionary
- 13. Strings • Set of characters represented in the quotation marks. Python allows for either pairs of single or double quotes • str = 'Hello World!' • print str # Prints complete string • print str[0] # Prints first character of the string • print str[2:5] # Prints characters starting from 3rd to 5th • print str[2:] # Prints string starting from 3rd character • print str * 2 # Prints string two times • print str + "TEST" # Prints concatenated string
- 14. Python Lists • A list contains items separated by commas and enclosed within square brackets ([]). To some extent, lists are similar to arrays in C. One difference between them is that all the items belonging to a list can be of different data type. • list = [ 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 ] ls = [123, 'john'] • print list # Prints complete list • print list[0] # Prints first element of the list • print list[1:3] # Prints elements starting from 2nd till 3rd • print list[2:] # Prints elements starting from 3rd element • print ls * 2 # Prints list two times • print list + ls # Prints concatenated lists
- 15. Python Lists • Add elements to a list 1. mylist.append(10) 2. mylist.extend(["Raju",20,30]) 3. mylist.insert(1,"Ammu") • Search within lists -mylist.index('Anu’) • Delete elements from a list - mylist.remove(20)
- 16. range function • The built-in range function in Python is very useful to generate sequences of numbers in the form of a list. • The given end point is never part of the generated list;
- 17. Basic list operations Length - len Concatenation : + Repetition - ['Hi!'] * 4 Membership - 3 in [1, 2, 3] Iteration- for x in [1, 2, 3]: print x,
- 18. Sorting an array - list.sort() fruits = ["lemon", "orange", "banana", "apple"] print fruits fruits.sort() for i in fruits: print i print "nnnReverse ordernnn" fruits.sort(reverse=True) for i in fruits: print i
- 19. Python Tuples • A tuple consists of a number of values separated by commas. Tuples are enclosed within parentheses. • The main differences between lists and tuples are: Lists are enclosed in brackets ( [ ] ) and their elements and size can be changed, while tuples are enclosed in parentheses ( ( ) ) and cannot be updated. • read-only lists
- 20. Tuple Example • tuple = ( 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 ) • tinytuple = (123, 'john') • print tuple # Prints complete list • print tuple[0] # Prints first element of the list • print tuple[1:3] # Prints elements starting from 2nd till 3rd • print tuple[2:] # Prints elements starting from 3rd element • print tinytuple * 2 # Prints list two times • print tuple + tinytuple # Prints concatenated lists
- 21. Operations on Tuple • 1 Accessing Values in Tuples • 2 Updating Tuples - not possible • 3 Delete Tuple Elements - not possible • 4 Create new tuple from existing tuples is possible • Functions - cmp ,len , max , min
- 22. Python Dictionary • Python's dictionaries are kind of hash table type. They work like associative arrays or hashes found in Perl and consist of key-value pairs • Dictionaries are enclosed by curly braces ({ }) and values can be assigned and accessed using square braces ([]).
- 23. Example • dict = {} • dict['one'] = "This is one" • dict[2] = "This is two" • tinydict = {'name': 'john','code':6734, 'dept': 'sales'} • print dict['one'] # Prints value for 'one' key • print dict[2] # Prints value for 2 key • print tinydict # Prints complete dictionary • print tinydict.keys() # Prints all the keys • print tinydict.values() # Prints all the values
- 24. Python Functions • Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the function name and parentheses ( ( ) ). • Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these parentheses. • The first statement of a function can be an optional statement - the documentation string of the function or docstring. . • The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally passing back an expression to the caller. A return statement with no arguments is the same as return None.
- 25. Example -1 Function for find maximum of two numbers Example -2 Function for Read and Display list Example -3 Function for search in a list Example -4 Function for prime numbers
- 26. Opening a File • The open() function is used to open files in Python. • The first parameter of this function contains the name of the file to be opened and the second parameter specifies in which mode the file should be opened Example • File=open(“macfast.txt” , “w”)
- 27. Modes Description r Read only. Starts at the beginning of the file r+ Read/Write. Starts at the beginning of the file w Write only. Opens and clears the contents of file; or creates a new file if it doesn't exist w+ Read/Write. Opens and clears the contents of file; or creates a new file if it doesn't exist a Append. Opens and writes to the end of the file or creates a new file if it doesn't exist a+ Read/Append. Preserves file content by writing to the end of the file
- 28. • Opening and Closing Files • The open Function file object = open(file_name [, access_mode][, buffering]) • file_name: The file_name argument is a string value that contains the name of the file that you want to access. • access_mode: The access_mode determines the mode in which the file has to be opened, i.e., read, write, append, etc. • The close() Method The close() method of a file object flushes any unwritten information and closes the file object, after which no more writing can be done.
- 29. • The write() Method • The write() method writes any string to an open file • The write() method does not add a newline character ('n') to the end of the string − # Open a file file = open(“test.txt", "wb") file.write( “ Two day workshop on Python "); # Close opend file File.close()
- 30. • The read() Method • The read() method reads a string from an open file. f= open(“test.txt", "r") str = f.read(); print str fo.close()
- 31. Regular Expression • Regular expressions are essentially a tiny, highly specialized programming language embedded inside Python and made available through the re module.
- 32. • Regular expressions are useful in a wide variety of text processing tasks, and more generally string processing • Data validation • Data scraping (especially web scraping), • Data wrangling, • Parsing, • Syntax highlighting systems
- 33. Various methods of Regular Expressions The ‘re’ package provides multiple methods to perform queries on an input string. Here are the most commonly used methods 1.re.match() 2.re.search() 3.re.findall() 4.re.split() 5.re.sub()
- 34. re.match() This method finds match if it occurs at start of the string str='MCA , MBA , BCA , BBA' re.match('MCA' , str) re.match("MBA" , str)
- 35. re.search() search() method is able to find a pattern from any position of the string but it only returns the first occurrence of the search pattern.
- 36. Re.findall • findall helps to get a list of all matching patterns import re str='MCA , MBA , BCA , BBA , MSC' result =re.findall (r"Mww" , str) if result: for i in result: print i else: print "Not Found"
- 37. Finding all Adverbs import re file= open(‘story.txt' , "r") str=file.read(); result=re.findall(r"w+ly",str) for i in result: print i
- 38. re.split() This methods helps to split string by the occurrences of given pattern. import re str = 'MCA MBA BCA MSC BBA BSc' result=re.split(" ",str) for i in result: print i
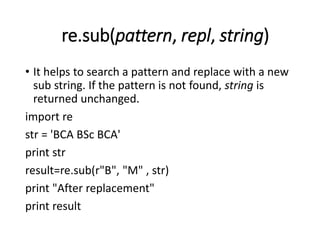
- 39. re.sub(pattern, repl, string) • It helps to search a pattern and replace with a new sub string. If the pattern is not found, string is returned unchanged. import re str = 'BCA BSc BCA' print str result=re.sub(r"B", "M" , str) print "After replacement" print result
- 40. Change gmail.com to macfast.org using re.sub() import re str = "[email protected] ,[email protected] ,[email protected]" print str newstr= re.sub(r"@w+.com" , "@macfast.org" , str) print "Change gmail.com to macfast.org " print newstr
- 41. Project -1 •Extract information from an Excel file using Python
- 42. What is SQLite? SQLite is an embedded SQL database engine •SQLite is ideal for both small and large applications •SQLite supports standard SQL •Open source software
- 43. Connection to a SQLite Database import sqlite3 conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db') Once you have a Connection, you can create a Cursor object and call its execute() method to perform SQL commands: c = conn.cursor()
- 44. Project Student Information System(SIS) Insert Data -> insertdata.py Update Data -> updatedata.py Delete Data ->deletedata.py Display Students List ->list.py
- 45. Thank You
Editor's Notes
- #19: TimSort is a sorting algorithm based on Insertion Sort and Merge Sort. A stable sorting algorithm works in O(n Log n) time Used in Java’s Arrays.sort() as well as Python’s sorted() and sort(). It was implemented by Tim Peters in 2002 for use in the Python programming language
- #32: Why we use regular expression?
- #33: Web Scraping (also termed Screen Scraping, Web Data Extraction, Web Harvesting etc.) is a technique employed to extract large amounts of data from websites whereby the data is extracted and saved to a local file in your computer or to a database in table (spreadsheet) format. Data wrangling (sometimes referred to as data munging) is the process of transforming and mapping data from one "raw" data form into another format with the intent of making it more appropriate and valuable for a variety of downstream purposes such as analytics.





![Reading Keyboard Input
• Python provides two built-in functions to read a line of text from
standard input, which by default comes from the keyboard. These
functions are −
• raw_input
• input
• The raw_input Function
• The raw_input([prompt]) function reads one line
from standard input and returns it as a string
(removing the trailing newline).
str = raw_input("Enter your input: ");
print "Received input is : ", str](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-5-320.jpg)
![• The input Function
• The input([prompt]) function is equivalent to
raw_input, except that it assumes the input is a
valid Python expression and returns the evaluated
result to you.
str = input("Enter your input: ");
print "Received input is : ", str](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-6-320.jpg)






![Strings
• Set of characters represented in the quotation marks.
Python allows for either pairs of single or double quotes
• str = 'Hello World!'
• print str # Prints complete string
• print str[0] # Prints first character of the string
• print str[2:5] # Prints characters starting from 3rd to 5th
• print str[2:] # Prints string starting from 3rd character
• print str * 2 # Prints string two times
• print str + "TEST" # Prints concatenated string](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-13-320.jpg)
![Python Lists
• A list contains items separated by commas and enclosed within
square brackets ([]). To some extent, lists are similar to arrays in C.
One difference between them is that all the items belonging to a
list can be of different data type.
• list = [ 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 ]
ls = [123, 'john']
• print list # Prints complete list
• print list[0] # Prints first element of the list
• print list[1:3] # Prints elements starting from 2nd till 3rd
• print list[2:] # Prints elements starting from 3rd element
• print ls * 2 # Prints list two times
• print list + ls # Prints concatenated lists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-14-320.jpg)
![Python Lists
• Add elements to a list
1. mylist.append(10)
2. mylist.extend(["Raju",20,30])
3. mylist.insert(1,"Ammu")
• Search within lists -mylist.index('Anu’)
• Delete elements from a list - mylist.remove(20)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-15-320.jpg)

![Basic list operations
Length - len
Concatenation : +
Repetition - ['Hi!'] * 4
Membership - 3 in [1, 2, 3]
Iteration- for x in [1, 2, 3]: print x,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-17-320.jpg)
![Sorting an array - list.sort()
fruits = ["lemon", "orange", "banana", "apple"]
print fruits
fruits.sort()
for i in fruits:
print i
print "nnnReverse ordernnn"
fruits.sort(reverse=True)
for i in fruits:
print i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-18-320.jpg)
![Python Tuples
• A tuple consists of a number of values separated by
commas. Tuples are enclosed within parentheses.
• The main differences between lists and tuples are:
Lists are enclosed in brackets ( [ ] ) and their
elements and size can be changed, while tuples are
enclosed in parentheses ( ( ) ) and cannot be
updated.
• read-only lists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-19-320.jpg)
![Tuple Example
• tuple = ( 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 )
• tinytuple = (123, 'john')
• print tuple # Prints complete list
• print tuple[0] # Prints first element of the list
• print tuple[1:3] # Prints elements starting from 2nd till 3rd
• print tuple[2:] # Prints elements starting from 3rd element
• print tinytuple * 2 # Prints list two times
• print tuple + tinytuple # Prints concatenated lists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-20-320.jpg)

![Python Dictionary
• Python's dictionaries are kind of hash table type.
They work like associative arrays or hashes found in
Perl and consist of key-value pairs
• Dictionaries are enclosed by curly braces ({ }) and
values can be assigned and accessed using square
braces ([]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-22-320.jpg)
![Example
• dict = {}
• dict['one'] = "This is one"
• dict[2] = "This is two"
• tinydict = {'name': 'john','code':6734, 'dept': 'sales'}
• print dict['one'] # Prints value for 'one' key
• print dict[2] # Prints value for 2 key
• print tinydict # Prints complete dictionary
• print tinydict.keys() # Prints all the keys
• print tinydict.values() # Prints all the values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-23-320.jpg)
![Python Functions
• Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed
by the function name and parentheses ( ( ) ).
• Any input parameters or arguments should be placed
within these parentheses.
• The first statement of a function can be an optional
statement - the documentation string of the function or
docstring.
.
• The statement return [expression] exits a function,
optionally passing back an expression to the caller. A
return statement with no arguments is the same as
return None.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-24-320.jpg)



![• Opening and Closing Files
• The open Function
file object = open(file_name [, access_mode][, buffering])
• file_name: The file_name argument is a string value that
contains the name of the file that you want to access.
• access_mode: The access_mode determines the mode in
which the file has to be opened, i.e., read, write, append,
etc.
• The close() Method
The close() method of a file object flushes any unwritten
information and closes the file object, after which no more
writing can be done.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminginpythonbytijithomas-171208004450/85/Programming-in-Python-28-320.jpg)