Since Java 8, the sorted() method is part of the Stream API and is used to sort the elements of a stream. By default, elements are sorted in the natural order, but we can apply for a custom order using a Comparator.
//Default sorting
List sortedList = unsortedList.stream().sorted().toList();
//Custom Sorting
Comparator comparator = ...;
List sortedList = unsortedList.stream().sorted(comparator).toList();1. Stream sort() is an Overloaded Method
The Stream interface provides two methods for sorting the elements:
- sorted() – Provides the default sorting
- sorted(Comparator) – Sorting based on the provided comparator.
1.1. Stream sorted()
Stream<T> sorted()sorted()is a stateful intermediate operation that returns a new Stream.- It returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to the natural order.
- If the elements of this stream are not
Comparable, ajava.lang.ClassCastExceptionmay be thrown when the terminal operation is executed. - For ordered streams, the sort is stable.
- For unordered streams, no stability guarantees are made.
1.2. Stream sorted(comparator)
Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator)- This is a stateful intermediate operation that returns a new stream.
- It returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to the provided Comparator..
- For ordered streams, the sort is stable.
- For unordered streams, no stability guarantees are made.
2. Stream sorted() Examples
2.1. Sorting Stream Elements in Natural Order
In the given Java example, we are sorting a List of integers in the natural order and printing them into the standard output.
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(2, 4, 1, 3, 7, 5, 9, 6, 8);
List<Integer> sortedList = list.stream()
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedList);Program output.
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]2.2. Sorting Stream Elements in Reverse Order
In the given Java example, we are sorting a stream of integers in reverse order using a Comparator.reverseOrder() and printing them into the standard output.
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(2, 4, 1, 3, 7, 5, 9, 6, 8);
List<Integer> sortedList = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedList);Program output.
[9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]2.3. Sort Stream Elements in Custom Order using Comparator
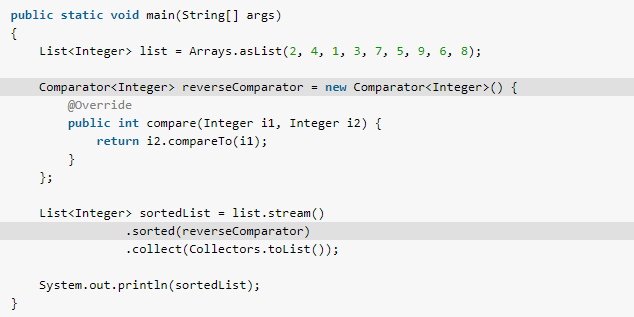
In the given Java example, we are sorting a stream of integers using a custom Comparator.
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(2, 4, 1, 3, 7, 5, 9, 6, 8);
Comparator<Integer> reverseComparator = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
return i2.compareTo(i1);
}
};
List<Integer> sortedList = list.stream()
.sorted(reverseComparator)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedList);Program output.
[9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]2.4. Stream Sorting using Lambda Expressions
Java example to sort a stream of integers in reverse order using lambda expression to specify the comparison logic.
We are rewriting the previous Comparator logic with an inline lambda expression.
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(2, 4, 1, 3, 7, 5, 9, 6, 8);
List<Integer> sortedList = list.stream()
.sorted( (i1, i2) -> i2.compareTo(i1) )
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedList);Program output.
[9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]3. Conclusion
In this Java 8 Stream tutorial, we learned the basics of sorting the stream elements using sorted() method. We learned to sort in default ascending order as well as custom order using a Comparator.
Happy Learning !!

Comments