Types of Computer Networks
Last Updated :
21 May, 2025
A computer network is a system that connects many independent computers to share information (data) and resources. The integration of computers and other different devices allows users to communicate more easily. It is a collection of two or more computer systems that are linked together. A network connection can be established using either cable or wireless media. Hardware and software are used to connect computers and tools in any network.
Uses of Computer Networks
- Communicating using email, video, instant messaging, etc.
- Sharing devices such as printers, scanners, etc.
- Sharing files.
- Sharing software and operating programs on remote systems.
- Allowing network users to easily access and maintain information.
Types of Computer Networks
There are mainly five types of Computer Networks
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Campus Area Network (CAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
 Types of Computer Networks
Types of Computer Networks1. Personal Area Network (PAN)
PAN is the most basic type of computer network. It is a type of network designed to connect devices within a short range, typically around one person. It allows your personal devices, like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearables, to communicate and share data with each other. PAN offers a network range of 1 to 100 meters from person to device providing communication. Its transmission speed is very high with very easy maintenance and very low cost. This uses Bluetooth, IrDA, and Zigbee as technology. Examples of PAN are USB, computer, phone, tablet, printer, PDA, etc.
Types of PAN
Wired Personal Area Network: A wired personal area network is constructed using a USB.
 Wired PAN
Wired PANWireless Personal Area Networks: Wireless Personal Area Networks are created by simply utilising wireless technologies such as WiFi and Bluetooth. It is a low-range network.
 Wireless PAN
Wireless PANAdvantages of PAN
- PAN is relatively flexible and provides high efficiency for short network ranges.
- It needs easy setup and relatively low cost.
- It does not require frequent installations and maintenance
- It is easy and portable.
- Needs fewer technical skills to use.
Disadvantages of PAN
- Low network coverage area/range.
- Limited to relatively low data rates.
- Devices are not compatible with each other.
- Inbuilt WPAN devices are a little bit costly.
Applications of PAN
- Home and Offices
- Organizations and the Business sector
- Medical and Hospital
- School and College Education
- Military and Defense
2. Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is the most frequently used network. A LAN is a computer network that connects computers through a common communication path, contained within a limited area, that is, locally. A LAN encompasses two or more computers connected over a server. The two important technologies involved in this network are Ethernet and Wi-fi. It ranges up to 2km & transmission speed is very high with easy maintenance and low cost. Examples of LAN are networking in a home, school, library, laboratory, college, office, etc.
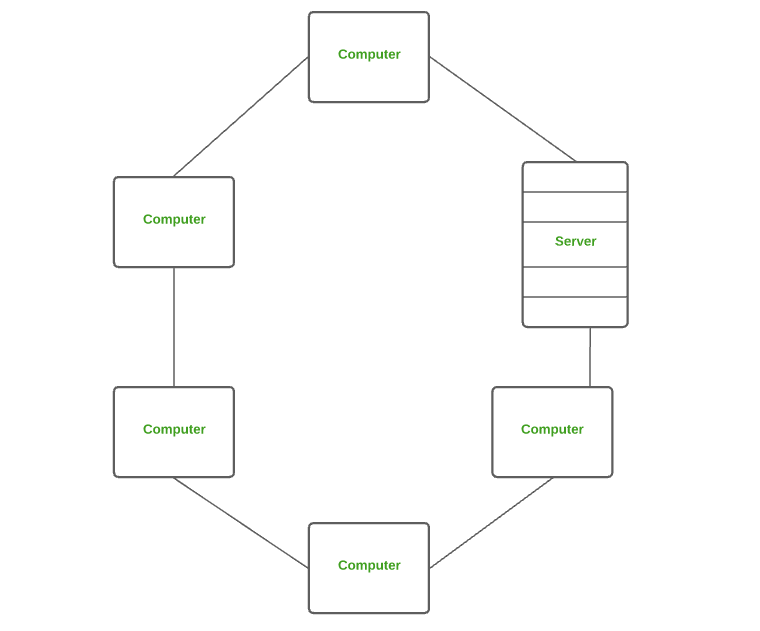 Local Area Network (LAN)
Local Area Network (LAN)Advantages of a LAN
- Privacy: LAN is a private network, thus no outside regulatory body controls it, giving it a privacy.
- High Speed: LAN offers a much higher speed(around 100 mbps) and data transfer rate comparatively to WAN.
- Supports different transmission mediums: LAN support a variety of communications transmission medium such as an Ethernet cable (thin cable, thick cable, and twisted pair), fiber and wireless transmission.
- Inexpensive and Simple: A LAN usually has low cost, installation, expansion and maintenance and LAN installation is relatively easy to use, good scalability.
Disadvantages of LAN
- The initial setup costs of installing Local Area Networks is high because there is special software required to make a server.
- Communication devices like an ethernet cable, switches, hubs, routers, cables are costly.
- LAN administrator can see and check personal data files as well as Internet history of each and every LAN user. Hence, the privacy of the users are violated
- LANs are restricted in size and cover only a limited area
- Since all the data is stored in a single server computer, if it can be accessed by an unauthorized user, can cause a serious data security threat.
3. Campus Area Network (CAN)
CAN is bigger than a LAN but smaller than a MAN. This is a type of computer network that is usually used in places like a school or colleges. This network covers a limited geographical area that is, it spreads across several buildings within the campus. CAN mainly use Ethernet technology with a range from 1km to 5km. Its transmission speed is very high with a moderate maintenance cost and moderate cost. Examples of CAN are networks that cover schools, colleges, buildings, etc.
 Campus Area Network (CAN)
Campus Area Network (CAN)Advantages of CAN
- Speed: Communication within a CAN takes place over Local Area Network (LAN) so data transfer rate between systems is little bit fast than Internet.
- Security: Network administrators of campus take care of network by continuous monitoring, tracking and limiting access. To protect network from unauthorized access firewall is placed between network and internet.
- Cost effective: With a little effort and maintenance, network works well by providing fast data transfer rate with multi-departmental network access. It can be enabled wirelessly, where wiring and cabling costs can be managed. So to work with in a campus using CAN is cost-effective in view of performance
4. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. This is the type of computer network that connects computers over a geographical distance through a shared communication path over a city, town, or metropolitan area. This network mainly uses FDDI, CDDI, and ATM as the technology with a range from 5km to 50km. Its transmission speed is average. It is difficult to maintain and it comes with a high cost. Examples of MAN are networking in towns, cities, a single large city, a large area within multiple buildings, etc.
 Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)Advantages of MAN
- MAN offers high-speed connectivity in which the speed ranges from 10-100 Mbps.
- The security level in MAN is high and strict as compared to WAN.
- It support to transmit data in both directions concurrently because of dual bus architecture.
- MAN can serve multiple users at a time with the same high-speed internet to all the users.
- MAN allows for centralized management and control of the network, making it easier to monitor and manage network resources and security.
Disadvantages of MAN
- The architecture of MAN is quite complicated hence, it is hard to design and maintain.
- This network is highly expensive because it required the high cost to set up fiber optics.
- It provides less fault tolerance.
- The Data transfer rate in MAN is low when compare to LANs.
5. Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN is a type of computer network that connects computers over a large geographical distance through a shared communication path. It is not restrained to a single location but extends over many locations. WAN can also be defined as a group of local area networks that communicate with each other with a range above 50km. Here we use Leased-Line & Dial-up technology. Its transmission speed is very low and it comes with very high maintenance and very high cost. The most common example of WAN is the Internet.
 Wide Area Network (WAN)
Wide Area Network (WAN)Advantages of WAN
- It covers large geographical area which enhances the reach of organisation to transmit data quickly and cheaply.
- The data can be stored in centralised manner because of remote access to data provided by WAN.
- The travel charges that are needed to cover the geographical area of work can be minimised.
- WAN enables a user or organisation to connect with the world very easily and allows to exchange data and do business at global level.
Disadvantages of WAN
- Traffic congestion in Wide Area Network is very high.
- The fault tolerance ability of WAN is very less.
- Noise and error are present in large amount due to multiple connection point.
- The data transfer rate is slow in comparison to LAN because of large distances and high number of connected system within the network.
Comparison between Different Computer Networks
| Parameters | PAN | LAN | CAN | MAN | WAN |
|---|
| Full Name | Personal Area Network | Local Area Network | Campus Area Network | Metropolitan Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Technology | Bluetooth, Zigbee | Ethernet & Wifi | Ethernet | FDDI, CDDi. ATM | Leased Line, Dial-Up |
| Range | 1-100 m | Upto 2km | 1 - 5 km | 5-50 km | Above 50 km |
| Transmission Speed | Very High | Very High | High | Average | Low |
| Ownership | Private | Private | Private | Private or Public | Private or Public |
| Maintenance | Very Easy | Easy | Moderate | Difficult | Very Difficult |
| Cost | Very Low | Low | Moderate | High | Very High |
Other Types of Computer Networks
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
- System-Area Network (SAN)
- Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
- Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Home Area Network (HAN)
1. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
WLAN is a type of computer network that acts as a local area network but makes use of wireless network technology like Wi-Fi. This network doesn't allow devices to communicate over physical cables like in LAN but allows devices to communicate wirelessly. The most common example of WLAN is Wi-Fi.
 Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)There are several computer networks available; more information is provided below.
2. Storage Area Network (SAN)
SAN is a type of computer network that is high-speed and connects groups of storage devices to several servers. This network does not depend on LAN or WAN. Instead, a SAN moves the storage resources from the network to its high-powered network. A SAN provides access to block-level data storage. Examples of SAN are a network of disks accessed by a network of servers.
 Storage Area Network (SAN)
Storage Area Network (SAN)3. Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
A POLAN is a type of computer network that is an alternative to a LAN. POLAN uses optical splitters to split an optical signal from a single strand of single-mode optical fiber to multiple signals to distribute users and devices. In short, POLAN is a point to multipoint LAN architecture.
 Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)4. Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
EPN is a type of computer network mostly used by businesses that want a secure connection over various locations to share computer resources.
 Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
Enterprise Private Network (EPN)5. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN is a type of computer network that extends a private network across the internet and lets the user send and receive data as if they were connected to a private network even though they are not. Through a virtual point-to-point connection users can access a private network remotely. VPN protects you from malicious sources by operating as a medium that gives you a protected network connection.
 Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)6. Home Area Network (HAN)
Many of the houses might have more than a computer. To interconnect those computers and with other peripheral devices, a network should be established similar to the local area network (LAN) within that home. Such a type of network that allows a user to interconnect multiple computers and other digital devices within the home is referred to as Home Area Network (HAN). HAN encourages sharing of resources, files, and programs within the network. It supports both wired and wireless communication.
 Home Area Network (HAN)
Home Area Network (HAN)Internetwork
An internet network is defined as two or more computer network LANs, WANs, or computer network segments that are connected by devices and configured with a local addressing system. The method is known as internetworking. There are two types of Internetwork.
- Intranet: An internal network within an organization that enables employees to share data, collaborate, and access resources. Intranets are not accessible to the public and use private IP addresses.
- Extranet: Extranets extend the intranet to authorized external users, such as business partners or clients. They provide controlled access to specific resources while maintaining security.
Advantages of Computer Network
- Central Storage of Data: Files are stored on a central storage database which helps to easily access and available to everyone.
- Connectivity: A single connection can be routed to connect multiple computing devices.
- Sharing of Files: Files and data can be easily shared among multiple devices which helps in easily communicating among the organization.
- Security through Authorization: Computer Networking provides additional security and protection of information in the system.
Disadvantages of Computer Network
- Virus and Malware: A virus is a program that can infect other programs by modifying them. Viruses and Malware can corrupt the whole network.
- High Cost of Setup: The initial setup of Computer Networking is expensive because it consists of a lot of wires and cables along with the device.
- loss of Information: In case of a System Failure, might lead to some loss of data.
- Management of Network: Management of a Network is somehow complex for a person, it requires training for its proper use.
Similar Reads
Computer Network Tutorial A Computer Network is a system where two or more devices are linked together to share data, resources and information. These networks can range from simple setups, like connecting two devices in your home, to massive global systems, like the Internet. Below are the main components of a computer netw
7 min read
Computer Network Basics
Basics of Computer NetworkingA computer network is a collection of interconnected devices that share resources and information. These devices can include computers, servers, printers, and other hardware. Networks allow for the efficient exchange of data, enabling various applications such as email, file sharing, and internet br
14 min read
Types of Computer NetworksA computer network is a system that connects many independent computers to share information (data) and resources. The integration of computers and other different devices allows users to communicate more easily. It is a collection of two or more computer systems that are linked together. A network
11 min read
Introduction to InternetComputers and their structures are tough to approach, and it is made even extra tough when you want to recognize phrases associated with the difficulty this is already utilized in regular English, Network, and the net will appear to be absolutely wonderful from one some other, however, they may seem
10 min read
Types of Network TopologyNetwork topology refers to the arrangement of different elements like nodes, links, or devices in a computer network. Common types of network topology include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree topologies, each with its advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will discuss different types of n
12 min read
Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Network devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with each other. Network devices like hubs, repeaters, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, and brouter help manage and direct data flow in a network. They ensure efficient communication betwe
9 min read
What is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI ModelThe OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model is a set of rules that explains how different computer systems communicate over a network. OSI Model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The OSI Model consists of 7 layers and each layer has specific functions and re
13 min read
TCP/IP ModelThe TCP/IP model (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a four-layer networking framework that enables reliable communication between devices over interconnected networks. It provides a standardized set of protocols for transmitting data across interconnected networks, ensuring efficie
7 min read
Difference Between OSI Model and TCP/IP ModelData communication is a process or act in which we can send or receive data. Understanding the fundamental structures of networking is crucial for anyone working with computer systems and communication. For data communication two models are available, the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model, an
5 min read
Physical Layer
Physical Layer in OSI ModelThe physical Layer is the bottom-most layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model which is a physical and electrical representation of the system. It consists of various network components such as power plugs, connectors, receivers, cable types, etc. The physical layer sends data bits from
4 min read
Types of Network TopologyNetwork topology refers to the arrangement of different elements like nodes, links, or devices in a computer network. Common types of network topology include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree topologies, each with its advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will discuss different types of n
12 min read
Transmission Modes in Computer Networks (Simplex, Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex)Transmission modes also known as communication modes, are methods of transferring data between devices on buses and networks designed to facilitate communication. They are classified into three types: Simplex Mode, Half-Duplex Mode, and Full-Duplex Mode. In this article, we will discuss Transmission
6 min read
Types of Transmission MediaTransmission media is the physical medium through which data is transmitted from one device to another within a network. These media can be wired or wireless. The choice of medium depends on factors like distance, speed, and interference. In this article, we will discuss the transmission media. In t
9 min read
Data Link Layer
Data Link Layer in OSI ModelThe data link layer is the second layer from the bottom in the OSI (Open System Interconnection) network architecture model. It is responsible for the node-to-node delivery of data within the same local network. Its major role is to ensure error-free transmission of information. DLL is also responsi
5 min read
What is Switching?Switching is the process of transferring data packets from one device to another in a network, or from one network to another, using specific devices called switches. A computer user experiences switching all the time for example, accessing the Internet from your computer device, whenever a user req
5 min read
Virtual LAN (VLAN)Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a concept in which we can divide the devices logically on layer 2 (data link layer). Generally, layer 3 devices divide the broadcast domain but the broadcast domain can be divided by switches using the concept of VLAN. A broadcast domain is a network segment in which if a devic
7 min read
Framing in Data Link LayerFrames are the units of digital transmission, particularly in computer networks and telecommunications. Frames are comparable to the packets of energy called photons in the case of light energy. Frame is continuously used in Time Division Multiplexing process. Framing is a point-to-point connection
6 min read
Error Control in Data Link LayerData-link layer uses the techniques of error control simply to ensure and confirm that all the data frames or packets, i.e. bit streams of data, are transmitted or transferred from sender to receiver with certain accuracy. Using or providing error control at this data link layer is an optimization,
4 min read
Flow Control in Data Link LayerFlow control is design issue at Data Link Layer. It is a technique that generally observes the proper flow of data from sender to receiver. It is very essential because it is possible for sender to transmit data or information at very fast rate and hence receiver can receive this information and pro
4 min read
Piggybacking in Computer NetworksPiggybacking is the technique of delaying outgoing acknowledgment temporarily and attaching it to the next data packet. When a data frame arrives, the receiver waits and does not send the control frame (acknowledgment) back immediately. The receiver waits until its network layer moves to the next da
5 min read
Network Layer
Network Layer in OSI ModelThe Network Layer is the 5th Layer from the top and the 3rd layer from the Bottom of the OSI Model. It is one of the most important layers which plays a key role in data transmission. The main job of this layer is to maintain the quality of the data and pass and transmit it from its source to its de
5 min read
Introduction of Classful IP AddressingAn IP address is an address that has information about how to reach a specific host, especially outside the LAN. An IP address is a 32-bit unique address having an address space of 232.Classful IP addressing is a way of organizing and managing IP addresses, which are used to identify devices on a ne
11 min read
Classless Addressing in IP AddressingThe Network address identifies a network on the internet. Using this, we can find a range of addresses in the network and total possible number of hosts in the network. Mask is a 32-bit binary number that gives the network address in the address block when AND operation is bitwise applied on the mas
7 min read
What is an IP Address?Imagine every device on the internet as a house. For you to send a letter to a friend living in one of these houses, you need their home address. In the digital world, this home address is what we call an IP (Internet Protocol) Address. It's a unique string of numbers separated by periods (IPv4) or
14 min read
IPv4 Datagram HeaderIP stands for Internet Protocol and v4 stands for Version Four (IPv4). IPv4 was the primary version brought into action for production within the ARPANET in 1983. IP version four addresses are 32-bit integers which will be expressed in decimal notation. In this article, we will discuss about IPv4 da
4 min read
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6In the digital world, where billions of devices connect and communicate, Internet Protocol (IP) Addresses play a crucial role. These addresses are what allow devices to identify and locate each other on a network.To know all about IP Addresses - refer to What is an IP Address?Currently, there are tw
9 min read
Difference between Private and Public IP addressesIP Address or Internet Protocol Address is a type of address that is required to communicate one computer with another computer for exchanging information, file, webpage, etc. Public and Private IP address are two important parts of device identity. In this article, we will see the differences betwe
6 min read
Introduction To SubnettingSubnetting is the process of dividing a large network into smaller networks called "subnets." Subnets provide each group of devices with their own space to communicate, which ultimately helps the network to work easily. This also boosts security and makes it easier to manage the network, as each sub
8 min read
What is Routing?The process of choosing a path across one or more networks is known as Network Routing. Nowadays, individuals are more connected on the internet and hence, the need to use Routing Communication is essential.Routing chooses the routes along which Internet Protocol (IP) packets get from their source t
10 min read
Network Layer ProtocolsNetwork Layer is responsible for the transmission of data or communication from one host to another host connected in a network. Rather than describing how data is transferred, it implements the technique for efficient transmission. In order to provide efficient communication protocols are used at t
9 min read
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Session Layer in OSI modelThe Session Layer is the 5th layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model which plays an important role in controlling the dialogues (connections) between computers. This layer is responsible for setting up, coordinating, and terminating conversations, exchanges, and dialogues between the ap
6 min read
Presentation Layer in OSI modelPresentation Layer is the 6th layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. This layer is also known as Translation layer, as this layer serves as a data translator for the network. The data which this layer receives from the Application Layer is extracted and manipulated here as per the req
4 min read
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)SSL or Secure Sockets Layer, is an Internet security protocol that encrypts data to keep it safe. It was created by Netscape in 1995 to ensure privacy, authentication, and data integrity in online communications. SSL is the older version of what we now call TLS (Transport Layer Security).Websites us
10 min read
PPTP Full Form - Point-to-Point Tunneling ProtocolPPTP Stands for Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is a widely used networking protocol designed to create a secure private connection over a public network like the internet. It is Developed by Microsoft and other tech companies in the 1990s It is one of the first protocols used for Virtual Private
5 min read
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (MIME) ProtocolMIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is a standard used to extend the format of email messages, allowing them to include more than just text. It enables the transmission of multimedia content such as images, audio, video, and attachments, within email messages, as well as other types of cont
4 min read
Application Layer
Application Layer in OSI ModelThe Application Layer of OSI (Open System Interconnection) model, is the top layer in this model and takes care of network communication. The application layer provides the functionality to send and receive data from users. It acts as the interface between the user and the application. The applicati
5 min read
Client-Server ModelThe Client-Server Model is a distributed application architecture that divides tasks or workloads between servers (providers of resources or services) and clients (requesters of those services). In this model, a client sends a request to a server for data, which is typically processed on the server
6 min read
World Wide Web (WWW)The World Wide Web (WWW), often called the Web, is a system of interconnected webpages and information that you can access using the Internet. It was created to help people share and find information easily, using links that connect different pages together. The Web allows us to browse websites, wat
6 min read
Introduction to Electronic MailIntroduction:Electronic mail, commonly known as email, is a method of exchanging messages over the internet. Here are the basics of email:An email address: This is a unique identifier for each user, typically in the format of [email protected] email client: This is a software program used to send,
4 min read
What is a Content Distribution Network and how does it work?Over the last few years, there has been a huge increase in the number of Internet users. YouTube alone has 2 Billion users worldwide, while Netflix has over 160 million users. Streaming content to such a wide demographic of users is no easy task. One can think that a straightforward approach to this
4 min read
Protocols in Application LayerThe Application Layer is the topmost layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. This layer provides several ways for manipulating the data which enables any type of user to access the network with ease. The Application Layer interface directly interacts with the application and provides c
7 min read
Advanced Topics
What is Network Security?Every company or organization that handles a large amount of data, has a degree of solutions against many cyber threats. This is a broad, all-encompassing phrase that covers software and hardware solutions, as well as procedures, guidelines, and setups for network usage, accessibility, and general t
10 min read
Computer Network | Quality of Service and MultimediaQuality of Service (QoS) is an important concept, particularly when working with multimedia applications. Multimedia applications, such as video conferencing, streaming services, and VoIP (Voice over IP), require certain bandwidth, latency, jitter, and packet loss parameters. QoS methods help ensure
7 min read
Authentication in Computer NetworkPrerequisite - Authentication and Authorization Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or information. User authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user when that user logs in to a computer system. There are different types of authentication systems wh
4 min read
Encryption, Its Algorithms And Its FutureEncryption plays a vital role in today’s digital world, serving a major role in modern cyber security. It involves converting plain text into cipher text, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure from unauthorized access. By making data unreadable to unauthorized parties, encryption helps
10 min read
Introduction of Firewall in Computer NetworkA firewall is a network security device either hardware or software-based which monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic and based on a defined set of security rules it accepts, rejects, or drops that specific traffic. It acts like a security guard that helps keep your digital world safe from unwa
10 min read
MAC Filtering in Computer NetworkThere are two kinds of network Adapters. A wired adapter allows us to set up a connection to a modem or router via Ethernet in a computer whereas a wireless adapter identifies and connects to remote hot spots. Each adapter has a distinct label known as a MAC address which recognizes and authenticate
10 min read
Wi-Fi Standards ExplainedWi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity, and it is developed by an organization called IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) they set standards for the Wi-Fi system. Each Wi-Fi network standard has two parameters : Speed - This is the data transfer rate of the network measured in Mbps
4 min read
What is Bluetooth?Bluetooth is used for short-range wireless voice and data communication. It is a Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) technology and is used for data communications over smaller distances. This generation changed into being invented via Ericson in 1994. It operates within the unlicensed, business,
6 min read
Generations of wireless communicationWe have made very huge improvements in wireless communication and have expanded the capabilities of our wireless communication system. We all have seen various generations in our life. Let's discuss them one by one. 0th Generation: Pre-cell phone mobile telephony technology, such as radio telephones
2 min read
Cloud NetworkingCloud Networking is a service or science in which a company’s networking procedure is hosted on a public or private cloud. Cloud Computing is source management in which more than one computing resources share an identical platform and customers are additionally enabled to get entry to these resource
11 min read
Practice
Top 50 Plus Networking Interview Questions and Answers for 2024Networking is defined as connected devices that may exchange data or information and share resources. A computer network connects computers to exchange data via a communication media. Computer networking is the most often asked question at leading organizations such Cisco, Accenture, Uber, Airbnb, G
15+ min read
Top 50 TCP/IP Interview Questions and Answers 2025Understanding TCP/IP is essential for anyone working in IT or networking. It's a fundamental part of how the internet and most networks operate. Whether you're just starting or you're looking to move up in your career, knowing TCP/IP inside and out can really give you an edge.In this interview prepa
15+ min read
Top 50 IP Addressing Interview Questions and AnswersIn today’s digital age, every device connected to the internet relies on a unique identifier called an IP Address. If you’re aiming for a career in IT or networking, mastering the concept of IP addresses is crucial. In this engaging blog post, we’ll explore the most commonly asked IP address intervi
15+ min read
Last Minute Notes for Computer NetworksComputer Networks is an important subject in the GATE Computer Science syllabus. It encompasses fundamental concepts like Network Models, Routing Algorithms, Congestion Control, TCP/IP Protocol Suite, and Network Security. These topics are essential for understanding how data is transmitted, managed
14 min read
Computer Network - Cheat SheetA computer network is an interconnected computing device that can exchange data and share resources. These connected devices use a set of rules called communication protocols to transfer information over physical or wireless technology. Modern networks offer more than just connectivity. Enterprises
15+ min read