How To Use AWS Lambda Layers for Code Reuse and Organization?
Last Updated :
02 Jan, 2025
AWS lambda is an AWS service that works with Serverless Architecture, The infrastructure management is automatically managed by the AWS. It facilitates the developers to focus on the Code development completely. AWS Lambda Layers extends the core functionalities of the AWS Lambda functions through an efficient approach for managing dependencies and reusability of code. Mainly lambda layers allow the users to separate and externalize the dependencies making the efficient code organization bringing develop enhancement in the workflow.
What are AWS Lambda Layers?
AWS Lambda Layers is a distribution mechanism for libraries, custom runtimes, and other function dependencies. Layers can be used to separate different components of an application, By separating these components, you can reuse the same code (in the form of layers) across multiple AWS lambda functions or even other AWS accounts.
For instance, we can separate our business logic and the application dependencies, so that our application will look organized, the common codes (layers) can be reused across other lambda functions, and we can even share the layers of other lambda functions which require the same dependencies.

Advantages of AWS Lambda Layers
1. Code Reusability
- Code reusability is the prime benefit of using Lambda Layers, it can be used to share common code or libraries across multiple Lambda functions. This reduces the need for duplicating code across functions and also makes it easier to update the code when needed.
2. Custom Binaries/Libraries Support
- By default, lambda provides us with very lightweighters is a distribution mechanism for libraries, custom runtimes, and other function dependencies. Layers can be used to separate different components of an application, By separating these components, you can reuse the same code (in the form of layers) across multiple lambda functions or even other AWS accounts .
- For instance, we can separate our business logic and the application dependencies, so that our application will look organized, the common codes (layers) can be reused across other lambda functions, and we can even share the layers of other lambda functions which require the same dependencies. These base images with only a few and most necessary libraries/binaries, and if we require any additional libraries/binaries which are not natively supported by AWS Lambda, we need to include them in our lambda application code.
3. Versioning
- Lambda Layers can be used to maintain different versions of the same code or libraries. This can be useful for rolling back to an earlier version of the code or libraries if needed.
4. Speed of Deployment
- Lambda Layers can help speed up the deployment of new Lambda functions. By sharing common code and libraries across functions, there is no need to download and install the same code and libraries repeatedly, so if there is any dependency update, we can release the patched dependencies layer quickly, and business logic need not be updated in this case which reduces the time to deployment.
Challenges of AWS Lambda Layers
1. Dependency Coordination
- Management of updates across multiple layers and ensuring their compatibility with layers and functions are quite challenging.
2. Learning Curve
- Learning and Implementing lambda layers are a bit difficult for those who are unfamiliar with the lambda and serverless concepts in adoption and maintenance initially.
3. Versioning Precision Struggle
- Providing the right balance in layer version maintenance is very crucial. Overcomplicating the degree of detailing in version control may lead to management challenges and an Insufficient degree of detailing might affect the compromise of the control with dependencies.
4. Integration Challenges
- Understanding and integrating existing workflow seamlessly raises the challenges in Integration with different functions and services, It requires proper planning, and careful requirement consideration is needed to resolve those.
Guidelines for Effective Usage of AWS Lambda Layer
The following are steps for effective Usage of AWS Lambda Layers to streamline the code management, simplify the deployment and enhance the resuability of shared resources across multiple lambda functions
Step 1: Create a Lambda Layer
- Navigate to the Lambda service in the AWS Management Console , go to the layers section in the sidebar, and then click on the "Create Layer" button.
- Specify the name, description, and runtime compatibility for your layer. After that upload your code or libraries as .zip files or provide a link to the package.
Step 2: Publish the Layer Version
- After once creating the layer, Select "Publish new Version" in the drop-down section of " Actions" and assign the Description and Version number to it.
Step 3: Adding Layer to Lambda Function
- Open the Lambda function that you want to add to the layer. Click on the "Add a layer" in the layers section of the function overview.
Step 4: Configuring the Lambda Function
- Try to cross-check whether the lambda function references the libraries or dependencies provided by the layer. To increase the performance of the shared resources try to modify the function's code.
Step 5: Deploy the Lambda Function
- Check the changes made to your lambda function after cross-checking confirmation and deploy the updated version.
Step 6 - Test the Lambda Function
- Triggering the Lambda function to verify whether the shared code or libraries working properly or not from the layer.
Step 7: Update Layer Version ( Optional )
- For updating the layer with new code or libraries, repeat the same process by creating a new version of the layer.
Step 8: Managing the Layer Permissions
- Try adjusting the permissions of the layer to ensure that necessary lambda functions have required access to the layer.
Layers And Layer Versions
Aspects | Layers | Layer Versions |
|---|
Definition | AWS Layers are meant sharing Packages, Libraries and Codes | AWS Layer Versions are meant for specifying the versions of a layer with containing its code or dependencies |
|---|
Attachment | These are attached to the lambda functions | These are also attached to the lambda functions but controlled with version specification. |
|---|
Reusability | It helps in reusability of Code and Dependencies | It allow reusage of specific versions of a layer for providing consistent behaviour |
|---|
Updation | Updation of content of the Layer is possible | Updation of specific versions of Layers can be done independently |
|---|
Management | It follows centralized managementers is a distribution mechanism for libraries, custom runtimes, and other function dependencies. Layers can be used to separate different components of an application, By separating these components, you can reuse the same code (in the form of layers) across multiple lambda functions or even other AWS accounts.
For instance, we can separate our business logic and the application dependencies, so that our application will look organized, the common codes (layers) can be reused across other lambda functions, and we can even share the layers of other lambda functions which require the same dependencies. | It follows granular control over different versions for better control |
|---|
Cost Implications | These are commonly shared across multiple functions | It shares only needed versions for cost Optimization |
|---|
Flexibility | It has the flexibility in management of shared resources | It offers specific version controls and rollback options |
|---|
Usage of Lambda Layers for Code Reuse and Organization
As discussed above, using Lambda Layers allows for code reuse and better organization by separating reusable code from function-specific code. Here In this section you are going to learn how to separate the dependencies of a Python application into layers and reuse it in other functions, and share it with other accounts as well.
Step by Step Implementation to Create a Lambda Layer for Python Application
The following steps of implementation to create a lambda layer for the dependencies of the Python application.
Step 1: Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv myvenv
Step 2: Activate the virtual environment
- Activate the virtual environment, by running the below command, Now install the dependencies in this isolated environment.
source myenv/bin/activate
.jpg)
Step 3: Install dependencies
- Install the dependencies using pip package manager, the dependencies of the application are listed in the requirements.txt file.
pip install -r requirements.txt
To know about automating the installation of dependencies in python, please refer the article - Automating Installation of python libraries
Step 4: Package the dependencies
After running the above command, The dependencies will be installed in myvenv/lib/python3.8/site-packages directory, here we need to package those dependencies inside the python directory so that they can be used inside the lambda function.
create a new directory with the name python, copy the dependencies to this directory, then compress this directory using the below command.
zip -r dependencies.zip python/
Step 5: Creating AWS Lambda Layer
- Open the Lambda service in the AWS console.
- Open the layers page (available at the left panel)
- Click on Create layer , fill in the layer details, and upload the compressed dependencies file.
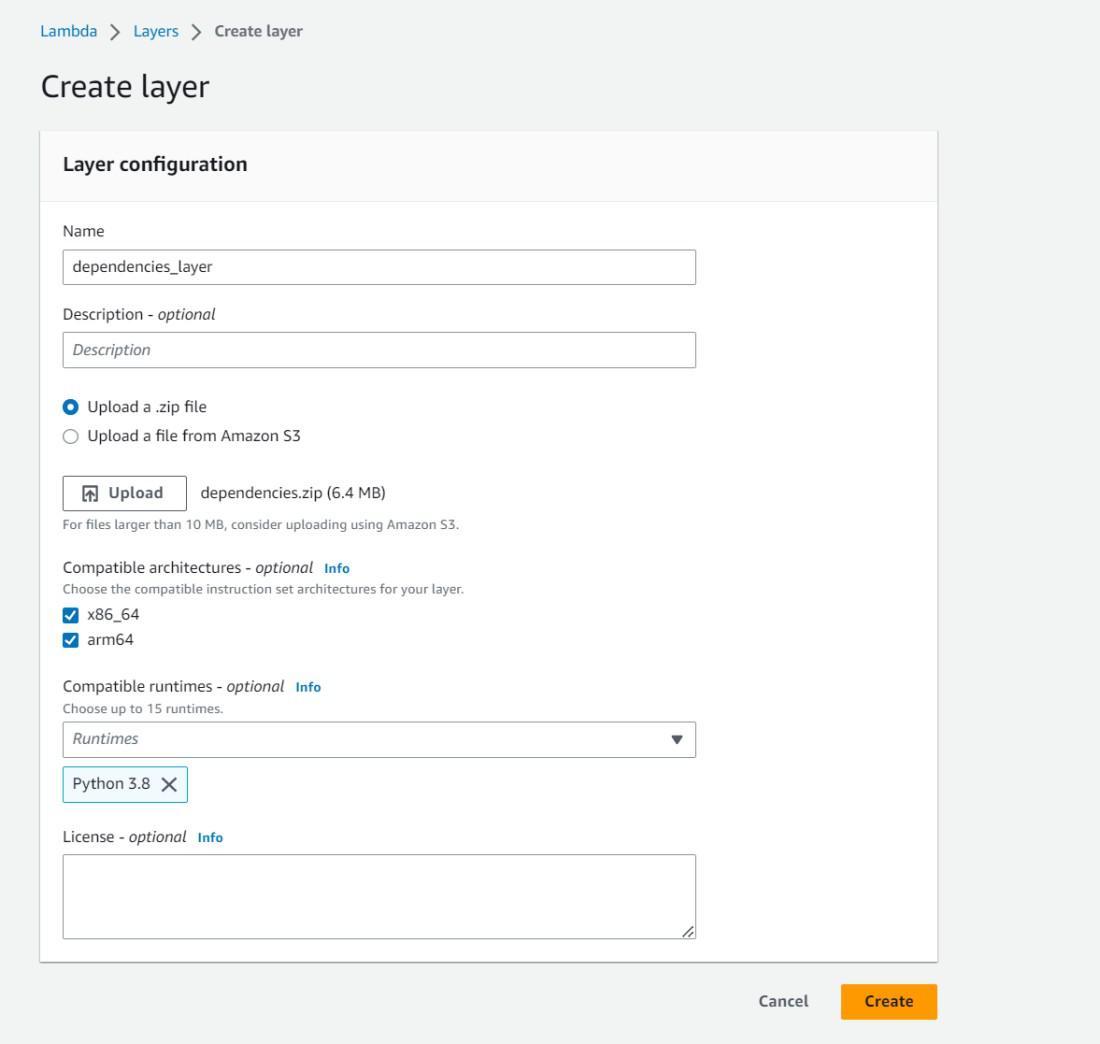
Step 6: Usage of Lambda Layer in Multiple Lambda Functions
After creating the layer successfully, you can now use them in any layer, to add any layer follow the below steps.
- Open Lambda Function.
- Under the Code tab, you can find the layers section.
- Click on Add Layer, and choose the layer you want to attach to this function.
- Click on save.

.jpg)
Now you can use any dependency in the layer, and you can reuse the same layer in multiple functions.
Sharing Layer with other Accounts
We can share the lambda layer with specific accounts/organizations or even you can make the layer public, using Serverless Application Repository.
As of now we can share layers using CLI only, run the below command to share the layer with all users (public).
aws lambda add-layer-version-permission
--layer-name dependencies_layer
--version-number 1
--statement-id ShareLayertoPublic
--principal "*"
--action lambda:GetLayerVersion
Using Shared Layer
You can use the shared layer ARN directly to use in the lambda function.
-(1).jpg)
AWS Lambda Layers Configurations and Permissions
Configuration Of Lambda Layers
Step 1: Creating Lambda Layer Archive
- Organizing your shared code and dependencies into a folder.
- Create an archived ZIP of the folder contents maintaining the structure.
Step 2: Publishing the Lambda Layer to AWS Lambda
- Navigate to Lambda Layer in AWS Management Console and click on the "Create Layer"
- Upload the ZIP archive by providing the name, description and select your compatible runtime, and finally click on "Create".
Step 3: Attaching the Lambda Layer to the Lambda Function
- Open the Lambda Functidon and scroll down to the "Layers" section.
- Click on "Add a Layer" and select the created layer along with specifying the version. Finally save your function as a final step of Configuration.
Permissions of Lambda Layers
Step 4: Create an IAM Policy for the Lambda Layer
- Navigate to the IAM from the AWS Management Console. Click on the "Create Policy " in the " Policies" section.
- Define the Permissions by specifying the action; attach the policies to the role.
Step 5: Attaching the IAM Role to the Lambda Function
- Go to the "Execution Role" section in the lambda function configurations. Click on the Role link and attach the IAM policies that are created in the previous step for the role.
Step 6: Granting Public Access to the Lambda Layer ( Optional )
- On using the command `add-layer-version-permission` command in AWS CLI with specifying the argumental information, you can grant the public access to the layer version.
Step 7: Verification of Configuration
- Try on testing the Lambda function for safe guarding its access and usage of shared layers.
Conclusion
In summarizing the enhancement of AWS Lambda Layers usage provides better code reusability in organization as a highly effective strategy. Management of command code and its dependencies into Lambda layers helping the developers facilitate an efficient deployment process by reducing the size of individual functional packages. It supports simple maintenance of updates to improve operational efficiency and promote a modular approach in a structured way. It contributes more scalable and manageable serverless architecture on the AWS Lambda platforms.
Similar Reads
Non-linear Components In electrical circuits, Non-linear Components are electronic devices that need an external power source to operate actively. Non-Linear Components are those that are changed with respect to the voltage and current. Elements that do not follow ohm's law are called Non-linear Components. Non-linear Co
11 min read
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
Class Diagram | Unified Modeling Language (UML) A UML class diagram is a visual tool that represents the structure of a system by showing its classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between them. It helps everyone involved in a project—like developers and designers—understand how the system is organized and how its components interact
12 min read
Steady State Response In this article, we are going to discuss the steady-state response. We will see what is steady state response in Time domain analysis. We will then discuss some of the standard test signals used in finding the response of a response. We also discuss the first-order response for different signals. We
9 min read
Backpropagation in Neural Network Back Propagation is also known as "Backward Propagation of Errors" is a method used to train neural network . Its goal is to reduce the difference between the model’s predicted output and the actual output by adjusting the weights and biases in the network.It works iteratively to adjust weights and
9 min read
Polymorphism in Java Polymorphism in Java is one of the core concepts in object-oriented programming (OOP) that allows objects to behave differently based on their specific class type. The word polymorphism means having many forms, and it comes from the Greek words poly (many) and morph (forms), this means one entity ca
7 min read
3-Phase Inverter An inverter is a fundamental electrical device designed primarily for the conversion of direct current into alternating current . This versatile device , also known as a variable frequency drive , plays a vital role in a wide range of applications , including variable frequency drives and high power
13 min read
What is Vacuum Circuit Breaker? A vacuum circuit breaker is a type of breaker that utilizes a vacuum as the medium to extinguish electrical arcs. Within this circuit breaker, there is a vacuum interrupter that houses the stationary and mobile contacts in a permanently sealed enclosure. When the contacts are separated in a high vac
13 min read
AVL Tree Data Structure An AVL tree defined as a self-balancing Binary Search Tree (BST) where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees for any node cannot be more than one. The absolute difference between the heights of the left subtree and the right subtree for any node is known as the balance factor of
4 min read
What Is Cloud Computing ? Types, Architecture, Examples and Benefits Nowadays, Cloud computing is adopted by every company, whether it is an MNC or a startup many are still migrating towards it because of the cost-cutting, lesser maintenance, and the increased capacity of the data with the help of servers maintained by the cloud providers. Cloud Computing means stori
15 min read