Java StringBufferInputStream Class
Last Updated :
21 Apr, 2025
The StringBufferInoutStream class in Java allows us to create an input stream from a string, so that we can read bytes from it. It only works with the lower 8 bits of each character, It can not handle the full range of character values. Instead of using this class, the best approach is to use ByteArrayInputStream, which does not have this limitation, it can read the full range of character values.
Note: The StringBufferInputStream has been deprecated by Oracle.
The Declaration of the StringBufferInputStream class is below:
public class StringBufferInputStream extends InputStream
This class consists of one constructor, with the help of which we can create an object of this class.
1. StringBufferInputStream(String str): This constructor is used to create a string input stream to read data from a specified string.
Syntax:
StringBufferInputStream(String str)
Example:
Java
// Demonstrating the working
// of StringBufferInputStream(String str)
import java.io.*;
public class Geeks{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a String to be used with StringBufferInputStream
String str = "Hello, World!";
// Creating StringBufferInputStream from the String
StringBufferInputStream is = new StringBufferInputStream(str);
// Reading bytes from the StringBufferInputStream
int data;
try {
while ((data = is.read()) != -1) {
// Print each byte as a character
System.out.print((char) data);
}
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Java StringBufferStream Methods
The image below demonstrates the methods of PipedWriter class.
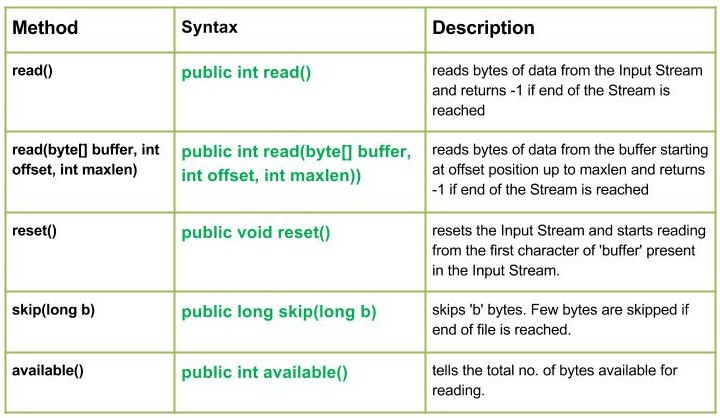
Now, we are going to discuss about each method one by one in detail:
1. read(): This method is used to reads a byte of data from the input stream
Syntax:
public int read()
- Parameter: This method does not take any parameter.
- Return Type: This method returns the read character as an integer otherwise returns -1, when the end of the stream is reached.
2. read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen): This method is used to read a specific number of characters from a buffer.
Syntax:
public int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)
- Parameter: This method takes three parameters, which are listed below:
- buffer: It is an array to store characters
- offset: It is the starting position from where to store character
- maxlen: It is the maximum number of characters to read.
- Return Type: This method returns the maximum number of character to read otherwise returns -1 when the end of the stream is reached.
3. reset(): This method is used to reset the stream and because of this the reading starts from the beginning.
Syntax:
public void reset()
- Parameter: This method does not take any parameter.
- Return Type: This method does not return anything.
4. skip(long n): This method is used to skip and ignore some characters in the input stream.
Syntax:
public long skip(long n)
- Parameter: This method takes a single paramter n, which is the number of bytes to skip
- Return Type: This method returns the actuall number of bytes skipped.
5. available(): This method tells how many characters are left to read in the input stream
Syntax:
public int available()
- Parameter: This method does not take any parameter
- Return Type: This method returns the number of characters that can be read from the input stream.
Now, in the below example we willl see the working of all the methods.
Example:
Java
// Demonstrating the working of
// read(), read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen),
// reset(), skip(long n), available()
import java.io.*;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s1 = "Hello Geeks";
String s2 = "GeeksForGeeks";
StringBufferInputStream b1 = new StringBufferInputStream(s1);
StringBufferInputStream b2 = new StringBufferInputStream(s2);
// available()
System.out.println("Use of available() 1: " + b1.available());
int a;
System.out.println("Use of read() method:");
while ((a = b1.read()) != -1) {
char c = (char) a;
System.out.println(c);
// skip()
b1.skip(1);
}
System.out.println("Use of available() 2: " + b2.available());
byte[] byteBuffer = new byte[15];
b2.read(byteBuffer, 1, 2);
int b;
System.out.print("Remaining characters after partial read: ");
while ((b = b2.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) b);
}
// reset()
b1.reset();
System.out.print("\nAfter reset(): ");
int i;
while ((i = b1.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) i);
}
}
}
OutputUse of available() 1: 11
Use of read() method:
H
l
o
G
e
s
Use of available() 2: 13
Remaining characters after partial read: eksForGeeks
After reset(): Hello Geeks
Similar Reads
Java Tutorial Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language used to build web apps, mobile applications, and enterprise software systems. It is known for its Write Once, Run Anywhere capability, which means code written in Java can run on any device that supports the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).Java s
10 min read
Java Interview Questions and Answers Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, known for its versatility, portability, and wide range of applications. Java is the most used language in top companies such as Uber, Airbnb, Google, Netflix, Instagram, Spotify, Amazon, and many more because of its features and per
15+ min read
Java OOP(Object Oriented Programming) Concepts Java Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs) is a fundamental concept in Java that every developer must understand. It allows developers to structure code using classes and objects, making it more modular, reusable, and scalable.The core idea of OOPs is to bind data and the functions that operate on it,
13 min read
Arrays in Java Arrays in Java are one of the most fundamental data structures that allow us to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable. They are useful for storing and managing collections of data. Arrays in Java are objects, which makes them work differently from arrays in C/C++ in terms of me
15+ min read
Inheritance in Java Java Inheritance is a fundamental concept in OOP(Object-Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in Java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class. In Java, Inheritance means creating new classes based on existing ones. A class that inherits from an
13 min read
Collections in Java Any group of individual objects that are represented as a single unit is known as a Java Collection of Objects. In Java, a separate framework named the "Collection Framework" has been defined in JDK 1.2 which holds all the Java Collection Classes and Interface in it. In Java, the Collection interfac
15+ min read
Java Exception Handling Exception handling in Java allows developers to manage runtime errors effectively by using mechanisms like try-catch block, finally block, throwing Exceptions, Custom Exception handling, etc. An Exception is an unwanted or unexpected event that occurs during the execution of a program, i.e., at runt
10 min read
Java Programs - Java Programming Examples In this article, we will learn and prepare for Interviews using Java Programming Examples. From basic Java programs like the Fibonacci series, Prime numbers, Factorial numbers, and Palindrome numbers to advanced Java programs.Java is one of the most popular programming languages today because of its
8 min read
Java Interface An Interface in Java programming language is defined as an abstract type used to specify the behaviour of a class. An interface in Java is a blueprint of a behaviour. A Java interface contains static constants and abstract methods. Key Properties of Interface:The interface in Java is a mechanism to
12 min read
Polymorphism in Java Polymorphism in Java is one of the core concepts in object-oriented programming (OOP) that allows objects to behave differently based on their specific class type. The word polymorphism means having many forms, and it comes from the Greek words poly (many) and morph (forms), this means one entity ca
7 min read