numpy.nanquantile() in Python
Last Updated :
02 Feb, 2023
numpy.nanquantile(arr, q, axis = None) : Compute the qth quantile of the given data (array elements) along the specified axis, ignoring the nan values. Quantiles plays a very important role in statistics.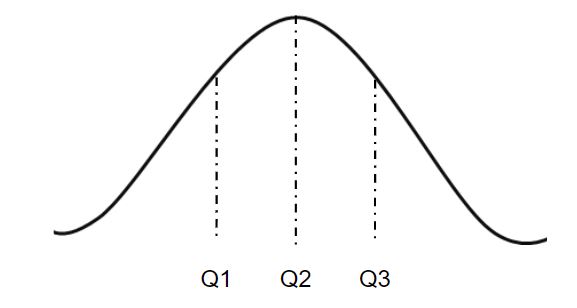
In the figure given above, Q2 is the median and Q3 - Q1 represents the Interquartile Range of the given dataset.
Parameters : arr : [array_like]input array. q : quantile value. axis : [int or tuples of int]axis along which we want to calculate the quantile value. Otherwise, it will consider arr to be flattened(works on all the axis). axis = 0 means along the column and axis = 1 means working along the row. out : [ndarray, optional]Different array in which we want to place the result. The array must have same dimensions as expected output. Results : qth quantile of the array (a scalar value if axis is none) or array with quantile values along specified axis, ignoring nan values.
Code #1 :
Python3
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.nanquantile() method
import numpy as np
# 1D array
arr = [20, 2, 7, np.nan, 34]
print("arr : ", arr)
print("\n-Q1 quantile of arr : ", np.quantile(arr, .50))
print("Q2 - quantile of arr : ", np.quantile(arr, .25))
print("Q3 - quantile of arr : ", np.quantile(arr, .75))
print("\nQ1 - nanquantile of arr : ", np.nanquantile(arr, .50))
print("Q2 - nanquantile of arr : ", np.nanquantile(arr, .25))
print("Q3 - nanquantile of arr : ", np.nanquantile(arr, .75))
Output :
arr : [20, 2, 7, nan, 34]
Q1 - quantile of arr : nan
Q2 - quantile of arr : nan
Q3 - quantile of arr : nan
Q1 - nanquantile of arr : 13.5
Q2 - nanquantile of arr : 5.75
Q3 - nanquantile of arr : 23.5
Code #2:
Python3
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.nanquantile() method
import numpy as np
# 2D array
arr = [[14, np.nan, 12, 33, 44],
[15, np.nan, 27, 8, 19],
[23, 2, np.nan, 1, 4, ]]
print("\narr : \n", arr)
# quantile of the flattened array
print("\nQ2 quantile of arr, axis = None : ", np.quantile(arr, .50))
print("\nQ2 quantile of arr, axis = None : ", np.nanquantile(arr, .50))
print("0th quantile of arr, axis = None : ", np.nanquantile(arr, 0))
Output:
arr :
[[14, nan, 12, 33, 44], [15, nan, 27, 8, 19], [23, 2, nan, 1, 4]]
Q2 quantile of arr, axis = None : nan
Q2 quantile of arr, axis = None : 14.5
0th quantile of arr, axis = None : 1.0
Code #3:
Python3
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.nanquantile() method
import numpy as np
# 2D array
arr = [[14, np.nan, 12, 33, 44],
[15, np.nan, 27, 8, 19],
[23, 2, np.nan, 1, 4, ]]
print("\narr : \n", arr)
# quantile along the axis = 0
print("\nQ2 quantile of arr, axis = 0 : ", np.nanquantile(arr, .50, axis=0))
print("0th quantile of arr, axis = 0 : ", np.nanquantile(arr, 0, axis=0))
# quantile along the axis = 1
print("\nQ2 quantile of arr, axis = 1 : ", np.nanquantile(arr, .50, axis=1))
print("0th quantile of arr, axis = 1 : ", np.nanquantile(arr, 0, axis=1))
print("\nQ2 quantile of arr, axis = 1 : \n",
np.nanquantile(arr, .50, axis=1, keepdims=True))
print("\n0th quantile of arr, axis = 1 : \n",
np.nanquantile(arr, 0, axis=1, keepdims=True))
Output:
arr :
[[14, nan, 12, 33, 44], [15, nan, 27, 8, 19], [23, 2, nan, 1, 4]]
Q2 quantile of arr, axis = 0 : [15. 2. 19.5 8. 19. ]
0th quantile of arr, axis = 0 : [14. 2. 12. 1. 4.]
Q2 quantile of arr, axis = 1 : [23.5 17. 3. ]
0th quantile of arr, axis = 1 : [12. 8. 1.]
Q2 quantile of arr, axis = 1 :
[[23.5]
[17. ]
[ 3. ]]
0th quantile of arr, axis = 1 :
[[12.]
[ 8.]
[ 1.]]
Similar Reads
numpy.nanpercentile() in Python numpy.nanpercentile() function compute the nth percentile of the given data (array elements) along the specified axis and ignores nan values. Example:Pythonimport numpy as np a = np.array([10, 20, np.nan, 40]) res = np.nanpercentile(a, 50) print(res)Output20.0 Explanation: The 50th percentile (media
2 min read
numpy.nansum() in Python numpy.nansum() function computes the sum of array elements over a given axis, treating NaN (Not a Number) values as zero. This is useful when you want to ignore missing or undefined values in your computation. For Example:Pythonimport numpy as np a = np.array([1.0, 2.0, np.nan, 4.0]) res = np.nansum
2 min read
numpy.nanmin() in Python numpy.nanmin()function is used when to returns minimum value of an array or along any specific mentioned axis of the array, ignoring any Nan value. Syntax : numpy.nanmin(arr, axis=None, out=None) Parameters : arr :Input array. axis :Axis along which we want the min value. Otherwise, it will consider
2 min read
numpy.nanvar() in Python numpy.nanvar(arr, axis = None) : Compute the variance of the given data (array elements) along the specified axis(if any), while ignoring NaN values. Example : x = 1 1 1 1 1 Standard Deviation = 0 . Variance = 0 y = 9, 2, 5, 4, 12, 7, 8, 11, 9, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 4, 10, 9, 6, 9, 4 Step 1 : Mean of dist
3 min read
numpy.negative() in Python numpy.negative() function is used when we want to compute the negative of array elements. It returns element-wise negative value of an array or negative value of a scalar. Syntax : numpy.negative(arr, /, out=None, *, where=True, casting='same_kind', order='K', dtype=None, subok=True[, signature, ext
2 min read
numpy.isnan() in Python The numpy.isnan() function tests element-wise whether it is NaN or not and returns the result as a boolean array. Syntax :Â numpy.isnan(array [, out]) Parameters :Â array : [array_like]Input array or object whose elements, we need to test for infinity out : [ndarray, optional]Output array placed wit
2 min read