SQL Query for Matching Multiple Values in the Same Column
Last Updated :
12 Dec, 2024
Querying multiple values within a single column is a vital skill in SQL, enabling users to filter and retrieve data based on specific criteria. Whether we're working with large datasets or simple tables, mastering techniques like the IN clause, LIKE operator, and comparison operators (e.g., >=) ensures efficient and precise data handling.
These methods are especially useful when dealing with scenarios that require matching patterns, comparing numerical values, or checking for multiple conditions simultaneously. This guide focuses on using these techniques in Microsoft SQL Server, with detailed examples to make the concepts accessible for both beginners and experienced professionals.
Step-by-Step Guide: Matching Multiple Values in a Single Column
Efficiently matching multiple values in a single column is essential for filtering and retrieving data in SQL. This guide walks us through practical techniques using operators like IN, LIKE, and comparison operators (>=) to streamline our queries and enhance data handling.
Step 1: Create a Table
Create a table CARS inside the database GeeksForGeeks. This table has three columns: CAR_NAME, COMPANY, and COST containing the name, company, and cost of various cars. This command defines the structure of the CARS table.
Query:
CREATE TABLE CARS(
CAR_NAME VARCHAR(10),
COMPANY VARCHAR(10),
COST INT);
Step 5: Insert Data into the Table
Populate the CARS table with sample data for demonstration purposes. Each INSERT statement adds a row to the CARS table. The data includes car names, their respective companies, and their costs. This sample data will be used for querying in subsequent steps.
Query:
INSERT INTO CARS VALUES('INNOVA','TOYOTA',10000);
INSERT INTO CARS VALUES('CAMRY','TOYOTA',20000);
INSERT INTO CARS VALUES('CIAZ','HONDA',30000);
INSERT INTO CARS VALUES('POLO','VOLKSWAGEN',50000);
INSERT INTO CARS VALUES('BENZ','MERCEDES',100000);Step 6: Display All Rows
Retrieve all rows from the CARS table to verify the inserted data. The SELECT * statement retrieves all columns and rows from the CARS table, displaying the current data stored in the table.
Query:
SELECT * FROM CARS;
Output
 Table Cars
Table CarsStep 7: Match Multiple Values Using IN
Retrieve the details of all the cars belonging to the companies TOYOTA and HONDA. The IN operator checks if the value in the COMPANY column matches any of the specified values (TOYOTA or HONDA). So, this query retrieves all cars manufactured by Toyota and Honda.
Syntax
SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME WHERE COLUMN_NAME IN (MATCHING_VALUE1,MATCHING_VALUE2);
Query:
SELECT * FROM CARS WHERE COMPANY IN ('TOYOTA','HONDA');Output
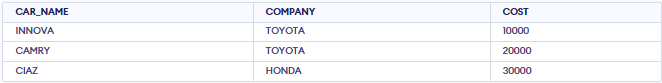 Match Multiple values using IN
Match Multiple values using INStep 8: Match Values Using LIKE
Retrieve the details of all the cars whose name starts with the letter C. The LIKE operator is used for pattern matching. The % symbol represents zero or more characters. This query retrieves all rows where the CAR_NAME starts with the letter 'C', such as CAMRY and CIAZ.
Syntax
SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME WHERE COLUMN_NAME LIKE 'STARTING_LETTER%';
Query:
SELECT * FROM CARS WHERE CAR_NAME LIKE 'C%';
Output
| CAR_NAME | COMPANY | COST |
|---|
| CAMRY | TOYOTA | 20000 |
| CIAZ | HONDA | 30000 |
Step 9: Filter Data Using >= Operator
Retrieve the details of all the cars having cost greater than or equal to 30000. The >= operator compares the COST column against the specified value. This query retrieves all rows where the cost is 30,000 or higher.
Syntax
SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME WHERE COLUMN_NAME >=VALUE;
Query:
SELECT * FROM CARS WHERE COST>=30000;
Output
| CAR_NAME | COMPANY | COST |
|---|
| CIAZ | HONDA | 30000 |
| POLO | VOLKSWAGEN | 50000 |
| BENZ | MERCEDES | 100000 |
Conclusion
In SQL, querying multiple values in the same column is a common task that can be efficiently handled using the IN, OR and EXISTS operators. These operators allow to filter rows based on the multiple matching criteria within a single column. When dealing with the more complex cases such as the matching multiple conditions for the multiple rows, GROUP BY, HAVING and JOIN operations come into the play. The Optimizing queries for the performance by choosing the right operator and index structure is crucial for the large datasets.
Similar Reads
How to Perform SQL Join on Multiple Columns in Same Table?
To perform a SQL JOIN on multiple columns in the same table, we use the Self Join. This technique allows us to create connections between different columns of the same table by comparing them directly. We can implement a Self Join using various types of joins such as “inner,†“left,†“right,†“full,
4 min read
SQL Query to Exclude Multiple Values
To exclude multiple values to be fetched from a table we can use multiple OR statements but when we want to exclude a lot of values it becomes lengthy to write multiple AND statements, To avoid this we can use the NOT IN clause with the array of values that need to be excluded with the WHERE stateme
2 min read
How to Find the Maximum of Multiple Columns in SQL
Finding the maximum value of multiple columns is one of the most common analytical tasks essential for making decisions and analyzing data. Using the MAX() function of SQL, users can find the maximum value in a single column. But to find the maximum value in multiple columns, users need to use other
2 min read
How to Query Multiple Tables in SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a powerful tool for managing and querying relational databases. One of its most valuable features is the ability to query multiple tables simultaneously, allowing us to retrieve and integrate related data efficiently. In this article, we will explain how to query m
4 min read
How to Return Multiple Matching Rows and Columns Using VLOOKUP in Excel?
VLOOKUP function is a premade (already made by Ms-Excel) function in Excel by which we can search for any information in a given spreadsheet. We can use the VLOOKUP function in two ways, first is VLOOKUP with an exact match and VLOOKUP with an approximate match. VLOOKUP with exact match means that k
4 min read
How to Find Duplicates Values Across Multiple Columns in SQL?
In SQL, identifying duplicate entries across multiple columns is crucial for ensuring data integrity and quality. Whether we're working with large datasets or trying to clean up existing data, we can efficiently find duplicates using GROUP BY and COUNT() functions. In this article, we'll focus on ho
3 min read
How To Update Multiple Columns in MySQL?
To update multiple columns in MySQL we can use the SET clause in the UPDATE statement. SET clause allows users to update values of multiple columns at a time. In this article, we will learn how to update multiple columns in MySQL using UPDATE and SET commands. We will cover the syntax and examples,
3 min read
How to check multiple R columns for a value
When working with data frames in R, you may encounter situations where you need to check whether a specific value exists in multiple columns. This task is common when analyzing datasets with several columns containing categorical or numerical data, and you want to identify rows that meet a particula
5 min read
How to Get Multiple Counts With Single Query in SQLite?
In data analysis, obtaining multiple counts for different categories is a common requirement. SQLite, a lightweight and versatile database management system, offers a powerful feature that allows us to achieve this efficiently. In this article, we'll explore how to use SQLite to retrieve multiple co
3 min read
How to Update Multiple Columns in Single Update Statement in SQL?
The SQL UPDATE statement is a important operation for modifying existing records in a database table. It allows us to change the values of one or more columns in a table based on specific conditions. In many cases, we may need to update multiple columns in a single operation to keep our data consist
4 min read