(chapter 8) A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java
- 1. 1A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Frank NIELSEN [email protected] A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java Chapter 8: Data-structures and object methods
- 2. 2A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen ● FIFO data-structures (= First In First Out) ● Heap data-structures ● Non-static methods (= object methods) ● Revisiting lists (OO-style) Agenda
- 3. 3A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen FIFOs: Mastering queues ● Objects are considered in turn, one by one ● Process each object according to their arrival time ● While objects are processed, others are queued ● First object should be first served! Basic examples: ● Waiting in a queue at the post office. ●Printing « jobs> on a printer. FIFO = First In First Out !
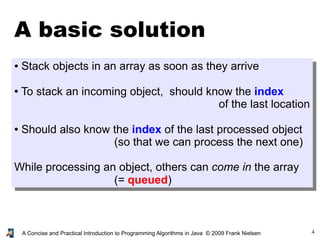
- 4. 4A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen A basic solution ● Stack objects in an array as soon as they arrive ● To stack an incoming object, should know the index of the last location ● Should also know the index of the last processed object (so that we can process the next one) While processing an object, others can come in the array (= queued)
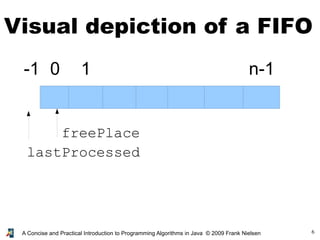
- 5. 5A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen A basic solution ● An array: container array for storing objects ● Two indices: lastProcessed and freePlace ● To add an object x, we do array[freePlace]=x and we then increment: freePlace++ ● To process an object, we increment lastProcessed and we process array[lastProcessed]
- 6. 6A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Visual depiction of a FIFO lastProcessed freePlace 0 1 n-1-1
- 7. 7A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen lastProcessed freePlace O1 FIFO: Queuing objects array[freePlace++]=O1;
- 8. 8A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen O1 Queuing another object O2 lastProcessed freePlace array[freePlace++]=O2;
- 9. 9A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen O1 Processing and queuing O2 O3 lastProcessed freePlace Process(array[lastProcessed++]); array[freePlace++]=O3; Processing and queuing can be done in parallel using threads
- 10. 10A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Programming queues static int lastProcessed=-1; static int freePlace=0; static double[] container=new double[1000]; static void add(double Object) { if (freePlace<1000) {container[freePlace]=Object; freePlace++;} } static double process() { if (freePlace-lastProcessed>1) { // Do something here lastProcessed++; return container[lastProcessed]; } else return -1.0; // special return code: no process }
- 11. 11A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen class QueueDouble { static int lastProcessed=-1; static int freePlace=0; // Max objects is set to 1000 static double[] container=new double[1000]; // Stack in FIFO order static void add(double a) {...} // Process in FIFO order static double process() {...} public static void main(String[] arg) { System.out.println("Queue demo:"); add(3.0); add(5.0); add(7.0); System.out.println(process()); System.out.println(process()); System.out.println(process()); System.out.println(process()); System.out.println(process()); } FIFO: First In First Out
- 12. 12A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Exercise: FIFO in action! Let A be a set of integers such that: ● 1 belongs to A, and ● If a belongs to A, then 2*a+1 and 3*a belongs to A Question: For a given n, display all integers less or equal to n that belong to A.
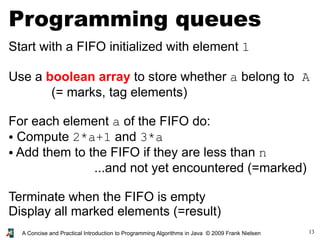
- 13. 13A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Programming queues Start with a FIFO initialized with element 1 Use a boolean array to store whether a belong to A (= marks, tag elements) For each element a of the FIFO do: ● Compute 2*a+1 and 3*a ● Add them to the FIFO if they are less than n ...and not yet encountered (=marked) Terminate when the FIFO is empty Display all marked elements (=result)
- 14. 14A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen final static int n=1000; static int lastProcessed=-1; static int freePlace=0; static int[] container=new int[n]; static boolean[] mark=new boolean[n]; static void add(int a) {if (freePlace<n) {container[freePlace]=a;freePlace++;}} static boolean Empty() { return ((freePlace-lastProcessed)==1); } static void process() {int a; lastProcessed++; a=container[lastProcessed]; if (a<n) mark[a]=true; if (2*a+1<n) add(2*a+1); if (3*a<n) add(3*a); } public static void main(String[] arg) {int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++) mark[i]=false; add(1); while(!Empty()) process(); for(i=0;i<n;i++) {if (mark[i]) System.out.print(i+" ");} System.out.println(""); }
- 15. 15A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen A few remarks on FIFOs ● Set beforehand the size of the array? ● Can wrap the array using mod MAX_SIZE (=circular ring, extend arrays, etc.) ...But how to check whether the queue is empty ... or full with circular arrrays?
- 16. 16A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Priority queues: Heaps (=tas) ● Objects are considered in turn ● Need to process them according to their priorities ● While processing an objects, other may arrive (= are being queued) ● Serve the object with the highest priority first Examples: ● Ressource request ● Operating system tasks
- 17. 17A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Defining mathematically heaps A heap is a sequence of integers: stored compactly in an array such that: For example: 37, 22, 3131, 16, 17, 2, 2323, 12, 6, 9 ( heap of 10 elements) i=7 j=(int)(7/2)=3
- 18. 18A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Drawing a heap ● Draw a heap as a tree (=special graph Vertex/Edge) ● Each node i contains a value t[i] and has 0, 1 or 2 siblings that contain nodes of values less than its parent ● Node i has children 2i and 2i+1 t[i] 37, 22, 31, 16, 17, 2, 23, 12, 6, 9: Read layer by layer, from the root til the leaves
- 19. 19A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Storing and manipulating heaps Easy to code with a linear arraypublic class Heap { int size; int [] label; static final int MAX_SIZE=10000; Heap() { this.size=0; this.label=new int[MAX_SIZE]; } public static void main(String[] args) {} }
- 20. 20A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Fundamental property of heaps Largest value is stored at the root of the tree, namely at the first element of the array. static int maxHeap(Heap h) { return h.label[0]; }
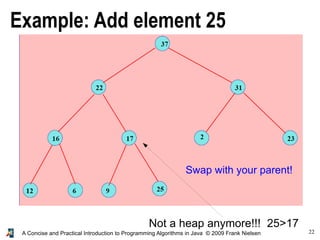
- 21. 21A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Adding an element in a heap ● Add the new element in position n (=n+1th element)... ● But the condition that the array is a heap is violated... ● So that we swap the element until... . ...it satisfies the heap constraint
- 22. 22A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Example: Add element 25 Not a heap anymore!!! 25>17 Swap with your parent!
- 23. 23A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Add element 25... and swap!!! It is a heap now!
- 24. 24A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Adding an element in the heap static void addHeap(int element, Heap h) { h.label[h.size]=element; h.size++; int i=h.size; int j=i/2; while (i>1 && h.label[i]>h.label[j]) { int tmp=h.label[i]; h.label[i]=h.label[j]; h.label[j]=tmp; i=j; // swap j=i/2; } }
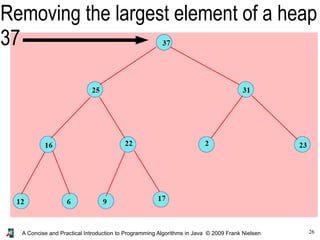
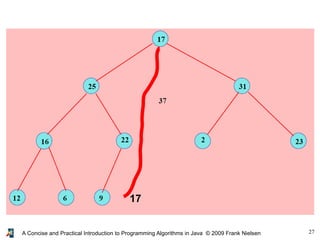
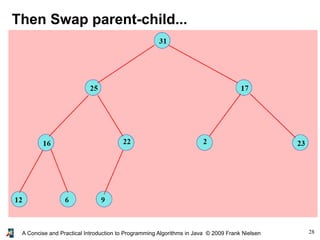
- 25. 25A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Removing the largest element of a heap ● We move the element at position (n-1) and put it at the root (position 0) ● But it is not anymore a heap... ● So we swap to the bottom until... ...the heap condition is satisfied
- 26. 26A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Removing the largest element of a heap 37
- 27. 27A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen 17
- 28. 28A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Then Swap parent-child...
- 29. 29A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen static int removeHeap(int element, Heap h) { h.label[0]=h.label[h.size-1]; h.size--; int i=0,j,k,tmp; while(2*i<=h.size) { j=2*i; if (j<h.size && h.label[j+1]>h.label[j]) j++; if (h.label[i]<h.label[j]) {tmp=h.label[i]; h.label[i]=h.label[j]; h.label[j]=tmp; i=j;} else break; } return h.label[h.size-1]; } Removing the largest element of a heap
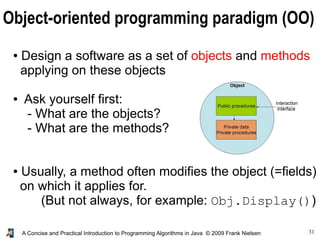
- 30. 30A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Non-static methods and objects ● Do not write static in front of the method ● Method is thus attached to the object for which it applies for ● For example, we prefer: u.display() rather than display(u) u.addElement(a) instead of addElement(a,u) ● To reference the object on which the method is called upon use this Object-oriented programming paradigm (OO)
- 31. 31A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Object-oriented programming paradigm (OO) ● Design a software as a set of objects and methods applying on these objects ● Ask yourself first: - What are the objects? - What are the methods? ● Usually, a method often modifies the object (=fields) on which it applies for. (But not always, for example: Obj.Display())
- 32. 32A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen OO style: object methods versus static functions class Box { double width, height, depth; Box(double w, double h, double d) { this.width=w; this.height=h; this.depth=d; } double Volume() {return this.width*this.height*this.depth;} } class OOstyle { static double Volume(Box box) {return box.width*box.height*box.depth;} public static void main(String[] s) { Box myBox=new Box(5,2,1); System.out.println("Volume by static method:"+Volume(myBox)); System.out.println("Volume by object method:"+myBox.Volume()); } } Object (non-static) method
- 33. 33A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen class Toolkit { static final double PI=3.14; static double Square(double x) {return x*x;} static double Cubic(double x) {return x*x*x;} } class StaticFuncStyle { public static void main(String[] s) { double radius=0.5; double volSphere=(4/3.0)*Toolkit.PI*Toolkit.Cubic(radius); double areaDisk=Toolkit.PI*Toolkit.Square(radius); } } Static methods are useful for defining: - Constants - Basic functions ....in a library.
- 34. 34A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Heaps revisited in Object-Oriented style int maxHeap() { return this.label[0]; } void add(int element) { ... } void removeTop() { ... } Observe that the keyword static has disappeared
- 35. 35A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen List in object-oriented style ● A cell stores information (say, an integer) and point/refer to the next one. ● Pointing to another cell means storing a reference to the corresponding cell.
- 36. 36A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Pay special attention to null !!! ● Remember that we cannot access fields of the null object ● Throw the exception nullPointerException ● Thus we need to check whether the current object is null or not, before calling the method ● In the reminder, we consider that all lists (also the void list) contain a first cell that stores no information.
- 37. 37A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen public class List { int element; List next; List(int el, List l) { this.element=el; this.next=l; } static List EmptyList() { return new List(0,null); } boolean isEmpty() { return (this.next==null); } } Revisiting the linked list (OO style)
- 38. 38A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen int length() { List u=this; int res=0; while(u!=null) {res++;u=u.next;} return res-1; } boolean belongsTo(int el) { List u=this.next; while(u!=null) { if (el==u.element) return true; u=u.next; } return false; } Revisiting the linked list (OO style)
- 39. 39A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen void add(int el) {List u=this.next; this.next=new List(el,u); } void delete(int el) { List v=this; List w=this.next; while(w!=null && w.element !=el) { v=w; w=w.next; } if (w!=null) v.next=w.next; } Revisiting the linked list (OO style)
- 40. 40A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen void display() { List u=this.next; while(u!=null) {System.out.print(u.element+"->"); u=u.next;} System.out.println("null"); } static List FromArray(int [] array) { List u=EmptyList(); for(int i=array.length-1; i>=0; i--) u.add(array[i]); return u; } Revisiting the linked list (OO style)
- 41. 41A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Revisiting the linked list (OO style) public static void main(String[] args) { int [] array={2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23}; List u=FromArray(array); u.add(1); u.display(); u.delete(5); u.display(); System.out.println(u.belongsTo(17)); System.out.println(u.belongsTo(24)); }
- 42. 42A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Stacks (LIFO): Last In First Out Two basic operations for that data-structure: ● Push: Add an element on top of the stack ● Pull: Remove the topmost element
- 43. 43A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Stacks (LIFO) using arrays class StackArray { int nbmax; int index; int [ ] array; // Constructors StackArray(int n) { this.nbmax=n; array=new int[nbmax]; index=-1; System.out.println("Succesfully created a stack array object..."); } // Methods void Push(int element) { if (index<nbmax-1) array[++index]=element; } int Pull() { if (index>=0 ) return array[index--]; else return -1; } }
- 44. 44A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen class DemoStack{ public static void main(String [] args) { StackArray myStack=new StackArray(10); int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) myStack.Push(i); for(i=0;i<15;i++) System.out.println(myStack.Pull()); }
- 45. 45A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Stacks (LIFO) using linked lists class List { int element; List next; // Constructor List(int el, List tail) { this.element=el; this.next=tail; } List insertHead(int el) { return new List(el,this); } }
- 46. 46A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen class Stack { List list; Stack() { list=null; } void Push(int el) { if (list!=null) list=list.insertHead(el); else list=new List(el,null); } int Pull() {int val; if (list!=null) {val=list.element; list=list.next;} else val=-1; return val; } }
- 47. 47A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen // Use a Java package here import java.util.Stack; public class MainClass { public static void main (String args[]) { Stack s = new Stack(); s.push("A"); s.push("B"); s.push("C"); System.out.println(s); } } Stacks: API
- 48. 48A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen class DemoStackList { public static void main(String [] args) { Stack myStack=new Stack(); int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) myStack.Push(i); for(i=0;i<15;i++) System.out.println(myStack.Pull()); } } Stacks (LIFO) using linked lists Notice: Same code as StackArray demo program.
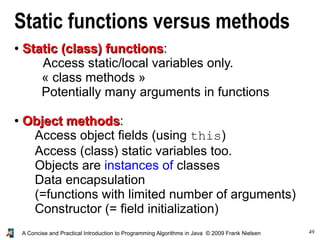
- 49. 49A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Static functions versus methods ● Static (class) functionsStatic (class) functions: Access static/local variables only. « class methods » Potentially many arguments in functions ● Object methodsObject methods: Access object fields (using this) Access (class) static variables too. Objects are instances of classes Data encapsulation (=functions with limited number of arguments) Constructor (= field initialization)
- 50. 50A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen



![5A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
A basic solution
● An array: container array for storing objects
● Two indices: lastProcessed and freePlace
● To add an object x, we do array[freePlace]=x and
we then increment: freePlace++
● To process an object, we increment lastProcessed and
we process array[lastProcessed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-5-320.jpg)
![7A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
lastProcessed
freePlace
O1
FIFO: Queuing objects
array[freePlace++]=O1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-7-320.jpg)
![8A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
O1
Queuing another object
O2
lastProcessed
freePlace
array[freePlace++]=O2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-8-320.jpg)
![9A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
O1
Processing and queuing
O2 O3
lastProcessed
freePlace
Process(array[lastProcessed++]);
array[freePlace++]=O3;
Processing and queuing can be done in parallel using threads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-9-320.jpg)
![10A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Programming queues
static int lastProcessed=-1;
static int freePlace=0;
static double[] container=new double[1000];
static void add(double Object)
{
if (freePlace<1000)
{container[freePlace]=Object;
freePlace++;}
}
static double process()
{
if (freePlace-lastProcessed>1)
{ // Do something here
lastProcessed++;
return container[lastProcessed];
}
else
return -1.0; // special return code: no process
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-10-320.jpg)
![11A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
class QueueDouble
{
static int lastProcessed=-1;
static int freePlace=0;
// Max objects is set to 1000
static double[] container=new double[1000];
// Stack in FIFO order
static void add(double a)
{...}
// Process in FIFO order
static double process()
{...}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
System.out.println("Queue demo:");
add(3.0);
add(5.0);
add(7.0);
System.out.println(process());
System.out.println(process());
System.out.println(process());
System.out.println(process());
System.out.println(process());
}
FIFO:
First In First Out](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-11-320.jpg)

![14A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
final static int n=1000; static int lastProcessed=-1;
static int freePlace=0; static int[] container=new int[n];
static boolean[] mark=new boolean[n];
static void add(int a)
{if (freePlace<n) {container[freePlace]=a;freePlace++;}}
static boolean Empty()
{ return ((freePlace-lastProcessed)==1); }
static void process()
{int a;
lastProcessed++; a=container[lastProcessed];
if (a<n) mark[a]=true;
if (2*a+1<n) add(2*a+1);
if (3*a<n) add(3*a);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) mark[i]=false;
add(1);
while(!Empty())
process();
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{if (mark[i])
System.out.print(i+" ");}
System.out.println("");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-14-320.jpg)



![18A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Drawing a heap
● Draw a heap as a tree (=special graph Vertex/Edge)
● Each node i contains a value t[i] and has
0, 1 or 2 siblings that contain nodes of values
less than its parent
● Node i has children 2i and 2i+1 t[i]
37, 22, 31, 16, 17, 2, 23, 12, 6, 9:
Read layer by layer,
from the root til the leaves](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-18-320.jpg)
![19A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Storing and manipulating heaps
Easy to code with a linear arraypublic class Heap
{
int size;
int [] label;
static final int MAX_SIZE=10000;
Heap()
{
this.size=0;
this.label=new int[MAX_SIZE];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-19-320.jpg)
![20A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Fundamental property of heaps
Largest value is stored at the root of the tree, namely
at the first element of the array.
static int maxHeap(Heap h)
{
return h.label[0];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-20-320.jpg)


![24A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Adding an element in the heap
static void addHeap(int element, Heap h)
{
h.label[h.size]=element;
h.size++;
int i=h.size;
int j=i/2;
while (i>1 && h.label[i]>h.label[j])
{
int tmp=h.label[i];
h.label[i]=h.label[j];
h.label[j]=tmp;
i=j; // swap
j=i/2;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-24-320.jpg)

![29A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
static int removeHeap(int element, Heap h)
{
h.label[0]=h.label[h.size-1];
h.size--;
int i=0,j,k,tmp;
while(2*i<=h.size)
{
j=2*i;
if (j<h.size && h.label[j+1]>h.label[j])
j++;
if (h.label[i]<h.label[j])
{tmp=h.label[i];
h.label[i]=h.label[j];
h.label[j]=tmp;
i=j;}
else break;
}
return h.label[h.size-1];
}
Removing the largest element of a heap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-29-320.jpg)

![32A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
OO style:
object methods
versus
static functions
class Box
{
double width, height, depth;
Box(double w, double h, double d)
{
this.width=w; this.height=h; this.depth=d;
}
double Volume()
{return this.width*this.height*this.depth;}
}
class OOstyle
{
static double Volume(Box box)
{return box.width*box.height*box.depth;}
public static void main(String[] s)
{
Box myBox=new Box(5,2,1);
System.out.println("Volume by static method:"+Volume(myBox));
System.out.println("Volume by object method:"+myBox.Volume());
}
} Object (non-static) method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-32-320.jpg)
![33A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
class Toolkit
{
static final double PI=3.14;
static double Square(double x)
{return x*x;}
static double Cubic(double x)
{return x*x*x;}
}
class StaticFuncStyle
{
public static void main(String[] s)
{
double radius=0.5;
double volSphere=(4/3.0)*Toolkit.PI*Toolkit.Cubic(radius);
double areaDisk=Toolkit.PI*Toolkit.Square(radius);
}
}
Static methods are
useful for defining:
- Constants
- Basic functions
....in a library.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-33-320.jpg)
![34A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Heaps revisited in Object-Oriented style
int maxHeap()
{
return this.label[0];
}
void add(int element)
{
...
}
void removeTop()
{
...
}
Observe that the keyword static has disappeared](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-34-320.jpg)





![40A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
void display()
{
List u=this.next;
while(u!=null)
{System.out.print(u.element+"->");
u=u.next;}
System.out.println("null");
}
static List FromArray(int [] array)
{
List u=EmptyList();
for(int i=array.length-1; i>=0; i--)
u.add(array[i]);
return u;
}
Revisiting the linked list (OO style)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-40-320.jpg)
![41A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Revisiting the linked list (OO style)
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int [] array={2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23};
List u=FromArray(array);
u.add(1);
u.display();
u.delete(5);
u.display();
System.out.println(u.belongsTo(17));
System.out.println(u.belongsTo(24));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-41-320.jpg)

![43A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Stacks (LIFO) using arrays
class StackArray
{
int nbmax;
int index;
int [ ] array;
// Constructors
StackArray(int n)
{
this.nbmax=n;
array=new int[nbmax]; index=-1;
System.out.println("Succesfully created a stack array object...");
}
// Methods
void Push(int element)
{
if (index<nbmax-1)
array[++index]=element; }
int Pull()
{
if (index>=0 ) return array[index--];
else return -1;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-43-320.jpg)
![44A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
class DemoStack{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
StackArray myStack=new StackArray(10);
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
myStack.Push(i);
for(i=0;i<15;i++)
System.out.println(myStack.Pull());
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-44-320.jpg)


![47A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
// Use a Java package here
import java.util.Stack;
public class MainClass {
public static void main (String args[]) {
Stack s = new Stack();
s.push("A");
s.push("B");
s.push("C");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Stacks: API](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-47-320.jpg)
![48A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
class DemoStackList
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Stack myStack=new Stack();
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
myStack.Push(i);
for(i=0;i<15;i++)
System.out.println(myStack.Pull());
}
}
Stacks (LIFO) using linked lists
Notice: Same code as StackArray demo program.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-8-140701005550-phpapp01/85/chapter-8-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-48-320.jpg)