3 programming-using-java introduction-to computer
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes174 views
What is a computer? Computer Organization Programming languages Java Class Libraries Typical Java development environment Case Study: Unified Modeling Language
1 of 22
Downloaded 13 times




















Ad
Recommended
4 programming-using-java intro-tojava20102011



4 programming-using-java intro-tojava20102011Mahmoud Alfarra First Program in Java
Discussion of the main concepts
Install the JDK and JCreator
Memory Concepts and Data Types
Variables and Identifiers
2 programming-using-java how to built application



2 programming-using-java how to built applicationMahmoud Alfarra This document discusses key concepts in programming using Java, including:
1. The programming life cycle consists of five stages: thinking, planning, designing, coding, and testing.
2. Algorithms can be represented through pseudo code and flow charts to document solutions before coding.
3. Several examples of algorithms are provided to calculate averages, check conditions, and iterate through loops.
7 programming-using-java decision-making220102011



7 programming-using-java decision-making220102011Mahmoud Alfarra This document discusses selection statements in Java including if-else statements, nested if-else statements, blocks, and switch statements. It provides examples of using these statements to check conditions, compare values, and select different code paths. It also assigns practice problems for students to write programs using selection statements to check grades, login credentials, and print days of the week.
Planning to computer program(southeast university)



Planning to computer program(southeast university)Arup deb nath This document contains information about computer programs and programming concepts. It discusses that computer programs are lists of instructions written in a way that computers can understand. There are three main types of programs: operating systems, utilities, and applications. It also discusses the importance of planning for programming and defines algorithms and methods for describing algorithms like flowcharts and pseudocode.
Lecture 22 - Error Handling



Lecture 22 - Error HandlingMd. Imran Hossain Showrov C Programming Language is the most popular computer language and most used programming language till now. It is very simple and elegant language. This lecture series will give you basic concepts of structured programming language with C.
notes on Programming fundamentals 



notes on Programming fundamentals ArghodeepPaul This document provides an introduction to computer programming concepts, including:
- A computer program is a sequence of instructions written in a programming language to perform a specified task on a computer. Programming languages include Python, Java, C++, and others.
- Computer programming, or coding, involves writing instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. It allows computers to perform tasks like displaying messages, performing calculations, and more.
- Key elements of programming languages include data types, variables, operators, functions, and control structures like conditionals and loops. These elements are used to write programs to solve problems.
6 programming-using-java decision-making20102011-



6 programming-using-java decision-making20102011-Mahmoud Alfarra What is the decision ?
Equality and relational operators.
Precedence and associatively of operations
How to use if ?
Practice
Compiler 



Compiler Md. Sumon Fakir The document discusses the different phases of a compiler:
1. The lexical analyzer converts source code into tokens.
2. The syntax tree verifies that strings of tokens are valid based on grammar rules and reports errors.
3. The semantic analyzer checks for semantic errors like type mismatches and ensures types are used consistently.
4. Intermediate code generation converts code into postfix notation or three-address code.
5. Code optimization improves code efficiency.
6. Code generation produces the final target code.
Programming Fundamentals lecture 2



Programming Fundamentals lecture 2REHAN IJAZ The document provides an introduction to programming. It discusses what a program is, the process of writing instructions known as programming, different types of programming languages including machine language, assembly language, C and C++. It provides examples of Hello World programs in C++ and the steps involved in writing, compiling, running and testing a program. These include coming up with an idea, designing the program structure, writing the code, alpha and beta testing to fix bugs before final release.
Compiler an overview



Compiler an overviewamudha arul This document provides an introduction to compilers. It discusses how compilers bridge the gap between high-level programming languages that are easier for humans to write in and machine languages that computers can actually execute. It describes the various phases of compilation like lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, code generation, and optimization. It also compares compilers to interpreters and discusses different types of translators like compilers, interpreters, and assemblers.
Compiler presentaion



Compiler presentaionShady A. Alefrangy A compiler is a program that translates source code written in one programming language into another target language. It performs several steps including lexical analysis, parsing, code generation and optimization. The compiler consists of a front end that checks syntax and semantics, a middle end that performs optimizations, and a back end that generates assembly code. Compilers can be single pass or multi pass and are used to translate from high-level languages like C to machine-executable object code.
Phases of compiler



Phases of compilerPANKAJKUMAR2519 The document describes the main phases of compilation: lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, intermediate code generation, code optimization, and code generation. Lexical analysis converts the source code into tokens. Syntax analysis groups the tokens into a parse tree. Semantic analysis checks that the program is semantically correct. Intermediate code generation outputs machine-independent code. Code optimization improves the intermediate code. Finally, code generation converts the optimized code into machine-dependent target code.
Intro To Programming Concepts



Intro To Programming ConceptsJussi Pohjolainen This document provides an introduction to computer programming concepts, including:
1) It defines what a computer program is and explains that programs get input from users and generate output.
2) It discusses the importance of program design, implementation, and testing according to a specification.
3) It explains that high-level programming languages are used instead of machine language, and compilers translate programs into machine language.
Phases of Compiler



Phases of CompilerA. S. M. Shafi The document discusses the phases of a compiler, which are typically divided into analysis and synthesis phases. The analysis phase includes lexical analysis, syntax analysis, and semantic analysis. The synthesis phase includes intermediate code generation, code optimization, and code generation. Other topics discussed include symbol tables, error handlers, examples of common compilers, and reasons for learning about compilers.
Types of system software



Types of system softwareInderbir Kaur Sandhu This document discusses different types of software and system software. It defines hardware as the physical components of a computer and software as programs that enhance hardware capabilities. There are three main types of software: application software designed for specific tasks, utility software for system maintenance, and system software that controls computer operations but does not solve specific problems. System software includes language translators like assemblers, compilers, and interpreters; macro processors; linkers; loaders; text editors; debuggers; and the operating system.
Basic Computer Programming



Basic Computer ProgrammingAllen de Castro This document provides an introduction to basic computer programming concepts including:
- Programs are sets of step-by-step instructions that direct a computer to perform tasks and produce outputs. Programming languages provide rules and instructions for computers.
- The programming process involves identifying problems, planning solutions with flowcharts or pseudocode, coding the program, testing it, and documenting it.
- There are different levels of programming languages from low-level machine languages to high-level languages like Visual Basic that resemble English. Procedural languages use sequential statements while object-oriented languages are event-driven.
- Basic commands in QBasic are introduced like PRINT, CLS, INPUT, IF/THEN/ELSE
Compiler



CompilerAchyuth Dorasala This document defines and describes compilers. It discusses that a compiler translates high-level programming languages into machine-level languages. The compiler process involves two main phases - analysis and synthesis. The analysis phase breaks down the source code and generates an intermediate representation through lexical, syntax and semantic analysis. The synthesis phase then generates target code from the intermediate representation, optimizing and outputting assembly code. The document also outlines the typical structure of a compiler into front-end, middle-end and back-end components and discusses native compilers, cross compilers and virtual machines.
Compiler Design(Nanthu)



Compiler Design(Nanthu)guest91cc85 This Compiler Design Notes is very useful to us. it has created by very short method.
anybody can understand it.
265 ge8151 problem solving and python programming - 2 marks with answers



265 ge8151 problem solving and python programming - 2 marks with answersvithyanila The document provides sample questions and answers related to problem solving and Python programming. It includes 20 multiple choice questions covering topics like algorithms, pseudo code, flowcharts, recursion, and more. An algorithm is provided to find the minimum of 3 numbers in a list. The key building blocks of an algorithm are also defined as statements, sequence, selection, repetition, and functions.
Lecture 2 - Introductory Concepts



Lecture 2 - Introductory ConceptsMd. Imran Hossain Showrov C Programming Language is the most popular computer language and most used programming language till now. It is very simple and elegant language. This lecture series will give you basic concepts of structured programming language with C.
Compiler design



Compiler designnazmul hoque The document discusses the different phases of a compiler:
1. Lexical analysis scans the source code as characters and converts them into tokens.
2. Syntax analysis takes the tokens and checks that they form a syntactically correct parse tree based on the language's grammar.
3. Semantic analysis checks that the parse tree follows the language's rules, such as compatible data types in assignments.
Techniques & applications of Compiler



Techniques & applications of CompilerPreethi AKNR A compiler is a program that translates a program written in a source language into an equivalent program in a target language. It has two major phases: analysis and synthesis. The analysis phase creates an intermediate representation using tools like a lexical analyzer, syntax analyzer, and semantic analyzer. The synthesis phase creates the target program from this representation using tools like an intermediate code generator, code optimizer, and code generator. Techniques used in compiler design like lexical analysis, parsing, and code generation have applications in other areas like text editors, databases, and natural language processing.
Phases of the Compiler - Systems Programming



Phases of the Compiler - Systems ProgrammingMukesh Tekwani The document describes the various phases of compilation:
1. Lexical analysis scans the source code and groups characters into tokens.
2. Syntax analysis checks syntax and constructs parse trees.
3. Semantic analysis generates intermediate code, checks for semantic errors using symbol tables, and enforces type checking.
4. Optional optimization improves programs by making them more efficient.
Java chapter 5



Java chapter 5Mukesh Tekwani The document discusses control flow statements in Java, which break up the sequential flow of execution and enable conditional execution of code blocks. It covers the following key control flow statements:
- If-then and if-then-else statements allow conditional execution based on boolean tests.
- Switch statements allow multiple possible execution paths based on a variable's value.
- Loops - while, do-while and for statements - repeatedly execute a block of code while/until a condition is met.
- Branching statements like break, continue and return alter the flow of loops or methods.
The document provides examples to illustrate the usage of each statement type.
Notacd07



Notacd07Azmiah Mahmud This document provides an introduction to basic programming concepts including programs, programming, programming languages, and careers in programming.
A program is a series of organized instructions that directs a computer to perform tasks. Programming involves creating a set of commands that direct a computer. Programming languages allow humans to communicate with computers through using words, symbols, and codes. There are many programming languages with different rules. Careers in programming include programmer, programmer analyst, computer scientist, and software engineer.
Error detection recovery



Error detection recoveryTech_MX The document discusses error detection and recovery in compilers. It describes how compilers should detect various types of errors and attempt to recover from them to continue processing the program. It covers lexical, syntactic and semantic errors and different strategies compilers can use for error recovery like insertion, deletion or replacement of tokens. It also discusses properties of good error reporting and handling shift-reduce conflicts.
Compiler 



Compiler IGZ Software house The document discusses the key components and functions of a compiler. A compiler acts as a translator that transforms human-oriented programming languages into machine languages. The major tasks of any compiler are analysis of the source program and synthesis of a machine-language program. A typical compiler consists of several main components - a scanner, parser, semantic routines, code generator, and optimizer. The scanner breaks the source code into tokens. The parser checks the syntax and generates a parse tree. Semantic routines perform analysis and translation to an intermediate representation. The code generator transforms the intermediate code to target machine code, and the optimizer improves the generated code.
Concept of compiler in details



Concept of compiler in detailskazi_aihtesham This document provides an overview of the key components and phases of a compiler. It discusses that a compiler translates a program written in a source language into an equivalent program in a target language. The main phases of a compiler are lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, intermediate code generation, code optimization, code generation, and symbol table management. Each phase performs important processing that ultimately results in a program in the target language that is equivalent to the original source program.
Lecture 1 introduction to_computersb(2)



Lecture 1 introduction to_computersb(2)xterribad The document provides an introduction to computers and their components. It discusses that a computer contains hardware components like the processor, memory, storage devices, and input/output devices. The processor interprets and executes instructions stored in memory. Memory is used to store programs and data temporarily. The document also introduces programming concepts like variables, data types, classes, methods, and the main method as the entry point of a Java program.
jhtp8_ch01.ppt



jhtp8_ch01.pptKPKumar15 This document provides an overview of Java programming and computer science concepts. It discusses the history and evolution of programming languages like Fortran, COBOL, Pascal, Ada, BASIC and Java. It also explains the core components of a computer and how programs are developed and executed. Specifically, it outlines the five phases of developing a Java program: edit, compile, load, verify and execute.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Programming Fundamentals lecture 2



Programming Fundamentals lecture 2REHAN IJAZ The document provides an introduction to programming. It discusses what a program is, the process of writing instructions known as programming, different types of programming languages including machine language, assembly language, C and C++. It provides examples of Hello World programs in C++ and the steps involved in writing, compiling, running and testing a program. These include coming up with an idea, designing the program structure, writing the code, alpha and beta testing to fix bugs before final release.
Compiler an overview



Compiler an overviewamudha arul This document provides an introduction to compilers. It discusses how compilers bridge the gap between high-level programming languages that are easier for humans to write in and machine languages that computers can actually execute. It describes the various phases of compilation like lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, code generation, and optimization. It also compares compilers to interpreters and discusses different types of translators like compilers, interpreters, and assemblers.
Compiler presentaion



Compiler presentaionShady A. Alefrangy A compiler is a program that translates source code written in one programming language into another target language. It performs several steps including lexical analysis, parsing, code generation and optimization. The compiler consists of a front end that checks syntax and semantics, a middle end that performs optimizations, and a back end that generates assembly code. Compilers can be single pass or multi pass and are used to translate from high-level languages like C to machine-executable object code.
Phases of compiler



Phases of compilerPANKAJKUMAR2519 The document describes the main phases of compilation: lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, intermediate code generation, code optimization, and code generation. Lexical analysis converts the source code into tokens. Syntax analysis groups the tokens into a parse tree. Semantic analysis checks that the program is semantically correct. Intermediate code generation outputs machine-independent code. Code optimization improves the intermediate code. Finally, code generation converts the optimized code into machine-dependent target code.
Intro To Programming Concepts



Intro To Programming ConceptsJussi Pohjolainen This document provides an introduction to computer programming concepts, including:
1) It defines what a computer program is and explains that programs get input from users and generate output.
2) It discusses the importance of program design, implementation, and testing according to a specification.
3) It explains that high-level programming languages are used instead of machine language, and compilers translate programs into machine language.
Phases of Compiler



Phases of CompilerA. S. M. Shafi The document discusses the phases of a compiler, which are typically divided into analysis and synthesis phases. The analysis phase includes lexical analysis, syntax analysis, and semantic analysis. The synthesis phase includes intermediate code generation, code optimization, and code generation. Other topics discussed include symbol tables, error handlers, examples of common compilers, and reasons for learning about compilers.
Types of system software



Types of system softwareInderbir Kaur Sandhu This document discusses different types of software and system software. It defines hardware as the physical components of a computer and software as programs that enhance hardware capabilities. There are three main types of software: application software designed for specific tasks, utility software for system maintenance, and system software that controls computer operations but does not solve specific problems. System software includes language translators like assemblers, compilers, and interpreters; macro processors; linkers; loaders; text editors; debuggers; and the operating system.
Basic Computer Programming



Basic Computer ProgrammingAllen de Castro This document provides an introduction to basic computer programming concepts including:
- Programs are sets of step-by-step instructions that direct a computer to perform tasks and produce outputs. Programming languages provide rules and instructions for computers.
- The programming process involves identifying problems, planning solutions with flowcharts or pseudocode, coding the program, testing it, and documenting it.
- There are different levels of programming languages from low-level machine languages to high-level languages like Visual Basic that resemble English. Procedural languages use sequential statements while object-oriented languages are event-driven.
- Basic commands in QBasic are introduced like PRINT, CLS, INPUT, IF/THEN/ELSE
Compiler



CompilerAchyuth Dorasala This document defines and describes compilers. It discusses that a compiler translates high-level programming languages into machine-level languages. The compiler process involves two main phases - analysis and synthesis. The analysis phase breaks down the source code and generates an intermediate representation through lexical, syntax and semantic analysis. The synthesis phase then generates target code from the intermediate representation, optimizing and outputting assembly code. The document also outlines the typical structure of a compiler into front-end, middle-end and back-end components and discusses native compilers, cross compilers and virtual machines.
Compiler Design(Nanthu)



Compiler Design(Nanthu)guest91cc85 This Compiler Design Notes is very useful to us. it has created by very short method.
anybody can understand it.
265 ge8151 problem solving and python programming - 2 marks with answers



265 ge8151 problem solving and python programming - 2 marks with answersvithyanila The document provides sample questions and answers related to problem solving and Python programming. It includes 20 multiple choice questions covering topics like algorithms, pseudo code, flowcharts, recursion, and more. An algorithm is provided to find the minimum of 3 numbers in a list. The key building blocks of an algorithm are also defined as statements, sequence, selection, repetition, and functions.
Lecture 2 - Introductory Concepts



Lecture 2 - Introductory ConceptsMd. Imran Hossain Showrov C Programming Language is the most popular computer language and most used programming language till now. It is very simple and elegant language. This lecture series will give you basic concepts of structured programming language with C.
Compiler design



Compiler designnazmul hoque The document discusses the different phases of a compiler:
1. Lexical analysis scans the source code as characters and converts them into tokens.
2. Syntax analysis takes the tokens and checks that they form a syntactically correct parse tree based on the language's grammar.
3. Semantic analysis checks that the parse tree follows the language's rules, such as compatible data types in assignments.
Techniques & applications of Compiler



Techniques & applications of CompilerPreethi AKNR A compiler is a program that translates a program written in a source language into an equivalent program in a target language. It has two major phases: analysis and synthesis. The analysis phase creates an intermediate representation using tools like a lexical analyzer, syntax analyzer, and semantic analyzer. The synthesis phase creates the target program from this representation using tools like an intermediate code generator, code optimizer, and code generator. Techniques used in compiler design like lexical analysis, parsing, and code generation have applications in other areas like text editors, databases, and natural language processing.
Phases of the Compiler - Systems Programming



Phases of the Compiler - Systems ProgrammingMukesh Tekwani The document describes the various phases of compilation:
1. Lexical analysis scans the source code and groups characters into tokens.
2. Syntax analysis checks syntax and constructs parse trees.
3. Semantic analysis generates intermediate code, checks for semantic errors using symbol tables, and enforces type checking.
4. Optional optimization improves programs by making them more efficient.
Java chapter 5



Java chapter 5Mukesh Tekwani The document discusses control flow statements in Java, which break up the sequential flow of execution and enable conditional execution of code blocks. It covers the following key control flow statements:
- If-then and if-then-else statements allow conditional execution based on boolean tests.
- Switch statements allow multiple possible execution paths based on a variable's value.
- Loops - while, do-while and for statements - repeatedly execute a block of code while/until a condition is met.
- Branching statements like break, continue and return alter the flow of loops or methods.
The document provides examples to illustrate the usage of each statement type.
Notacd07



Notacd07Azmiah Mahmud This document provides an introduction to basic programming concepts including programs, programming, programming languages, and careers in programming.
A program is a series of organized instructions that directs a computer to perform tasks. Programming involves creating a set of commands that direct a computer. Programming languages allow humans to communicate with computers through using words, symbols, and codes. There are many programming languages with different rules. Careers in programming include programmer, programmer analyst, computer scientist, and software engineer.
Error detection recovery



Error detection recoveryTech_MX The document discusses error detection and recovery in compilers. It describes how compilers should detect various types of errors and attempt to recover from them to continue processing the program. It covers lexical, syntactic and semantic errors and different strategies compilers can use for error recovery like insertion, deletion or replacement of tokens. It also discusses properties of good error reporting and handling shift-reduce conflicts.
Compiler 



Compiler IGZ Software house The document discusses the key components and functions of a compiler. A compiler acts as a translator that transforms human-oriented programming languages into machine languages. The major tasks of any compiler are analysis of the source program and synthesis of a machine-language program. A typical compiler consists of several main components - a scanner, parser, semantic routines, code generator, and optimizer. The scanner breaks the source code into tokens. The parser checks the syntax and generates a parse tree. Semantic routines perform analysis and translation to an intermediate representation. The code generator transforms the intermediate code to target machine code, and the optimizer improves the generated code.
Concept of compiler in details



Concept of compiler in detailskazi_aihtesham This document provides an overview of the key components and phases of a compiler. It discusses that a compiler translates a program written in a source language into an equivalent program in a target language. The main phases of a compiler are lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, intermediate code generation, code optimization, code generation, and symbol table management. Each phase performs important processing that ultimately results in a program in the target language that is equivalent to the original source program.
Similar to 3 programming-using-java introduction-to computer (20)
Lecture 1 introduction to_computersb(2)



Lecture 1 introduction to_computersb(2)xterribad The document provides an introduction to computers and their components. It discusses that a computer contains hardware components like the processor, memory, storage devices, and input/output devices. The processor interprets and executes instructions stored in memory. Memory is used to store programs and data temporarily. The document also introduces programming concepts like variables, data types, classes, methods, and the main method as the entry point of a Java program.
jhtp8_ch01.ppt



jhtp8_ch01.pptKPKumar15 This document provides an overview of Java programming and computer science concepts. It discusses the history and evolution of programming languages like Fortran, COBOL, Pascal, Ada, BASIC and Java. It also explains the core components of a computer and how programs are developed and executed. Specifically, it outlines the five phases of developing a Java program: edit, compile, load, verify and execute.
Introduction To Computer and Java



Introduction To Computer and JavaPRN USM This document provides an overview of computers and programming languages. It discusses the goals of programming and components of computers like hardware, software, CPU, memory and I/O devices. It also describes different types of programming languages from machine language to assembly language to high-level languages like Java. The document explains how a Java program is compiled into bytecode and run on a Java Virtual Machine. It discusses common errors in programming like syntax errors, runtime errors and logic errors.
Plc part 1



Plc part 1Taymoor Nazmy This document provides information about a programming languages concepts course, including details about the course code, title, lecturer, and description. The course aims to describe the evolution of programming languages and understand different computation models or paradigms like imperative, functional, logic and object-oriented programming. It will cover topics like syntax, semantics, data types, expressions and control structures over 13 weeks. Students will complete an assignment on MATLAB/Octave and two term exams. The course objectives are listed as understanding different programming language paradigms and concepts to select the proper language to solve problems.
Software programming and development



Software programming and developmentAli Raza The document provides an overview of software programming and development. It defines key concepts like software, hardware, programming languages, compilers, interpreters, and algorithms. It discusses low-level languages like machine code and assembly, and high-level languages like C/C++, Java, and .NET. It also explains the planning process for computer programs using algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudocode and the differences between compilers and interpreters. The document aims to introduce foundational topics in software engineering.
CHAPTER-1.ppt



CHAPTER-1.pptTekle12 The document provides an introduction to programming and problem solving using computers. It discusses the following key points:
- Problem solving involves determining the inputs, outputs, and steps to solve a problem. Computers can be programmed to solve problems more quickly if they involve extensive inputs/outputs or complex/time-consuming methods.
- The software development process includes requirements specification, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and documentation. Algorithms using pseudocode or flowcharts are designed to solve problems.
- Programming languages have evolved from low-level machine languages to high-level languages. Earlier generations like assembly language were more machine-oriented while modern languages are more portable, problem-oriented, and easier for humans to read and write
An overview of computers and programming languages 



An overview of computers and programming languages Ahmad Idrees This chapter discusses computers and programming languages. It explains that a computer system consists of hardware and software components. Programming languages allow users to communicate instructions to the computer, with compilers translating programs into machine language. The chapter then covers algorithms for problem solving, and structured and object-oriented programming methodologies. Key topics include how Java programs are processed, the evolution of programming languages, and the components of a computer system.
Lecture 1



Lecture 1Dhanikonda Srinivasarao This document contains lecture notes on programming with C from GITAM University. It introduces computers and their basic components like the input, arithmetic logic, control, memory and output units. It then discusses the different generations of computers and programming languages, from first generation machine languages to fourth generation very high level languages. Sample programs using while loops and review questions are also provided.
Csc240 lecture 1



Csc240 lecture 1Ainuddin Yousufzai The document outlines the course objectives, outline, textbooks, and lecture topics for an Introduction to Programming course. The course will cover computer systems and how they work, programming concepts like flowcharts and algorithms, and implementing concepts in C++. Lectures will include introductions to computers and organization, programming languages, and personal, distributed, and client/server computing models.
Savitch ch 01



Savitch ch 01Terry Yoast This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 1 of an introduction to computers and C++ programming textbook. It discusses computer systems, including hardware components and memory; programming concepts like algorithms, problem solving, and the software development process; an introduction to C++ as a programming language; and strategies for testing and debugging programs. Key terms and ideas are presented through a series of slides with explanations and examples.
Savitch ch 01



Savitch ch 01Terry Yoast This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 1 of an introduction to computers and C++ programming textbook. It discusses computer systems, including hardware components and memory; programming concepts like algorithms, problem solving, and the software development process; an introduction to C++ as a programming language; and strategies for testing and debugging programs. Key terms and ideas are presented through a series of slides with explanations and examples.
Introduction to Programming Concepts By Aamir Saleem Ansari



Introduction to Programming Concepts By Aamir Saleem AnsariTech Get the free powerpoint slide of introduction to programming concepts from Techora. Learn programming and other things from using our slides. For more visit : www.techora.net
This introductory slide program teaches you the foundational skills all programmers use, whether they program mobile apps, create web pages, or analyze data.
Computer programs are collections of instructions that tell a computer how to interact with the user, interact with the computer hardware and process data. The first programmable computers required the programmers to write explicit instructions to directly manipulate the hardware of the computer. This “machine language” was very tedious to write by hand since even simple tasks such as printing some output on the screen require 10 or 20 machine language commands. Machine language is often referred to as a “low level language” since the code directly manipulates the hardware of the computer.
By contrast, higher level languages such as “C”, C++, Pascal, Cobol, Fortran, ADA and Java are called “compiled languages”. In a compiled language, the programmer writes more general instructions and a compiler (a special piece of software) automatically translates these high level instructions into machine language. The machine language is then executed by the computer. A large portion of software in use today is programmed in this fashion.
Assembly Langauge Assembly Langauge Assembly Langauge



Assembly Langauge Assembly Langauge Assembly Langaugemustafkhalid The document provides an introduction to assembly language and how it relates to high-level languages and machine language. It discusses how assembly language allows programmers to understand how computers work at a low level while still using mnemonics and symbolic addresses to write readable code. It provides an example of translating a simple math problem into assembly code for an Intel Pentium processor.
02_Intro to Programming Language.pptx



02_Intro to Programming Language.pptxJhunBrianAndam The document provides an introduction to programming concepts including:
- The Analytical Engine was an early general purpose computer conceived by Charles Babbage in the 1830s to perform mathematical calculations. Ada Lovelace made early contributions to the concept of programming.
- There are different levels of programming languages from machine language that uses binary code to assembly language that uses symbolic codes to high-level languages that resemble English.
- Popular high-level languages include Ada, BASIC, C, C++, Java and Python. Programs in high-level languages must be translated before execution.
- Operating systems control and monitor system activities, allocate resources, and schedule operations to make efficient use of hardware for running application
UNIT 2 ECSE-2.pptx



UNIT 2 ECSE-2.pptxAdharshKokkula The document discusses several key topics in computer science and programming:
1. It defines programming languages as sets of instructions used to communicate with computers and develop applications. It distinguishes between low-level languages like machine code and assembly, and high-level languages like Python, Java, and C++.
2. It also covers markup languages like HTML and XML used to structure documents, and scripting languages like Python, Ruby, and Perl used to integrate systems.
3. The document outlines the program development process of understanding problems, designing solutions, writing code, and testing programs. It introduces flowcharts, pseudocode, and algorithms used in the design process.
4. Finally, it provides an overview
Savitch Ch 01



Savitch Ch 01Terry Yoast This document is the first chapter of an introduction to computers and C++ programming textbook. It covers computer systems, including hardware components and memory; programming concepts like algorithms, problem solving, and the program design process; an introduction to C++ as a programming language; and testing and debugging programs. The chapter contains slides with explanations and examples to describe these topics at a high level.
Ad
More from Mahmoud Alfarra (20)
Computer Programming, Loops using Java - part 2



Computer Programming, Loops using Java - part 2Mahmoud Alfarra Computer Programming, Loops part 2 using Java
Mahmoud Rafeek Alfarra
00972597393906
Computer Programming, Loops using Java



Computer Programming, Loops using JavaMahmoud Alfarra This document discusses repetition statements in Java, including while, for, and do-while loops. It provides examples of using each loop type, such as calculating the average of test grades in a class and summing even integers. The break and continue statements are also covered, along with examples of how they alter loop flow. Key aspects of counter-controlled repetition like loop counters, initialization, increment/decrement, and continuation conditions are defined.
Chapter 10: hashing data structure



Chapter 10: hashing data structureMahmoud Alfarra This document provides an outline and overview of hashing and hash tables. It defines hashing as a technique for storing data to allow for fast insertion, retrieval, and deletion. A hash table uses an array and hash function to map keys to array indices. Collision resolution techniques like linear probing are discussed. The document also summarizes the Hashtable class in .NET, which uses buckets and load factor to avoid collisions. Examples of hash functions and using the Hashtable class are provided.
Chapter9 graph data structure



Chapter9 graph data structureMahmoud Alfarra This document discusses graphs and their representation in code. It defines graphs as consisting of vertices and edges, with edges specified as pairs of vertices. It distinguishes between directed and undirected graphs. Key graph terms like paths, cycles, and connectivity are defined. Real-world systems that can be modeled as graphs are given as an example. The document then discusses representing vertices and edges in code, choosing an adjacency matrix to represent the edges in the graph.
Chapter 8: tree data structure



Chapter 8: tree data structureMahmoud Alfarra The document discusses trees and binary trees as data structures. It defines what a tree is, including parts like the root, parent, child, leaf nodes. It then defines binary trees as trees where each node has no more than two children. Binary search trees are introduced as binary trees where all left descendants of a node are less than or equal to the node and all right descendants are greater. The document concludes by discussing how to build a binary search tree class with Node objects.
Chapter 7: Queue data structure



Chapter 7: Queue data structureMahmoud Alfarra This document provides an outline and overview of the queue data structure. It defines a queue as a first-in, first-out (FIFO) structure where new items are added to the rear of the queue and items are removed from the front. The key queue operations of enqueue and dequeue are described. Code examples are provided for implementing a queue using a linked list structure with classes for the queue, its nodes, and methods for common queue operations like enqueue, dequeue, peek, clear, print, and search. Different types of queues like linear, circular, and double-ended queues are also mentioned.
Chapter 6: stack data structure



Chapter 6: stack data structureMahmoud Alfarra The document provides an overview of stack data structures, including definitions and examples. It discusses key stack operations like push, pop, peek, clear, print all, and search. Code examples are given for an Employee class and Stack class implementation to demonstrate how these operations work on a stack of employee objects. The document aims to teach the fundamentals of stack data structures and provide code samples to practice stack operations.
Chapter 5: linked list data structure



Chapter 5: linked list data structureMahmoud Alfarra This document provides an outline and overview of linked lists. It defines a linked list as a collection of nodes that are linked together by references to the next node. Each node contains a data field and a reference field. It describes how to implement a linked list using a self-referential class with fields for data and a reference to the next node. It then outlines common linked list operations like insertion and deletion at different positions as well as sorting and searching the linked list.
Chapter 4: basic search algorithms data structure



Chapter 4: basic search algorithms data structureMahmoud Alfarra 1) The document discusses two common search algorithms: sequential search and binary search. Sequential search looks at each item in a list sequentially until the target is found. Binary search works on a sorted list and divides the search space in half at each step.
2) It provides pseudocode examples of how each algorithm works step-by-step to find a target value in a list or array.
3) Binary search is more efficient than sequential search when the list is sorted, as it can significantly reduce the number of comparisons needed to find the target. Sequential search is used when the list is unsorted.
Chapter 3: basic sorting algorithms data structure



Chapter 3: basic sorting algorithms data structureMahmoud Alfarra The document provides an outline and introduction for a chapter on basic sorting algorithms, including bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort algorithms. It includes pseudocode examples and explanations of each algorithm. It notes that bubble sort is one of the slowest but simplest algorithms, involving values "floating" to their correct positions. Selection sort finds the smallest element and places it in the first position, then repeats to find the next smallest. Insertion sort works by moving larger elements to the right to make room for smaller elements inserted from the left.
Chapter 2: array and array list data structure



Chapter 2: array and array list data structureMahmoud Alfarra Chapter 2: array and array list data structures
Chapter1 intro toprincipleofc#_datastructure_b_cs



Chapter1 intro toprincipleofc#_datastructure_b_csMahmoud Alfarra This document is a presentation on data structures in C# by Mr. Mahmoud R. Alfarra. It introduces C# and its uses in different applications. It covers various data types in C#, calculations and logical operations, control statements like if/else and loops. The document also discusses arrays, methods, and classes in C#. It provides examples to explain concepts like selection statements, iteration, and calling methods. The presentation aims to provide an introduction to the principles of C# for learning purposes.
Chapter 0: introduction to data structure



Chapter 0: introduction to data structureMahmoud Alfarra This document provides an introduction and outline for a course on data structures. It introduces the lecturer, Mahmoud Rafeek Alfarra, and lists his qualifications. It outlines the course objectives, resources, guidelines, assessment, and schedule. Key topics that will be covered include arrays, sorting and searching algorithms, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees and graphs. The document provides classifications of different types of data structures such as linear vs nonlinear, static vs dynamic memory allocation. It concludes with information about how students can be successful in the course.
3 classification



3 classificationMahmoud Alfarra Definition of classification
Basic principles of classification
Typical
How Does Classification Works?
Difference between Classification & Prediction.
Machine learning techniques
Decision Trees
k-Nearest Neighbors
8 programming-using-java decision-making practices 20102011



8 programming-using-java decision-making practices 20102011Mahmoud Alfarra This document is a lecture on decision making practices in Java. It identifies errors in code snippets involving if/else statements and while loops. It also contains examples to trace code with variables and determine output based on variable values. The document is in Arabic and English and presented by Mahmoud R. Alfarra on using Java and correcting errors in code involving conditional and iterative structures.
5 programming-using-java intro-tooop20102011



5 programming-using-java intro-tooop20102011Mahmoud Alfarra This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming concepts like classes, objects, and methods in Java. It defines classes as templates that define attributes and behaviors of objects as variables and methods. Objects are instances of classes. The document explains how to declare a class with access modifiers, variables, constructors, and methods. It also demonstrates how to create objects using the new keyword and access object attributes and methods.
1 programming-using-java -introduction



1 programming-using-java -introductionMahmoud Alfarra Who is Lecturer ?!
Course objectives
Resources
Course guidelines
Assessment
A word about lectures
Sending Home works & Questions
Office Hours
How to be successfully ?!
Course outlines
What is Programming?
Why Programming?
تلخيص النصوص تلقائيا



تلخيص النصوص تلقائياMahmoud Alfarra مقدمة حول موضوع تلخيص النصوص تلقائيا Automated Text Summarization وهو من المواضيع المميزة في تنقيب البيانات، ولا تزال مجالا للبحث وانتاج المعرفة.
4×4×4 لتحصيل التميز



4×4×4 لتحصيل التميزMahmoud Alfarra 12 نقطة لتحصيل التميز الدراسي في الحياة الجامعية
في البيت
في المحاضرة
ووقت الامتحان
لتقديم تدريب عن بعد أو مباشر يمكنك التواصل معي عبر:
[email protected]
whatsapp: 00972597393906
بالتوفيق للجميع
Data preparation and processing chapter 2



Data preparation and processing chapter 2Mahmoud Alfarra This document provides an overview of key aspects of data preparation and processing for data mining. It discusses the importance of domain expertise in understanding data. The goals of data preparation are identified as cleaning missing, noisy, and inconsistent data; integrating data from multiple sources; transforming data into appropriate formats; and reducing data through feature selection, sampling, and discretization. Common techniques for each step are outlined at a high level, such as binning, clustering, and regression for handling noisy data. The document emphasizes that data preparation is crucial and can require 70-80% of the effort for effective real-world data mining.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Webcrawler_Mule_AIChain_MuleSoft_Meetup_Hyderabad



Webcrawler_Mule_AIChain_MuleSoft_Meetup_HyderabadVeera Pallapu 1. MuleSoft AI Chain Concept Introduction
2. Demo on Mule AI Chain Connector
3. Q/A
4. Wrap up
Pests of Rice: Damage, Identification, Life history, and Management.pptx



Pests of Rice: Damage, Identification, Life history, and Management.pptxArshad Shaikh Rice pests can significantly impact crop yield and quality. Major pests include the brown plant hopper (Nilaparvata lugens), which transmits viruses like rice ragged stunt and grassy stunt; the yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas), whose larvae bore into stems causing deadhearts and whiteheads; and leaf folders (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis), which feed on leaves reducing photosynthetic area. Other pests include rice weevils (Sitophilus oryzae) and gall midges (Orseolia oryzae). Effective management strategies are crucial to minimize losses.
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big Cycle



Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big CycleDadang Solihin A complete and practical understanding of the Big Debt Cycle. A much more practical understanding of how supply and demand really work compared to the conventional economic thinking. A complete and practical understanding of the Overall Big Cycle, which is driven by the Big Debt Cycle and the other major cycles, including the big political cycle within countries that changes political orders and the big geopolitical cycle that changes world orders.
How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18



How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18Celine George Efficient maintenance management is crucial for keeping equipment and work centers running smoothly in any business. Odoo 18 provides a Maintenance module that helps track, schedule, and manage maintenance requests efficiently.
june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptx



june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptxroger malina art science is over -talk by roger malina for jack madden group
Analysis of Quantitative Data Parametric and non-parametric tests.pptx



Analysis of Quantitative Data Parametric and non-parametric tests.pptxShrutidhara2 This presentation covers the following points--
Parametric Tests
• Testing the Significance of the Difference between Means
• Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) - One way and Two way
• Analysis of Co-variance (One-way)
Non-Parametric Tests:
• Chi-Square test
• Sign test
• Median test
• Sum of Rank test
• Mann-Whitney U-test
Moreover, it includes a comparison of parametric and non-parametric tests, a comparison of one-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA, and one-way ANCOVA.
How to Manage Upselling of Subscriptions in Odoo 18



How to Manage Upselling of Subscriptions in Odoo 18Celine George Subscriptions in Odoo 18 are designed to auto-renew indefinitely, ensuring continuous service for customers. However, businesses often need flexibility to adjust pricing or quantities based on evolving customer needs.
Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...



Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...National Information Standards Organization (NISO) This presentation was provided by Nicole 'Nici" Pfeiffer of the Center for Open Science (COS), during the first session of our 2025 NISO training series "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communications." Session One was held June 5, 2025.
Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptx



Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptxbobby205207 Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptx
How to Create a Rainbow Man Effect in Odoo 18



How to Create a Rainbow Man Effect in Odoo 18Celine George In Odoo 18, the Rainbow Man animation adds a playful and motivating touch to task completion. This cheerful effect appears after specific user actions, like marking a CRM opportunity as won. It’s designed to enhance user experience by making routine tasks more engaging.
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024



BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS BRINGS T0 YOU A FUN-FILLED, SEAT EDGE BUSINESS QUIZ
DIVE INTO THE PRELIMS OF BIZCOM 2024
QM: GOWTHAM S
BCom (2022-25)
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS
Module 4 Presentation - Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Y...



Module 4 Presentation - Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Y...GeorgeDiamandis11 Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Youth Work
How to Configure Vendor Management in Lunch App of Odoo 18



How to Configure Vendor Management in Lunch App of Odoo 18Celine George The Vendor management in the Lunch app of Odoo 18 is the central hub for managing all aspects of the restaurants or caterers that provide food for your employees.
Diptera: The Two-Winged Wonders, The Fly Squad: Order Diptera.pptx



Diptera: The Two-Winged Wonders, The Fly Squad: Order Diptera.pptxArshad Shaikh Diptera, commonly known as flies, is a large and diverse order of insects that includes mosquitoes, midges, gnats, and horseflies. Characterized by a single pair of wings (hindwings are modified into balancing organs called halteres), Diptera are found in almost every environment and play important roles in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and food sources. Some species, however, are significant pests and disease vectors, transmitting diseases like malaria, dengue, and Zika virus.
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd



Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecdrazelitouali Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
How to Create an Event in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 Slides



How to Create an Event in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 SlidesCeline George Creating an event in Odoo 18 is a straightforward process that allows you to manage various aspects of your event efficiently.
Odoo 18 Events Module is a powerful tool for organizing and managing events of all sizes, from conferences and workshops to webinars and meetups.
Rai dyansty Chach or Brahamn dynasty, History of Dahir History of Sindh NEP.pptx



Rai dyansty Chach or Brahamn dynasty, History of Dahir History of Sindh NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
In the seventh century, the rule of Sindh state was in the hands of Rai dynasty. We know the names of five kings of this dynasty- Rai Divji, Rai Singhras, Rai Sahasi, Rai Sihras II and Rai Sahasi II. During the time of Rai Sihras II, Nimruz of Persia attacked Sindh and killed him. After the return of the Persians, Rai Sahasi II became the king. After killing him, one of his Brahmin ministers named Chach took over the throne. He married the widow of Rai Sahasi and became the ruler of entire Sindh by suppressing the rebellions of the governors.
Trends Spotting Strategic foresight for tomorrow’s education systems - Debora...



Trends Spotting Strategic foresight for tomorrow’s education systems - Debora...EduSkills OECD Deborah Nusche, Senior Analyst, OECD presents at the OECD webinar 'Trends Spotting: Strategic foresight for tomorrow’s education systems' on 5 June 2025. You can check out the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/ Other speakers included: Deborah Nusche, Senior Analyst, OECD
Sophie Howe, Future Governance Adviser at the School of International Futures, first Future Generations Commissioner for Wales (2016-2023)
Davina Marie, Interdisciplinary Lead, Queens College London
Thomas Jørgensen, Director for Policy Coordination and Foresight at European University Association
Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...



Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024



BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
Rai dyansty Chach or Brahamn dynasty, History of Dahir History of Sindh NEP.pptx



Rai dyansty Chach or Brahamn dynasty, History of Dahir History of Sindh NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
3 programming-using-java introduction-to computer
- 1. Using Java MINISTRY OF EDUCATION & HIGHER EDUCATION COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY KHANYOUNIS- PALESTINE
- 2. What is computer? Computer Organization Programming languages Java Class Libraries Typical Java development environment Case Study: Unified Modeling Language Emank X Mezank 2Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 3. A computer is a device capable of performing computations and making logical decisions at speeds millions (even billions) of times faster than human beings can. Computers process data under the control of sets of instructions called computer programs. 3Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 4. A computer consists of various devices referred to as hardware. e.g.: The keyboard. Screen. Mouse. Disks … The programs that run on a computer are referred to as software. 4Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 5. computer may be envisioned as divided into six logical units : 1. Input unit. This is the "receiving" section of the computer. It obtains information from input devices and places this information at the disposal of the other units so that it can be processed. 5Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 6. 2. Output unit. This is the "shipping" section of the computer. It takes information that the computer has processed and places it on various output devices to make the information available for use outside the computer. 3. Memory unit. This is the rapid-access, relatively low-capacity "warehouse" section of the computer. 6Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
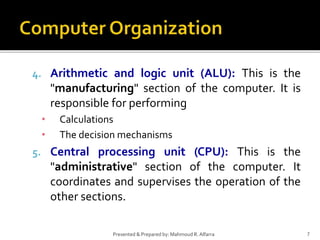
- 7. 7Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra 4. Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU): This is the "manufacturing" section of the computer. It is responsible for performing • Calculations • The decision mechanisms 5. Central processing unit (CPU): This is the "administrative" section of the computer. It coordinates and supervises the operation of the other sections.
- 8. 6. Secondary storage unit. This is the long-term, high-capacity "warehousing" section of the computer. 8Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 9. Programming languages may be divided into three general types: 1.Machine languages 2.Assembly languages 3.High-level languages 9Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra In two pages, write what is algorithm, why and how do they represented ?HW 2.1
- 10. Any computer can directly understand only its own machine language. It is defined by the computer hardware design. Machine languages are machine dependent (i.e., a particular machine language can be used on only one type of computer). 10Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 11. Machine languages generally consist of strings of numbers (0,1). So, It was simply: Too slow Tedious for most programmers 11Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 12. Programmers began using English-like abbreviations to represent elementary operations. These abbreviations formed the basis of assembly languages. 12Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
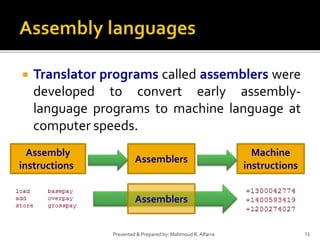
- 13. Translator programs called assemblers were developed to convert early assembly- language programs to machine language at computer speeds. 13Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra Assembly instructions Assemblers Machine instructions Assemblers
- 14. To speed the programming process, high-level languages were developed in which single statements could be written to accomplish substantial tasks. Translator programs called compilers convert high- level language programs into machine language. 14Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra high-level languages Compilers Machine instructions Compilers
- 15. Java programs consist of pieces called classes. Classes include pieces called methods that perform tasks and return information when they complete them. 15Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra Java Class methods Instructions
- 16. 16Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra The collections of existing classes in the Java class libraries, are also known as the Java APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
- 17. 17Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 18. 18 Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 19. 19Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra UML: a graphical language that allows people who design software systems to use an industry standard notation to represent them. Study the case study from the text book of the course, section 1.16HW3.1
- 20. Fill in the blanks in each of the following statements: 1. The logical unit of the computer that receives information from outside the computer for use by the computer is the __________. 2. The process of instructing the computer to solve a problems is called ________. 3. __________ is a type of computer language that uses English-like abbreviations for machine-language instructions. 4. __________ is a logical unit of the computer that sends information which has already been processed by the computer to various devices so that it may be used outside the computer. 5. __________ and __________ are logical units of the computer that retain information. 6. __________ is a logical unit of the computer that performs calculations. 7. __________ is a logical unit of the computer that makes logical decisions. 8. __________ languages are most convenient to the programmer for writing programs quickly and easily. 9. The only language that a computer can directly understand is that computer's __________. 10. __________ is a logical unit of the computer that coordinates the activities of all the other logical units. 20Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra Solve the following practice… HW3.2
- 21. َر َْننع ،ُهْنَع هللا َي ِضَر َةَماَمُأ يِبَأ َْنعُ َِّلله اِىنََ ِ َِّلله ِِنلُسِهنْيَىَع َِناَق ،َمِىَسَل:(ِِاَمنِِّ َّللش ََ ِِناََ ِنِإِ نِس َمنَىََْشَّلل ُُنَفْرَيِشَاعناَس َّلل ِلَأ ِئِطْخُمْشَّلل ِمِىْسُمْشَّلل ِدْبَعْشَّلل َِنعْسَّللَل َمِدَن ْنِإَف ،ِيءِسُمْشَ َِّلله َرَفْغَت َةد َِِّللَل ْ َبِتُك الِإَل ،اَهاََْشَأ اَهْنِم)األلباني حسنـه 21Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra
- 22. Main concepts of Programming 22Presented & Prepared by: Mahmoud R. Alfarra


![Ch.01-2.ppt java[27/11, 11:00 am] Sumaya👸🏻✨️: Mida kale waqtiga wuba kudhamaa...](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/ch-241202055830-248c61fe-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)



