A new algorithm for data compression technique using vlsi
- 1. PROJECT REPORT ON A NEW ALGORITHM (K-RLE )FOR DATA COMPRESSION TECHNIQUE USING VLSI AVR & SVR ENGINEERING COLLEGE NANDYAL UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF Mr. M.MAHABOOB BASHA, M.Tech, (Ph D) 1
- 2. presented by…………… B.THEJESWARA REDDY (10AM1A04A9) E.SURESH (10AM1A04A3) T.SHABARISH (10AM1A0475) C. RAMA KRISHNA (10AM1A0469) N.SATYANARAYANA RAJU (102J1A0465) S. SANTHOSH (10AM1A0493) 2 A NEW ALGORITHM (K-RLE) FOR DATA COMPRESSION TECHNIQUE USING VLSI
- 4. INTRODUCTION In this article, we want to introduce in-network processing technique in order to save energy. In-network processing techniques allow the reduction of the amount of data to be transmitted. The well known in-network processing technique is data compression and/or data aggregation. Data compression is a process that reduces the amount of data in order to reduce data transmitted and/or decreases transfer time because the size of the data is reduced.
- 5. Recent technological breakthrough in low power processing units and communication devices have enabled the development of distributed autonomous nodes able to sense environmental data, compute and transmit it using wireless communication to a base station known as Sink for future analysis; thus, forming a Wireless Sensor Network . However, Wireless Sensor Network is driven by a severe constraint which is power management. This power management has led researchers to explore scheduling sensor states. Scheduling sensor states is a technique that decides which sensor may change its state (transmit, receive, idle, Sleep), according to the current and anticipated communications needs. The most common technique for saving energy is the use of sleep mode where significant parts of the sensor’s transceiver are switched off. The question is how to keep the same data rate sent to the base station by reducing the number of transmission.
- 6. In computer science and information theory, data compression or source coding is the process of encoding information using fewer bits (or other information-bearing units) than an un encoded representation would use, through use of specific encoding schemes. To reduce the volume of data to be transmitted (text, fax, images) To reduce the bandwidth required for transmission and to reduce storage requirements (speech, audio, video) To reduce power consumption (saving energy) Reduces data transfer time keeping same data rate.
- 7. DATA COMPRESSION ALGORITHMS Compression is useful because it helps reduce the consumption of expensive resources, such as hard disk space or transmission bandwidth On the downside, compressed data must be decompressed to be used, and this extra processing may be detrimental to some applications. For instance, a compression scheme for video may require expensive hardware for the video to be decompressed fast enough to be viewed as it is being decompressed (the option of decompressing the video in full before watching it may be inconvenient, and requires storage space for the decompressed video). The design of data compression schemes therefore involves trade-offs among various factors, including the degree of compression, the amount of distortion introduced (if using a lossy compression scheme, and the computational resources required to compress and uncompress the data.
- 8. LOSSY COMPRESSION Lossy image compression is used in digital cameras, to increase storage capacities with minimal degradation of picture quality. Similarly, DVDs use the lossy MPEG-2 Video codec for video compression. In lossy audio compression, methods of psychoacoustics are used to remove non-audible (or less audible) components of the signal. Compression of human speech is often performed with even more specialized techniques, so that "speech compression" or "voice coding" is sometimes distinguished as a separate discipline from "audio compression". Different audio and speech compression standards are listed under audio codecs. Voice compression is used in Internet telephony for example, while audio compression is used for CD ripping and is decoded by audio players
- 9. LOSSLESS COMPRESSION Lossless compression algorithms usually exploit statistical redundancy in such a way as to represent the sender's data more concisely without error. Lossless compression is possible because most real- world data has statistical redundancy. For example, in English text, the letter 'e' is much more common than the letter 'z', and the probability that the letter 'q' will be followed by the letter 'z' is very small.
- 10. LOSSLESS VERSUS LOSSY COMPRESSION Lossless compression algorithms usually exploit statistical redundancy in such a way as to represent the sender's data more concisely without error. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data has statistical redundancy. For example, in English text, the letter 'e' is much more common than the letter 'z', and the probability that the letter 'q' will be followed by the letter 'z' is very small. Another kind of compression, called lossy data compression or perceptual coding, is possible if some loss of fidelity is acceptable. Generally, a lossy data compression will be guided by research on how people perceive the data in question. For example, the human eye is more sensitive to subtle variations in luminance than it is to variations in color. JPEG image compression works in part by "rounding off" some of this less-important information. Lossy data compression provides a way to obtain the best fidelity for a given amount of compression. In some cases, transparent (unnoticeable) compression is desired
- 11. Run-length encoding (RLE) If a data item d occurs n consecutive times in the input stream, we replace the n occurrences with the single pair nd . For example, consider a screen containing plain black text on a solid white background. There will be many long runs of white pixels in the blank space, and many short runs of black pixels within the text. Let us take a hypothetical single scan line, with B representing a black pixel and W representing white: WWWWWWWWWWWWBWWWWWWWWWWWWBBBW WWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWBWWWW WWWWWWWWWW If we apply the run-length encoding (RLE) data compression algorithm to the above hypothetical scan line, we get the following: 12W1B12W3B24W1B14W
- 12. OVERVIEW OF K-RLE DATA COMPRESSION TECHNIQUE In this thesis implemented a new data compression technique that is the K-RLE data compression technique, In general the run length encoding algorithm is data compression algorithm and basic idea of this: If a data item d occurs n consecutive times in the input stream, we replace the n occurrences with the single pair nd and K-RLE algorithm is very efficient compression technique which decreases the ratio of compression when compared to traditional RLE compression technique. the behind the new algorithm islet K be a number, If a data item d or data between d+K and d-K occur n consecutive times in the input stream, we replace the n occurrences with the single pair nd.
- 13. K-RUN-LEGTH-ENCODING ALGORITHM FOR DATA COMPRESSION The idea behind this new algorithm is this: let K be a number, If a data item d or data between d+K and d-K occur n consecutive times in the input stream, we replace the n occurrences with the single pair nd. We introduce a parameter K which is a precision. K is defined as: δ= σ/ K With a minimum estimate of the Allan standard deviation i.e. σ is a representative of the instrument measurement noise below which the precision is no longer significant. If K = 0, K-RLE is RLE. K has the same unit as the dataset values, in this case degree. However, the change on RLE using the K-precision introduces data modified. Indeed, while RLE is a lossless compression algorithm K-RLE is a lossy compression algorithm. This algorithm is lossless at the user level because it chooses K considering that there is no difference between the data item d, d+K or d-K according to the application.
- 14. Sen0 Sen1 Sen2 Sen3 Sen4 Sen5 Sen6 Sen7 Ch0[7:0] Ch7[7:0] ADCMUX ADCFIFO 32x8 ADCData[7:0] Clk ChSel[2:0] ChCntr CntOvr ScanCntr ScanOvr ScanEna SampleEna Rst ADCEna FIFOWr FIFORd FIFOEna WrClk RdClk Rst Dreg1 Dreg2 CountDataVal Compress Controller KRLECompressor Block DataI[7:0] ComFIFO 32x8 WrClk RdClk Rst DataO[7:0] SMC
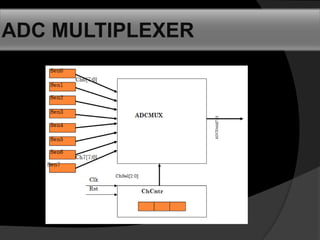
- 15. ADC MULTIPLEXER
- 18. FIFO SCHEMATIC
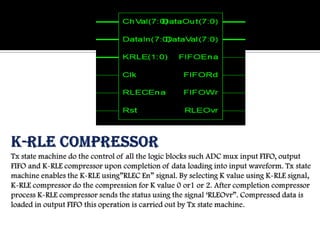
- 24. SIMULATION WAVEFORM FOR K-RLE COMPRESSOR (PART-1)
- 27. CONCLUSION The project presented a new compression algorithm for data compression and this data compression algorithm is a LOW POWER COMPRESSION ALGORITHM. K- RLE is a lossy compression algorithm it is lossless at the user level, because it chooses K considering that there is no difference between the data item d, d+k, d-k . This algorithm inspired from RLE named K-RLE which increases the compression ratio compared to RLE. For K=2 this algorithm increases the ratio by 40% compared to RLE. With this approach a fast transmission of data with MINIMUM HARDWARE REQUIREMENT and less power consumption is possible.
- 28. This project implemented an efficient compression processes. Since RLE doesn’t have great compression ratio K-RLE uses less energy and high compression efficiency compared to RLE Future work of this project is modifying algorithm for LOSSLESS COMPRESSION with equal compression efficiency and low power consumption.
- 29. REFERENCES [1] Yang-Kiefer algorithms for data compression En-hui ,Yang Da-ke He [2] A Generalized Method for Encoding and Decoding Run-Length-Limited Binary Sequences G. F. M. BEENKER AND K. A. SCHOUHAMER IMMINK [3] N. Kimura and S. Latifi. A survey on data compression in wireless sensor networks. In Information Technology: Coding and Computing, [4] F. Marcelloni and M. Vecchio. A simple algorithm for data compression in wireless sensor networks. Communications Letters, IEEE, 12(6):411–413, June 2008. [5] Croce, Silvia, Marcelloni, Francesco, Vecchio, and Massimo. Reducing power consumption in wireless sensor networks using a novel approach to data aggregation. Computer Journal, 51(2):227–239, March 2008.
- 30. That’s all about MY PROJECT …!!! Thank you and queries…!!!













![Sen0
Sen1
Sen2
Sen3
Sen4
Sen5
Sen6
Sen7
Ch0[7:0]
Ch7[7:0]
ADCMUX
ADCFIFO
32x8
ADCData[7:0]
Clk
ChSel[2:0]
ChCntr CntOvr ScanCntr
ScanOvr
ScanEna
SampleEna
Rst
ADCEna
FIFOWr
FIFORd
FIFOEna
WrClk
RdClk
Rst
Dreg1 Dreg2
CountDataVal
Compress Controller
KRLECompressor Block
DataI[7:0]
ComFIFO
32x8
WrClk
RdClk
Rst
DataO[7:0]
SMC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anewalgorithmfordatacompressiontechniqueusingvlsi-140518003028-phpapp02/85/A-new-algorithm-for-data-compression-technique-using-vlsi-14-320.jpg)












![REFERENCES
[1] Yang-Kiefer algorithms for data
compression En-hui ,Yang Da-ke He
[2] A Generalized Method for Encoding
and Decoding Run-Length-Limited Binary
Sequences G. F. M. BEENKER AND K. A.
SCHOUHAMER IMMINK
[3] N. Kimura and S. Latifi. A survey on
data compression in wireless sensor
networks. In Information Technology:
Coding and Computing,
[4] F. Marcelloni and M. Vecchio. A simple
algorithm for data compression in wireless
sensor networks. Communications Letters,
IEEE, 12(6):411–413, June 2008.
[5] Croce, Silvia, Marcelloni, Francesco,
Vecchio, and Massimo. Reducing power
consumption in wireless sensor networks
using a novel approach to data
aggregation. Computer Journal,
51(2):227–239, March 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anewalgorithmfordatacompressiontechniqueusingvlsi-140518003028-phpapp02/85/A-new-algorithm-for-data-compression-technique-using-vlsi-29-320.jpg)
