Algorithm and Programming (Introduction of dev pascal, data type, value, and identifier)
- 1. Adam Mukharil Bachtiar English Class Informatics Engineering 2011 Algorithms and Programming Introduction of Dev Pascal, Data Type, Value, and Identifier
- 2. Steps of the Day Let’s Start Dev Pascal Data Type Value and Identifier
- 3. Dev Pascal Definition and Instalation
- 4. DefinitionofDEVPascal An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) for PASCAL language that was built by BLOODSHEED. It’s Freeware.
- 6. Step 1 Open Dev Pascal application
- 7. Step 2 Make a New File or New Project
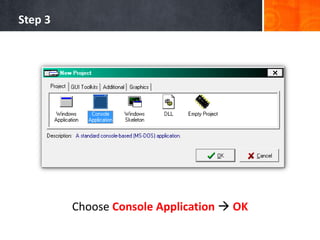
- 8. Step 3 Choose Console Application OK
- 9. Step 4 Give a name to project (Name can contain space character) WARNING: Name of project should be same with name of its folder. One folder is only for one project (in my class)
- 10. Step 5 Save the project in the folder that had been provided
- 11. Step 6 If you have done with all steps correctly, you will get this view on your computer
- 12. Step 7 Save this file in the same folder that contains the project
- 13. Step 8 Give an icon to your project. Click Project Project options in menu bar. WARNING: Icon is an mandatory thing in Dev Pascal project
- 14. Step 9 Click Load icon then choose an icon that you want. Click OK to finish this step.
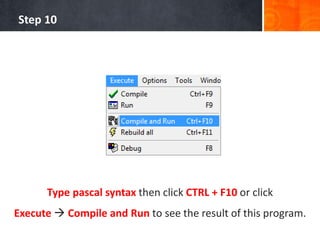
- 15. Step 10 Type pascal syntax then click CTRL + F10 or click Execute Compile and Run to see the result of this program.
- 17. Example of Algorithm Notation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 { ini adalah notasi algoritma } komentar Algoritma judul_algoritma {I.S.: diisi keadaan yang terjadi di awal algoritma} {F.S.: diisi keadaan yang terjadi di akhir algoritma} Kamus/Deklarasi: {diisi pendefinisian konstanta} {diisi deklarasi variabel beserta tipe data} Algoritma/Deskripsi: {diisi dengan input, proses, dan output}
- 18. Example of Pascal Notation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 { ini adalah notasi pascal} komentar program judul_program; var {diisi pendefinisian konstanta} {diisi deklarasi variabel beserta tipe data} begin {diisi dengan input, proses, dan output} end.
- 19. Algorithm Notation VS Pascal Notation Num ALGORITHM PASCAL 1 Kamus: var 2 Algoritma: begin end. 3 input(variabel) readln(variabel); read(variabel); 4 output(‘...........................’) write(‘................................’); atau writeln(‘..............................’); 5 output(‘.................’,variabel) write(‘.............................’,variabel); atau writeln(‘...........................’,variabel); 6 output(variabel) write(variabel); atau writeln(variabel); 7 :=
- 20. Your First Pascal Program 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 program Program_Pertama; uses crt; {pemanggilan unit crt untuk readkey()} begin writeln(‘Selamat Datang’); write(‘Di’); writeln(‘ UNIKOM’); writeln(‘Bandung’); writeln(); write(‘Tekan sembarang tombol untuk menutup.’); readkey(); end.
- 22. Exchange value with additional variabel (Algorithm) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Algoritma Tukar_Nilai {I.S.: Nilai variabel a dan b dimasukkan oleh user} {F.S.: Menampilkan hasil penukaran nilai variabel a dan b} Kamus: a,b: integer bantu:integer Algoritma: output(‘Masukkan nilai a: ‘) input(a) output(‘Masukkan nilai b: ‘) input(b) bantua ab bbantu output(‘Nilai a sekarang : ‘,a) output(‘Nilai b sekarang : ‘,b)
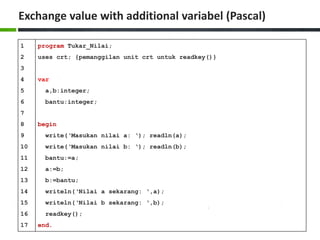
- 23. Exchange value with additional variabel (Pascal) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 program Tukar_Nilai; uses crt; {pemanggilan unit crt untuk readkey()} var a,b:integer; bantu:integer; begin write(‘Masukan nilai a: ‘); readln(a); write(‘Masukan nilai b: ‘); readln(b); bantu:=a; a:=b; b:=bantu; writeln(‘Nilai a sekarang: ‘,a); writeln(‘Nilai b sekarang: ‘,b); readkey(); end.
- 24. Exchange value without additional variabel (Algorithm) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Algoritma Tukar_Nilai {I.S.: Nilai variabel a dan b dimasukkan oleh user} {F.S.: Menampilkan hasil penukaran nilai variabel a dan b} Kamus: a,b: integer Algoritma: input(a,b) aa+b ba-b aa-b output(‘Nilai a sekarang : ‘,a) output(‘Nilai b sekarang : ‘,b)
- 25. Exchange value with additional variabel (Pascal) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 program Tukar_Nilai; uses crt; {pemanggilan unit crt untuk readkey()} var a,b:integer; begin write(‘Masukan nilai a: ‘); readln(a); write(‘Masukan nilai b: ‘); readln(b); a:=a+b; b:=a-b; a:=a-b; writeln(‘Nilai a sekarang: ‘,a); writeln(‘Nilai b sekarang: ‘,b); readkey(); end.
- 26. Data Type Data Type in Algorithm and Pascal
- 27. KindofDataTypes • Tipe Data Dasar (Predefined Data Type) • Tipe Data Bentukan (user-defined Data Type)
- 28. Predefined Data Type • Have been known in daily life. • Such as: logic number, integer, real number, characters, and string.
- 29. Logic Number • Name : boolean • Value : True and False • Can be initialized as 0 or 1 in number.
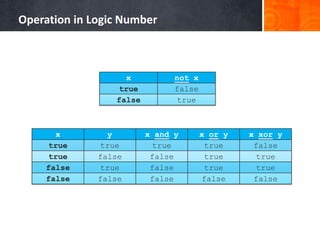
- 30. Operation in Logic Number x not x true false false true x y x and y x or y x xor y true true true true false true false false true true false true false true true false false false false false
- 31. Integer • Name : integer • Value : - (~) until + (~) (without .) • Arithmetic : +, -, *, /, div, mod • Comparison : < , ≤ , > , ≥ , = , ≠.
- 32. Real • Name : real • Value : - (~) until + (~) • Arithmetic : +, -, *, / • Comparison : < , ≤ , > , ≥ , = , ≠.
- 33. Characters • Name : char • Value : all alphabet, decimal number, punctuation mark, arithmetic operator, and ASCII • Comparation : < , ≤ , > , ≥ , = , ≠.
- 34. String • Name : String • Value : set of characters (flanked with ’ ’) • Comparison : < , ≤ , > , ≥ , = , ≠.
- 35. User-defined Data Type • Predefined Data Type that was named with a new one. • Structure type.
- 36. Modified Predefined Data Type • Reason : Easy to remember and High readibility. • Keyword : type • Example: type pecahan : real { : can be replaced with = }
- 37. Structure Type • Reason : set of data that have different data type. • Example : type Mahasiswa = record < NIM : integer, {0..9} Nama : string, {‘A’..’Z’, ‘a’..’z’} Nilai : real {0..100} >
- 38. Structure Type • If mhs1 is mahasiswa type, so to access each field in mhs1 can be done with these statement: a. mhs1.NIM b. mhs1.Nama c. mhs1.Nilai
- 39. Data Type in Algorithm and Pascal Algorithm Pascal Range in Pascal boolean boolean true dan false integer byte 0..255 shortint -128..127 word 0..65535 integer -32768..32767 longint -2147483648..2147483647 real real 2.9 x 10-39..1.7 x 1038 single 1.5 x 10-45..3.4 x 1038 double 5.0 x 10-324..1.7 x 10308 extended 3.4 x 10-4932..1.1 x 104932 char char string string string[n] type varrecord:record < field1:type1, field2:type2, ... field_n:type_n > type varrecord=record field1:type1; field2:type2; ... field_n:type_n; end;
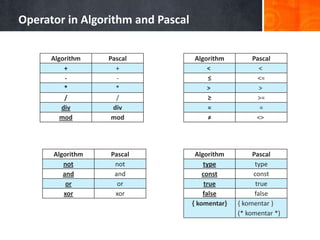
- 40. Operator in Algorithm and Pascal Algorithm Pascal + + - - * * / / div div mod mod Algorithm Pascal < < ≤ <= > > ≥ >= = = ≠ <> Algorithm Pascal not not and and or or xor xor Algorithm Pascal type type const const true true false false { komentar} { komentar } (* komentar *)
- 41. Identifier Definition, Rules and Expression
- 42. DefinitionofIdentifier Identifiers can be used to access something in algorithm or program.
- 44. Rules of Naming • Name must be started with alphabet. • Upper case and lower case are the same thing in Pascal (case insensitive) Suggest: should be consistent. • Name only consists of alphabet, number, and underscore. • Identifier can’t contain arithmetic operator, relational, and punctuation mark, space. • Choose the name that easy to remember.
- 45. Variable VS Constants • Variable and Constants was used to store the value in memory. • Variable can change the value in the middle of running time. • Constants will keep the value permanently while running time.
- 46. Variable VS Constants Variable Declaration Constants Declaration Nama_variabel:tipe_data Example: x,y:integer type const nama_konstanta = nilai_konstanta Contoh: type const phi =3.14
- 47. Math and Algorithm Notation • Prefix *79 , *+a/bc-d*ef • Infix 7*9 , a+b/c*d-e*f • Postfix 68* , abc/+def*-*
- 48. Math and Algorithm Notation • luas= 1 2 (alas.tinggi) luas1/2*(alas*tinggi) • a= 10𝑏+3𝑐 5𝑑 a (10*b + 3*c)/(5*d)
- 49. EXERCISE
- 50. Exercise 1 Declare user-defined data type for cases: • SIM • KTP • Lecturer Data
- 51. Exercise 2 Convert these math notations into algorithm notations: • m= 𝑎−𝑏 3𝑎𝑐 (1- 𝑏𝑐𝑑 𝑓𝑔ℎ ) • x= −𝑏+2𝑐2+4𝑎𝑏𝑐 2𝑐(3𝑎+4𝑐)
- 52. Contact Person: Adam Mukharil Bachtiar Informatics Engineering UNIKOM Jalan Dipati Ukur Nomor. 112-114 Bandung 40132 Email: [email protected] Blog: http://adfbipotter.wordpress.com Copyright © Adam Mukharil Bachtiar 2011


































![Data Type in Algorithm and Pascal
Algorithm Pascal Range in Pascal
boolean boolean true dan false
integer byte 0..255
shortint -128..127
word 0..65535
integer -32768..32767
longint -2147483648..2147483647
real real 2.9 x 10-39..1.7 x 1038
single 1.5 x 10-45..3.4 x 1038
double 5.0 x 10-324..1.7 x 10308
extended 3.4 x 10-4932..1.1 x 104932
char char
string string
string[n]
type
varrecord:record
< field1:type1,
field2:type2,
...
field_n:type_n >
type
varrecord=record
field1:type1;
field2:type2;
...
field_n:type_n;
end;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-introductionofdevpascaldatatypevalueandidentifier-161018111100/85/Algorithm-and-Programming-Introduction-of-dev-pascal-data-type-value-and-identifier-39-320.jpg)