Algorithms practice and problem solving - dynamic programming
- 1. Algorithms Practice & Problem Solving Women Who Code
- 2. Meet the Organizers Xochitl Watts Twitter: @XochitlWatts https://www.a2omini.com Kelly KappJennifer Sweezey
- 3. What are algorithms? (In mathematics, computing, and related subjects) An algorithm is an effective method for solving a problem using a finite sequence of actions to be performed. - Wikipedia
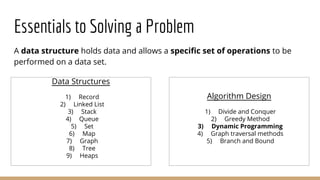
- 4. Essentials to Solving a Problem A data structure holds data and allows a specific set of operations to be performed on a data set. Data Structures 1) Record 2) Linked List 3) Stack 4) Queue 5) Set 6) Map 7) Graph 8) Tree 9) Heaps Algorithm Design 1) Divide and Conquer 2) Greedy Method 3) Dynamic Programming 4) Graph traversal methods 5) Branch and Bound
- 5. Dynamic Programming (DP) 1) DP builds its solution by constructing solutions to smaller instances of the same problem. 2) A problem has an optimal substructure if the sub-solutions of an optimal solution of the problem are optimal solutions for their sub-problems. 3) The problem contains overlapping sub-problems. 4) DP arrives to a solution using bottom up traversal, building the solution to many sub-problems that may or may not be required. Memoize & re-use solutions to subproblems that help solve the problem
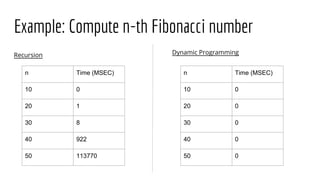
- 6. Example: Compute n-th Fibonacci number Recursion function fib(int n) { If (n <= 2) { return 1; } return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } Dynamic Programming long a[] = new long[n + 1]; a[1] = a[2] = 1 for (int i=3; i <=n; i++) { a[i] = a[i-1] + a[i-2]; } return a[n];
- 7. Memoization Memoization aims to prevent recomputations by storing (memorizing) the return values of the function calls. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memoization
- 8. Example: Compute n-th Fibonacci number Recursion Dynamic Programming n Time (MSEC) 10 0 20 1 30 8 40 922 50 113770 n Time (MSEC) 10 0 20 0 30 0 40 0 50 0
- 9. DP Template - NORA 1) Notation: Develop a mathematical notation that can express any solution and any sub-solution for the problem at hand. 2) Optimality: Prove that the optimal substructure holds - sub-solutions of an optimal solution are optimal solutions for sub-problems. 3) Recurrence: Develop a recurrence relation that relates a solution to its sub-solutions using math notation. 4) Algorithm: Write out the algorithm, iterate over all the parameters of the recurrence relation to compute the results for the actual problem that needed to be solved.
- 12. Python Solution: Fibonacci Finding Challenge def fibonacci(n): if n < 2: return n if not n in memory.keys(): memory[n] = fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2) return memory[n] memory = {} n = int(raw_input()) print(fibonacci(n))
- 13. Python Solution: Coin Change Challenge Recursion def count(sum_, coins): if len(coins) == 0: return 0 if sum_ < 0: return 0 if sum_ == 0: return 1 return count(sum_ - coins[0], coins) + count(sum_, coins[1:]) if __name__ == "__main__": import sys N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' ')) coins = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' ')) print count(N, coins)
- 14. Python Solution: Coin Change Challenge Memoization count_dict = {} def count(sum_, coins): if len(coins) == 0: return 0 if sum_ < 0: return 0 if sum_ == 0: return 1 key = (sum_, tuple(coins)) if key not in count_dict: count_dict[key] = count(sum_ - coins[0], coins) + count(sum_, coins[1:]) return count_dict[key] if __name__ == "__main__": import sys N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' ')) coins = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' ')) print count(N, coins)
- 15. Python Solution: Coin Change Challenge Dynamic Programming def count(N, coins): numWays = [[1] + N * [0] for j in xrange(len(coins) + 1)] for i in xrange(1, len(coins) + 1): for j in xrange(1, N + 1): numWays[i][j] = numWays[i-1][j] + (numWays[i][j - coins[i-1]] if coins[i-1] <= j else 0) return numWays[-1][-1] if __name__ == "__main__": import sys N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' ')) coins = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' ')) print count(N, coins)
- 16. Reference Analysis and Design of Algorithms - It takes 4 hours to read the whole book.




![Example: Compute n-th Fibonacci number
Recursion
function fib(int n) {
If (n <= 2) {
return 1;
}
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
Dynamic Programming
long a[] = new long[n + 1];
a[1] = a[2] = 1
for (int i=3; i <=n; i++) {
a[i] = a[i-1] + a[i-2];
}
return a[n];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmspracticeandproblemsolving-dynamicprogramming-170304043754/85/Algorithms-practice-and-problem-solving-dynamic-programming-6-320.jpg)




![Python Solution: Fibonacci Finding Challenge
def fibonacci(n):
if n < 2:
return n
if not n in memory.keys():
memory[n] = fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
return memory[n]
memory = {}
n = int(raw_input())
print(fibonacci(n))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmspracticeandproblemsolving-dynamicprogramming-170304043754/85/Algorithms-practice-and-problem-solving-dynamic-programming-12-320.jpg)
![Python Solution: Coin Change Challenge
Recursion
def count(sum_, coins):
if len(coins) == 0:
return 0
if sum_ < 0:
return 0
if sum_ == 0:
return 1
return count(sum_ - coins[0], coins) + count(sum_, coins[1:])
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' '))
coins = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' '))
print count(N, coins)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmspracticeandproblemsolving-dynamicprogramming-170304043754/85/Algorithms-practice-and-problem-solving-dynamic-programming-13-320.jpg)
![Python Solution: Coin Change Challenge
Memoization
count_dict = {}
def count(sum_, coins):
if len(coins) == 0:
return 0
if sum_ < 0:
return 0
if sum_ == 0:
return 1
key = (sum_, tuple(coins))
if key not in count_dict:
count_dict[key] = count(sum_ - coins[0], coins) + count(sum_, coins[1:])
return count_dict[key]
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' '))
coins = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' '))
print count(N, coins)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmspracticeandproblemsolving-dynamicprogramming-170304043754/85/Algorithms-practice-and-problem-solving-dynamic-programming-14-320.jpg)
![Python Solution: Coin Change Challenge
Dynamic Programming
def count(N, coins):
numWays = [[1] + N * [0] for j in xrange(len(coins) + 1)]
for i in xrange(1, len(coins) + 1):
for j in xrange(1, N + 1):
numWays[i][j] = numWays[i-1][j] + (numWays[i][j - coins[i-1]]
if coins[i-1] <= j else 0)
return numWays[-1][-1]
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' '))
coins = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip().split(' '))
print count(N, coins)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmspracticeandproblemsolving-dynamicprogramming-170304043754/85/Algorithms-practice-and-problem-solving-dynamic-programming-15-320.jpg)
