Array implementation and linked list as datat structure
Download as pptx, pdf22 likes27,517 views
The document discusses arrays and linked lists. It defines arrays as collections of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory. Linked lists store elements in memory locations that are not contiguous. Each element of a linked list contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. This allows for efficient insertion and deletion of nodes compared to arrays. The document provides examples of implementing common linked list operations like insertion at the head, tail, and deletion.
1 of 33
Downloaded 563 times

![ An array is a collection of elements of similar
datatype.
Contiguous memory allocation takes place.
An array is a DS in which we can access every
element directly using position variable .
It is rather an organizational concept.
Array elements can be accessed individually.
Syntax: datatype nameofarray [dimension];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayimplementationandlinkedlistasdatatstructure-120916130606-phpapp01/85/Array-implementation-and-linked-list-as-datat-structure-2-320.jpg)

![Creation of integer array
int
7 a[0] i=0 a[10]={7,1,32,58,0,5,8,16,9,23}
14 a[1] i=1 ;
32 a[2] i=2 Integer array “a”.
58 a[3] i=3
It is of dimension 10 (from 0
0 a[4] i=4 to 9).
5 a[5] i=5 Take positing variable i.
8 a[6] i=6
Its storage will be continuous
16 a[7] i=7 20 bytes(2 bytes each).
9 a[8] i=8
23 a[9] i=9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayimplementationandlinkedlistasdatatstructure-120916130606-phpapp01/85/Array-implementation-and-linked-list-as-datat-structure-5-320.jpg)
![1. DECLARATION
N SIZE
2. OPERATION
Repeat for i= 0 to (size-1)
arr[i]= num
end repeat
3. OUTPUT
RETURN(arr[i])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayimplementationandlinkedlistasdatatstructure-120916130606-phpapp01/85/Array-implementation-and-linked-list-as-datat-structure-6-320.jpg)
![ DECLARATION
i rows
j coloumn
OPERATION
◦ Repeat for i=0 to (rows-1)
Repeat for j=0 to (coloumn-1)
Array[i][j]=num
End repeat
◦ End repeat
OUTPUT
Return(Array[i][j])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayimplementationandlinkedlistasdatatstructure-120916130606-phpapp01/85/Array-implementation-and-linked-list-as-datat-structure-7-320.jpg)























Ad
Recommended
Professional responsibility and the role of the engineer



Professional responsibility and the role of the engineerRick Case, PMP, P.E. This presentation discusses the role and responsibilities of engineers in society. It explores definitions of engineering as applying scientific knowledge to meet societal needs and connect science to society. As such, engineers have a social responsibility to consider the impacts and consequences of their work on public safety, well-being, and the environment. The presentation outlines various ways engineers can demonstrate this responsibility through their work and advocacy.
2. INFORMATION GATHERING.pptx Computer Applications in Pharmacy



2. INFORMATION GATHERING.pptx Computer Applications in PharmacyVedika Narvekar B.Pharm sem 2
Computer Applications in Pharmacy
requirement and feasibility analysis, data flow diagrams, process
specifications, input/output design, process life cycle, planning and
managing the project
Database architecture



Database architectureVENNILAV6 Database architecture uses programming languages to design software for businesses, focusing on designing, developing, implementing, and maintaining computer programs. The architecture of a database system depends on the computer system it runs on, and a database system can be centralized or use a client-server model with client machines for users and a server for the database system.
Interrupts and types of interrupts



Interrupts and types of interruptsMuhammad Sheharyar Asif This method of checking the signal in the system for processing is called Polling Method. In this method, the problem is that the processor has to waste number of clock cycles just for checking the signal in the system, by this processor will become busy unnecessarily. If any signal came for the process, processor will take some time to process the signal due to the polling process in action. So system performance also will be degraded and response time of the system will also decrease.
Constitution of India (PPT)



Constitution of India (PPT)Krushang Thakor Constitution of India - History - Objectives - Functions - Characteristics.
Presentation on Constitution of India latest amendment.
Types of mould 



Types of mould Veer Singh 1. The document describes different types of moulds used in plastic injection molding including two plate, three plate, split cavity, side core, and hot runner moulds.
2. A split cavity mould is suitable for moulding components with all-round external undercuts and uses sliding splits, angular lifts, or pins for actuation.
3. A side core or side cavity mould is used for components with local external undercuts and can be actuated via finger cams, dog leg cams, cam tracks, springs, or hydraulics.
Data Manipulation Language



Data Manipulation LanguageJas Singh Bhasin The DBMS provides a set of operations or a language called the data manipulation language (DML) for modification of the data.
Data manipulation can be performed either by typing SQL statements or by using a graphical interface, typically called Query-By-Example (QBE).
Queue ppt



Queue pptSouravKumar328 The document discusses different types of queues, including simple, circular, priority, and double-ended queues. It describes the basic queue operations of enqueue and dequeue, where new elements are added to the rear of the queue and existing elements are removed from the front. Circular queues are more memory efficient than linear queues by connecting the last queue element back to the first, forming a circle. Priority queues remove elements based on priority rather than order of insertion. Double-ended queues allow insertion and removal from both ends. Common applications of queues include CPU and disk scheduling, synchronization between asynchronous processes, and call center phone systems.
Array data structure



Array data structuremaamir farooq An array is a data structure that stores fixed number of items of the same type. It allows fast access of elements using indices. Basic array operations include traversing elements, inserting/deleting elements, searching for elements, and updating elements. Arrays are zero-indexed and elements are accessed via their index.
Linear Search Presentation



Linear Search PresentationMarkajul Hasnain Alif Linear search, also called sequential search, is a method for finding a target value within a list by sequentially checking each element until a match is found or all elements are searched. It works by iterating through each element of a data structure (such as an array or list), comparing it to the target value, and returning the index or position of the target if found. The key aspects covered include definitions of data, structure, data structure, and search. Pseudocode and examples of linear search on a phone directory are provided. Advantages are that it is simple and works for small data sets, while disadvantages are that search time increases linearly with the size of the data set.
Quick sort-Data Structure



Quick sort-Data StructureJeanie Arnoco Quicksort is a divide and conquer sorting algorithm that works by partitioning an array around a pivot value. It then recursively sorts the sub-arrays on each side. The key steps are: 1) Choose a pivot element to split the array into left and right halves, with all elements on the left being less than the pivot and all on the right being greater; 2) Recursively quicksort the left and right halves; 3) Combine the now-sorted left and right halves into a fully sorted array. The example demonstrates quicksorting an array of 6 elements by repeatedly partitioning around a pivot until the entire array is sorted.
Algorithms Lecture 4: Sorting Algorithms I



Algorithms Lecture 4: Sorting Algorithms IMohamed Loey The document discusses three sorting algorithms: bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort. Bubble sort works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements that are in the wrong order. Selection sort finds the minimum element and swaps it into the sorted portion of the array. Insertion sort inserts elements into the sorted portion of the array, swapping as needed to put the element in the correct position. Both selection sort and insertion sort have a time complexity of O(n^2) in the worst case.
Merge sort algorithm



Merge sort algorithmShubham Dwivedi Merge sort is a sorting technique based on divide and conquer technique. With worst-case time complexity being Ο(n log n), it is one of the most respected algorithms.
Merge sort first divides the array into equal halves and then combines them in a sorted manner.
BINARY TREE REPRESENTATION.ppt



BINARY TREE REPRESENTATION.pptSeethaDinesh Binary trees are a non-linear data structure where each node has at most two children, used to represent hierarchical relationships, with nodes connected through parent-child links and traversed through preorder, inorder, and postorder methods; they can be represented through arrays or linked lists and support common operations like search, insert, and delete through comparing node values and restructuring child pointers.
deque and it applications



deque and it applicationsSathasivam Rangasamy This document discusses deque, or double-ended queue, which is an abstract data type that allows elements to be added or removed from either end. It describes two types of deques, input-restricted and output-restricted, and common operations like push, pop, and isEmpty. Examples are given of using a deque for palindrome checking, A-Steal job scheduling, and undo-redo operations in software.
Linked list



Linked listakshat360 Linked lists are linear data structures where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. There are two types: singly linked lists where each node has a single next pointer, and doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers. Common operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion which have O(1) time complexity for singly linked lists but require changing multiple pointers for doubly linked lists. Linked lists are useful when the number of elements is dynamic as they allow efficient insertions and deletions without shifting elements unlike arrays.
Queue in Data Structure 



Queue in Data Structure Janki Shah Contents:
1. What is Queue?
2. Operations perform on Queue with Algorithm & Example
3. Types of Queue with required example
Binary Tree Traversal



Binary Tree TraversalDhrumil Panchal This presentation is useful to study about data structure and topic is Binary Tree Traversal. This is also useful to make a presentation about Binary Tree Traversal.
Singly link list



Singly link listRojin Khadka A singly linked list is a linear data structure composed of nodes, where each node contains a data element and a link to the next node. The first node is referenced by a pointer called the head. Each node's link points to the next node in the list, with the last node's link pointing to null. Operations like insertion and deletion on singly linked lists can be performed by updating the links between nodes in constant time regardless of the list's size.
Quick sort data structures



Quick sort data structureschauhankapil Quick sort is a fast sorting algorithm that uses a divide and conquer approach. It works by selecting a pivot element and partitioning the list around the pivot so that all elements less than the pivot come before it and all elements greater than the pivot come after it. The list is then divided into smaller sub-lists and the process continues recursively until the list is fully sorted.
Queue and its operations



Queue and its operationsV.V.Vanniaperumal College for Women This document discusses queues, including:
1. Queues follow a First-In First-Out (FIFO) methodology where the first item stored is the first item accessed.
2. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, with two pointers - a front pointer and rear pointer - to keep track of the first and last elements.
3. The basic queue operations are enqueue, which adds an item to the rear, and dequeue, which removes an item from the front.
Presentation on Elementary data structures



Presentation on Elementary data structuresKuber Chandra Presentation is on Various Data Structures And Operations Related to it. Brief Description Of Operations Using Examples.
Ppt on Linked list,stack,queue



Ppt on Linked list,stack,queueSrajan Shukla This document discusses different types of linked lists, including singly linked lists, circular linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It provides examples of circular linked lists and explains that in a circular linked list, the last node contains the address of the first node so that the list can be traversed repeatedly. The document also discusses common linked list operations like insertion and deletion of nodes. Finally, it covers stacks and queues, defining them as LIFO and FIFO data structures, respectively, and providing examples of their implementation and different types.
Doubly Linked List



Doubly Linked ListNinad Mankar Each node in a doubly linked list contains two pointers - one pointing to the next node and one pointing to the previous node. This allows traversal in both directions through the list. A doubly linked list supports common operations like insertion and deletion at both ends of the list as well as anywhere in the list by updating the relevant pointer fields of the nodes. While requiring more space per node, doubly linked lists allow easy traversal backwards through the list and reversing of the list.
Data Structures and Algorithm - Module 1.pptx



Data Structures and Algorithm - Module 1.pptxEllenGrace9 This document provides an introduction to data structures and algorithms from instructor Ellen Grace Porras. It defines data structures as ways of organizing data to allow for efficient operations. Linear data structures like arrays, stacks, and queues arrange elements sequentially, while non-linear structures like trees and graphs have hierarchical relationships. The document discusses characteristics of good data structures and algorithms, provides examples of common algorithms, and distinguishes between linear and non-linear data structures. It aims to explain the fundamentals of data structures and algorithms.
Heaps



HeapsHafiz Atif Amin This document provides information about priority queues and binary heaps. It defines a binary heap as a nearly complete binary tree where the root node has the maximum/minimum value. It describes heap operations like insertion, deletion of max/min, and increasing/decreasing keys. The time complexity of these operations is O(log n). Heapsort, which uses a heap data structure, is also covered and has overall time complexity of O(n log n). Binary heaps are often used to implement priority queues and for algorithms like Dijkstra's and Prim's.
Queue data structure



Queue data structureanooppjoseph A queue is a non-primitive linear data structure that follows the FIFO (first-in, first-out) principle. Elements are added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front. Common operations on a queue include insertion (enqueue) and deletion (dequeue). Queues have many real-world applications like waiting in lines and job scheduling. They can be represented using arrays or linked lists.
Hashing



HashingAmar Jukuntla Hashing is a technique used to uniquely identify objects by assigning each object a key, such as a student ID or book ID number. A hash function converts large keys into smaller keys that are used as indices in a hash table, allowing for fast lookup of objects in O(1) time. Collisions, where two different keys hash to the same index, are resolved using techniques like separate chaining or linear probing. Common applications of hashing include databases, caches, and object representation in programming languages.
Searching and Sorting Techniques in Data Structure



Searching and Sorting Techniques in Data StructureBalwant Gorad Linear Search
Binary Search
Sorting Techniques - Bubble, Selection, Insertion, Merge, Radix, Shell and Heap Sort
Double linked list



Double linked listraviahuja11 This document describes a C program that implements a double linked list. It includes functions to insert, delete, search, and display nodes in the list. The insert function allocates a new node, gets the insertion position and data from the user, and adds the new node to the list by updating the next and prev pointers of neighboring nodes. It checks for special cases like insertion at the head or end of the list. The other functions are not described in detail.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Array data structure



Array data structuremaamir farooq An array is a data structure that stores fixed number of items of the same type. It allows fast access of elements using indices. Basic array operations include traversing elements, inserting/deleting elements, searching for elements, and updating elements. Arrays are zero-indexed and elements are accessed via their index.
Linear Search Presentation



Linear Search PresentationMarkajul Hasnain Alif Linear search, also called sequential search, is a method for finding a target value within a list by sequentially checking each element until a match is found or all elements are searched. It works by iterating through each element of a data structure (such as an array or list), comparing it to the target value, and returning the index or position of the target if found. The key aspects covered include definitions of data, structure, data structure, and search. Pseudocode and examples of linear search on a phone directory are provided. Advantages are that it is simple and works for small data sets, while disadvantages are that search time increases linearly with the size of the data set.
Quick sort-Data Structure



Quick sort-Data StructureJeanie Arnoco Quicksort is a divide and conquer sorting algorithm that works by partitioning an array around a pivot value. It then recursively sorts the sub-arrays on each side. The key steps are: 1) Choose a pivot element to split the array into left and right halves, with all elements on the left being less than the pivot and all on the right being greater; 2) Recursively quicksort the left and right halves; 3) Combine the now-sorted left and right halves into a fully sorted array. The example demonstrates quicksorting an array of 6 elements by repeatedly partitioning around a pivot until the entire array is sorted.
Algorithms Lecture 4: Sorting Algorithms I



Algorithms Lecture 4: Sorting Algorithms IMohamed Loey The document discusses three sorting algorithms: bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort. Bubble sort works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements that are in the wrong order. Selection sort finds the minimum element and swaps it into the sorted portion of the array. Insertion sort inserts elements into the sorted portion of the array, swapping as needed to put the element in the correct position. Both selection sort and insertion sort have a time complexity of O(n^2) in the worst case.
Merge sort algorithm



Merge sort algorithmShubham Dwivedi Merge sort is a sorting technique based on divide and conquer technique. With worst-case time complexity being Ο(n log n), it is one of the most respected algorithms.
Merge sort first divides the array into equal halves and then combines them in a sorted manner.
BINARY TREE REPRESENTATION.ppt



BINARY TREE REPRESENTATION.pptSeethaDinesh Binary trees are a non-linear data structure where each node has at most two children, used to represent hierarchical relationships, with nodes connected through parent-child links and traversed through preorder, inorder, and postorder methods; they can be represented through arrays or linked lists and support common operations like search, insert, and delete through comparing node values and restructuring child pointers.
deque and it applications



deque and it applicationsSathasivam Rangasamy This document discusses deque, or double-ended queue, which is an abstract data type that allows elements to be added or removed from either end. It describes two types of deques, input-restricted and output-restricted, and common operations like push, pop, and isEmpty. Examples are given of using a deque for palindrome checking, A-Steal job scheduling, and undo-redo operations in software.
Linked list



Linked listakshat360 Linked lists are linear data structures where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. There are two types: singly linked lists where each node has a single next pointer, and doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers. Common operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion which have O(1) time complexity for singly linked lists but require changing multiple pointers for doubly linked lists. Linked lists are useful when the number of elements is dynamic as they allow efficient insertions and deletions without shifting elements unlike arrays.
Queue in Data Structure 



Queue in Data Structure Janki Shah Contents:
1. What is Queue?
2. Operations perform on Queue with Algorithm & Example
3. Types of Queue with required example
Binary Tree Traversal



Binary Tree TraversalDhrumil Panchal This presentation is useful to study about data structure and topic is Binary Tree Traversal. This is also useful to make a presentation about Binary Tree Traversal.
Singly link list



Singly link listRojin Khadka A singly linked list is a linear data structure composed of nodes, where each node contains a data element and a link to the next node. The first node is referenced by a pointer called the head. Each node's link points to the next node in the list, with the last node's link pointing to null. Operations like insertion and deletion on singly linked lists can be performed by updating the links between nodes in constant time regardless of the list's size.
Quick sort data structures



Quick sort data structureschauhankapil Quick sort is a fast sorting algorithm that uses a divide and conquer approach. It works by selecting a pivot element and partitioning the list around the pivot so that all elements less than the pivot come before it and all elements greater than the pivot come after it. The list is then divided into smaller sub-lists and the process continues recursively until the list is fully sorted.
Queue and its operations



Queue and its operationsV.V.Vanniaperumal College for Women This document discusses queues, including:
1. Queues follow a First-In First-Out (FIFO) methodology where the first item stored is the first item accessed.
2. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, with two pointers - a front pointer and rear pointer - to keep track of the first and last elements.
3. The basic queue operations are enqueue, which adds an item to the rear, and dequeue, which removes an item from the front.
Presentation on Elementary data structures



Presentation on Elementary data structuresKuber Chandra Presentation is on Various Data Structures And Operations Related to it. Brief Description Of Operations Using Examples.
Ppt on Linked list,stack,queue



Ppt on Linked list,stack,queueSrajan Shukla This document discusses different types of linked lists, including singly linked lists, circular linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It provides examples of circular linked lists and explains that in a circular linked list, the last node contains the address of the first node so that the list can be traversed repeatedly. The document also discusses common linked list operations like insertion and deletion of nodes. Finally, it covers stacks and queues, defining them as LIFO and FIFO data structures, respectively, and providing examples of their implementation and different types.
Doubly Linked List



Doubly Linked ListNinad Mankar Each node in a doubly linked list contains two pointers - one pointing to the next node and one pointing to the previous node. This allows traversal in both directions through the list. A doubly linked list supports common operations like insertion and deletion at both ends of the list as well as anywhere in the list by updating the relevant pointer fields of the nodes. While requiring more space per node, doubly linked lists allow easy traversal backwards through the list and reversing of the list.
Data Structures and Algorithm - Module 1.pptx



Data Structures and Algorithm - Module 1.pptxEllenGrace9 This document provides an introduction to data structures and algorithms from instructor Ellen Grace Porras. It defines data structures as ways of organizing data to allow for efficient operations. Linear data structures like arrays, stacks, and queues arrange elements sequentially, while non-linear structures like trees and graphs have hierarchical relationships. The document discusses characteristics of good data structures and algorithms, provides examples of common algorithms, and distinguishes between linear and non-linear data structures. It aims to explain the fundamentals of data structures and algorithms.
Heaps



HeapsHafiz Atif Amin This document provides information about priority queues and binary heaps. It defines a binary heap as a nearly complete binary tree where the root node has the maximum/minimum value. It describes heap operations like insertion, deletion of max/min, and increasing/decreasing keys. The time complexity of these operations is O(log n). Heapsort, which uses a heap data structure, is also covered and has overall time complexity of O(n log n). Binary heaps are often used to implement priority queues and for algorithms like Dijkstra's and Prim's.
Queue data structure



Queue data structureanooppjoseph A queue is a non-primitive linear data structure that follows the FIFO (first-in, first-out) principle. Elements are added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front. Common operations on a queue include insertion (enqueue) and deletion (dequeue). Queues have many real-world applications like waiting in lines and job scheduling. They can be represented using arrays or linked lists.
Hashing



HashingAmar Jukuntla Hashing is a technique used to uniquely identify objects by assigning each object a key, such as a student ID or book ID number. A hash function converts large keys into smaller keys that are used as indices in a hash table, allowing for fast lookup of objects in O(1) time. Collisions, where two different keys hash to the same index, are resolved using techniques like separate chaining or linear probing. Common applications of hashing include databases, caches, and object representation in programming languages.
Viewers also liked (18)
Searching and Sorting Techniques in Data Structure



Searching and Sorting Techniques in Data StructureBalwant Gorad Linear Search
Binary Search
Sorting Techniques - Bubble, Selection, Insertion, Merge, Radix, Shell and Heap Sort
Double linked list



Double linked listraviahuja11 This document describes a C program that implements a double linked list. It includes functions to insert, delete, search, and display nodes in the list. The insert function allocates a new node, gets the insertion position and data from the user, and adds the new node to the list by updating the next and prev pointers of neighboring nodes. It checks for special cases like insertion at the head or end of the list. The other functions are not described in detail.
Individual-In-The-Loop (for Ethically Aligned Artificial Intelligence)



Individual-In-The-Loop (for Ethically Aligned Artificial Intelligence)John C. Havens This presentation was created as a speech for the launch of the Privacy & Sustainable Computing Lab at WU Vienna (http://www.privacylab.at/events/launch/).
Insertion and Deletion in Binary Search Trees (using Arrays and Linked Lists)



Insertion and Deletion in Binary Search Trees (using Arrays and Linked Lists)Lovelyn Rose Simple algorithm to insert and delete elements in binary search tree explained using animation. Algorithms for array and linked list implementation are given.
Cyber Crime



Cyber CrimeAbhishek L.R Presentation on Cyber Crime and the Prevention Measures which helps you to be safe from the Cyber Criminals in the Present World.
Linked list



Linked listTrupti Agrawal This document discusses linked lists and polynomials represented as linked lists. It provides details on singly linked lists, including how to implement insertion and deletion of nodes. It also describes how to represent stacks and queues as dynamically linked lists. Finally, it discusses representing polynomials using arrays or linked lists, and how to perform addition and multiplication of polynomials in each representation.
6. Linked list - Data Structures using C++ by Varsha Patil



6. Linked list - Data Structures using C++ by Varsha Patilwidespreadpromotion The document discusses linked lists as a dynamic data structure. It defines a linked list as a collection of data elements called nodes that together represent a sequence. Each node contains a data field for the element and a link to the next node. This allows elements to be added or removed without reorganizing the entire structure. The document covers different types of linked lists including singly linked, doubly linked, circular, and their applications for storing polynomials and implementing stacks. It also discusses operations like traversal, insertion, and deletion of nodes.
Data structure using c module 1



Data structure using c module 1smruti sarangi This file contains the concepts of Array, Sparse Matrix,
Stack, Queue, Linked List, Polynomial Representation and Dynamic Storage Management.
Linked List, Types of Linked LIst, Various Operations, Applications of Linked...



Linked List, Types of Linked LIst, Various Operations, Applications of Linked...Balwant Gorad Linked List, Types of Linked LIst,Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular Linked List, Various Operations - Create, Display, Search, Insert at end, start, middle, Delete at End, Start, Middle, Applications of Linked List
7 Myths of AI



7 Myths of AICrowdFlower When it comes to AI and its applications, there are a number of myths being perpetuated by the mainstream media. It's time to dispel these myths because the opportunity to apply AI to your business is real.
linked list 



linked list Narendra Chauhan This document contains a presentation on linked lists. It includes:
1. An introduction to linked lists describing their representation using linked allocation and algorithms for inserting and deleting nodes.
2. Algorithms for inserting a node at the first, last, and ordered positions in a single linked list, as well as deleting a node and copying a linked list.
3. A section on linear linked list multiple choice questions.
Trees data structure



Trees data structureSumit Gupta This document defines and describes trees and graphs as non-linear data structures. It explains that a tree is similar to a linked list but allows nodes to have multiple children rather than just one. The document defines key tree terms like height, ancestors, size, and different types of binary trees including strict, full, and complete. It provides properties of binary trees such as the number of nodes in full and complete binary trees based on height.
358 33 powerpoint-slides_8-linked-lists_chapter-8



358 33 powerpoint-slides_8-linked-lists_chapter-8sumitbardhan The document discusses different types of linked lists including singly linked lists, circular linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It provides algorithms for common operations on linked lists such as traversing, inserting nodes, deleting nodes, and searching. Key points include that each node contains data and a pointer to the next node, and a linked list is traversed using a starting pointer that points to the first node. Circular linked lists have the last node point to the first node. Doubly linked lists have pointers to both the next and previous nodes.
Doubly linked list



Doubly linked listFahd Allebdi A doubly linked list allows traversal in both directions by storing references to both the next and previous nodes. Each node contains two references - a next link pointing to the next node and a prev link pointing to the previous node. This allows for quick insertion and removal at both ends as well as the middle of the list. Sentinel nodes are added at the beginning and end to simplify programming, with the header pointing forward and the trailer pointing backward.
Binary Search Tree



Binary Search TreeAbhishek L.R Presentation On Binary Search Tree using Linked List Concept which includes Traversing the tree in Inorder, Preorder and Postorder Methods and also searching the element in the Tree
Open Legal Data Workshop at Stanford



Open Legal Data Workshop at StanfordHarry Surden On May 19, 2016 I hosted a workshop at Stanford's Codex Center about ways to make legal data more open and accessible for computation. These are the slides from my presentation framing the issue.
Harry Surden - Artificial Intelligence and Law Overview

Harry Surden - Artificial Intelligence and Law OverviewHarry Surden This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence. It defines AI as using computers to solve problems or make automated decisions for tasks typically requiring human intelligence. The two major AI techniques are logic and rules-based approaches, and machine learning based approaches. Machine learning algorithms find patterns in data to infer rules and improve over time. While AI is limited and cannot achieve human-level abstract reasoning, pattern-based machine learning is powerful for automation and many tasks through proxies without requiring true intelligence. Successful AI systems are often hybrids of the approaches or work with human intelligence.
AI and Machine Learning Demystified by Carol Smith at Midwest UX 2017



AI and Machine Learning Demystified by Carol Smith at Midwest UX 2017Carol Smith What is machine learning? Is UX relevant in the age of artificial intelligence (AI)? How can I take advantage of cognitive computing? Get answers to these questions and learn about the implications for your work in this session. Carol will help you understand at a basic level how these systems are built and what is required to get insights from them. Carol will present examples of how machine learning is already being used and explore the ethical challenges inherent in creating AI. You will walk away with an awareness of the weaknesses of AI and the knowledge of how these systems work.
Ad
Similar to Array implementation and linked list as datat structure (20)
Introduction in Data Structure - stack, Queue



Introduction in Data Structure - stack, QueueBharathiKrishna6 A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data. There are several basic and advanced types of data structures, all designed to arrange data to suit a specific purpose.
Unit i(dsc++)



Unit i(dsc++)Durga Devi The document contains the syllabus for the second semester of the first year of a B.Tech. program. It outlines 6 units that will be covered related to data structures and C++ programming. Unit I introduces concepts like abstract data types, stacks, queues and their implementations. Unit II covers linked lists and representing stacks and queues with linked lists. Unit III discusses trees and graphs. Unit IV covers searching and sorting algorithms. Units V and VI cover object-oriented programming concepts in C++ like classes, objects, inheritance and templates. The document also lists lab assignments related to implementing various data structures and algorithms in C programming language.
singly link list project in dsa.....by rohit malav



singly link list project in dsa.....by rohit malavRohit malav Singly Linked Lists are a type of data structure. In a singly linked list, each node in the list stores the contents and a pointer or reference to the next node in the list. It does not store any pointer or reference to the previous node. ... The last node in a single linked list points to nothing.
03_LinkedLists_091.ppt



03_LinkedLists_091.pptsoniya555961 Singly linked lists allow for efficient insertion and deletion of elements without shifting other elements. They have dynamic size and use less memory than arrays if the list is sparsely populated. However, random access is not efficient as elements are not stored contiguously in memory. Common operations like search, insertion, and deletion have O(n) time complexity due to the need to traverse the list sequentially. Space complexity is O(n) to store the elements and references between nodes.
1.ppt



1.pptArifKamal36 Singly linked lists allow for efficient insertion and deletion of elements without shifting other elements. They have dynamic size and use less memory than arrays if the list is sparsely populated. However, random access is not efficient as elements are not stored contiguously in memory. Common operations like search, insertion, and deletion have O(n) time complexity due to the need to traverse the list sequentially. Space complexity is O(n) to store the elements and references between nodes.
Fundamentals of data structures



Fundamentals of data structuresNiraj Agarwal The document discusses different data structures and their implementations and applications. It covers arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, binary trees, and binary search. The key points are:
- Arrays allow fast access but have fixed size; linked lists can grow dynamically but access is slower.
- Binary trees allow fast (O(log n)) search, insertion, and deletion operations due to their hierarchical structure.
- Stacks and queues are useful for modeling LIFO and FIFO data access with applications like function calls and job scheduling.
- Binary search runs in O(log n) time by recursively dividing the search space for sorted data.
Fjdkkdnncmckkgkhkhkkhkhkhkhkhkhkhkhkhkhhl



FjdkkdnncmckkgkhkhkkhkhkhkhkhkhkhkhkhkhhlBorraramkumar Hekdkdhjfjfnfnfngngngmgmmgmgkgkckkckckfkgkfmkfmfkfkfmgmgmvmmgmgmgmgmmgmgmgmgmgkgkkgkgkgkgkgkgkgkkkkkkkk
Sorting & Linked Lists



Sorting & Linked ListsJ.T.A.JONES The document discusses sorting algorithms, abstract data types (ADTs), and linked lists. It describes selection sort and insertion sort algorithms for sorting arrays. It then explains that linked lists are a more flexible data structure than arrays and defines a singly linked list as an ADT with nodes that point to the next node in the list. Functions for typical linked list operations like insertion, deletion, checking if empty, and printing the list are discussed.
Chapter 5 ds



Chapter 5 dsHanif Durad The document outlines the key concepts of linked lists including:
- Linked lists allow for dynamic resizing and efficient insertion/deletion unlike arrays.
- A linked list contains nodes that have a data field and a pointer to the next node.
- Common operations on linked lists include insertion, deletion, searching, and traversing the list.
- The time complexity of these operations depends on whether it's at the head, tail, or interior node.
- Linked lists can be implemented using classes for the node and linked list objects.
Lec3



Lec3Nikhil Chilwant The document discusses different data structures for representing queues and linked lists, including their implementations and operations. Queues follow FIFO ordering and can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Linked lists allow efficient insertion/removal at both ends and can be used to implement double-ended queues (deques). Deques support efficient insertion/removal from both ends and can implement stacks and queues. Sequences generalize vectors and linked lists, introducing the concept of positions to provide implementation independence.
Bsc cs ii dfs u-2 linklist,stack,queue



Bsc cs ii dfs u-2 linklist,stack,queueRai University The document discusses different data structures including stacks, queues, linked lists, and their implementations. It defines stacks as LIFO structures that can add and remove items from one end only. Queues are FIFO structures that add to one end and remove from the other. Linked lists store data in nodes that point to the next node. Stacks, queues and linked lists can all be implemented using arrays or by linking nodes. Priority queues and deques are also discussed.
Linked list1.ppt



Linked list1.pptKasthuriKAssistantPr Linked lists are dynamic data structures that can change size during program execution. Each element contains a data field and a pointer to the next element. Elements are linked together using these pointers. There are several types of linked lists including singly linked, doubly linked, circular linked lists. Basic operations on linked lists include traversing the list, inserting elements, and deleting elements. Linked lists are suitable when the number of elements is unknown or the list needs to be rearranged efficiently.
Funddamentals of data structures



Funddamentals of data structuresGlobalidiots we are innovative,we are different,we are genius so they call us idiots
Visit us for movies,videos,documentaries,sports,funny pics and many more join www.globalidiots.com
Lec3



Lec3Anjneya Varshney Queues and linked lists are common data structures. Queues follow FIFO ordering and allow insertion at the rear and removal from the front. Linked lists provide efficient insertion and removal by using nodes connected by pointers. Doubly linked lists allow efficient insertion and removal from both ends, enabling implementations of double-ended queues. Positions abstract the concept of location in a data structure and allow node-based operations on linked lists. Iterators encapsulate traversal of a data structure.
Bca ii dfs u-2 linklist,stack,queue



Bca ii dfs u-2 linklist,stack,queueRai University The document discusses different data structures including stacks, queues, linked lists, and their implementations. It defines stacks as LIFO structures that allow push and pop operations. Queues are FIFO structures that allow enqueue and dequeue operations. Linked lists store data in nodes that link to the next node, allowing flexible sizes. Stacks and queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, with special handling needed at the ends. Priority queues allow deletion based on priority rather than order. Circular linked lists connect the last node to the first to allow continuous traversal.
Data structures



Data structuresJauhar Amir The document discusses data structures and abstract data types (ADTs). It provides examples of linear lists and linked lists as implementations of the ADT linear list. Key points made include:
- An ADT defines operations on a data structure without specifying its implementation.
- Linked lists provide flexibility for insertion and deletion compared to arrays.
- The main linked list operations are insertion, deletion, finding an element, and traversal.
- Queues and stacks are examples of linear lists with restricted insertion/deletion points.
Ad
More from Tushar Aneyrao (7)
Varaiational formulation fem 



Varaiational formulation fem Tushar Aneyrao The document discusses the variational formulation and Rayleigh-Ritz method for solving systems. The variational approach involves calculating the total potential of a system and finding the stationary value where the potential is zero. The Rayleigh-Ritz method assumes the form of the unknown solution in terms of known trial functions with adjustable parameters. The functional is expressed in terms of these parameters and differentiated to obtain equations that are set to zero to solve for the parameters.
General purpose simulation System (GPSS)



General purpose simulation System (GPSS)Tushar Aneyrao GPSS is one of the earliest discrete event simulation languages developed in the 1960s. It uses a network of blocks to model systems, with each block performing a specific function. Transactions representing entities move through the blocks. Common blocks include Generate to create transactions, Queue to queue transactions, and Advance to impose delays. GPSS is not programmed like other languages but rather models the system as a network of interconnected blocks through which transactions flow.
Safety of vehicles



Safety of vehiclesTushar Aneyrao The document discusses vehicle safety technologies. It describes the brake override system, which uses sensors and a computer to reduce engine power and engage the brakes if both the accelerator and brake are applied simultaneously. It also describes hill start assist, which uses sensors and electronic control to hold the vehicle briefly on an incline to prevent rolling backwards when the driver releases the brake. These systems improve safety by preventing accidental acceleration and making starting on hills easier.
Seminar on cim 02



Seminar on cim 02Tushar Aneyrao The document summarizes a seminar on scheduling, knowledge-based scheduling, computer hierarchy control, and supervisory control. It discusses that scheduling is important for manufacturing efficiency and productivity. Knowledge-based scheduling uses a database, knowledge base, and inference engine. Computer hierarchy control uses multiple process control stations throughout a plant networked to a central control room. Supervisory control manages integrated unit operations to achieve economic objectives for a process.
Presentation on robotics



Presentation on roboticsTushar Aneyrao This presentation provides an overview of robotics. It defines a robot and discusses robot anatomy, including joints and links. It classifies robots based on physical configuration (such as Cartesian or cylindrical) and motion/control characteristics. The presentation outlines various industrial applications of robots like material handling, welding, and assembly. It also discusses some non-industrial uses and concludes by noting advantages like increased safety/production but also disadvantages like high costs and limited duties.
Seminar o nm aterial enginering



Seminar o nm aterial engineringTushar Aneyrao The document summarizes key information about three materials: aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, and diamond. It discusses their crystal structures, properties like hardness and thermal conductivity, common processing methods, and applications. Aluminum oxide is used as an abrasive and refractory material. Silicon carbide is very hard and used for abrasives, armor, and power electronics. Diamond is the hardest known material and used in drilling, cutting, and jewelry due to its optical properties.
Seminar on fatigue



Seminar on fatigueTushar Aneyrao 1. The document discusses fatigue, which is structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading below its tensile strength.
2. It describes how fatigue occurs through repeated loading and unloading causing microscopic cracks, and how factors like stress concentration, material properties, and the environment affect fatigue life.
3. The document outlines an experiment to determine the fatigue life of aluminum specimens under different stress levels using a fatigue testing machine. Results are analyzed to find the safe stress level for 1 million reversals.
Recently uploaded (20)
Edge-banding-machines-edgeteq-s-200-en-.pdf



Edge-banding-machines-edgeteq-s-200-en-.pdfAmirStern2 מכונת קנטים המתאימה לנגריות קטנות או גדולות (כמכונת גיבוי).
מדביקה קנטים מגליל או פסים, עד עובי קנט – 3 מ"מ ועובי חומר עד 40 מ"מ. בקר ממוחשב המתריע על תקלות, ומנועים מאסיביים תעשייתיים כמו במכונות הגדולות.
cnc-drilling-dowel-inserting-machine-drillteq-d-510-english.pdf



cnc-drilling-dowel-inserting-machine-drillteq-d-510-english.pdfAmirStern2 CNC מכונות קידוח drillteq d-510
Cisco ISE Performance, Scalability and Best Practices.pdf



Cisco ISE Performance, Scalability and Best Practices.pdfsuperdpz Cisco ISE Performance, Scalability and Best Practices
AI Agents in Logistics and Supply Chain Applications Benefits and Implementation



AI Agents in Logistics and Supply Chain Applications Benefits and ImplementationChristine Shepherd AI agents are reshaping logistics and supply chain operations by enabling automation, predictive insights, and real-time decision-making across key functions such as demand forecasting, inventory management, procurement, transportation, and warehouse operations. Powered by technologies like machine learning, NLP, computer vision, and robotic process automation, these agents deliver significant benefits including cost reduction, improved efficiency, greater visibility, and enhanced adaptability to market changes. While practical use cases show measurable gains in areas like dynamic routing and real-time inventory tracking, successful implementation requires careful integration with existing systems, quality data, and strategic scaling. Despite challenges such as data integration and change management, AI agents offer a strong competitive edge, with widespread industry adoption expected by 2025.
Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account



Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean accountangelo60207 Prevent infrastructure costs from becoming a significant line item on your startup’s budget! Serial entrepreneur and software architect Angelo Mandato will share his experience with AWS Activate (startup credits from AWS) and knowledge on how to architect a lean and mean AWS account ideal for budget minded and bootstrapped startups. In this session you will learn how to manage a production ready AWS account capable of scaling as your startup grows for less than $100/month before credits. We will discuss AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, architect priorities, and the importance of having flexible, optimized Infrastructure as Code. We will wrap everything up discussing opportunities where to save with AWS services such as S3, EC2, Load Balancers, Lambda Functions, RDS, and many others.
Integration of Utility Data into 3D BIM Models Using a 3D Solids Modeling Wor...



Integration of Utility Data into 3D BIM Models Using a 3D Solids Modeling Wor...Safe Software Jacobs has developed a 3D utility solids modelling workflow to improve the integration of utility data into 3D Building Information Modeling (BIM) environments. This workflow, a collaborative effort between the New Zealand Geospatial Team and the Australian Data Capture Team, employs FME to convert 2D utility data into detailed 3D representations, supporting enhanced spatial analysis and clash detection.
To enable the automation of this process, Jacobs has also developed a survey data standard that standardizes the capture of existing utilities. This standard ensures consistency in data collection, forming the foundation for the subsequent automated validation and modelling steps. The workflow begins with the acquisition of utility survey data, including attributes such as location, depth, diameter, and material of utility assets like pipes and manholes. This data is validated through a custom-built tool that ensures completeness and logical consistency, including checks for proper connectivity between network components. Following validation, the data is processed using an automated modelling tool to generate 3D solids from 2D geometric representations. These solids are then integrated into BIM models to facilitate compatibility with 3D workflows and enable detailed spatial analyses.
The workflow contributes to improved spatial understanding by visualizing the relationships between utilities and other infrastructure elements. The automation of validation and modeling processes ensures consistent and accurate outputs, minimizing errors and increasing workflow efficiency.
This methodology highlights the application of FME in addressing challenges associated with geospatial data transformation and demonstrates its utility in enhancing data integration within BIM frameworks. By enabling accurate 3D representation of utility networks, the workflow supports improved design collaboration and decision-making in complex infrastructure projects
Trends Artificial Intelligence - Mary Meeker



Trends Artificial Intelligence - Mary MeekerClive Dickens Mary Meeker’s 2024 AI report highlights a seismic shift in productivity, creativity, and business value driven by generative AI. She charts the rapid adoption of tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney, likening today’s moment to the dawn of the internet. The report emphasizes AI’s impact on knowledge work, software development, and personalized services—while also cautioning about data quality, ethical use, and the human-AI partnership. In short, Meeker sees AI as a transformative force accelerating innovation and redefining how we live and work.
Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too Late



Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too LateMichael Furman In today's cloud-native landscape, Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for orchestrating containerized applications, but its inherent complexity introduces unique security challenges. Are you one YAML away from disaster?
This presentation, "Kubernetes Security: Act Now Before It’s Too Late," is your essential guide to understanding and mitigating the critical security risks within your Kubernetes environments. This presentation dives deep into the OWASP Kubernetes Top Ten, providing actionable insights to harden your clusters.
We will cover:
The fundamental architecture of Kubernetes and why its security is paramount.
In-depth strategies for protecting your Kubernetes Control Plane, including kube-apiserver and etcd.
Crucial best practices for securing your workloads and nodes, covering topics like privileged containers, root filesystem security, and the essential role of Pod Security Admission.
Don't wait for a breach. Learn how to identify, prevent, and respond to Kubernetes security threats effectively.
It's time to act now before it's too late!
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free Download



Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free DownloadPuppy jhon ➡ 🌍📱👉COPY & PASTE LINK👉👉👉 ➤ ➤➤ https://drfiles.net/
Wondershare Filmora Crack is a user-friendly video editing software designed for both beginners and experienced users.
Floods in Valencia: Two FME-Powered Stories of Data Resilience



Floods in Valencia: Two FME-Powered Stories of Data ResilienceSafe Software In October 2024, the Spanish region of Valencia faced severe flooding that underscored the critical need for accessible and actionable data. This presentation will explore two innovative use cases where FME facilitated data integration and availability during the crisis. The first case demonstrates how FME was used to process and convert satellite imagery and other geospatial data into formats tailored for rapid analysis by emergency teams. The second case delves into making human mobility data—collected from mobile phone signals—accessible as source-destination matrices, offering key insights into population movements during and after the flooding. These stories highlight how FME's powerful capabilities can bridge the gap between raw data and decision-making, fostering resilience and preparedness in the face of natural disasters. Attendees will gain practical insights into how FME can support crisis management and urban planning in a changing climate.
Boosting MySQL with Vector Search -THE VECTOR SEARCH CONFERENCE 2025 .pdf



Boosting MySQL with Vector Search -THE VECTOR SEARCH CONFERENCE 2025 .pdfAlkin Tezuysal As the demand for vector databases and Generative AI continues to rise, integrating vector storage and search capabilities into traditional databases has become increasingly important. This session introduces the *MyVector Plugin*, a project that brings native vector storage and similarity search to MySQL. Unlike PostgreSQL, which offers interfaces for adding new data types and index methods, MySQL lacks such extensibility. However, by utilizing MySQL's server component plugin and UDF, the *MyVector Plugin* successfully adds a fully functional vector search feature within the existing MySQL + InnoDB infrastructure, eliminating the need for a separate vector database. The session explains the technical aspects of integrating vector support into MySQL, the challenges posed by its architecture, and real-world use cases that showcase the advantages of combining vector search with MySQL's robust features. Attendees will leave with practical insights on how to add vector search capabilities to their MySQL systems.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI Professional



Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI ProfessionalVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI Professional
Ben Blair - Operating Safely in a Vibe Coding World



Ben Blair - Operating Safely in a Vibe Coding WorldAWS Chicago AWS Community Day Midwest 2025
Ben Blair
Operating Safely in a Vibe Coding World
Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Cases



Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Casespanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/domino-iq-what-to-expect-first-steps-and-use-cases/
HCL Domino iQ Server – From Ideas Portal to implemented Feature. Discover what it is, what it isn’t, and explore the opportunities and challenges it presents.
Key Takeaways
- What are Large Language Models (LLMs) and how do they relate to Domino iQ
- Essential prerequisites for deploying Domino iQ Server
- Step-by-step instructions on setting up your Domino iQ Server
- Share and discuss thoughts and ideas to maximize the potential of Domino iQ
Mastering AI Workflows with FME - Peak of Data & AI 2025



Mastering AI Workflows with FME - Peak of Data & AI 2025Safe Software Harness the full potential of AI with FME: From creating high-quality training data to optimizing models and utilizing results, FME supports every step of your AI workflow. Seamlessly integrate a wide range of models, including those for data enhancement, forecasting, image and object recognition, and large language models. Customize AI models to meet your exact needs with FME’s powerful tools for training, optimization, and seamless integration
Bridging the divide: A conversation on tariffs today in the book industry - T...



Bridging the divide: A conversation on tariffs today in the book industry - T...BookNet Canada A collaboration-focused conversation on the recently imposed US and Canadian tariffs where speakers shared insights into the current legislative landscape, ongoing advocacy efforts, and recommended next steps. This event was presented in partnership with the Book Industry Study Group.
Link to accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/bridging-the-divide-a-conversation-on-tariffs-today-in-the-book-industry/
Presented by BookNet Canada and the Book Industry Study Group on May 29, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...



“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/state-space-models-vs-transformers-for-ultra-low-power-edge-ai-a-presentation-from-brainchip/
Tony Lewis, Chief Technology Officer at BrainChip, presents the “State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
At the embedded edge, choices of language model architectures have profound implications on the ability to meet demanding performance, latency and energy efficiency requirements. In this presentation, Lewis contrasts state-space models (SSMs) with transformers for use in this constrained regime. While transformers rely on a read-write key-value cache, SSMs can be constructed as read-only architectures, enabling the use of novel memory types and reducing power consumption. Furthermore, SSMs require significantly fewer multiply-accumulate units—drastically reducing compute energy and chip area.
New techniques enable distillation-based migration from transformer models such as Llama to SSMs without major performance loss. In latency-sensitive applications, techniques such as precomputing input sequences allow SSMs to achieve sub-100 ms time-to-first-token, enabling real-time interactivity. Lewis presents a detailed side-by-side comparison of these architectures, outlining their trade-offs and opportunities at the extreme edge.
Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025



Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025Infrassist Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Azure vs. AWS is a common comparison when businesses evaluate cloud platforms for performance, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...



“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025



Azure vs AWS Which Cloud Platform Is Best for Your Business in 2025Infrassist Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Array implementation and linked list as datat structure
- 2. An array is a collection of elements of similar datatype. Contiguous memory allocation takes place. An array is a DS in which we can access every element directly using position variable . It is rather an organizational concept. Array elements can be accessed individually. Syntax: datatype nameofarray [dimension];
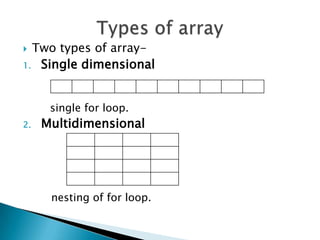
- 3. Two types of array- 1. Single dimensional single for loop. 2. Multidimensional nesting of for loop.
- 4. Array can be of integer ,character and string. Integer and character array can be implemented by same logic Implementation of string array is quiet different from the two. We can study the array implementation using integer array.
- 5. Creation of integer array int 7 a[0] i=0 a[10]={7,1,32,58,0,5,8,16,9,23} 14 a[1] i=1 ; 32 a[2] i=2 Integer array “a”. 58 a[3] i=3 It is of dimension 10 (from 0 0 a[4] i=4 to 9). 5 a[5] i=5 Take positing variable i. 8 a[6] i=6 Its storage will be continuous 16 a[7] i=7 20 bytes(2 bytes each). 9 a[8] i=8 23 a[9] i=9
- 6. 1. DECLARATION N SIZE 2. OPERATION Repeat for i= 0 to (size-1) arr[i]= num end repeat 3. OUTPUT RETURN(arr[i])
- 7. DECLARATION i rows j coloumn OPERATION ◦ Repeat for i=0 to (rows-1) Repeat for j=0 to (coloumn-1) Array[i][j]=num End repeat ◦ End repeat OUTPUT Return(Array[i][j])
- 8. No need to declare large number of variables individually. Variables are not scattered in memory , they are stored in contiguous memory. Ease the handling of large no of variables of same datatype.
- 9. Rigid structure. Can be hard to add/remove elements. Cannot be dynamically resized in most languages. Memory loss.
- 10. AS A DATA STRUCTURE
- 11. Each element (node) inside a linked list is linked to the previous node and successor (next) node. This allows for more efficient insertion and deletion of nodes. 5 3 14 2 continued
- 12. Each item has a data part (one or more data members), and a link that points to the next item. One natural way to implement the link is as a pointer; that is, the link is the address of the next item in the list. It makes good sense to view each item as an object, that is, as an instance of a class. We call that class: Node The last item does not point to anything. We set its link member to NULL. This is denoted graphically by a self-loop
- 13. Insert a new item ◦ At the head of the list, or ◦ At the tail of the list, or ◦ Inside the list, in some designated position Search for an item in the list ◦ The item can be specified by position, or by some value Delete an item from the list ◦ Search for and locate the item, then remove the item, and finally adjust the surrounding pointers
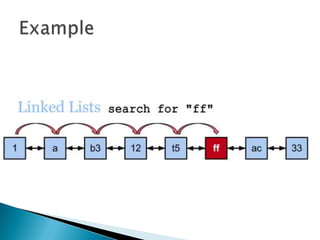
- 14. Suppose you want to find the item whose data value is A You have to search sequentially starting from the head item rightward until the first item whose data member is equal to A is found. At each item searched, a comparison between the data member and A is performed.
- 15. LOGIC FOR SEARCHING A LINKED LIST •Since nodes in a linked list have no names, we use two pointers, pre (for previous) and cur (for current). •At the beginning of the search, the pre pointer is null and the cur pointer points to the first node. •The search algorithm moves the two pointers together towards the end of the list.
- 16. Declaration ◦ Current 0 Searching ◦ for (current = first; current != NULL; current = current->next) ◦ if (searchItem == current(data)) ◦ return (current); ◦ Break Output ◦ return (NULL);
- 18. Insertion of an Element at the Head : Before the insertion: head next next next element element element Rome Seattle Toronto
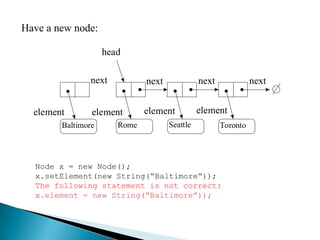
- 19. Have a new node: head next next next next element element element element Baltimore Rome Seattle Toronto Node x = new Node(); x.setElement(new String(“Baltimore”)); The following statement is not correct: x.element = new String(“Baltimore”));
- 20. After the insertion: head next next next next element element element element Baltimore Rome Seattle Toronto x.setNext(head); head = x;
- 21. Deleting an Element at the Head : Before the deletion: head next next next next element element element element Baltimore Rome Seattle Toronto
- 22. Remove the node from the list: head next next next next element element element element Baltimore Rome Seattle Toronto head = head.getNext();
- 23. After the deletion: head next next next element element element Rome Seattle Toronto
- 24. Insertion of an Element at the Tail : Before the insertion: head tail next next next element element element Rome Seattle Toronto
- 25. Have a new node: head tail next next next next element element element element Rome Seattle Toronto Baltimore Node x = new Node( ); x.setElement(new String(“Baltimore”)); x.setNext(null); tail.setNext(x); tail = x;
- 26. After the insertion: head tail next next next next element element element element Rome Seattle Toronto Baltimore
- 27. Deleting an Element at the Tail : Deletion of an element at the tail of a singly linked list takes more effort. The difficulty is related with the fact that the last node does not have a link to the previous node which will become the new tail of the list.
- 28. Before the deletion: head tail next next next next element element element element Rome Seattle Toronto Baltimore
- 29. Remove the node: How can we find the new tail? head tail ? next next next next element element element element Rome Seattle Toronto Baltimore should be removed
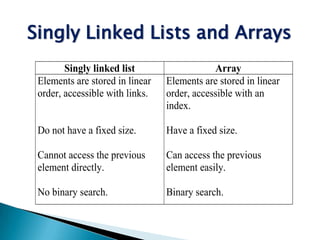
- 30. Singly Linked Lists and Arrays Singly linked list Array Elements are stored in linear Elements are stored in linear order, accessible with links. order, accessible with an index. Do not have a fixed size. Have a fixed size. Cannot access the previous Can access the previous element directly. element easily. No binary search. Binary search.
- 31. Advantages of linked lists Linked lists are dynamic, they can grow or shrink as necessary Linked lists are non-contiguous; the logical sequence of items in the structure is decoupled from any physical ordering in memory CS314 Linked Lists 31
- 32. Applications of linked lists •A linked list is a very efficient data structure for sorted list that will go through many insertions and deletions. •A linked list is a dynamic data structure in which the list can start with no nodes and then grow as new nodes are needed. A node can be easily deleted without moving other nodes, as would be the case with an array. •For example, a linked list could be used to hold the records of students in a school. Each quarter or semester, new students enroll in the school and some students leave or graduate.






