Chapter 1 Basic Programming (Python Programming Lecture)
- 3. Topic • Operator • Arithmetic Operation • Assignment Operation • Arithmetic Operation More Example • More Built in Function Example • More Math Module Example
- 4. Operator in Python • Operators are special symbols in that carry out arithmetic or logical computation. • The value that the operator operates on is called the operand. • Type of Operator in Python • Arithmetic operators • Assignment operators • Comparison operators • Logical operators • Bitwise operators • Identity operators • Membership operators
- 5. PYTHON PROGRAMMING Chapter 1 Lecture 1.1.0 Basic Arithmetic Operator
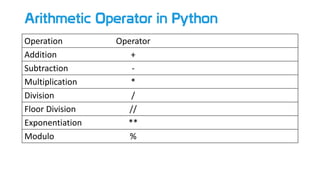
- 6. Arithmetic Operator in Python Operation Operator Addition + Subtraction - Multiplication * Division / Floor Division // Exponentiation ** Modulo %
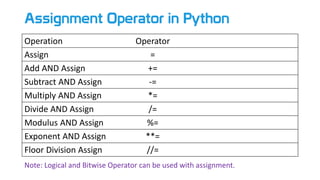
- 7. Assignment Operator in Python Operation Operator Assign = Add AND Assign += Subtract AND Assign -= Multiply AND Assign *= Divide AND Assign /= Modulus AND Assign %= Exponent AND Assign **= Floor Division Assign //= Note: Logical and Bitwise Operator can be used with assignment.
- 8. Summation of two number a = 5 b = 4 sum = a + b print(sum)
- 9. Summation of two number – User Input a = int(input()) b = int(input()) sum = a + b print(sum)
- 10. Difference of two number a = int(input()) b = int(input()) diff = a - b print(diff)
- 11. Product of two number a = int(input()) b = int(input()) pro = a * b print(pro)
- 12. Quotient of two number a = int(input()) b = int(input()) quo = a / b print(quo)
- 13. Reminder of two number a = int(input()) b = int(input()) rem = a % b print(rem)
- 14. Practice Problem 1.1 Input two Number form User and calculate the followings: 1. Summation of two number 2. Difference of two number 3. Product of two number 4. Quotient of two number 5. Reminder of two number
- 15. Any Question? Like, Comment, Share Subscribe
- 17. PYTHON PROGRAMMING Chapter 1 Lecture 1.1.1 More Arithmetic Operator
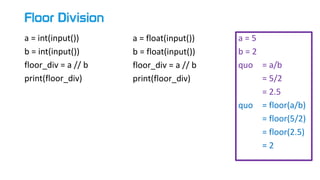
- 18. Floor Division a = int(input()) b = int(input()) floor_div = a // b print(floor_div) a = float(input()) b = float(input()) floor_div = a // b print(floor_div) a = 5 b = 2 quo = a/b = 5/2 = 2.5 quo = floor(a/b) = floor(5/2) = floor(2.5) = 2
- 19. Find Exponent (a^b). [1] a = int(input()) b = int(input()) # Exponent with Arithmetic Operator # Syntax: base ** exponent exp = a ** b print(exp)
- 20. Find Exponent (a^b). [2] a = int(input()) b = int(input()) # Exponent with Built-in Function # Syntax: pow(base, exponent) exp = pow(a,b) print(exp)
- 21. Find Exponent (a^b). [3] a = int (input()) b = int(input()) # Return Modulo for Exponent with Built-in Function # Syntax: pow(base, exponent, modulo) exp = pow(a,b,2) print(exp) a = 2 b = 4 ans = (a^b)%6 = (2^4)%6 = 16%6 = 4
- 22. Find Exponent (a^b). [4] a = int(input()) b = int(input()) # Using Math Module import math exp = math.pow(a,b) print(exp)
- 23. Find absolute difference of two number. [1] a = int(input()) b = int(input()) abs_dif = abs(a - b) print(abs_dif) a = 4 b = 2 ans1 = abs(a-b) = abs(4-2) = abs(2) = 2 ans2 = abs(b-a) = abs(2-4) = abs(-2) = 2
- 24. Find absolute difference of two number. [2] import math a = float(input()) b = float(input()) fabs_dif = math.fabs(a - b) print(fabs_dif)
- 25. Built-in Function • abs(x) • pow(x,y[,z]) https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/functions.html
- 26. Practice Problem 1.2 Input two number from user and calculate the followings: (use necessary date type) 1. Floor Division with Integer Number & Float Number 2. Find Exponential (a^b) using Exponent Operator, Built-in pow function & Math Module pow function 3. Find Exponent with modulo (a^b%c) 4. Find absolute difference of two number using Built-in abs function & Math Module fabs function
- 27. Any Question? Like, Comment, Share Subscribe
- 29. PYTHON PROGRAMMING Chapter 1 Lecture 1.2 Arithmetic Operation Example
- 30. Average of three numbers. a = float(input()) b = float(input()) c = float(input()) sum = a + b + c avg = sum/3 print(avg)
- 31. Area of Triangle using Base and Height. b = float(input()) h = float(input()) area = (1/2) * b * h print(area)
- 32. Area of Triangle using Length of 3 sides. import math a = float(input()) b = float(input()) c = float(input()) s = (a+b+c) / 2 area = math.sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c)) print(area) 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 = 𝑠 ∗ (s−a)∗(s−b)∗(s−c) 𝑠 = 𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 2
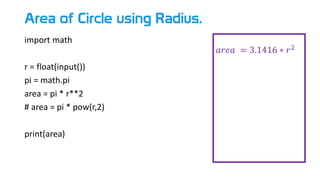
- 33. Area of Circle using Radius. import math r = float(input()) pi = math.pi area = pi * r**2 # area = pi * pow(r,2) print(area) 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 = 3.1416 ∗ 𝑟2
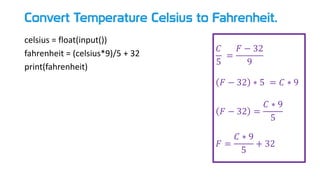
- 34. Convert Temperature Celsius to Fahrenheit. celsius = float(input()) fahrenheit = (celsius*9)/5 + 32 print(fahrenheit) 𝐶 5 = 𝐹 − 32 9 𝐹 − 32 ∗ 5 = 𝐶 ∗ 9 𝐹 − 32 = 𝐶 ∗ 9 5 𝐹 = 𝐶 ∗ 9 5 + 32
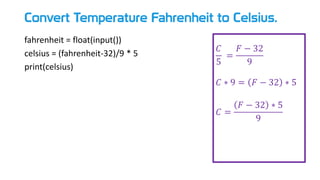
- 35. Convert Temperature Fahrenheit to Celsius. fahrenheit = float(input()) celsius = (fahrenheit-32)/9 * 5 print(celsius) 𝐶 5 = 𝐹 − 32 9 𝐶 ∗ 9 = 𝐹 − 32 ∗ 5 𝐶 = 𝐹 − 32 ∗ 5 9
- 36. Convert Second to HH:MM:SS. # 1 Hour = 3600 Seconds # 1 Minute = 60 Seconds totalSec = int(input()) hour = int(totalSec/3600) min_sec = int(totalSec%3600) minute = int(min_sec/60) second = int(min_sec%60) print("{}H {}M {}S".format(hour,minute,second)) #print(f"{hour}H {minute}M {second}S") # 1 Hour = 3600 Seconds # 1 Minute = 60 Seconds totalSec = int(input()) hour = totalSec//3600 min_sec = totalSec%3600 minute = min_sec//60 second = min_sec%60 print("{}H {}M {}S".format(hour,minute,second)) #print(f"{hour}H {minute}M {second}S")
- 37. Math Module • math.pow(x, y) • math.sqrt(x) • math.pi https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/math.html
- 38. Practice Problem 1.3 1. Average of three numbers. 2. Area of Triangle using Base and Height. 3. Area of Triangle using Length of 3 sides. 4. Area of Circle using Radius. 5. Convert Temperature Celsius to Fahrenheit. 6. Convert Temperature Fahrenheit to Celsius. 7. Convert Second to HH:MM:SS.
- 39. Any Question? Like, Comment, Share Subscribe
- 41. PYTHON PROGRAMMING Chapter 1 Lecture 1.2 More Operator
- 42. Comparison Operator in Python Operation Operator Equality == Not Equal != Greater Than > Less Than < Greater or Equal >= Less or Equal <=
- 43. Logical Operator in Python Operation Operator Logical And and Logical Or or Logical Not not
- 44. Bitwise Operator in Python Operation Operator Bitwise And & Bitwise Or | Bitwise Xor ^ Left Shift << Right Shift >>
- 45. Other Operator in Python • Membership Operator (in, not in) • Identity Operator (is, not is)
- 46. Any Question? Like, Comment, Share Subscribe
















![Find Exponent (a^b). [1]
a = int(input())
b = int(input())
# Exponent with Arithmetic Operator
# Syntax: base ** exponent
exp = a ** b
print(exp)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-19-320.jpg)
![Find Exponent (a^b). [2]
a = int(input())
b = int(input())
# Exponent with Built-in Function
# Syntax: pow(base, exponent)
exp = pow(a,b)
print(exp)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-20-320.jpg)
![Find Exponent (a^b). [3]
a = int (input())
b = int(input())
# Return Modulo for Exponent with Built-in Function
# Syntax: pow(base, exponent, modulo)
exp = pow(a,b,2)
print(exp)
a = 2
b = 4
ans = (a^b)%6
= (2^4)%6
= 16%6
= 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-21-320.jpg)
![Find Exponent (a^b). [4]
a = int(input())
b = int(input())
# Using Math Module
import math
exp = math.pow(a,b)
print(exp)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-22-320.jpg)
![Find absolute difference of two number. [1]
a = int(input())
b = int(input())
abs_dif = abs(a - b)
print(abs_dif)
a = 4
b = 2
ans1 = abs(a-b)
= abs(4-2)
= abs(2)
= 2
ans2 = abs(b-a)
= abs(2-4)
= abs(-2)
= 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-23-320.jpg)
![Find absolute difference of two number. [2]
import math
a = float(input())
b = float(input())
fabs_dif = math.fabs(a - b)
print(fabs_dif)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-24-320.jpg)
![Built-in Function
• abs(x)
• pow(x,y[,z])
https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/functions.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1basicprogramming-190204135836/85/Chapter-1-Basic-Programming-Python-Programming-Lecture-25-320.jpg)