(chapter 2) A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java
- 1. 1A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen 1 Frank NIELSEN [email protected] A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java Chapter 2: Conditional structures and loops
- 2. 2A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Upper case versus Lower case Java distinguishes between uppercases (A..Z) and lowercases (a..z) Unix differentiates upper/lower case filenames class UpperLowerCase { public static void main (String arguments[]) { int MyVar; // this variable is different from MyVar int myvar; // Generate a syntax error at compile time: // cannot find symbol variable myVar System.out.println(myVar); } }
- 3. 3A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Reserved keywords Reserved keywords in Java: You cannot choose reserved keywordsreserved keywords for variable names: class ReservedKeyword {public static void main (String arg[]){ double x,y; // Generate a syntax error: // "not a statement" int import; } }
- 4. 4A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Displaying versus Computing ● You need to display if you'd like to see the result of evaluating an expression ● System.out.println displays on the console with a return carriage ● System.out.print displays on the console without a return carriage Java is not Maple nor SciLab! Confusing in Maple: Interpreter: compute:display
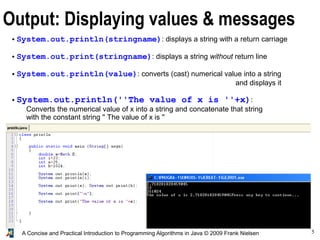
- 5. 5A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Output: Displaying values & messages ● System.out.println(stringname): displays a string with a return carriage ● System.out.print(stringname): displays a string without return line ● System.out.println(value): converts (cast) numerical value into a string and displays it ● System.out.println(''The value of x is ''+x): Converts the numerical value of x into a string and concatenate that string with the constant string '' The value of x is '' Display=write to console or to text file if it is redirected (as in java toto > result.txt )
- 6. 6A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen More on System.out.print[ln] Equivalences of stream output: System.out.print(''n'') = System.out.println(''''); System.out.print(''Hello INF311 n'') = System.out.println(''INF311''); Priority order+casting operations...
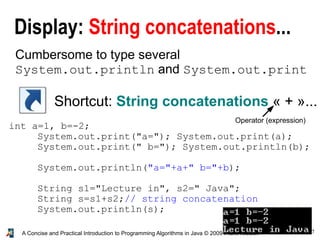
- 7. 7A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Display: String concatenations... Cumbersome to type several System.out.println and System.out.print Shortcut: String concatenations « + »... int a=1, b=-2; System.out.print("a="); System.out.print(a); System.out.print(" b="); System.out.println(b); System.out.println("a="+a+" b="+b); String s1="Lecture in", s2=" Java"; String s=s1+s2;// string concatenation System.out.println(s); Operator (expression)
- 8. 8A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen /* Declare a constant (not a variable) to bypass using Math.PI */ final double PI = 3.14; // constant Declaring constants Numeric bug in predicate !// Constant final double PI = 3.14; int a=1; double b=a+PI; if (b==4.14) // Equality test are dangerous!!! System.out.println("Correct result"); else {System.out.println("Incorrect result"); System.out.println("a="+a+" b="+b+" PI="+PI); } }
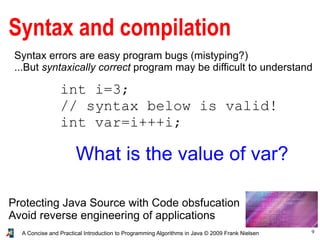
- 9. 9A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Syntax and compilation Syntax errors are easy program bugs (mistyping?) ...But syntaxically correct program may be difficult to understand Protecting Java Source with Code obsfucation Avoid reverse engineering of applications int i=3; // syntax below is valid! int var=i+++i; What is the value of var?
- 10. 10A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Program: Data,computations + workflow The control structures define the set of instructions being executed (aiguillage des trains) For example, a branching condition: if (a<b) [then] c=a; // Do-something-1 else c=b; // Do-something-2 There are two potential instructions paths depending on the predicate: ● a<b, -> c=a; or ● a>=b, -> c=b; c is selected as the minimum of a and b In Java, we do not use the word then
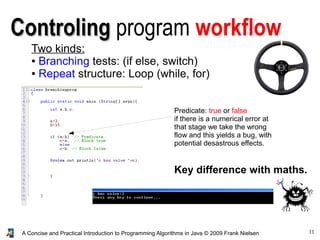
- 11. 11A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen ControlingControling program workflow Two kinds: ● Branching tests: (if else, switch) ● Repeat structure: Loop (while, for) Predicate: true or false if there is a numerical error at that stage we take the wrong flow and this yields a bug, with potential desastrous effects. Key difference with maths.
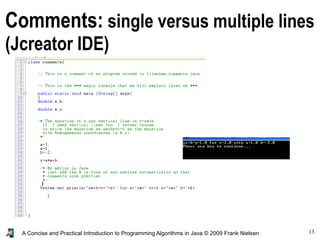
- 12. 12A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Annotating programs: comments! Writing comments is good for (1) yourself and for (2) others to proofread and debug your code In fact, there are some paradigms to write in a single file both ● the clean documentations, and ● the code. Exempla gratia (e.g.) cweb, Literate programming, etc. http://www.literateprogramming.com/ In INF311, we rather write short programs, so we consider the standard comments: // This is a single line comment /* I can also write comments on several lines by using these delimiters */ D. Knuth
- 13. 13A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Comments: single versus multiple lines (Jcreator IDE)
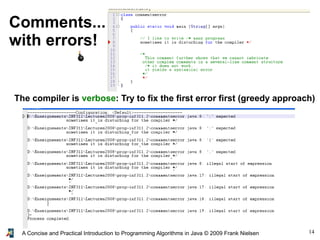
- 14. 14A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Comments... with errors! The compiler is verbose: Try to fix the first error first (greedy approach)
- 15. 15A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Comments... repaired... = Syntaxically correct program Do not forget: Writing good comments is as important as writing source code You will thank yourself for doing this once you look back at your programs months later
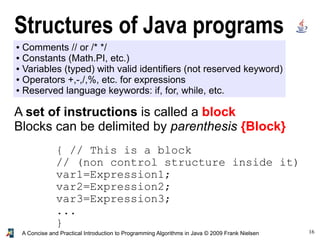
- 16. 16A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Structures of Java programs ● Comments // or /* */ ● Constants (Math.PI, etc.) ● Variables (typed) with valid identifiers (not reserved keyword) ● Operators +,-,/,%, etc. for expressions ● Reserved language keywords: if, for, while, etc. A set of instructions is called a block Blocks can be delimited by parenthesis {Block} { // This is a block // (non control structure inside it) var1=Expression1; var2=Expression2; var3=Expression3; ... }
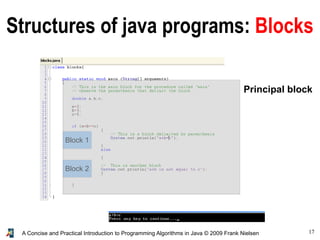
- 17. 17A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Structures of java programs: Blocks Block 2 Block 1 Principal block
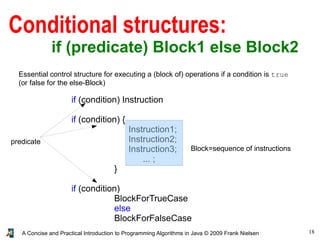
- 18. 18A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Conditional structures: if (predicate) Block1 else Block2 Essential control structure for executing a (block of) operations if a condition is true (or false for the else-Block) if (condition) Instruction if (condition) { Instruction1; Instruction2; Instruction3; ... ; } if (condition) BlockForTrueCase else BlockForFalseCase Block=sequence of instructions predicate
- 19. 19A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Conditional structures: Compact form if (predicate) Inst1 else Inst2 Conditional instruction for singe instruction block can be called using the ternary operator (3 operands) « ? : » BoolOperand1 ? TypeOperandTrue2 : TypeOperandFalse3 2.718281828459045 difference with max=0.423310825130748 double x1=Math.PI; double x2=Math.E; double min=(x1>x2)? x2 : x1; // min value double diff= (x1>x2)? x1-x2 : x2-x1; // absolute val. System.out.println(min+" difference with max="+diff);
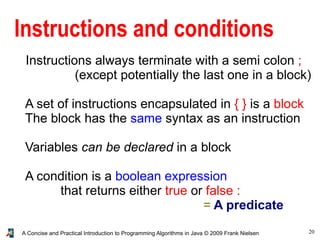
- 20. 20A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Instructions and conditions Instructions always terminate with a semi colon ; (except potentially the last one in a block) A set of instructions encapsulated in { } is a block The block has the same syntax as an instruction Variables can be declared in a block A condition is a boolean expression that returns either true or false : = A predicate
- 21. 21A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Variables and blocks Very different from C++! (Java better controls the syntax of programs, better semantic) We cannot declare twice a same variable in encapsulated block
- 22. 22A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Variables and blocks: Scopes Error!!! Variable l is not defined in the block it here
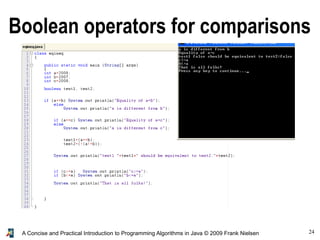
- 23. 23A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Boolean operators for comparisons a==b Test of equality (for basic types) a!=b Test for difference [ equivalent to ! (a==b) ] Inequalities: a<b True if and only if (iff.) a<b a<=b True iff. a<b or a=b a>b True iff. a>b a>=b True iff. a>b or a=b Beware: a=b is assignment not test (test of equality is ==) Typing helps you avoid this mistake: int a=3; if (a=3) System.out.println("THEN-PART"); else System.out.println("ELSE-PART"); incompatible types found : int required: boolean
- 24. 24A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Boolean operators for comparisons
- 25. 25A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen (6-2) == 4 evalutes to true but 22/7 == 3+1.0/7 evaluates to false Boolean operators for comparisons Boolean comparisons are of type boolean class Boolean{ public static void main(String[] args) { boolean b1 = (6-2) == 4; boolean b2 = 22/7 == 3+1/7.0 ; boolean b3 = 22/7 == 3+ 1/7; System.out.println(b1); // true System.out.println(b2); // false System.out.println(b3); // true } }
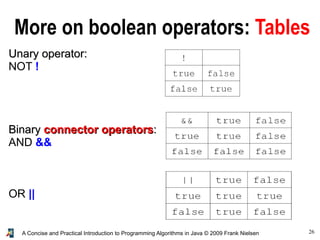
- 26. 26A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen More on boolean operators: Tables Unary operator:Unary operator: NOT ! BinaryBinary connector operatorsconnector operators:: AND && OR ||
- 27. 27A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Priority order for boolean expressions Lazy evaluation of boolean binary operators: ● If a is false we do not need to evaluate b in a && b ● If a is true we do not need either to evaluate b in a || b
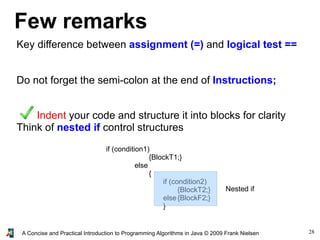
- 28. 28A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Few remarks Key difference between assignment (=) and logical test == Do not forget the semi-colon at the end of Instructions; Indent your code and structure it into blocks for clarity Think of nested if control structures if (condition1) {BlockT1;} else { if (condition2) {BlockT2;} else{BlockF2;} } Nested if
- 29. 29A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Nested conditionals (nested if) Set curly brackets { } to increase code readibility
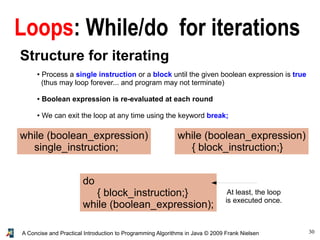
- 30. 30A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: While/do for iterations Structure for iterating ● Process a single instruction or a block until the given boolean expression is true (thus may loop forever... and program may not terminate) ● Boolean expression is re-evaluated at each round ● We can exit the loop at any time using the keyword break; while (boolean_expression) single_instruction; while (boolean_expression) { block_instruction;} do { block_instruction;} while (boolean_expression); At least, the loop is executed once.
- 31. 31A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: Euclid' GCD algorithm While Do Greatest common divisor of two integers a and b
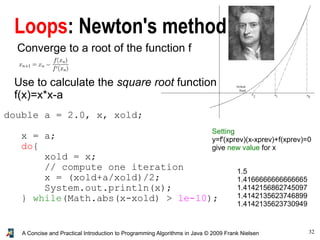
- 32. 32A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: Newton's method Converge to a root of the function f Setting y=f'(xprev)(x-xprev)+f(xprev)=0 give new value for x Use to calculate the square root function f(x)=x*x-a double a = 2.0, x, xold; x = a; do{ xold = x; // compute one iteration x = (xold+a/xold)/2; System.out.println(x); } while(Math.abs(x-xold) > 1e-10); 1.5 1.4166666666666665 1.4142156862745097 1.4142135623746899 1.4142135623730949
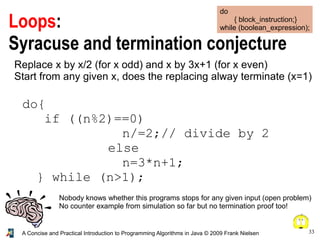
- 33. 33A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: Syracuse and termination conjecture do { block_instruction;} while (boolean_expression); Nobody knows whether this programs stops for any given input (open problem) No counter example from simulation so far but no termination proof too! Replace x by x/2 (for x odd) and x by 3x+1 (for x even) Start from any given x, does the replacing alway terminate (x=1) do{ if ((n%2)==0) n/=2;// divide by 2 else n=3*n+1; } while (n>1);
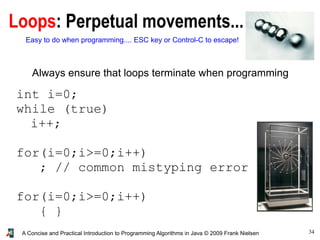
- 34. 34A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: Perpetual movements... Always ensure that loops terminate when programming int i=0; while (true) i++; for(i=0;i>=0;i++) ; // common mistyping error for(i=0;i>=0;i++) { } Easy to do when programming.... ESC key or Control-C to escape!
- 35. 35A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: Breaking the loop with break Read a sequence of non-negative natural integers and compute the cumulative sum of the sequence. Observe the shortcut: sum+=n; that is equivalent to assignment sum=sum+n;
- 36. 36A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: For... iterations ● Allows one to execute a block of instructions, and ● Increment the counter at each round ● Semantically equivalent to a while loop ● Often used for program readibility (e.g., for a range of integers) for(instruction1; boolean_condition; instruction2) block_instruction3; instruction1; while (boolean_condition) {block_instruction3; instruction2;} Equivalence with While construction
- 37. 37A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loops: For... iterations for(instruction1; boolean_condition; instruction2) block_instruction3; class ForLoop { public static void main(String args[]) { int i, n=10; int cumulLoop=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) cumulLoop+=i; int cumul=(n*(n-1))/2; // closed-form solution System.out.println(cumulLoop+" closed-form:"+cumul); } } We get 45
- 38. 38A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen int cumulLoop=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) cumulLoop+=i; Loops: For... iterations (unlooping) int cumulLoop=0; i=0; // Initialization cumulLoop+=i; i++; // i=1 now // i<n so we continue... cumulLoop+=i; i++; // i=2 now // i<n so we continue... cumulLoop+=i; ... cumulLoop+=i; // i=n-1 i++; // i=n now // i is not i<n so we stop... Unlooping...
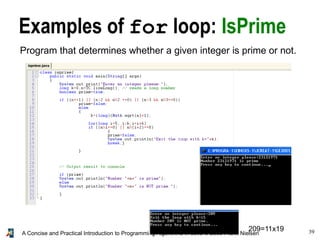
- 39. 39A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Examples of for loop: IsPrime Program that determines whether a given integer is prime or not. 209=11x19
- 40. 40A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Multiple choices: switch Avoid nested if-else structures for multiple choices class ProgSwitch {public static void main(String arg[]){ System.out.print("Input a digit in [0..9]:"); int n=TC.lireInt(); switch(n) { case 0: System.out.println("zero"); break; case 1: System.out.println("one"); break; case 2: System.out.println("two"); break; case 3: System.out.println("three"); break; default: System.out.println("Above three!"); break; }}}
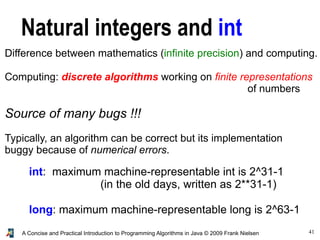
- 41. 41A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Natural integers and int Difference between mathematics (infinite precision) and computing. Computing: discrete algorithms working on finite representations of numbers Source of many bugs !!! Typically, an algorithm can be correct but its implementation buggy because of numerical errors. int: maximum machine-representable int is 2^31-1 (in the old days, written as 2**31-1) long: maximum machine-representable long is 2^63-1
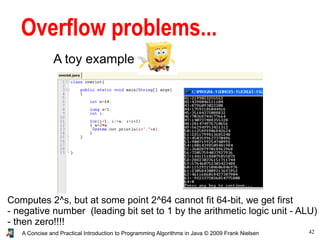
- 42. 42A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Overflow problems... A toy example Computes 2^s, but at some point 2^64 cannot fit 64-bit, we get first - negative number (leading bit set to 1 by the arithmetic logic unit - ALU) - then zero!!!!
- 43. 43A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Overflow problems: revisited Declaration inside the For Increment: i++ or ++i Multiplication is just a bit shift << to the right
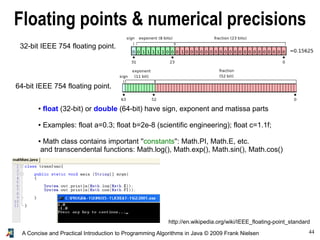
- 44. 44A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Floating points & numerical precisions 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_floating-point_standard ● float (32-bit) or double (64-bit) have sign, exponent and matissa parts ● Examples: float a=0.3; float b=2e-8 (scientific engineering); float c=1.1f; ● Math class contains important ''constants'': Math.PI, Math.E, etc. and transcendental functions: Math.log(), Math.exp(), Math.sin(), Math.cos() 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point.
- 45. 45A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loosing numerical precision... A bug Usually, difficult to test for the zero (use threshold or better analysis)
- 46. 46A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Loosing associativity rule Rounding & truncations to fit the standard yields the loss of associativity Better to add numbers having already the same exponent decomposition...
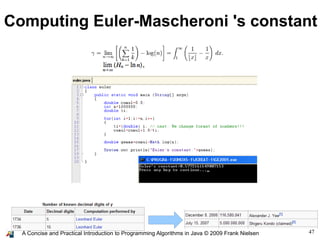
- 47. 47A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Computing Euler-Mascheroni 's constant
- 48. 48A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Types and conversions: Cast operator ● All variables and constants are typed: Math.PI is a (static) double ● Variables should be declared according to their type: double x; int i; etc ● The type of variable determines the operator and meaning: Exempla gratia, 3.0+2.1 (double) or ''Hello ''+'' INF311'' (String) ● The expression is also typed (by the compiler) ● For assignment =, the left-hand side (variable) and right-hand side (expression) should have the same type. Casting types with parenthesis (type): double x=3.14; int i=(int)x; double x=(double)i;
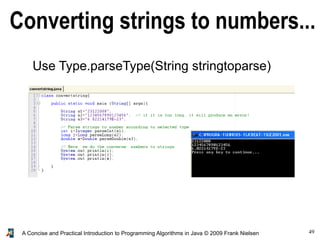
- 49. 49A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Converting strings to numbers... Use Type.parseType(String stringtoparse)
- 50. 50A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Declaring functions in Java class INF311{ public static typeF F(type1 arg1, ..., typeN argN) { // Description Block of instructions; } } ● This kind of function is also called a static method ● Functions must be defined inside classes ● A function not returning a result has type void (also known as a procedure) A glimpse at functions
- 51. 51A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen Defining the body of a function in Java class INF311{ public static typeF F(type1 arg1, ..., typeN argN) { // Description Block of instructions; } } Body of a function Body should contain an instruction return to indicate the result If branching structures are used (if or switch) , then a return should be written for all different branches. Otherwise we get a compiler error! (why? => not type safe!)
- 52. 52A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen A few examples of basic functions class FuncDecl{ public static int square(int x) {return x*x;} public static boolean isOdd(int p) {if ((p%2)==0) return false; else return true;} public static double distance(double x, double y) {if (x>y) return x-y; else return y-x;} public static void display(double x, double y) {System.out.println("("+x+","+y+")"); return; // return void } public static void main (String[] args) { display(square(2),distance(5,9)); int p=123124345; if (isOdd(p)) System.out.println("p is odd"); else System.out.println("p is even"); } }
- 53. 53A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen 53


![2A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Upper case versus Lower case
Java distinguishes between
uppercases (A..Z) and lowercases (a..z)
Unix differentiates upper/lower case filenames
class UpperLowerCase
{
public static void main (String arguments[])
{
int MyVar;
// this variable is different from MyVar
int myvar;
// Generate a syntax error at compile time:
// cannot find symbol variable myVar
System.out.println(myVar);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-2-320.jpg)
![3A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Reserved keywords
Reserved keywords in Java:
You cannot choose reserved keywordsreserved keywords for variable names:
class ReservedKeyword
{public static void main (String arg[]){
double x,y;
// Generate a syntax error:
// "not a statement"
int import;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-3-320.jpg)

![6A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
More on System.out.print[ln]
Equivalences of stream output:
System.out.print(''n'') = System.out.println('''');
System.out.print(''Hello INF311 n'') = System.out.println(''INF311'');
Priority order+casting operations...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-6-320.jpg)

![10A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Program: Data,computations + workflow
The control structures define the set of instructions being executed
(aiguillage des trains)
For example, a branching condition:
if (a<b) [then]
c=a; // Do-something-1
else
c=b; // Do-something-2
There are two potential instructions paths depending on the predicate:
● a<b, -> c=a;
or
● a>=b, -> c=b;
c is selected as
the minimum
of a and b
In Java, we do not use the word then](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-10-320.jpg)





![23A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Boolean operators for comparisons
a==b Test of equality (for basic types)
a!=b Test for difference [ equivalent to ! (a==b) ]
Inequalities:
a<b True if and only if (iff.) a<b
a<=b True iff. a<b or a=b
a>b True iff. a>b
a>=b True iff. a>b or a=b
Beware: a=b is assignment not test (test of equality is ==)
Typing helps you avoid this mistake:
int a=3;
if (a=3) System.out.println("THEN-PART");
else System.out.println("ELSE-PART");
incompatible types found : int
required: boolean](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-23-320.jpg)
![25A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
(6-2) == 4 evalutes to true but 22/7 == 3+1.0/7 evaluates to false
Boolean operators for comparisons
Boolean comparisons are of type boolean
class Boolean{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean b1 = (6-2) == 4;
boolean b2 = 22/7 == 3+1/7.0 ;
boolean b3 = 22/7 == 3+ 1/7;
System.out.println(b1); // true
System.out.println(b2); // false
System.out.println(b3); // true
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-25-320.jpg)





![37A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Loops: For... iterations
for(instruction1; boolean_condition; instruction2)
block_instruction3;
class ForLoop
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i, n=10;
int cumulLoop=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) cumulLoop+=i;
int cumul=(n*(n-1))/2; // closed-form solution
System.out.println(cumulLoop+" closed-form:"+cumul);
}
} We get 45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-37-320.jpg)

![40A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
Multiple choices: switch
Avoid nested if-else structures for multiple choices
class ProgSwitch
{public static void main(String arg[]){
System.out.print("Input a digit in [0..9]:");
int n=TC.lireInt();
switch(n)
{
case 0: System.out.println("zero"); break;
case 1: System.out.println("one"); break;
case 2: System.out.println("two"); break;
case 3: System.out.println("three"); break;
default: System.out.println("Above three!");
break;
}}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-40-320.jpg)






![52A Concise and Practical Introduction to Programming Algorithms in Java © 2009 Frank Nielsen
A few examples of basic functions
class FuncDecl{
public static int square(int x)
{return x*x;}
public static boolean isOdd(int p)
{if ((p%2)==0) return false; else return true;}
public static double distance(double x, double y)
{if (x>y) return x-y; else return y-x;}
public static void display(double x, double y)
{System.out.println("("+x+","+y+")");
return; // return void
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
display(square(2),distance(5,9));
int p=123124345;
if (isOdd(p)) System.out.println("p is odd");
else System.out.println("p is even");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingalgorithmsjava-2-140701005236-phpapp01/85/chapter-2-A-Concise-and-Practical-Introduction-to-Programming-Algorithms-in-Java-52-320.jpg)























































































