Collection Framework in Java | Generics | Input-Output in Java | Serialization | Inner Classes | Java class 4
- 1. Java Class 5 “Once a Programmer always a Programmer.” •Collection Framework in Java •Generics •Input-Output in Java •Serialization •Inner Classes
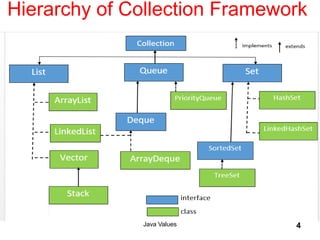
- 2. Java Values 2 Collection Framework in Java
- 3. Java Values 3 Collections in Java The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate the group of objects. Java Collections can achieve all the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion. Java Collection means a single unit of objects. Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet). Its come in java.util package.
- 4. Hierarchy of Collection Framework Java Values 4
- 5. Methods of Collection interface Java Values 5 And many more…
- 6. List Interface List interface is the child interface of Collection interface. It inhibits a list type data structure in which we can store the ordered collection of objects. It can have duplicate values. List interface is implemented by the classes ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, and Stack. To instantiate the List interface List <data-type> list1= new ArrayList(); List <data-type> list2 = new LinkedList(); List <data-type> list3 = new Vector(); List <data-type> list4 = new Stack(); Example: List <String> list = new ArrayList(); Java Values 6
- 7. ArrayList The ArrayList class implements the List interface. It uses a dynamic array to store the duplicate element of different data types. The ArrayList class maintains the insertion order and is non-synchronized. The elements stored in the ArrayList class can be randomly accessed. Java Values 7
- 8. Array List Example import java.util.*; class TestJavaCollection1{ public static void main(String args[]){ ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating arraylist list.add("Ravi");//Adding object in arraylist list.add("Vijay"); list.add("Ravi"); list.add("Ajay"); //Traversing list through Iterator Iterator itr=list.iterator(); while(itr.hasNext()){ System.out.println(itr.next()); } } } Java Values 8 Output?
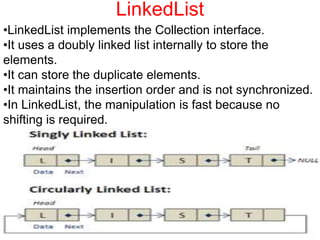
- 9. LinkedList Java Values 9 •LinkedList implements the Collection interface. •It uses a doubly linked list internally to store the elements. •It can store the duplicate elements. •It maintains the insertion order and is not synchronized. •In LinkedList, the manipulation is fast because no shifting is required.
- 10. Example import java.util.*; public class TestJavaCollection2{ public static void main(String args[]){ LinkedList<String> al=new LinkedList<String>(); al.add("Ravi"); al.add("Vijay"); al.add("Ravi"); al.add("Ajay"); Iterator<String> itr=al.iterator(); while(itr.hasNext()){ System.out.println(itr.next()); } } } Java Values 10
- 11. Vector - Stack Vector uses a dynamic array to store the data elements. It is similar to ArrayList. It’s a legacy class . Why it is legacy class? However, It is synchronized and contains many methods that are not the part of Collection framework. The stack is the subclass of Vector. It implements the last-in-first-out data structure, i.e., Stack. The stack contains all of the methods of Vector class and also provides its methods like boolean push(), boolean peek(), boolean push(object o), which defines its properties. Java Values 11
- 12. Example import java.util.*; public class TestJavaCollection4{ public static void main(String args[]){ Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); stack.push("Ayush"); stack.push("Garvit"); stack.push("Amit"); stack.push("Ashish"); stack.push("Garima"); stack.pop(); Iterator<String> itr=stack.iterator(); while(itr.hasNext()){ System.out.println(itr.next()); } } } Java Values 12 Output??
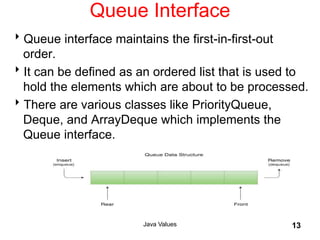
- 13. Queue Interface Queue interface maintains the first-in-first-out order. It can be defined as an ordered list that is used to hold the elements which are about to be processed. There are various classes like PriorityQueue, Deque, and ArrayDeque which implements the Queue interface. Java Values 13
- 14. Priority Queue The PriorityQueue class implements the Queue interface. It holds the elements or objects which are to be processed by their priorities. PriorityQueue doesn't allow null values to be stored in the queue. Deque: Deque interface extends the Queue interface. In Deque, we can remove and add the elements from both the side. Deque stands for a double-ended queue which enables us to perform the operations at both the ends.
- 15. ArrayDeque ArrayDeque class implements the Deque interface. It facilitates us to use the Deque. Unlike queue, we can add or delete the elements from both the ends. ArrayDeque is faster than ArrayList and Stack and has no capacity restrictions. Deque<String> deque = new ArrayDeque<String>(); deque.add("Gautam"); deque.add("Karan"); deque.add("Ajay"); for (String str : deque) { //Traversing elements System.out.println(str); } } Java Values 15 Output?
- 16. Set Interface Set Interface in Java is present in java.util package. It extends the Collection interface. It represents the unordered set of elements which doesn't allow us to store the duplicate items. We can store at most one null value in Set. Set is implemented by HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet. Java Values 16
- 17. HashSet class implements Set Interface. It represents the collection that uses a hash table for storage. Hashing is used to store the elements in the HashSet. It contains unique items. LinkedHashSet class represents the LinkedList implementation of Set Interface. It extends the HashSet class and implements Set interface. Like HashSet, It also contains unique elements. It maintains the insertion order and permits null elements. SortedSet is the alternate of Set interface that provides a total ordering on its elements. The elements of the SortedSet are arranged in the increasing (ascending) order. The SortedSet provides the additional methods that inhibit the natural ordering of the elements. Java Values 17
- 18. Java TreeSet class implements the Set interface that uses a tree for storage. Like HashSet, TreeSet also contains unique elements. However, the access and retrieval time of TreeSet is quite fast. The elements in TreeSet stored in ascending order. public void setexample(){ // same way we can used HashSet()<>, LinkedHashSet()<> TreeSet<String> set=new TreeSet<String>(); set.add("Ravi"); set.add("Vijay"); set.add("Ravi"); set.add("Ajay"); //traversing elements Iterator<String> itr=set.iterator(); while(itr.hasNext()){ System.out.println(itr.next()); } } Java Values 18
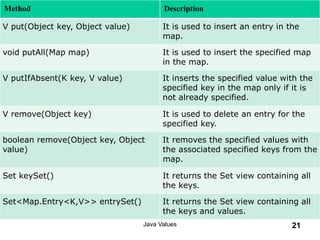
- 19. Java Map Interface A map contains values on the basis of key, i.e. key-value pair. Each key and value pair is known as an entry. A Map contains unique keys. A Map is useful if you have to search, update or delete elements on the basis of a key. Java Values 19
- 20. Java Values 20 Class Description HashMap HashMap is the implementation of Map, but it doesn't maintain any order. LinkedHashMap LinkedHashMap is the implementation of Map. It inherits HashMap class. It maintains insertion order. TreeMap TreeMap is the implementation of Map and SortedMap. It maintains ascending order. •A Map doesn't allow duplicate keys, but you can have duplicate values. •A Map can't be traversed, so you need to convert it into Set using keySet() or entrySet() method.
- 21. Method Description V put(Object key, Object value) It is used to insert an entry in the map. void putAll(Map map) It is used to insert the specified map in the map. V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) It inserts the specified value with the specified key in the map only if it is not already specified. V remove(Object key) It is used to delete an entry for the specified key. boolean remove(Object key, Object value) It removes the specified values with the associated specified keys from the map. Set keySet() It returns the Set view containing all the keys. Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() It returns the Set view containing all the keys and values. Java Values 21
- 22. Example of Map Public void MapExample(){ Map map=new HashMap(); //Adding elements to map map.put(1,"Amit"); map.put(5,"Rahul"); map.put(2,"Jai"); map.put(6,"Amit"); //Traversing Map Set set=map.entrySet();//Converting to Set so that we can traverse Iterator itr=set.iterator(); while(itr.hasNext()){ //Converting to Map.Entry so that we can get key and value separately Map.Entry entry=(Map.Entry)itr.next(); System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue()); } Java Values 22 Output?
- 23. Java Values 23
- 24. Java Values 24
- 25. Sorting collections using utility methods Example :Collections.sort(); equals () and hash Code contract in Java collections object value and there reference Overriding equals and hash Code methods in Java. To get the value which is save in hashmap or tree map. hashCode() It returns the hashcode value as an Integer. Hashcode value is mostly used in hashing based collections like HashMap, HashSet, HashTable….etc. This method must be overridden in every class which overrides equals() method. Java Values 25
- 26. Java Values 26
- 27. Java Values 27 Java Values.com •The Java Generics programming is introduced in J2SE 5 to deal with type-safe objects. •It makes the code stable by detecting the bugs at compile time. •Before generics, we can store any type of objects in the collection, i.e., non-generic. •Now generics force the java programmer to store a specific type of objects. •There are mainly 3 advantages of generics. They are as follows: 1. Type-safety 2. Type casting is not required 3. Compile-Time Checking
- 28. Wildcard in Java Generics Java Values 28 •The ? (question mark) symbol represents the wildcard element. It means any type. •If we write <? extends Number>, it means any child class of Number, e.g., Integer, Float, and double. •Now we can call the method of Number class through any child class object. •We can use a wildcard as a type of a parameter, field, return type, or local variable. •However, it is not allowed to use a wildcard as a type argument for a generic method invocation, a generic class instance creation, or a supertype.
- 29. import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class LowerBoundWildcard { public static void addNumbers(List<? super Integer> list) { for(Object n:list) { System.out.println(n); } } public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> l1=Arrays.asList(1,2,3); System.out.println("displaying the Integer values"); addNumbers(l1); List<Number> l2=Arrays.asList(1.0,2.0,3.0); System.out.println("displaying the Number values"); addNumbers(l2); } } Java Values 29 Output?
- 30. Serialization and Deserialization Serialization in Java is a mechanism of writing the state of an object into a byte-stream. It is mainly used in Hibernate, RMI, JPA, EJB and JMS technologies. The reverse operation of serialization is called deserialization where byte-stream is converted into an object. The serialization and deserialization process is platform- independent, it means you can serialize an object in a platform and deserialize in different platform. For serializing the object, we call the writeObject() method ObjectOutputStream, and for deserialization we call the readObject() method of ObjectInputStream class. Java Values 30
- 32. Java Values 32 import java.io.*; class Persist{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ Student s1 =new Student(211,"ravi"); //Creating the object FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream("f.txt"); //Creating stream and writing the object ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(fout); out.writeObject(s1); out.flush(); //closing the stream out.close(); System.out.println("success"); }catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);} } } import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable{ int id; String name; public Student(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } } Output?
- 33. Java Values 33 import java.io.*; class Depersist{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ //Creating stream to read the object ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("f.txt")); Student s=(Student)in.readObject(); //printing the data of the serialized object System.out.println(s.id+" "+s.name); //closing the stream in.close(); }catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);} } } import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable{ int id; String name; public Student(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } } Output?
- 34. Inner Classes Inner Classes Local Classes Anonymous Classes Static Nested Classes Java Values 34
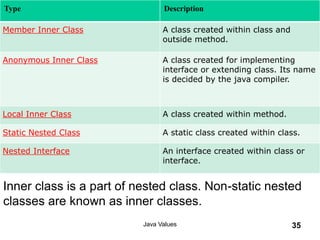
- 35. Type Description Member Inner Class A class created within class and outside method. Anonymous Inner Class A class created for implementing interface or extending class. Its name is decided by the java compiler. Local Inner Class A class created within method. Static Nested Class A static class created within class. Nested Interface An interface created within class or interface. Java Values 35 Inner class is a part of nested class. Non-static nested classes are known as inner classes.
- 36. Advantage of java inner classes There are basically three advantages of inner classes in java. They are as follows: 1) Nested classes represent a special type of relationship that is it can access all the members (data members and methods) of outer class including private. 2) Nested classes are used to develop more readable and maintainable code because it logically group classes and interfaces in one place only. 3) Code Optimization: It requires less code to write. Java Values 36
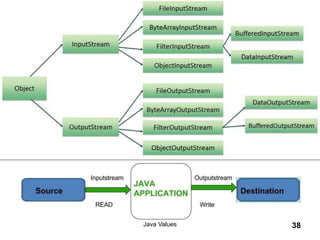
- 37. JAVA Input Output The Stream is a sequence of Bytes. Output Stream: Writing Data to a Stream. Input Stream: Reading Data from a Stream. If a stream has a buffer in memory then it is Buffered Stream. Character stream have character data and are used for storing and retrieving the text. Java Values 37
- 38. Java Values 38
- 39. There are four types of abstract Streams class 1. Reader: Read Character 2. Writer: Write Character 3. InputStream: A stream to read binary data. 4. OutputStream: A Stream to write binary data. Generally we are using BufferedInputStream, BufferedOutputStream, BufferedReader and BufferedWriter for better performance of Buffered I/O Classes. Java Values 39
- 40. Byte Stream Classes Java Values 40
- 41. Character Stream I/O Classes Java Values 41
- 42. InputStream Used to read binary data. FileInputStream enables easy reading from a file. BufferInputStream provides data buffering . InputStream class has three read method overloads. 1. public abstract int read(int b1) 2. public int read(byte[] data) 3. public int read(byte[] data, int offset, int length) Where the offset stands for the first bytes should be placed. Java Values 42
- 43. The Predefined Streams Java programs automatically import the java.lang package. This package defines a class calledSystem, which encapsulates several aspects of the run-time environment. System also contains three predefined stream variables: in, out, and err. These fields are declared as public, static, and final within System. This means that they can be used by any other part of your program and without reference to a specific System object. System.in is an object of type InputStream; System.out and System.err are objects of type PrintStream. These are byte streams, even though they typically are used to read and write characters from and to the console. Java Values 43
- 44. File File object is used to obtain or manipulate the information associated with a disk file such as permission, time, date and directory path. File object can refer to either file or directory. File f1 = new File(“mcaii.txt”); File f1 = new File(“c:mcaii.txt”); Files are stored in binary form. The following constructors can be used to create File objects: File(String directoryPath) File(String directoryPath, String filename) File(File dirObj, String filename) File(URI uriObj) Java Values 44
- 45. FileInputStream The FileInputStream class creates an InputStream that you can use to read bytes from a file. Its two most common constructors are shown here: FileInputStream(String filepath) FileInputStream(File fileObj) FileOutputStream FileOutputStream creates an OutputStream that you can use to write bytes to a file. Its most commonly used constructors are shown here: FileOutputStream(String filePath) FileOutputStream(File fileObj) FileOutputStream(String filePath, boolean append) FileOutputStream(File fileObj, boolean append) Java Values 45
- 46. The PrintWriter Class PrintWriter is one of the character-based classes. Using a character-based class for console output makes it easier to internationalize your program. PrintWriter defines several constructors. The one we will use is shown here: PrintWriter(OutputStream outputStream, boolean flushOnNewline) Here, outputStream is an object of type OutputStream, and flushOnNewline controls whether Java flushes the output stream every time a println( ) method is called. PrintWriter supports the print( ) and println( ) methods for all types including Object. Java Values 46
- 47. The following application illustrates using a PrintWriter to handle console output // Demonstrate PrintWriter import java.io.*; public class PrintWriterDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(System.out, true); pw.println("This is a string"); int i = -7; pw.println(i); double d = 4.5e-7; pw.println(d); } } Java Values 47
- 48. Reading and Writing Files Two of the most often-used stream classes are FileInputStream and FileOutputStream, which create byte streams linked to files. To open a file, you simply create an object of one of these classes, specifying the name of the file as an argument to the constructor. The following are the forms that we will be using: FileInputStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException FileOutputStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException DataOutputStream and DataInputStream DataOutputStream and DataInputStream enable you to write or read primitive data to or from a stream. They implement the DataOutput and DataInput interfaces, respectively. Java Values 48
- 49. Summary Collection Framework in Java The Collections Framework - Set Interface- List Interface - Map Interface - Queue Interface -Sorting collections using utility methods equals () and hash Code contract in Java collections Overriding equals and hash Code methods in Java Generics Generics for Collections, class and methods Input-Output in Java What is a stream? ,Bytes vs. Characters, Java IO API ,Reading a file; writing to a file using various APIs Reading User input from console , PrintWriter Class Serialization Object Serialization , Serializable Interface , De-Serializable Inner Classes Inner Classes ,Member Classes, Local Classes, Anonymous Classes, Static Nested Classes Java Values 49
- 50. Java Values 50 Thank you !!! If you like my training session please feel free to give me star in my git-hub account !!! https://github.com/eewsagar







![Array List Example
import java.util.*;
class TestJavaCollection1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Ravi");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Vijay");
list.add("Ravi");
list.add("Ajay");
//Traversing list through Iterator
Iterator itr=list.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
Java Values 8
Output?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-8-320.jpg)
![Example
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection2{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<String> al=new LinkedList<String>();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Ajay");
Iterator<String> itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
Java Values 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-10-320.jpg)

![Example
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection4{
public static void main(String args[]){
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
stack.push("Ayush");
stack.push("Garvit");
stack.push("Amit");
stack.push("Ashish");
stack.push("Garima");
stack.pop();
Iterator<String> itr=stack.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
Java Values 12
Output??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-12-320.jpg)














![import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class LowerBoundWildcard {
public static void addNumbers(List<? super Integer> list) {
for(Object n:list)
{
System.out.println(n);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> l1=Arrays.asList(1,2,3);
System.out.println("displaying the Integer values");
addNumbers(l1);
List<Number> l2=Arrays.asList(1.0,2.0,3.0);
System.out.println("displaying the Number values");
addNumbers(l2);
}
}
Java Values 29
Output?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-29-320.jpg)


![Java Values 32
import java.io.*;
class Persist{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
Student s1 =new Student(211,"ravi"); //Creating the object
FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream("f.txt"); //Creating stream and writing the object
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(fout);
out.writeObject(s1);
out.flush(); //closing the stream
out.close();
System.out.println("success");
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable{
int id;
String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
Output?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-32-320.jpg)
![Java Values 33
import java.io.*;
class Depersist{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
//Creating stream to read the object
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("f.txt"));
Student s=(Student)in.readObject();
//printing the data of the serialized object
System.out.println(s.id+" "+s.name);
//closing the stream
in.close();
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable{
int id;
String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
Output?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-33-320.jpg)






![InputStream
Used to read binary data.
FileInputStream enables easy reading from a
file.
BufferInputStream provides data buffering .
InputStream class has three read method overloads.
1. public abstract int read(int b1)
2. public int read(byte[] data)
3. public int read(byte[] data, int offset, int length)
Where the offset stands for the first bytes should be
placed.
Java Values 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-42-320.jpg)




![ The following application illustrates using a PrintWriter to
handle console output
// Demonstrate PrintWriter
import java.io.*;
public class PrintWriterDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(System.out, true);
pw.println("This is a string");
int i = -7;
pw.println(i);
double d = 4.5e-7;
pw.println(d);
}
}
Java Values 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaclass4-200719123024/85/Collection-Framework-in-Java-Generics-Input-Output-in-Java-Serialization-Inner-Classes-Java-class-4-47-320.jpg)









































![Java Collection Interview Questions [Updated]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/javacollectioninterviewquestions-220601125432-4167b0b1-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






































