Computer programming - variables constants operators expressions and statements
Download as pptx, pdf1 like889 views
The document discusses key concepts in C programming including variables, constants, operators, expressions, and statements. It defines variables as identifiers that store values, and constants as fixed values that cannot be changed. Common data types are described along with type modifiers. Local and global variables as well as formal parameters are explained. Arithmetic, relational, and logical operators are classified. Expressions are defined as combinations of operators, constants, and variables that evaluate to a value. Operator precedence is also covered. Examples are provided to illustrate various concepts.
1 of 37
Downloaded 13 times




































Ad
Recommended
OOP concepts -in-Python programming language
OOP concepts -in-Python programming languageSmritiSharma901052 The document discusses object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in Python. It defines OOP, classes, objects, attributes, methods, inheritance, and polymorphism. Key points include:
- OOP uses classes as templates for objects with identities, states, and behaviors.
- Classes define attributes and methods. Objects are instances of classes.
- Inheritance allows classes to inherit attributes and methods from parent classes. There are different types of inheritance.
- Polymorphism means the same message can be displayed in different forms. Abstraction and encapsulation hide unnecessary details from users.
1. importance of c
1. importance of cAlamgir Hossain The document discusses the importance of the C programming language for computer science graduates, highlighting potential job fields and notable software companies in Bangladesh. It outlines the advantages of C, such as its status as a middle-level language, speed of execution, and its relevance in embedded programming. Additionally, it emphasizes C's structured programming capabilities and suggests software for C programming development.
Introduction to Basic C programming 01
Introduction to Basic C programming 01Wingston Here is a C program to produce a spiral array as described in the task:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int n = 5;
int arr[n][n];
int num = 1;
int rowBegin = 0;
int rowEnd = n-1;
int colBegin = 0;
int colEnd = n-1;
while(rowBegin <= rowEnd && colBegin <= colEnd) {
// Top row
for(int i=colBegin; i<=colEnd; i++) {
arr[rowBegin][i] = num++;
}
rowBegin++;
// Right column
for(int i=rowBegin;
Vb6.0 Introduction
Vb6.0 IntroductionTennyson Visual Basic (VB) is a programming language and development environment created by Microsoft for building graphical user interface (GUI) applications. It uses an event-driven programming model and is ideal for rapid application development (RAD). Some key points about VB include that it has a large user base, enables access to databases, and allows building of Windows applications using pre-built components in an easy-to-understand syntax.
Programming Fundamental Presentation
Programming Fundamental Presentationfazli khaliq The document provides an introduction to C and C++ programming languages, highlighting their characteristics and features. C is described as a powerful, high-level language developed in 1972, suitable for various programming tasks, while C++ is an object-oriented extension of C developed in 1982, featuring clearer syntax and richer library functions. Both languages support user-defined data types and allow for efficient programming.
Character Attribute in computer graphics
Character Attribute in computer graphicsHariTharshiniBscIT1 Character attributes such as font, size, color, and orientation can be set for entire text strings or individual characters. Text attributes include font style, underlining, bolding, italics, and color. Character size is specified in points, while height is the distance from the baseline to capline. Text size, width, spacing, path, alignment, precision and marker symbols can all be customized through PHIGS functions that set attribute parameters like font, color index, character height, expansion factor, spacing, up vector, horizontal and vertical alignment, and precision. Marker types include dots, crosses, circles and more that can be displayed in different sizes and colors.
visual basic v6 introduction
visual basic v6 introductionbloodyedge03 Visual Basic is a tool for developing Windows GUI applications. It is event-driven, meaning code only runs in response to events like button clicks. Developers draw the user interface, assign control properties, and attach code to events. The interface has modes for design, running, and debugging applications. Key windows include the form, toolbox, properties, and code editor. Variables follow naming conventions and have different scopes depending on where they are declared.
Programming flowcharts for C Language
Programming flowcharts for C LanguageAryan Ajmer The document discusses flowcharts, which are graphical representations of algorithms and programming logic. It provides examples of common flowchart symbols like terminals, inputs/outputs, processes, decisions, and connectors. It also outlines the typical steps for programming practices and techniques, which include defining requirements, creating a flowchart, dry running the flowchart to check for errors, writing source code, debugging, and documentation. Finally, it provides examples of flowcharts for simple programs like printing a message, calculating the sum of two numbers, and checking if a number is even or odd.
8 Array
8 ArrayKwan Lee The document covers programming methods related to arrays, detailing their definition, characteristics, and how to declare, assign values, and process them, including two-dimensional and higher-dimensional arrays. It explains the concept of partially filled arrays and provides examples such as input/output operations, looping through arrays, and calculating gross pay for employees. Additionally, the document includes pseudocode, flowcharts, and alerts about common errors like off-by-one errors in array indexing.
Basic elements of java
Basic elements of java Ahmad Idrees Chapter 2 covers the fundamental components of a Java program, including methods, symbols, identifiers, primitive data types, and arithmetic operators. It discusses program structure, input and output operations, the importance of classes and methods, and good programming style. The chapter concludes with examples demonstrating the creation of Java applications and the essential concepts needed for successful programming.
Clipping
ClippingMohd Arif Clipping is a technique that identifies parts of an image that are inside or outside a defined clipping region or window. There are different types of clipping including point, line, polygon, curve, and text clipping. The Cohen-Sutherland algorithm is commonly used for line clipping. It assigns 4-bit codes to line endpoints to determine if they are fully inside, outside, or intersect the clipping window boundary. Intersecting line segments are then subdivided and clipped. Midpoint subdivision is another algorithm that divides partially visible lines at their midpoint into shorter segments.
Procedural vs. object oriented programming
Procedural vs. object oriented programmingHaris Bin Zahid The document discusses the differences between procedural-oriented programming (POP) and object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting how OOP allows for better code reuse, data hiding, and easier updates. It provides real-world examples illustrating how adding or modifying features can be simpler in OOP through class inheritance and method updates. The document emphasizes that OOP helps create reliable, reusable, and extensible software systems by organizing code into classes and objects with defined characteristics, responsibilities, and relationships.
Datatypes in python
Datatypes in pythoneShikshak The document discusses various Python datatypes. It explains that Python supports built-in and user-defined datatypes. The main built-in datatypes are None, numeric, sequence, set and mapping types. Numeric types include int, float and complex. Common sequence types are str, bytes, list, tuple and range. Sets can be created using set and frozenset datatypes. Mapping types represent a group of key-value pairs like dictionaries.
Introduction to Algorithm
Introduction to AlgorithmChristopherEsteban2 The document discusses the fundamentals of algorithms and flowcharting, defining algorithms as logical procedures to solve problems and emphasizing pseudocode as a language-independent method for outlining algorithms. It details the steps for creating an extension cord and explains the function of flowcharts as graphical representations of algorithms using specific symbols. Additionally, it provides references for further reading on these concepts.
Presentation on C++ Programming Language
Presentation on C++ Programming Languagesatvirsandhu9 This document provides an overview of the C++ programming language. It discusses why C++ is used, how it compares to Fortran, and the basic structure and components of a C++ program. The key topics covered include data types, variables, operators, selection statements, iteration statements, functions, arrays, pointers, input/output, preprocessor instructions, and comments. The document is intended to teach the basics of C++ programming in a structured way over multiple sections.
Function overloading ppt
Function overloading pptProf. Dr. K. Adisesha This document discusses function overloading, inline functions, and friend functions in C++. It defines function overloading as having two or more functions with the same name but different parameters, allowing for compile-time polymorphism. Inline functions have their body inserted at call sites for faster execution. Friend functions are non-member functions that have access to private members of a class. Examples are provided to demonstrate overloaded functions, inline functions checking for prime numbers, and using a friend function to check if a number is even or odd. Important concepts and questions for discussion are also outlined.
Python programming : Classes objects
Python programming : Classes objectsEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd The document explains the concept of classes and objects in programming, detailing the structure of classes, including attributes and methods. It illustrates constructors, instance variables, class variables, and various types of methods like instance, class, and static methods, as well as the concept of namespaces. Additionally, it introduces the idea of inner classes and shows examples of how to implement them in code.
JAVA-PPT'S.pptx
JAVA-PPT'S.pptxRaazIndia The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts and Java programming. It discusses key OOP concepts like abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism and classes. It then covers the history and development of Java, describing how it was initially created at Sun Microsystems to develop software for consumer electronics but was later targeted towards internet programming. The document also lists some of Java's key characteristics like being simple, secure, portable, object-oriented, robust and multithreaded.
PROCEDURAL ORIENTED PROGRAMMING VS OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMING
PROCEDURAL ORIENTED PROGRAMMING VS OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMING Uttam Singh This document compares procedure-oriented programming and object-oriented programming. Procedure-oriented programming divides programs into functions, uses global data, and does not support overloading or access specifiers. Object-oriented programming divides programs into objects, supports access specifiers like public and private, allows overloading, and hides data to provide more security. The document provides examples of how object-oriented programming makes it easier to add new classes and update existing classes compared to procedure-oriented programming.
Software Engineering
Software EngineeringUMA PARAMESWARI The document discusses software development lifecycles and strategies. It describes:
1) Common lifecycle activities like planning, development, testing and maintenance. Different models can be used depending on the product.
2) Solution strategies are developed to determine the nature of possible solutions and provide a framework for design and implementation. The best strategies are developed by trained groups using techniques like brainstorming.
3) The phased lifecycle model involves a series of defined activities with inputs, processes, and outputs at each phase. Resources are required to complete each defined phase.
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
Introduction to Object Oriented ProgrammingMoutaz Haddara This document provides an introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), outlining its history and core concepts such as classes and objects. It discusses the evolution of programming languages from machine languages to high-level languages like OOP languages which focus on modeling data. Key principles of OOP include encapsulation, inheritance, abstraction, and polymorphism, showcasing the advantages and disadvantages of this programming paradigm.
Date and Time Module in Python | Edureka
Date and Time Module in Python | EdurekaEdureka! The document provides an overview of Python's time and datetime modules, detailing various built-in functions and their descriptions. Key functions include time(), ctime(), sleep(), and datetime constructors like datetime.today() and datetime.now(). It also outlines attributes of the struct_time class and the utilization of timedelta for calculating differences between dates or times.
Abstract class in c++
Abstract class in c++Sujan Mia This document discusses abstract classes in C++. It defines an abstract class as a class designed to be used as a base class that cannot be instantiated and must contain at least one pure virtual function. It provides an example of how to declare an abstract class with a pure virtual function and how to derive a class from an abstract class, overriding the pure virtual functions. The importance of abstract classes is that they allow common functionality to be defined for derived classes while leaving implementation details to the derived classes.
Algorithm and flowchart
Algorithm and flowchartElizabeth de Leon Aler This document introduces algorithms and the process of program development. It defines an algorithm as a precise list of instructions that terminates after a finite number of steps to solve a problem. It discusses methods of specifying algorithms like pseudocode and flowcharts. Properties of algorithms include being finite, unambiguous, and having a defined sequence of execution and input/output. The steps of program development are stated as understanding the problem, planning instructions, coding the program, running and debugging it. Flowcharting guidelines and common symbols are provided. Sample exercises demonstrate writing programs to calculate simple formulas.
Identifiers
Identifiers Then Murugeshwari An identifier is a name given to variables, objects, and methods in Java. Identifiers must start with a letter, underscore (_), or dollar sign ($) and can include numbers but cannot be a Java keyword. Common conventions are to use lowercase names for variables and methods with uppercase names for constants. The document provides examples of valid and invalid Java identifiers.
Dart ppt
Dart pptKrishna Teja Dart is an object-oriented programming language developed by Google that can be used to build web, server, and mobile applications. Some key points about Dart include:
- It is influenced by languages like Smalltalk, JavaScript, Java and C#
- Dart was first released in 2013 and the latest version is 2.2 from 2019
- It supports concepts like classes, libraries, functions and operators
- Dart can be used to create single page web apps and has been used by Google for apps like Gmail and Google Maps
CSS L07 - Preparing the Installer
CSS L07 - Preparing the InstallerMarvin Bronoso The document provides a detailed guide on creating bootable USB drives for installing operating systems, including Windows and Linux. It outlines the necessary software and procedures for both legacy BIOS and UEFI motherboards, detailing steps to prepare the USB drive, select the appropriate options, and boot from the drive. Additionally, it lists various programs like Rufus and UNetbootin that can be used to create bootable USBs, specifying their features and suitable use cases.
struct and class deferences
struct and class deferencesNaseer Khan Noor Structures are collections of variables of different data types, while classes can also contain functions. The main differences are: structures have public access by default, are used for small data groups, and objects are stored on the stack. Classes have private access by default, are used for larger amounts of data with abstraction and inheritance, and objects are stored on the heap. Both allow variables, functions, constructors/destructors, and inheritance, but classes provide more robust features for object-oriented programming.
Introduction to c
Introduction to cAjeet Kumar The document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses the fundamentals of C including data types, variables, operators, control structures, arrays, functions, pointers, structures, unions, and file handling. The three key modules covered are: 1) C fundamentals, 2) arrays, functions, and strings, and 3) pointers, structures, unions, and file handling.
CSE 1201: Structured Programming Language
CSE 1201: Structured Programming LanguageZubayer Farazi This document provides an overview of the Structured Programming Language course offered at Notre Dame University in Bangladesh. The course covers topics such as programming language definition, the history of the C programming language, flow charts, pseudo code, control structures, decision making, operators, data types, variables, constants, and identifiers. It is presented by Stein Joachim Rebeiro, Zubayer Farazi, and Raisa Fabiha for Professor Abul Hasnat Md. Saiful Islam's Computer Science department.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
8 Array
8 ArrayKwan Lee The document covers programming methods related to arrays, detailing their definition, characteristics, and how to declare, assign values, and process them, including two-dimensional and higher-dimensional arrays. It explains the concept of partially filled arrays and provides examples such as input/output operations, looping through arrays, and calculating gross pay for employees. Additionally, the document includes pseudocode, flowcharts, and alerts about common errors like off-by-one errors in array indexing.
Basic elements of java
Basic elements of java Ahmad Idrees Chapter 2 covers the fundamental components of a Java program, including methods, symbols, identifiers, primitive data types, and arithmetic operators. It discusses program structure, input and output operations, the importance of classes and methods, and good programming style. The chapter concludes with examples demonstrating the creation of Java applications and the essential concepts needed for successful programming.
Clipping
ClippingMohd Arif Clipping is a technique that identifies parts of an image that are inside or outside a defined clipping region or window. There are different types of clipping including point, line, polygon, curve, and text clipping. The Cohen-Sutherland algorithm is commonly used for line clipping. It assigns 4-bit codes to line endpoints to determine if they are fully inside, outside, or intersect the clipping window boundary. Intersecting line segments are then subdivided and clipped. Midpoint subdivision is another algorithm that divides partially visible lines at their midpoint into shorter segments.
Procedural vs. object oriented programming
Procedural vs. object oriented programmingHaris Bin Zahid The document discusses the differences between procedural-oriented programming (POP) and object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting how OOP allows for better code reuse, data hiding, and easier updates. It provides real-world examples illustrating how adding or modifying features can be simpler in OOP through class inheritance and method updates. The document emphasizes that OOP helps create reliable, reusable, and extensible software systems by organizing code into classes and objects with defined characteristics, responsibilities, and relationships.
Datatypes in python
Datatypes in pythoneShikshak The document discusses various Python datatypes. It explains that Python supports built-in and user-defined datatypes. The main built-in datatypes are None, numeric, sequence, set and mapping types. Numeric types include int, float and complex. Common sequence types are str, bytes, list, tuple and range. Sets can be created using set and frozenset datatypes. Mapping types represent a group of key-value pairs like dictionaries.
Introduction to Algorithm
Introduction to AlgorithmChristopherEsteban2 The document discusses the fundamentals of algorithms and flowcharting, defining algorithms as logical procedures to solve problems and emphasizing pseudocode as a language-independent method for outlining algorithms. It details the steps for creating an extension cord and explains the function of flowcharts as graphical representations of algorithms using specific symbols. Additionally, it provides references for further reading on these concepts.
Presentation on C++ Programming Language
Presentation on C++ Programming Languagesatvirsandhu9 This document provides an overview of the C++ programming language. It discusses why C++ is used, how it compares to Fortran, and the basic structure and components of a C++ program. The key topics covered include data types, variables, operators, selection statements, iteration statements, functions, arrays, pointers, input/output, preprocessor instructions, and comments. The document is intended to teach the basics of C++ programming in a structured way over multiple sections.
Function overloading ppt
Function overloading pptProf. Dr. K. Adisesha This document discusses function overloading, inline functions, and friend functions in C++. It defines function overloading as having two or more functions with the same name but different parameters, allowing for compile-time polymorphism. Inline functions have their body inserted at call sites for faster execution. Friend functions are non-member functions that have access to private members of a class. Examples are provided to demonstrate overloaded functions, inline functions checking for prime numbers, and using a friend function to check if a number is even or odd. Important concepts and questions for discussion are also outlined.
Python programming : Classes objects
Python programming : Classes objectsEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd The document explains the concept of classes and objects in programming, detailing the structure of classes, including attributes and methods. It illustrates constructors, instance variables, class variables, and various types of methods like instance, class, and static methods, as well as the concept of namespaces. Additionally, it introduces the idea of inner classes and shows examples of how to implement them in code.
JAVA-PPT'S.pptx
JAVA-PPT'S.pptxRaazIndia The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts and Java programming. It discusses key OOP concepts like abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism and classes. It then covers the history and development of Java, describing how it was initially created at Sun Microsystems to develop software for consumer electronics but was later targeted towards internet programming. The document also lists some of Java's key characteristics like being simple, secure, portable, object-oriented, robust and multithreaded.
PROCEDURAL ORIENTED PROGRAMMING VS OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMING
PROCEDURAL ORIENTED PROGRAMMING VS OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMING Uttam Singh This document compares procedure-oriented programming and object-oriented programming. Procedure-oriented programming divides programs into functions, uses global data, and does not support overloading or access specifiers. Object-oriented programming divides programs into objects, supports access specifiers like public and private, allows overloading, and hides data to provide more security. The document provides examples of how object-oriented programming makes it easier to add new classes and update existing classes compared to procedure-oriented programming.
Software Engineering
Software EngineeringUMA PARAMESWARI The document discusses software development lifecycles and strategies. It describes:
1) Common lifecycle activities like planning, development, testing and maintenance. Different models can be used depending on the product.
2) Solution strategies are developed to determine the nature of possible solutions and provide a framework for design and implementation. The best strategies are developed by trained groups using techniques like brainstorming.
3) The phased lifecycle model involves a series of defined activities with inputs, processes, and outputs at each phase. Resources are required to complete each defined phase.
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
Introduction to Object Oriented ProgrammingMoutaz Haddara This document provides an introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), outlining its history and core concepts such as classes and objects. It discusses the evolution of programming languages from machine languages to high-level languages like OOP languages which focus on modeling data. Key principles of OOP include encapsulation, inheritance, abstraction, and polymorphism, showcasing the advantages and disadvantages of this programming paradigm.
Date and Time Module in Python | Edureka
Date and Time Module in Python | EdurekaEdureka! The document provides an overview of Python's time and datetime modules, detailing various built-in functions and their descriptions. Key functions include time(), ctime(), sleep(), and datetime constructors like datetime.today() and datetime.now(). It also outlines attributes of the struct_time class and the utilization of timedelta for calculating differences between dates or times.
Abstract class in c++
Abstract class in c++Sujan Mia This document discusses abstract classes in C++. It defines an abstract class as a class designed to be used as a base class that cannot be instantiated and must contain at least one pure virtual function. It provides an example of how to declare an abstract class with a pure virtual function and how to derive a class from an abstract class, overriding the pure virtual functions. The importance of abstract classes is that they allow common functionality to be defined for derived classes while leaving implementation details to the derived classes.
Algorithm and flowchart
Algorithm and flowchartElizabeth de Leon Aler This document introduces algorithms and the process of program development. It defines an algorithm as a precise list of instructions that terminates after a finite number of steps to solve a problem. It discusses methods of specifying algorithms like pseudocode and flowcharts. Properties of algorithms include being finite, unambiguous, and having a defined sequence of execution and input/output. The steps of program development are stated as understanding the problem, planning instructions, coding the program, running and debugging it. Flowcharting guidelines and common symbols are provided. Sample exercises demonstrate writing programs to calculate simple formulas.
Identifiers
Identifiers Then Murugeshwari An identifier is a name given to variables, objects, and methods in Java. Identifiers must start with a letter, underscore (_), or dollar sign ($) and can include numbers but cannot be a Java keyword. Common conventions are to use lowercase names for variables and methods with uppercase names for constants. The document provides examples of valid and invalid Java identifiers.
Dart ppt
Dart pptKrishna Teja Dart is an object-oriented programming language developed by Google that can be used to build web, server, and mobile applications. Some key points about Dart include:
- It is influenced by languages like Smalltalk, JavaScript, Java and C#
- Dart was first released in 2013 and the latest version is 2.2 from 2019
- It supports concepts like classes, libraries, functions and operators
- Dart can be used to create single page web apps and has been used by Google for apps like Gmail and Google Maps
CSS L07 - Preparing the Installer
CSS L07 - Preparing the InstallerMarvin Bronoso The document provides a detailed guide on creating bootable USB drives for installing operating systems, including Windows and Linux. It outlines the necessary software and procedures for both legacy BIOS and UEFI motherboards, detailing steps to prepare the USB drive, select the appropriate options, and boot from the drive. Additionally, it lists various programs like Rufus and UNetbootin that can be used to create bootable USBs, specifying their features and suitable use cases.
struct and class deferences
struct and class deferencesNaseer Khan Noor Structures are collections of variables of different data types, while classes can also contain functions. The main differences are: structures have public access by default, are used for small data groups, and objects are stored on the stack. Classes have private access by default, are used for larger amounts of data with abstraction and inheritance, and objects are stored on the heap. Both allow variables, functions, constructors/destructors, and inheritance, but classes provide more robust features for object-oriented programming.
Similar to Computer programming - variables constants operators expressions and statements (20)
Introduction to c
Introduction to cAjeet Kumar The document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses the fundamentals of C including data types, variables, operators, control structures, arrays, functions, pointers, structures, unions, and file handling. The three key modules covered are: 1) C fundamentals, 2) arrays, functions, and strings, and 3) pointers, structures, unions, and file handling.
CSE 1201: Structured Programming Language
CSE 1201: Structured Programming LanguageZubayer Farazi This document provides an overview of the Structured Programming Language course offered at Notre Dame University in Bangladesh. The course covers topics such as programming language definition, the history of the C programming language, flow charts, pseudo code, control structures, decision making, operators, data types, variables, constants, and identifiers. It is presented by Stein Joachim Rebeiro, Zubayer Farazi, and Raisa Fabiha for Professor Abul Hasnat Md. Saiful Islam's Computer Science department.
Introduction to c
Introduction to csunila tharagaturi C is a procedural programming language developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs, characterized by its simplicity, speed, and modularity. The document outlines the structure of a C program, including key components such as variables, data types, operators, control structures, and functions, with examples illustrating each aspect. It provides detailed explanations on how to write, compile, and execute C programs, along with information on constants, keywords, identifiers, and various types of operators.
Basic concept of c++
Basic concept of c++shashikant pabari The document provides an overview of basic object-oriented programming concepts, particularly in C and C++, covering identifiers, constants, variables, operators, type casting, enumerated data types, and control structures. It includes rules for naming identifiers, types of constants, variable declaration, various operators (arithmetic, relational, logical), and control structures like loops and selection statements. The content serves as an introductory guide for understanding programming fundamentals and the syntax used in C/C++.
Esoft Metro Campus - Programming with C++
Esoft Metro Campus - Programming with C++Rasan Samarasinghe The document is a comprehensive guide to programming in C++, covering fundamental concepts such as language overview, syntax, variables, operators, control constructs, functions, arrays, and strings. It also details practical elements like C++ program structure, compilation, and execution procedures. In addition, it includes examples and explanations about various topics, making it a valuable resource for learning C++ programming.
BCP_u2.pptxBCP_u2.pptxBCP_u2.pptxBCP_u2.pptx
BCP_u2.pptxBCP_u2.pptxBCP_u2.pptxBCP_u2.pptxRutviBaraiya This document provides a comprehensive overview of the C programming language, detailing its history, features, syntax, and various components such as tokens, operators, and data types. It highlights the significance of C in computer science, its application in developing operating systems and applications, and discusses code structure, comments, and practical examples. Additionally, it outlines exercises for practicing basic C programming concepts.
M.Florence Dayana / Basics of C Language
M.Florence Dayana / Basics of C LanguageDr.Florence Dayana The document provides an overview of the C programming language, detailing its history, features, and structure. It explains the fundamental components such as keywords, data types, operators, and I/O functions, emphasizing C's role in system and application programming. Additionally, it introduces coding conventions, including syntax rules and the use of comments.
Ma3696 Lecture 3
Ma3696 Lecture 3Brunel University The document discusses using variables and constants in VBA code. It covers declaring variables and constants, specifying data types, naming conventions, assigning values, and different scopes including disposable, local, and global. It emphasizes declaring all variables at the top of procedures or modules and assigning values after declarations. Structuring code in a logical order is also discussed.
Fundamentals of computers - C Programming
Fundamentals of computers - C ProgrammingMSridhar18 The document provides an overview of computer fundamentals, including the definition of a computer, its basic functions, and types. It covers the evolution of computer generations, an introduction to programming languages, and problem-solving techniques in programming. Additionally, it explores the C programming language, its components like variables, constants, operators, and formatted input/output functions.
PROGRAMMING IN C UNIT II.pdfFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
PROGRAMMING IN C UNIT II.pdfFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFdinesh620610 DIPLOMA C LANUGAE UNIT I
C programming language
C programming languageAbin Rimal This document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses that C was developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs to create the UNIX operating system. C is a structured, procedural programming language that is widely used to develop operating systems, databases, networks, and more. The document then covers some key concepts in C including functions, header files, variables, data types, operators, and escape sequences. It provides examples of basic C programs and exercises for practicing programming concepts.
Escape Sequences and Variables
Escape Sequences and Variablesyarkhosh This document discusses basic concepts in programming related to escape sequences, variables, constants, data types, and comments in the C language. It defines variables as memory locations for data, differentiates between constants and variables, and outlines rules for naming identifiers and variables. Additionally, it covers data types like int, float, and char, and emphasizes the importance of comments in code for clarity.
C intro
C introSHIKHA GAUTAM The document provides information on C language basics. It discusses that C is a system programming language useful for writing system programs like compilers, drivers, etc. It is a structured language that supports functions and modular programming. C has many built-in functions and is portable, efficient, and can access hardware. Some key aspects covered include data types in C, variables, operators, conditional statements, and input/output functions. Examples of basic C programs are also included.
Lecture 1 .
Lecture 1 .SwatiHans10 The document provides an overview of Python programming, including its installation, basic syntax, and fundamental concepts such as identifiers, variables, and operators. It outlines steps for installing Python on Windows and describes how to verify the installation. Additionally, it covers various types of operators and their functionalities, including arithmetic, assignment, and comparison operators.
Chapter 2: Elementary Programming
Chapter 2: Elementary ProgrammingEric Chou The document outlines the essentials of C programming, focusing on tokens, keywords, identifiers, and constants. It explains variable declaration, initialization, and the usage of different data types, including integers and floating-point numbers. Additionally, it covers operators, expressions, and the importance of understanding operator precedence in programming.
C Language Part 1
C Language Part 1Thapar Institute This document discusses various data types in C programming language. It begins by defining what a data type is and then provides examples of common data types like char, int, float, and double. It explains that each data type requires a different amount of memory and has an associated range for storing values. The document then provides a table listing the typical ranges and memory requirements for each data type on a 32-bit compiler. It also includes an example C program demonstrating the usage of different data types.
c#.pptx
c#.pptxJoselitoJMebolos This document provides an introduction to fundamentals of programming with C#, including definitions of key concepts like algorithms, variables, data types, operators, and conditional statements. It explains that programming involves describing what you want the computer to do as a sequence of steps or algorithms. The stages of software development are outlined as gathering requirements, planning/design, implementation, testing, deployment, support, and documentation. An overview of C# programming language fundamentals is also provided, such as basic syntax structure, defining classes and methods, and using the console for input/output.
CP c++ programing project Unit 1 intro.pdf
CP c++ programing project Unit 1 intro.pdfShivamYadav886008 The document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses the basic components of a C program including documentation, header files, definitions, global declarations, the main function, and subprograms. It also covers various C programming concepts such as data types, variables, constants, operators, and sample programs. The document is intended to teach students and professionals the fundamentals of C programming.
Ad
More from John Paul Espino (20)
Religion Education - Sa kabataang Pilipino - A La Juventud Filipina
Religion Education - Sa kabataang Pilipino - A La Juventud FilipinaJohn Paul Espino Ang tula na isinulat ni John Paul Espino ay nagtatampok ng hamon sa kabataang Pilipino na maging mulat sa kanilang paligid. Ito ang kauna-unahang tulang nakasulat sa wikang Espanyol na lumalarawan sa konsepto ng pagkamabayan ng mga Pilipino. Ang mensahe nito ay naglalayong maging inspirasyon at pag-asa para sa mga kabataan upang ipagpatuloy ang pag-aaral at pag-unlad.
Religion Education - Human Dignity - Freedom and Responsibility
Religion Education - Human Dignity - Freedom and ResponsibilityJohn Paul Espino Human dignity is divided into freedom and responsibility. There are two kinds of freedom: internal freedom, which is freedom as a power within oneself that can be exercised even when compelled; and external freedom, which is the freedom of action to do whatever one wants. Threats to internal freedom come from within through ignorance and passion, which can blur one's vision and lead to impulsive reactions. Responsibility has different areas including being responsible for the material world, the community, and oneself.
Public Speaking and Leadership -Process of Reading
Public Speaking and Leadership -Process of ReadingJohn Paul Espino The document discusses the process of reading and how it is an active, constructive process that involves interaction between the reader's background knowledge and the text. It involves predicting, inferring, and drawing implications to arrive at meaning. Reading comprehension depends on the reader's background knowledge, accuracy in understanding written material, and understanding the message of the text. Both top-down and bottom-up processing are used, along with different types of knowledge like syntactic, morphological, world, sociocultural, topic, and genre knowledge.
Environmental Engineering - Case Study - The Minamata Disease Disaster
Environmental Engineering - Case Study - The Minamata Disease DisasterJohn Paul Espino The Minamata Bay pollution disaster in Japan from 1932 to 1968 exposed local residents to methylmercury released as a byproduct of a chemical plant. Over time, residents developed neurological symptoms and the cause was traced to eating fish and shellfish contaminated with mercury from the plant's wastewater. While the company denied responsibility, over 2,000 victims were eventually certified with more receiving compensation. Decades later, protests and media coverage helped bring awareness and democratization around the environmental and human impacts of industrial pollution.
Computer Programming - if Statements & Relational Operators
Computer Programming - if Statements & Relational OperatorsJohn Paul Espino If statements and relational operators allow programmers to control program flow based on conditions. There are three types of if statements: if, if-else, and if-else-if. Relational operators like ==, <, > are used to form conditions. The if statement executes code if the condition is true, while if-else executes one block if true and another if false. Boolean logic and data type bool can be used to build more complex conditional expressions. Examples demonstrate using if statements and relational operators to check values, qualify ages to vote, and determine positive/negative numbers.
Philippine Constitution - Parliamentary Immunity
Philippine Constitution - Parliamentary Immunity John Paul Espino The document outlines the concept of parliamentary immunity, detailing the privileges and limitations of members of Congress regarding arrest and speech during sessions. It describes the processes for legislative and non-legislative powers, the steps for bill passage, and the various types of appropriations, emphasizing the 'power of the purse' held by Congress. Additionally, it discusses the role and functions of electoral tribunals and the commission on appointments, along with the rules governing taxation and appropriations.
Philippine Constitution - Article XI - Accountability of Public Officers
Philippine Constitution - Article XI - Accountability of Public OfficersJohn Paul Espino The document outlines the principles of accountability for public officers, emphasizing that public office is a trust and necessitates integrity and responsibility. It details the impeachment process for high-ranking officials, the grounds for impeachment, and the roles of the ombudsman and the anti-graft court (Sandiganbayan) in addressing corruption. The qualifications and appointment process for the ombudsman and their deputies are also specified, highlighting their independence and the requirement for a clean legal record.
Philippine Constitution - Article X - Local Government
Philippine Constitution - Article X - Local GovernmentJohn Paul Espino The document discusses the structure and functions of local governments in the Philippines, highlighting their autonomy and the process of decentralization from national to local levels. It outlines the reasons for local autonomy, the terms of office for local officials, and the distinctions between highly urbanized cities and component cities. Additionally, it covers the legislative powers granted to autonomous regions, including various administrative and developmental matters.
Philippine Constitution - Article VIII - Judicial Department
Philippine Constitution - Article VIII - Judicial DepartmentJohn Paul Espino The document outlines the structure and powers of the judicial department, detailing the supreme court's authority and the appointment process for justices and judges. It emphasizes the safeguards ensuring judicial independence, establishes criteria for judicial appointments, and defines key legal concepts like justiciable and political questions. Additionally, it outlines the conditions under which the president can exercise emergency powers and the timeline for resolving cases within the judicial system.
Philippine Constitution - Article VII - Executive Department
Philippine Constitution - Article VII - Executive DepartmentJohn Paul Espino The document outlines the powers and responsibilities of the President of the Philippines according to Article VII of the Philippine Constitution. It details that the executive power is vested in the President, who is tasked with enforcing laws and administering the government. It also discusses the qualifications, terms of office, succession order, and impeachment process for the President and Vice President. Furthermore, it examines the specific powers granted to the President, including appointment powers, removal powers, military powers, pardon powers, borrowing powers, and budgetary powers. Conditions for declaring martial law and exercising emergency powers are also summarized.
Philippine Constitution - Article VI - Legislative Power
Philippine Constitution - Article VI - Legislative PowerJohn Paul Espino This document summarizes key aspects of the legislative power and Congress as established in Article VI of the Philippine Constitution. It outlines that legislative power is vested in Congress, which is a bicameral body consisting of the Senate and House of Representatives. It provides details on the composition, qualifications, terms of office, and salaries of Senators and House Representatives. It also discusses concepts like gerrymandering and the process for filling vacancies.
Philippine Constitution - ARTICLE IX - Constitutional Commissions
Philippine Constitution - ARTICLE IX - Constitutional Commissions John Paul Espino The document outlines the structure and regulations of three independent constitutional commissions in the Philippines: the Civil Service Commission, the Commission on Elections, and the Commission on Audit. Each commission has specific qualifications for its members, terms of office, powers, and functions stated in the constitution, emphasizing the merit principle in public service. The Civil Service Commission aims to create a professionalized body of public servants, while the other commissions focus on election conduct and government auditing, respectively.
Philosophy - the aesthetic attitude and the sublime
Philosophy - the aesthetic attitude and the sublime John Paul Espino The document discusses the aesthetic attitude and the sublime. It provides background on key thinkers in aesthetics like Edward Bullough, who introduced the concept of "psychical distance" in aesthetic experience. Bullough viewed the aesthetic attitude as a state of mind that allows one to view experiences in an artistic or appreciative way. The document also discusses the sublime in nature, such as mighty waterfalls, which impress through sheer power rather than beauty. Key concepts of contemplation and distance are elements of the aesthetic attitude.
Philosophy - the aestheic attidude and the sublime
Philosophy - the aestheic attidude and the sublimeJohn Paul Espino This document discusses the aesthetic attitude and the sublime. It explains that the aesthetic attitude, according to Bullough, locates aesthetic experience primarily with the observer rather than the object itself. It involves viewing something with a distinctive attitude that allows contemplation and psychical distance. The document also discusses the sublime in nature, such as a mighty waterfall, which impresses through its sheer power rather than beauty. Key figures discussed include Bullough, who introduced the concept of psychical distance, and Kant, who was interested in natural rather than artistic beauty.
Information literacy - effects of social networking to students thesis presen...
Information literacy - effects of social networking to students thesis presen...John Paul Espino This document discusses a study on the effects of social networking sites on students' lives. It begins by introducing the growing popularity of sites like Facebook and Twitter, particularly among young people and students. The study aims to understand both the benefits and harmful effects of social networking use. It outlines a theoretical framework drawing from Carl Rogers' interpersonal relationship theory. The methodology section describes using a descriptive research design with cluster random sampling of students from De La Salle University. Survey results found most students use Facebook the most, spending 1-2 hours daily on social sites, and benefits included feeling connection while potential harms require further investigation.
Fundamentals of Accounting - Posting & Trial Balance
Fundamentals of Accounting - Posting & Trial BalanceJohn Paul Espino 1. The document discusses the accounting cycle and posting procedures for the general ledger and subsidiary ledgers.
2. It provides examples of accounts that would appear in a chart of accounts, including asset, liability, equity, revenue and expense accounts.
3. It also shows how to open and post transactions to general ledger accounts, with debits and credits, to keep track of account balances.
Fundamentals of accounting - manufacturing
Fundamentals of accounting - manufacturingJohn Paul Espino This document provides an overview of fundamentals of accounting for manufacturing businesses. It defines manufacturing as making products and then selling them. The key costs in manufacturing include direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead. Direct materials are raw materials used to make the product, direct labor is labor directly involved in production, and factory overhead includes other manufacturing expenses. The document contrasts merchandising and manufacturing businesses and explains how cost of goods sold is calculated differently for each.
Fundamentals of accounting - cost value profit (cvp)
Fundamentals of accounting - cost value profit (cvp)John Paul Espino The document discusses cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis and its key concepts. It defines variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs. It also explains contribution margin, break-even point, and how to use contribution margin to determine the volume needed to achieve a target profit level. Sample calculations are provided to illustrate computing contribution margin, contribution margin ratio, unit contribution margin, and using unit contribution margin to calculate break-even point.
Ethics - nicomachean ethics section 7 - 9
Ethics - nicomachean ethics section 7 - 9 John Paul Espino This document summarizes key sections from Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics regarding virtues and vices. It includes a table outlining Aristotle's spheres of virtues and their excess, mean, and deficiency. The document then summarizes sections 7-9, focusing on the virtues of truthfulness and wittiness, and their opposing vices of boastfulness, self-deprecation, buffoonery, and boorishness. It concludes with a summary of shamelessness versus shame.
Ethics - aristotle's ethics
Ethics - aristotle's ethicsJohn Paul Espino This document provides an overview of Aristotle's views on ethics and virtue. It discusses that for Aristotle, happiness is the highest good that is pursued for its own sake. Living well and flourishing requires developing moral virtues like courage, generosity, and honesty through consistent habits of acting virtuously. Virtues are excellences that involve moderation between deficiencies and excesses of emotions and actions. Practical wisdom is needed to determine the virtuous mean in different situations. An act is right if a virtuous person would tend to do it, where virtue involves acting for the right reason at the right time in the right way.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdf
vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdfAmirStern2 מכונות CNC קידוח אנכיות הן הבחירה הנכונה והטובה ביותר לקידוח ארונות וארגזים לייצור רהיטים. החלק נוסע לאורך ציר ה-x באמצעות ציר דיגיטלי מדויק, ותפוס ע"י צבת מכנית, כך שאין צורך לבצע setup (התאמות) לגדלים שונים של חלקים.
MuleSoft for AgentForce : Topic Center and API Catalog
MuleSoft for AgentForce : Topic Center and API Catalogshyamraj55 This presentation dives into how MuleSoft empowers AgentForce with organized API discovery and streamlined integration using Topic Center and the API Catalog. Learn how these tools help structure APIs around business needs, improve reusability, and simplify collaboration across teams. Ideal for developers, architects, and business stakeholders looking to build a connected and scalable API ecosystem within AgentForce.
Down the Rabbit Hole – Solving 5 Training Roadblocks
Down the Rabbit Hole – Solving 5 Training RoadblocksRustici Software Feeling stuck in the Matrix of your training technologies? You’re not alone. Managing your training catalog, wrangling LMSs and delivering content across different tools and audiences can feel like dodging digital bullets. At some point, you hit a fork in the road: Keep patching things up as issues pop up… or follow the rabbit hole to the root of the problems.
Good news, we’ve already been down that rabbit hole. Peter Overton and Cameron Gray of Rustici Software are here to share what we found. In this webinar, we’ll break down 5 training roadblocks in delivery and management and show you how they’re easier to fix than you might think.
ENERGY CONSUMPTION CALCULATION IN ENERGY-EFFICIENT AIR CONDITIONER.pdf
ENERGY CONSUMPTION CALCULATION IN ENERGY-EFFICIENT AIR CONDITIONER.pdfMuhammad Rizwan Akram DC Inverter Air Conditioners are revolutionizing the cooling industry by delivering affordable,
energy-efficient, and environmentally sustainable climate control solutions. Unlike conventional
fixed-speed air conditioners, DC inverter systems operate with variable-speed compressors that
modulate cooling output based on demand, significantly reducing energy consumption and
extending the lifespan of the appliance.
These systems are critical in reducing electricity usage, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and
promoting eco-friendly technologies in residential and commercial sectors. With advancements in
compressor control, refrigerant efficiency, and smart energy management, DC inverter air conditioners
have become a benchmark in sustainable climate control solutions
Reducing Conflicts and Increasing Safety Along the Cycling Networks of East-F...
Reducing Conflicts and Increasing Safety Along the Cycling Networks of East-F...Safe Software In partnership with the Belgian Province of East-Flanders this project aimed to reduce conflicts and increase safety along a cycling route between the cities of Oudenaarde and Ghent. To achieve this goal, the current cycling network data needed some extra key information, including: Speed limits for segments, Access restrictions for different users (pedestrians, cyclists, motor vehicles, etc.), Priority rules at intersections. Using a 360° camera and GPS mounted on a measuring bicycle, we collected images of traffic signs and ground markings along the cycling lanes building up mobile mapping data. Image recognition technologies identified the road signs, creating a dataset with their locations and codes. The data processing entailed three FME workspaces. These included identifying valid intersections with other networks (e.g., roads, railways), creating a topological network between segments and intersections and linking road signs to segments and intersections based on proximity and orientation. Additional features, such as speed zones, inheritance of speed and access to neighbouring segments were also implemented to further enhance the data. The final results were visualized in ArcGIS, enabling analysis for the end users. The project provided them with key insights, including statistics on accessible road segments, speed limits, and intersection priorities. These will make the cycling paths more safe and uniform, by reducing conflicts between users.
OpenACC and Open Hackathons Monthly Highlights June 2025
OpenACC and Open Hackathons Monthly Highlights June 2025OpenACC The OpenACC organization focuses on enhancing parallel computing skills and advancing interoperability in scientific applications through hackathons and training. The upcoming 2025 Open Accelerated Computing Summit (OACS) aims to explore the convergence of AI and HPC in scientific computing and foster knowledge sharing. This year's OACS welcomes talk submissions from a variety of topics, from Using Standard Language Parallelism to Computer Vision Applications. The document also highlights several open hackathons, a call to apply for NVIDIA Academic Grant Program and resources for optimizing scientific applications using OpenACC directives.
FME for Distribution & Transmission Integrity Management Program (DIMP & TIMP)
FME for Distribution & Transmission Integrity Management Program (DIMP & TIMP)Safe Software Peoples Gas in Chicago, IL has changed to a new Distribution & Transmission Integrity Management Program (DIMP & TIMP) software provider in recent years. In order to successfully deploy the new software we have created a series of ETL processes using FME Form to transform our gas facility data to meet the required DIMP & TIMP data specifications. This presentation will provide an overview of how we used FME to transform data from ESRI’s Utility Network and several other internal and external sources to meet the strict data specifications for the DIMP and TIMP software solutions.
Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME Flow
Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME FlowSafe Software This presentation will showcase an adapter for FME Flow that provides REST endpoints for FME Workspaces following the OGC API Processes specification. The implementation delivers robust, user-friendly API endpoints, including standardized methods for parameter provision. Additionally, it enhances security and user management by supporting OAuth2 authentication. Join us to discover how these advancements can elevate your enterprise integration workflows and ensure seamless, secure interactions with FME Flow.
Integration of Utility Data into 3D BIM Models Using a 3D Solids Modeling Wor...
Integration of Utility Data into 3D BIM Models Using a 3D Solids Modeling Wor...Safe Software Jacobs has developed a 3D utility solids modelling workflow to improve the integration of utility data into 3D Building Information Modeling (BIM) environments. This workflow, a collaborative effort between the New Zealand Geospatial Team and the Australian Data Capture Team, employs FME to convert 2D utility data into detailed 3D representations, supporting enhanced spatial analysis and clash detection.
To enable the automation of this process, Jacobs has also developed a survey data standard that standardizes the capture of existing utilities. This standard ensures consistency in data collection, forming the foundation for the subsequent automated validation and modelling steps. The workflow begins with the acquisition of utility survey data, including attributes such as location, depth, diameter, and material of utility assets like pipes and manholes. This data is validated through a custom-built tool that ensures completeness and logical consistency, including checks for proper connectivity between network components. Following validation, the data is processed using an automated modelling tool to generate 3D solids from 2D geometric representations. These solids are then integrated into BIM models to facilitate compatibility with 3D workflows and enable detailed spatial analyses.
The workflow contributes to improved spatial understanding by visualizing the relationships between utilities and other infrastructure elements. The automation of validation and modeling processes ensures consistent and accurate outputs, minimizing errors and increasing workflow efficiency.
This methodology highlights the application of FME in addressing challenges associated with geospatial data transformation and demonstrates its utility in enhancing data integration within BIM frameworks. By enabling accurate 3D representation of utility networks, the workflow supports improved design collaboration and decision-making in complex infrastructure projects
AI VIDEO MAGAZINE - June 2025 - r/aivideo
AI VIDEO MAGAZINE - June 2025 - r/aivideo1pcity Studios, Inc AI VIDEO MAGAZINE - r/aivideo community newsletter – Exclusive Tutorials: How to make an AI VIDEO from scratch, PLUS: How to make AI MUSIC, Hottest ai videos of 2025, Exclusive Interviews, New Tools, Previews, and MORE - JUNE 2025 ISSUE -
AudGram Review: Build Visually Appealing, AI-Enhanced Audiograms to Engage Yo...
AudGram Review: Build Visually Appealing, AI-Enhanced Audiograms to Engage Yo...SOFTTECHHUB AudGram changes everything by bridging the gap between your audio content and the visual engagement your audience craves. This cloud-based platform transforms your existing audio into scroll-stopping visual content that performs across all social media platforms.
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/why-its-critical-to-have-an-integrated-development-methodology-for-edge-ai-a-presentation-from-lattice-semiconductor/
Sreepada Hegade, Director of ML Systems and Software at Lattice Semiconductor, presents the “Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
The deployment of neural networks near sensors brings well-known advantages such as lower latency, privacy and reduced overall system cost—but also brings significant challenges that complicate development. These challenges can be addressed effectively by choosing the right solution and design methodology. The low-power FPGAs from Lattice are well poised to enable efficient edge implementation of models, while Lattice’s proven development methodology helps to mitigate the challenges and risks associated with edge model deployment.
In this presentation, Hegade explains the importance of an integrated framework that tightly consolidates different aspects of edge AI development, including training, quantization of networks for edge deployment, integration with sensors and inferencing. He also illustrates how Lattice’s simplified tool flow helps to achieve the best trade-off between power, performance and efficiency using low-power FPGAs for edge deployment of various AI workloads.
Security Tips for Enterprise Azure Solutions
Security Tips for Enterprise Azure SolutionsMichele Leroux Bustamante Delivering solutions to Azure may involve a variety of architecture patterns involving your applications, APIs data and associated Azure resources that comprise the solution. This session will use reference architectures to illustrate the security considerations to protect your Azure resources and data, how to achieve Zero Trust, and why it matters. Topics covered will include specific security recommendations for types Azure resources and related network security practices. The goal is to give you a breadth of understanding as to typical security requirements to meet compliance and security controls in an enterprise solution.
Supporting the NextGen 911 Digital Transformation with FME
Supporting the NextGen 911 Digital Transformation with FMESafe Software Next Generation 911 involves the transformation of our 911 system from an old analog one to the new digital internet based architecture. The evolution of NG911 opens up a host of new opportunities to improve the system. This includes everything from device based location, to real time text. This can improve location accuracy dramatically as well as provide live updates from the citizen in need along with real time sensor updates. There is also the opportunity to provide multi-media attachments and medical records if the end user approves. This digital transformation and enhancements all require the support of new NENA and CRTC standards, along with integration across a variety of data streams.
This presentation will focus on how FME has supported NG911 transformations to date, and how we are positioning FME to support the enhanced capabilities to come. This session will be of interest to emergency services, municipalities and anyone who may be interested to know more about how emergency services are being improved to provide more accurate, localized information in order to improve the speed and relevance of emergency response and ultimately save more lives and provide better outcomes for those in need.
Creating Inclusive Digital Learning with AI: A Smarter, Fairer Future
Creating Inclusive Digital Learning with AI: A Smarter, Fairer FutureImpelsys Inc. Have you ever struggled to read a tiny label on a medicine box or tried to navigate a confusing website? Now imagine if every learning experience felt that way—every single day.
For millions of people living with disabilities, poorly designed content isn’t just frustrating. It’s a barrier to growth. Inclusive learning is about fixing that. And today, AI is helping us build digital learning that’s smarter, kinder, and accessible to everyone.
Accessible learning increases engagement, retention, performance, and inclusivity for everyone. Inclusive design is simply better design.
“From Enterprise to Makers: Driving Vision AI Innovation at the Extreme Edge,...
“From Enterprise to Makers: Driving Vision AI Innovation at the Extreme Edge,...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/from-enterprise-to-makers-driving-vision-ai-innovation-at-the-extreme-edge-a-presentation-from-sony-semiconductor-solutions/
Amir Servi, Edge Deep Learning Product Manager at Sony Semiconductor Solutions, presents the “From Enterprise to Makers: Driving Vision AI Innovation at the Extreme Edge” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
Sony’s unique integrated sensor-processor technology is enabling ultra-efficient intelligence directly at the image source, transforming vision AI for enterprises and developers alike. In this presentation, Servi showcases how the AITRIOS platform simplifies vision AI for enterprises with tools for large-scale deployments and model management.
Servi also highlights his company’s collaboration with Ultralytics and Raspberry Pi, which brings YOLO models to the developer community, empowering grassroots innovation. Whether you’re scaling vision AI for industry or experimenting with cutting-edge tools, this presentation will demonstrate how Sony is accelerating high-performance, energy-efficient vision AI for all.
Bridging the divide: A conversation on tariffs today in the book industry - T...
Bridging the divide: A conversation on tariffs today in the book industry - T...BookNet Canada A collaboration-focused conversation on the recently imposed US and Canadian tariffs where speakers shared insights into the current legislative landscape, ongoing advocacy efforts, and recommended next steps. This event was presented in partnership with the Book Industry Study Group.
Link to accompanying resource: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/bridging-the-divide-a-conversation-on-tariffs-today-in-the-book-industry/
Presented by BookNet Canada and the Book Industry Study Group on May 29, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free Download
Viral>Wondershare Filmora 14.5.18.12900 Crack Free DownloadPuppy jhon ➡ 🌍📱👉COPY & PASTE LINK👉👉👉 ➤ ➤➤ https://drfiles.net/
Wondershare Filmora Crack is a user-friendly video editing software designed for both beginners and experienced users.
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL?
(POSETTE: An Event for Postgres 2025)
June 11, 2025
Shinya Kato
NTT DATA Japan Corporation
FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon.pptx
FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon.pptxFIDO Alliance FIDO Seminar: Authentication for a Billion Consumers - Amazon
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...
“Why It’s Critical to Have an Integrated Development Methodology for Edge AI,...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
“From Enterprise to Makers: Driving Vision AI Innovation at the Extreme Edge,...
“From Enterprise to Makers: Driving Vision AI Innovation at the Extreme Edge,...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
Computer programming - variables constants operators expressions and statements
- 1. VARIABLES, CONSTANTS, OPERATORS, EXPRESSIONS AND STATEMENTS By: John Paul Espino De La Salle University – Dasmarinas Facebook.com/Johnpaul.dss
- 3. KEYWORDS • Reserved words that have a special meaning. • May not be redefined by the programmer.
- 4. 32 KEYWORDS • auto • break • case • char • const • continue • default • do • double • else • enum • extern • float • for • goto • if • int • long • register • return • short • signed • sizeof • static • struct • switch • typedef • union • unsigned • void • volatile • while
- 5. LITERALS • values that identifiers can hold. • Numeric literals – accepts numeric values • No comma • No space between unary sign and the digits • Must begin and end with a digit
- 6. • Non-numeric literals - may be a character or sequence of characters • Example: ‘a’ ‘+’ ‘B’ “De La Salle University” “BCS”
- 7. IDENTIFIERS • are the names that are used to reference variables, function labels and various user-defined objects.
- 8. RULES FOR NAMING VALID IDENTIFIERS 1. An identifier in Turbo C can vary from 1 to 32 characters. 2. The first letter must be a letter or an underscore (_), followed optionally by sequence of letters, digits and/or underscore.
- 9. RULES FOR NAMING VALID IDENTIFIERS 3. Turbo C also allows the $ to be used in an identifier name, but this is non-standard so it’s use is not recommended. 4. An identifier should not include embedded blanks. 5. You cannot use any of the Turbo C keyword as your variable or identifier name. 6. You should not call your variable by the same name as other functions.
- 10. EXERCISES Identify the if the identifier is valid or invalid. 1. _ 2. a$ 3. Hello_World 4. _1 5. A 6. main 7. scanf 8. num1 9. tot sales 10. x-1 11. lname 12. Void Invalid: 2,3,6,7,9,10 Valid: 1,4,5,8,11,12
- 11. integer1 45 integer2 72 sum 117 VARIABLES • are identifiers in C where we want to store values (data). Variables are important since they contain the values need for manipulation and evaluation. Variable names are stored in the computer’s memory.
- 12. TYPE BITWIDTH RANGE char 8 0 to 255 int 16 -32768 to 32767 float 32 3.4E-32 to 3.4 E+38 double 64 1.7E-308 to 1.7 E+308 void 0 valueless DATA TYPES type of data that a variable can hold
- 13. TYPE EXAMPLES char ‘A’ ‘b’ ‘$’ ‘9’ ‘ab’‘10’ int 1 250 4500 float 3.5 42.56 345.6789 double 3.5647290… 486.145875... void valueless MORE ON DATA TYPES
- 14. TYPE MODIFIERS is used to alter the meaning of the base type to fit the needs of various situations more precisely. The four type modifiers in C are: signed unsigned long short Note: Type modifiers can be applied to char and int except long which can also be applied to double
- 15. TYPE BITWIDTH RANGE long int 32 -2147483648 to 2147483647 short int 16 -32768 to 32767 signed 32 -2147483648 to 2147483647 long int unsigned 32 0 to 4294967295 long int SOME COMBINATIONS OF C’S BASIC DATA TYPES AND MODIFIERS
- 16. DECLARATION OF VARIABLES • All variables must be declared before they are used. • Syntax: type variable_list; • where: type is a valid data type variable_list is 1 or more identifier names with comma separator
- 17. Local variables are variables that are declared inside a function. They are also called automatic variables. Local variables can only be referenced by statements that are inside the block in which the variables are declared. Example: #include <stdio.h> main () { int a,b,c; } Function block LOCAL VARIABLES
- 18. Example: #include <stdio.h> int a,b,c; main () { } GLOBAL VARIABLES • variables are known throughout the entire program and may be used by any piece of code. Also, they will hold their values during the entire execution of the program. Global variables are created by declaring them outside any function.
- 19. Example: #include <stdio.h> main () { int a,b,c; } Example: #include <stdio.h> int a,b,c; main () { } LOCAL VARIABLES GLOBAL VARIABLES
- 20. Example: #include <stdio.h> main () { } test_function (int a, float b); { } FORMAL PARAMETERS • behave like local variables in a function. Their declaration occurs inside parentheses that follow the function name.
- 21. CONSTANTS • Constants refer to fixed values that may not be altered by the program. • Turbo C supports one other type of constant in addition to those of the pre-defined data types. This is known as the string. All string constants are enclosed in double quote (“”). • Example: #define TEXT “Hello World” •
- 22. DECLARATION OF CONSTANT • are identifiers that can store a value that cannot be changed during program execution. const type iden_name = value; where: type is a valid data type iden_name is a valid identifier value is a constant value of the identifier
- 23. ASSIGNMENT STATEMENT Recall the assignment statement in flowcharting The general form of an assignment statement is var_name = expression where: var_name should be a variable, not a function or constant. expression may be a single constant or a complex combination of variables, operators and constants. Number = 5
- 24. Examples: char ch = ‘a’; int first = 0; float num = 1.5; type var_name = constant You can give variables a value at the time they are declared by placing an equal sign (=) and a constant after the variable name. This is called initialization and it’s general form is: semicolon VARIABLE INITIALIZATION
- 25. • Global variables are initialized at the start of the program • Local variables are initialized each time the block in which they are declared is entered • All global and local variables are initialized to zero (0) if no other initialization is specified. REMINDERS IN INITIALIZATION
- 26. Variables of type const may not be changed during execution of the program. Variables of this type get value from initialization or by some hardware-dependent means. The modifier volatile is used to tell the compiler that a variable’s value can be changed in ways not explicitly specified by the program. ACCESS MODIFIERS
- 27. REVIEW EXERCISES 1. Variables of type ___________are used to hold integer quantities. 2. Values of type character are used to hold ________characters or any 8-bit quantity. 3. __________in C are reserved words that have special meaning. 4. Values of type ________ and ________ are used to hold real numbers. 5. Real numbers have both an ________ and a fractional component. int ASCII Keywords float double integer
- 28. 6. Identifiers are composed of ________, ________, and underscore. 7. Variables that are declared inside a function are called ______________. 8. _________ are identifiers that can store a value that cannot be changed. letters digits local variables Constants
- 29. OPERATORS • Symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical manipulations. • Classification • arithmetic operators • relational operators • logical operators
- 30. A. ARITHMETIC OPERATORS - subtraction, unary minus +addition *multiplication / division % modulus division -- decrement ++ incrementNote: • When / is applied to an integer, any remainder is truncated • % cannot be used on type float or double
- 31. B. RELATIONAL & LOGICAL OPERATORS • Relational Operators shows the relationship values have with one another. • Logical operators show the ways these relationships can be connected together using rules of formal logic.
- 32. RELATIONAL OPERATORS Operator Action > greater than >= greater than or equal to < less than <= less than or equal to = = equal != not equal
- 33. C. LOGICAL OPERATORS && AND || OR ! NOT
- 34. EXPRESSION • Is any valid combination of operators, constants and variables that evaluates to a value.
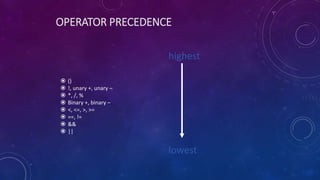
- 35. OPERATOR PRECEDENCE () !, unary +, unary – *, /, % Binary +, binary – <, <=, >, >= ==, != && || highest lowest
- 36. EVALUATE THE FOLLOWING: 1. Given: z = 5; a = 3, b = 9, w = 2, y = -5 Expression: z – a * b / 2 + w * y 2. Given: a = 5, b = 2, y = 3, c = 4, x = 1 Expression: (a * b + 2) * -y / ( c + x ) -18 7
- 37. 3. Given: dei = 0; y = 4.0; z = 2.0; x = 3.0 Expression: !dei || ( y + z >= x – z ) 4. Given: x = 3; y = 2; j = 5; k = 3 Expression: (x-y) <= (j-k ==3) 1 0
