Cross Context Scripting attacks & exploitation
- 1. From alert(‘xss’) to Meterpreter with a single click Roberto Suggi Liverani Ruhr-Universität Bochum HackPra 2012/2013 1
- 2. Who am I? A guy who likes to find bugs Speaker at various cons: DefCON, EUSecWest, HITB, OWASP Twitter: @malerisch Research blog: blog.malerisch.net 2
- 3. Outline Cross Context Scripting (XCS) Past research Recent discoveries Further attack surface 3
- 4. Cross Context Scripting (XCS) 4
- 5. Some concepts Same origin policy (SOP) Policy designed to govern interaction between different web sites ○ Domain name ○ Application protocol ○ Port W3C definition Although the same-origin policy differs between APIs, the overarching intent is to let users visit untrusted web sites without those web sites interfering with the user's session with honest web sites 5
- 6. Cross Context Scripting (XCS) XCS or Cross-zone scripting Cross Zone Scripting coined for IE http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-zone_scripting XCS coined for Firefox and injection in chrome:// What is XCS? An XSS in a privileged browser zone An indirect Same-Origin Policy (SOP) bypass ? Each browser has a trusted/privileged zone: FF - chrome:// Chrome - chrome:// Opera - opera:// Maxthon - mx:// Avant - browser:// 6
- 7. 7
- 8. XCS Browser privileged/trusted zone Access to internal API interfaces: ○ Browser Browser settings Bookmarks, storage, etc. ○ OS File system – I/O Example ○ Firefox model Firefox addons can run privileged code 8
- 9. FF Addon Example - FireFTP 9
- 10. Google Chrome – Settings Page 10
- 11. Opera History 11
- 12. XCS exploitation XCS exploits are 100% reliable No memory corruption Trusted zone Allows possible direct or indirect invokation of special functions/objects Challenge 1st - find injection point in trusted zone 2nd - make use of privileged functions/object to achieve code execution 12
- 13. Past Research 13
- 14. Past research Pioneers 2005 - Mark Pilgrim - Greasemonkey bug 2006 - Pdp & Michael Daw – publishing Sage xss 2008 - Kuza55 & Stefano Di Paola – Attacking rich internet applications – Tamper Data XSS demo My research Opera XSS found in opera:history ○ RCE exploit in opera:config (Kuza55 / Stefano Di Paola / Aviv Raff) Firefox extensions research with Nick Freeman ○ Multiple RCE exploits released in FF extensions 14
- 15. Opera XSS history (1/3) Opera XSS history – CVE 2008-4696 Metasploit - 'egypt', # msf module Step 1 - Injection in opera:history via the fragment part 15
- 16. Opera XSS Exploit (2/3) Step 2 - Force redirection to opera:history to trigger execution Note : SOP bypass 16
- 17. Opera XSS Exploit (3/3) Step 3 – Execute exploit payload 17
- 19. Firefox extensions Firefox and extensions security model Extension code is fully trusted by Firefox No security boundaries between extensions Extensions vulnerabilities are platform independent Lack of security policies to allow/deny Firefox access to internal API, XPCOM components, etc. After 3 years… No much change A vulnerable extension can still be used to compromise a system 19
- 20. Cool Previews Vulnerable version: 2.7.2 Injection point: ○ Add to stack function (right-click) Exploit: Link with a data: uri + base64 encoded payload ○ <a href=‘data:text/html,base64;payload’>A</a> 20
- 21. Remote Code Execution Invoking cmd.exe 21
- 23. FireFTP Vulnerable version: <1.1.4 Injection point: Server’s welcome message Exploit: Simple HTML and JavaScript payload directly evaluated in chrome:// 23
- 24. Feed Sidebar Vulnerable version: 3.2 Injection point: RSS feed Exploit: Use of data: uri + base64 encoded payload ○ <iframe src="data:text/html;base64,base64enco dedjavascript"></iframe> 24
- 25. Sage Vulnerable Version: <=1.4.3 Injection point: RSS feed <description> and <link> tags Exploit: Use of HTML encoded JavaScript payload ○ <description><script>dosomethingbad();<sc ript></description> Use of data: uri + base64 encoded payload ○ <link>data:text/html;base64,payload</link> 25
- 26. InfoRSS Vulnerable version: <= 1.1.4.2 Injection point: RSS feed <description> tag Exploit: Use of data: uri + base64 encoded payload ○ <iframe src="data:text/html;base64,base64enco dedjavascript"></iframe> 26
- 27. Yonoo Vulnerable Version: 6.1.1 Injection point: Drag & dropping a malicious image into the preview window Exploit: Use event handler e.g. onload ○ <img src=‘http://somewebsite.tld/lolcatpicture.jpg’ onLoad=‘evilJavaScript’> 27
- 30. Compromising NoScript Whitelisting malicious site 30
- 31. Reverse VNC using XHR 31
- 33. Maxthon – case study Developed by: Maxthon International (China) Architecture ○ Supports Trident and Webkit layout engines ○ Focus on performance and extra features Some stats - according to Maxthon 130 million users Users spread over 120 countries 500,000,000 downloads in 2k10 33
- 34. Maxthon: XCS via location.hash Status: UNPATCHED! Maliciouspage.html – performs redirection Injected payload executes in about:history 34
- 35. Maxthon: XCS via RSS Status: UNPATCHED! Injection via <title>, <link>, <description> tags 35
- 36. Exploitation issues Maxthon major changes DOM Program object removed in latest versions ○ Cannot invoke exe directly anymore ○ Can only read/write files via maxthon.io Personal exploit challenge No user interaction Targets: Windows XP and Windows 7 36
- 37. XCS Exploit – Windows XP Windows XP Overwrite any exe which can be directly invoked via HTML/Javascript ○ e.g. Outlook express (wab.exe) Then use window.location=“ldap://blabla” Works perfectly! 37
- 38. XCS Exploit – Windows 7 In Windows 7 (universal approach) User is prompted using WinXP approach Overwrite registry hives? Touch registry? Dirty approach but effective: ○ Overwrite one of the exe when Java applet is rendered ○ jp2launcher.exe is a good candidate Then point to an iframe with a java applet = WIN! 38
- 39. Metasploit modules https://github.com/malerisch/metasploit- framework/blob/maxthon3/modules/exploits/windows/browser/maxt hon_history_xcs.rb https://github.com/malerisch/metasploit- framework/blob/maxthon3/modules/exploits/windows/browser/maxt hon_rss_xcs.rb 39
- 40. DEMO Maxthon – about:history http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N- 5BkgJX8sI 40
- 41. Demo Maxthon XCS – RSS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d- 55asVLqNI 41
- 42. Maxthon: Trusted site over HTTP Status: PATCHED i.maxthon.com sets privileged DOM objects ○ runtime ○ maxthon 42
- 43. Exploit Leveraging XSS in a trusted “internet” page Design Issues i.maxthon.com = trusted domain i.maxthon.com allows direct access to privileged APIs No control on resolution of IP address No use of SSL MiTM Bug DNS poisoning ○ Force resolution of i.maxthon.com to a controlled IP address HTTP MiTM ○ i.maxthon.com served over HTTP – malicious proxy which alters page content Other implications XSS in real i.maxthon.com site 43
- 44. DEMO – i.maxthon.com (DNS compromised) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1IqZBS0 O2Hs 44
- 45. Avant Browser Avant Browser - Avant Force (China) Custom web browser application Designed to expand services provided by IE Two versions: lite (only IE) & ultimate (IE, FF, Chrome) More downloads than Chrome, IE and Opera in CNET 45
- 46. A bit about Avant (1/3) Firefox wrapped version Arguments passed to firefox.exe Avant.exe - parent of firefox.exe 46
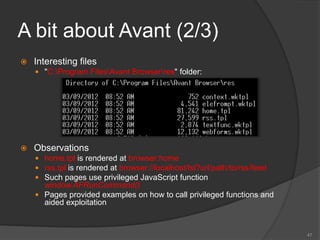
- 47. A bit about Avant (2/3) Interesting files "C:Program FilesAvant Browserres" folder: Observations home.tpl is rendered at browser:home rss.tpl is rendered at browser://localhost/lst?url/path/to/rss/feed Such pages use privileged JavaScript function window.AFRunCommand() Pages provided examples on how to call privileged functions and aided exploitation 47
- 48. A bit about Avant (3/3) Testing AFRunCommand() Undocumented Avant browser function Try{}/Catch{} no output Bruteforce only option – passing a single parameter: ○ 60003 - window.external.HistoryUrls() - [used in exploit] ○ 60011 - prompt for download ○ 10021 - add to ad block specified site ○ 3 - spawns an empty tab ○ 10010 - reloads the page ○ 10013 - search for keywords ○ 10014 - pop up blocker ○ 10016 - download a video (argument passed as URL) ○ 10017 - add task for download scheduler ○ 10025 - search keywords 48
- 49. Avant Browser – SOP Bypass Status: UNPATCHED! Works if Firefox is set as the rendering engine 49
- 51. DEMO – BeEF Module In Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I4LiSfT muM0 51
- 52. Avant Browser – XCS in browser:home Status: UNPATCHED Injection via <title> HTML element Cross Site Scripting Payload Rendered In browser:home Privileged Zone 52
- 53. DEMO – Avant Browser – XCS in browser:home via <title> http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cHHtsO pYGH4 53
- 54. Avant Browser – Stored XSS via RSS Injection via <title>, <link> and <description> tags 54
- 55. DEMO – Avant Browser – RSS Stored XSS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=- mShxsspxy8 55
- 57. Injection in bookmarks Attack based on: Origin inheritance – injection using javascript: uri Input validation – injecting into bookmark trusted zone Injection via bookmarks using javascript: Ancient bug reported in 2k5 by M. Krax User is lured into bookmarking a malicious javascript: URI + payload User clicks on malicious bookmark Focus on standard web page – Impact: XSS Focus on privileged browser zone – Impact: XCS Many ways to fool users: Security controls on status bar can be partially fooled JavaScript can be compressed and obfuscated 57
- 58. javascript: I invented the javascript: URL along with JavaScript in 1995, and intended that javascript: URLs could be used as any other kind of URL, including being bookmark-able. In particular, I made it possible to generate a new document by loading, e.g. javascript:'hello, world', but also (key for bookmarklets) to run arbitrary script against the DOM of the current document, e.g.javascript:alert(document.links[0].href). The difference is that the latter kind of URL uses an expression that evaluates to the undefined type in JS. I added the void operator to JS before Netscape 2 shipped to make it easy to discard any non-undefined value in a javascript: URL. —Brendan Eich 58
- 59. Firefox Case Firefox 10.0.2 vulnerable Malicious bookmark clicked while using an extension (from chrome://) Payload will execute in chrome:// Issue fixed in FF >11 59
- 60. Demo – Firefox XCS via bookmark http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gSuLV9 RjhGQ 60
- 61. Opera Opera 12.10 javascript: can be bookmarked Origin inheritance - opera:config vulnerable to XCS if javascript:// bookmarklet is triggered Mail app handler can be set with a UNC path e.g. myremotemeterpreter.exe 61
- 62. Demo – Opera XCS via Bookmarks http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wWtLHi 4Imr4 62
- 63. Maxthon - XCS in bookmarks 63
- 64. Demo – Maxthon XCS in bookmarks http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YR0RQ z45t3M 64
- 65. Conclusions More browser capability/functionality increased attack surface for XCS Untrusted content - rendering options about:blank Security model for extensions/addons Sandbox 65
- 66. Questions? Roberto Suggi Liverani - @malerisch blog.malerisch.net 66
- 67. References Blog – Roberto Suggi Liverani http://blog.malerisch.net/ Twitter account - @malerisch https://twitter.com/malerisch Security-Assessment.com Research http://www.security- assessment.com/page/archive.htm Nick Freeman – Publications http://atta.cked.me/publications 67
- 68. References Cross Context Scripting with Firefox - http://malerisch.net/docs/cross_context_scr ipting/cross_context_scripting_with_firefox. pdf Opera - XCS in opera:history http://malerisch.net/docs/advisories/opera_ stored_cross_site_scripting.html Firefox addon Coolpreviews – XCS - http://malerisch.net/docs/advisories/coolpre views_chrome_privileged_code_injection.h tml 68
- 69. References Firefox addon Update Scanner - XCS - http://malerisch.net/docs/advisories/updatesca nner_chrome_privileged_code_injection.html Exploiting XCS in Firefox - http://www.security- assessment.com/files/whitepapers/Exploiting_ Cross_Context_Scripting_vulnerabilities_in_Fir efox.pdf HITB2012AMS - Browser Bug Hunting in 2012 - http://www.security- assessment.com/files/documents/presentation s/window_shopping_browser_bug_hunting_in _2012_roberto_suggi_liverani_scott_bell.pdf 69
Editor's Notes
- #15: http://www.gnucitizen.org/blog/cross-context-scripting-with-sage/ http://mozdev.org/pipermail/greasemonkey/2005-July/004022.html
- #50: Split in two slides
- #55: Increase font size for each screen shot
- #58: Bug id 288164 -> in the thread, no one mentions about the fact that chrome:// is used by addons too and not just within the bookmark zone Ref: https://bug338459.bugzilla.mozilla.org/attachment.cgi?id=222524 http://www.agarri.fr/op00.html















































![A bit about Avant (3/3)
Testing AFRunCommand()
Undocumented Avant browser function
Try{}/Catch{} no output
Bruteforce only option – passing a single parameter:
○ 60003 - window.external.HistoryUrls() - [used in exploit]
○ 60011 - prompt for download
○ 10021 - add to ad block specified site
○ 3 - spawns an empty tab
○ 10010 - reloads the page
○ 10013 - search for keywords
○ 10014 - pop up blocker
○ 10016 - download a video (argument passed as URL)
○ 10017 - add task for download scheduler
○ 10025 - search keywords
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hackpracrosscontextscriptinginternetversion-121129175337-phpapp02/85/Cross-Context-Scripting-attacks-exploitation-48-320.jpg)









![javascript:
I invented the javascript: URL along with JavaScript in
1995, and intended that javascript: URLs could be used
as any other kind of URL, including being bookmark-able.
In particular, I made it possible to generate a new
document by loading, e.g. javascript:'hello, world', but also
(key for bookmarklets) to run arbitrary script against
the DOM of the current document,
e.g.javascript:alert(document.links[0].href). The difference
is that the latter kind of URL uses an expression that
evaluates to the undefined type in JS. I added the void
operator to JS before Netscape 2 shipped to make it easy
to discard any non-undefined value in a javascript: URL.
—Brendan Eich
58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hackpracrosscontextscriptinginternetversion-121129175337-phpapp02/85/Cross-Context-Scripting-attacks-exploitation-58-320.jpg)










