Data structure & Algorithms - Programming in C
- 1. 21CSC201J DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS UNIT-1 Topic : Programming in C and Primitive Data Types
- 2. Programming in C - Background • C was originally developed in the 1970s, by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Telephone Laboratories, Inc • C is a structured programming language. • It is considered a high-level language because it allows the programmer to concentrate on the problem at hand and not worry about the machine that the program will be using. • That is another reason why it is used by software developers whose applications have to run on many different hardware platforms. • C contains certain additional features that allows it to be used at a lower level , acting as bridge between machine language and the high level languages. • This allows C to be used for system programming as well as for applications programming
- 3. Programming in C – Structure of C Program
- 4. Programming in C – Example of C Program The Greeting Program
- 5. Programming in C – Example of C Program The Greeting Program
- 6. Programming in C – Comments Example of Block Comments
- 7. Programming in C – Comments Example of Line Comments
- 8. Programming in C – Identifiers •One feature present in all computer languages is the identifier. •Identifiers allow us to name data and other objects in the program. Each identified object in the computer is stored at a unique address. •Rules for Identifiers: C is a case-sensitive language. Note
- 9. Programming in C – Identifiers •Examples of Valid and Invalid identifiers:
- 10. Programming in C – Identifiers (Keywords) •Keywords are nothing but system defined identifiers. •Keywords are reserved words of the language. •They have specific meaning in the language and cannot be used by the programmer as variable or constant names •32 Keywords in C Programming auto double int struct break else long switch case enum register typedef char extern return union const float short unsigned continue for signed void default goto sizeof volatile do if static while
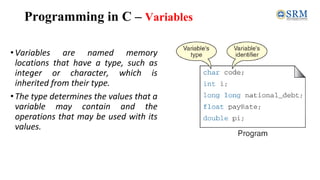
- 11. Programming in C – Variables •Variables are named memory locations that have a type, such as integer or character, which is inherited from their type. •The type determines the values that a variable may contain and the operations that may be used with its values.
- 12. Programming in C – Variable Declarations Examples of Variable Declarations Examples of Variable Initialization
- 13. Programming in C – Constants • Constants are data values that cannot be changed during the execution of a program. • eg. const double PI = 3.14 • Here, PI is a constant. Basically what it means is that, PI and 3.14 is same for this program. • Like variables, constants have a type. Integer constants • A integer constant is a numeric constant (associated with number) without any fractional or exponential part. There are three types of integer constants in C programming: • decimal constant(base 10) • octal constant(base 8) • hexadecimal constant(base 16)
- 14. Programming in C – Constants Floating-point constants • A floating point constant is a numeric constant that has either a fractional form or an exponent form. • For example: 2.0,0.0000234,-0.22E-5 Character constants • A character constant is a constant which uses single quotation around characters. For example: 'a', 'l', 'm', 'F' String constants • String constants are the constants which are enclosed in a pair of double-quote marks. • For example: "good" ,"x","Earth is roundn"
- 15. Programming in C – Escape Sequences • Sometimes, it is necessary to use characters which cannot be typed or has special meaning in C programming. • For example: newline(enter), tab, question mark etc. In order to use these characters, escape sequence is used. SequencesCharacter • b Backspace • f Form feed • n Newline • r Return • t Horizontal tab • v Vertical tab • Backslash • ' Single quotation mark • " Double quotation mark • ? Question mark • 0 Null character
- 16. Programming in C – Data Types •Each variable in C has an associated data type. •It specifies the type of data that the variable can store like integer, character, floating, double, etc. •Each data type requires different amounts of memory and has some specific operations which can be performed over it. •The data type is a collection of data with values having fixed values, meaning as well as its characteristics.
- 17. Programming in C – Data Types
- 18. Programming in C – Primitive Data Types •Integer Data Type •The integer datatype in C is used to store the whole numbers without decimal values. Octal values, hexadecimal values, and decimal values can be stored in int data type in C. •Range: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 •Size: 4 bytes •Format Specifier: %d
- 19. Programming in C – Primitive Data Types •Integer Types sizeof (short) ≤ sizeof (int) ≤ sizeof (long) ≤ sizeof (long long) Note
- 20. Programming in C – Primitive Data Types Typical Integer Sizes and Values for Signed Integers
- 21. Programming in C – Primitive Data Types •Float Data Type •Float in C is used to store decimal and exponential values. It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point values) with single precision. •Range: 1.2E-38 to 3.4E+38 •Size: 4 bytes •Format Specifier: %f
- 22. Programming in C – Primitive Data Types •Floating Point Types Note sizeof (float) ≤ sizeof (double) ≤ sizeof (long double)
- 23. Programming in C – Primitive Data Types •Void Data Types •The void data type in C is used to specify that no value is present. It does not provide a result value to its caller. •It has no values and no operations. It is used to represent nothing. •Void is used in multiple ways as function return type, function arguments as void etc.
- 24. Programming in C – Sizeof Data Types •Size of Data Types in C •The size of the data types in C is dependent on the size of the architecture, so we cannot define the universal size of the data types. •For that, the C language provides the sizeof() operator to check the size of the data types.
- 25. Programming in C – Sizeof Example // C Program to print size of different data type in C #include <stdio.h> int main() { int size_of_int = sizeof(int); int size_of_char = sizeof(char); int size_of_float = sizeof(float); int size_of_double = sizeof(double); printf("The size of int data type : %dn", size_of_int); printf("The size of char data type : %dn", size_of_char); printf("The size of float data type : %dn", size_of_float); printf("The size of double data type : %d", size_of_double); return 0; } Output The size of int data type : 4 The size of char data type : 1 The size of float data type : 4 The size of double data type : 8