Data Structure (Dynamic Array and Linked List)
Download as ppsx, pdf6 likes930 views
The document discusses dynamic arrays and linked lists, explaining their definitions and memory management functions such as allocation and deallocation. It also covers types of linked lists, operations such as insertion and deletion, and procedures for managing linked list nodes. Additionally, it includes examples and algorithms for various linked list operations like front, back, and middle insertions and deletions.
1 of 72
Downloaded 67 times







































































Ad
Recommended
Data Structure (Double Linked List)
Data Structure (Double Linked List)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar The document describes the structure and operations of a double linked list, detailing the node structure with 'prev' and 'next' connection fields. It outlines operations including creation, insertion (front, back, and middle), deletion (front, back, and middle), and traversal. Example code and procedural steps are provided for each operation, accompanied by contact information for further inquiries.
Data Structure (Circular Linked List)
Data Structure (Circular Linked List)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar The document defines circular linked lists, highlighting their differences from linear linked lists, particularly the absence of null values in connection fields. It details operations like creation, insertion, deletion, and traversal, with examples for front and back insertion and deletion. The document emphasizes caution against overlooping due to the circular nature and provides contact information for the author.
Linked list
Linked listakshat360 Linked lists are linear data structures where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. There are two types: singly linked lists where each node has a single next pointer, and doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers. Common operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion which have O(1) time complexity for singly linked lists but require changing multiple pointers for doubly linked lists. Linked lists are useful when the number of elements is dynamic as they allow efficient insertions and deletions without shifting elements unlike arrays.
Algo>ADT list & linked list
Algo>ADT list & linked listAin-ul-Moiz Khawaja This document discusses linked lists and their implementation. It begins by defining a list as a sequence of zero or more elements of a given type that can be linearly ordered. Linked lists are introduced as a flexible data structure that uses nodes connected by pointers to dynamically allocate elements in memory. The key operations on linked lists are described, including appending, traversing, inserting, deleting nodes. Code examples are provided to implement these operations using a ListNode struct containing a data element and pointer to the next node. Functions like appendNode and displayList are demonstrated, with appendNode adding to the end of the list and displayList traversing the list to output each element.
Array implementation and linked list as datat structure
Array implementation and linked list as datat structureTushar Aneyrao The document discusses arrays and linked lists. It defines arrays as collections of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory. Linked lists store elements in memory locations that are not contiguous. Each element of a linked list contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. This allows for efficient insertion and deletion of nodes compared to arrays. The document provides examples of implementing common linked list operations like insertion at the head, tail, and deletion.
Unit ii(dsc++)
Unit ii(dsc++)Durga Devi This document discusses different types of linked lists including singly linked lists, circular linked lists, and doubly linked lists. It provides details on representing stacks and queues using linked lists. Key advantages of linked lists over arrays are that linked lists can dynamically grow in size as needed, elements can be inserted and deleted without shifting other elements, and there is no memory wastage. Operations like insertion, deletion, traversal, and searching are described for singly linked lists along with sample C code to implement a linked list, stack, and queue.
Linked List Static and Dynamic Memory Allocation
Linked List Static and Dynamic Memory AllocationProf Ansari The document discusses the concepts of static and dynamic memory allocation, explaining how memory is allocated at compile time and the advantages of dynamic memory allocation through functions like malloc() and calloc(). It introduces linked lists as a way to overcome memory wastage in static arrays by linking nodes dynamically, and details operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal. Additionally, it covers various linked list types, including singly linked, doubly linked, and circular linked lists, and their applications in data structures like stacks and queues.
Linked List - Insertion & Deletion
Linked List - Insertion & DeletionAfaq Mansoor Khan The document provides a comprehensive guide on linked lists, detailing insertion and deletion techniques at various positions, including the start, end, and middle of the list. It covers algorithms and implementations for adding and removing nodes, as well as handling specific cases like deleting nodes with a particular value. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of linked lists compared to arrays, along with their applications.
Linked lists in Data Structure
Linked lists in Data StructureMuhazzab Chouhadry A linked list is a data structure made up of nodes that are connected to each other via pointers. Each node contains a data field as well as a pointer to the next node. Linked lists allow dynamic sizes and efficient insertion/deletion of nodes. Common linked list operations include appending nodes to the end, inserting nodes in a sorted order, traversing the list to display nodes, and deleting nodes. The code sample shows a template for a linked list class with functions to implement these operations by traversing the list and manipulating the node pointers accordingly.
Operations on linked list
Operations on linked listSumathi Kv A linked list is a linear data structure consisting of nodes that are connected to each other through pointers. Each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. Linked lists allow for efficient insertion and removal of nodes and are more flexible than arrays in terms of memory allocation. Common types of linked lists include singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, circular linked lists, and header linked lists.
Linear data structure concepts
Linear data structure conceptsAkila Krishnamoorthy The document provides an in-depth overview of linked lists, detailing their structure, advantages, and basic operations such as insertion, deletion, and searching. It also compares linked lists with arrays, highlights variations like circular and doubly linked lists, and outlines the corresponding operations for each type. Furthermore, it includes code snippets for implementing these operations in C++.
Mca ii dfs u-3 linklist,stack,queue
Mca ii dfs u-3 linklist,stack,queueRai University The document defines and describes stacks, queues, and linked lists. It defines a stack as a LIFO data structure that allows push and pop operations. A queue is defined as a FIFO data structure that allows enqueue and dequeue operations. Linked lists are collections of nodes that contain data and a pointer to the next node. The document discusses implementations of stacks, queues, and linked lists using arrays and linked nodes. It also covers priority queues, deques, and circular linked lists.
CSE240 Doubly Linked Lists
CSE240 Doubly Linked ListsGarrett Gutierrez This document discusses doubly linked lists. A doubly linked list is a list where each node contains a pointer to the next node and previous node. This allows traversal in both directions. The document explains how to implement a doubly linked list using a struct with next and previous pointers. It covers insertion, deletion, searching, and printing nodes in a doubly linked list by traversing forwards and backwards. Key operations like adding a node to the beginning, middle or end of the list are demonstrated along with deleting nodes and freeing memory.
Stacks,queues,linked-list
Stacks,queues,linked-listpinakspatel A stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (last in, first out) principle. Elements are inserted and removed from the top of the stack. Common stack operations include push to add an element and pop to remove the top element. Stacks can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Stacks are useful for operations like converting infix expressions to postfix and evaluating postfix expressions using a stack to hold operands. Queues follow the FIFO (first in, first out) principle with elements added to the rear and removed from the front. Common queue operations are enqueue to add and dequeue to remove elements. Queues can also be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Linked lists store elements in nodes with each node
Linked list
Linked listVONI The document discusses linked lists, including their definition as a dynamic linear data structure composed of connected nodes where each node contains a data element and a pointer, common operations on linked lists such as traversal, insertion, and deletion, and variations like single vs. double linked lists and circular lists. Algorithms for searching, inserting, and deleting nodes from a singly linked list are presented along with advantages of linked lists over arrays for dynamic data structures.
Unit 5 linked list
Unit 5 linked listDabbal Singh Mahara The document discusses linked lists and their implementation in C. It defines linked lists as dynamic data structures that store data in nodes linked together via pointers. The key operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion of nodes, as well as traversing and searching the list. It describes implementing linked lists as singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists. Functions are provided for basic linked list operations like insertion, deletion, display on singly linked lists, and implementations of stacks and queues using linked lists.
linked list
linked list Narendra Chauhan This document contains a presentation on linked lists. It includes:
1. An introduction to linked lists describing their representation using linked allocation and algorithms for inserting and deleting nodes.
2. Algorithms for inserting a node at the first, last, and ordered positions in a single linked list, as well as deleting a node and copying a linked list.
3. A section on linear linked list multiple choice questions.
Data structure , stack , queue
Data structure , stack , queueRajkiran Nadar The document discusses data structures including stacks, queues, and linked lists, emphasizing their importance for efficient data management in complex applications. It defines basic operations for each structure, highlights their implementations in C++, and outlines the associated algorithms for operations like push, pop, enqueue, and dequeue. The document also explains different types of linked lists and their operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal.
Linked list
Linked listTrupti Agrawal This document discusses linked lists and polynomials represented as linked lists. It provides details on singly linked lists, including how to implement insertion and deletion of nodes. It also describes how to represent stacks and queues as dynamically linked lists. Finally, it discusses representing polynomials using arrays or linked lists, and how to perform addition and multiplication of polynomials in each representation.
Doubly & Circular Linked Lists
Doubly & Circular Linked ListsAfaq Mansoor Khan The document discusses double and circular linked lists. It covers inserting and deleting nodes from doubly linked lists and circular linked lists. Specifically, it describes how to insert nodes at different positions in a doubly linked list, such as at the front, after a given node, at the end, and before a given node. It also explains how to delete nodes from a doubly linked list. For circular linked lists, it outlines how to insert nodes in an empty list, at the beginning, at the end, and between nodes. It also provides the steps to delete nodes from a circular linked list.
Sorting & Linked Lists
Sorting & Linked ListsJ.T.A.JONES The document discusses sorting algorithms, abstract data types (ADTs), and linked lists. It describes selection sort and insertion sort algorithms for sorting arrays. It then explains that linked lists are a more flexible data structure than arrays and defines a singly linked list as an ADT with nodes that point to the next node in the list. Functions for typical linked list operations like insertion, deletion, checking if empty, and printing the list are discussed.
linked list using c
linked list using cVenkat Reddy The document discusses linked lists and their advantages over arrays. It defines a linked list as a linear data structure composed of nodes, where each node contains data and a pointer to the next node. The key points are:
- Linked lists have dynamic sizes while arrays are fixed. Inserting and deleting from linked lists is more efficient as it doesn't require shifting elements.
- Linked lists don't allow random access so operations like sorting are less efficient, while arrays don't waste space if fully filled.
- The document then describes the basic operations on a singly linked list like creation, insertion, deletion and searching and provides algorithms to implement these operations.
linked list (c#)
linked list (c#)swajahatr The document discusses list data structures and their implementation using arrays and linked memory. It describes common list operations like insertion, removal, searching, and provides examples of how to implement them with arrays and linked lists. Key list operations include adding and removing elements from different positions, accessing elements by index or pointer, and traversing the list forward and backward. Linked lists offer more flexibility than arrays by not requiring predefined memory allocation.
Data Structures - Lecture 7 [Linked List]
Data Structures - Lecture 7 [Linked List]Muhammad Hammad Waseem - A linked list is a data structure where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node.
- It allows dynamic size and efficient insertion/deletion compared to arrays.
- A doubly linked list adds a pointer to the previous node, allowing traversal in both directions.
- A circular linked list connects the last node back to the first node, making it a continuous loop.
- Variations require changes to the node structure and functions like append/delete to handle the added previous/next pointers.
Data structure lecture 5
Data structure lecture 5Kumar Here are the key steps to insert a new node into a linked list:
1. Check for available memory (node)
2. Create the new node and set its data
3. If inserting at head, update head pointer; else insert after the given node by updating next pointers.
4. Return
Linked lists
Linked listsGowriKumar Chandramouli The document provides a detailed implementation of linked lists in C, including the structure definition and functions for initialization, insertion at various positions, searching for elements, and deletion. It showcases examples of function calls to manipulate the linked list, demonstrating operations like inserting at the beginning, end, and specific positions, as well as finding and deleting nodes. The main function illustrates how to create a linked list and use these operations in practice.
Linked list
Linked listRahulGandhi110 The document discusses various types of linked lists including circular linked lists, linked implementation of stacks and queues, and applications of linked lists. Circular linked lists form a closed loop where the last node points to the first node. Linked stacks and queues can be implemented using linked lists which allows dynamic memory allocation instead of fixed size arrays. Applications of linked lists include representing polynomials for arithmetic operations, adding long integers, and non-integer/heterogeneous lists.
linked list
linked listShaista Qadir The document presents an overview of linked lists, including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists, detailing their structure and functions. It outlines algorithms for insertion, deletion, and searching within these lists, illustrated with class definitions and operations for singly and doubly linked lists. Additionally, specific methods for adding and removing nodes are provided, alongside descriptions of how these structures can be utilized in programming.
Splay Tree
Splay TreeDr Sandeep Kumar Poonia The document describes splay trees, a type of self-adjusting binary search tree. Splay trees differ from other balanced binary search trees in that they do not explicitly rebalance after each insertion or deletion, but instead perform a process called "splaying" in which nodes are rotated to the root. This splaying process helps ensure search, insert, and delete operations take O(log n) amortized time. The document explains splaying operations like zig, zig-zig, and zig-zag that rotate nodes up the tree, and analyzes how these operations affect the tree's balance over time through a concept called the "rank" of the tree.
Data Management (Data Mining Klasifikasi)
Data Management (Data Mining Klasifikasi)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen tersebut memberikan penjelasan mengenai konsep dasar data mining klasifikasi, proses klasifikasi menggunakan algoritma Naive Bayes, serta contoh kasus klasifikasi menggunakan atribut usia, pendapatan, pekerjaan, dan punya deposito atau tidak.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Linked lists in Data Structure
Linked lists in Data StructureMuhazzab Chouhadry A linked list is a data structure made up of nodes that are connected to each other via pointers. Each node contains a data field as well as a pointer to the next node. Linked lists allow dynamic sizes and efficient insertion/deletion of nodes. Common linked list operations include appending nodes to the end, inserting nodes in a sorted order, traversing the list to display nodes, and deleting nodes. The code sample shows a template for a linked list class with functions to implement these operations by traversing the list and manipulating the node pointers accordingly.
Operations on linked list
Operations on linked listSumathi Kv A linked list is a linear data structure consisting of nodes that are connected to each other through pointers. Each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. Linked lists allow for efficient insertion and removal of nodes and are more flexible than arrays in terms of memory allocation. Common types of linked lists include singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, circular linked lists, and header linked lists.
Linear data structure concepts
Linear data structure conceptsAkila Krishnamoorthy The document provides an in-depth overview of linked lists, detailing their structure, advantages, and basic operations such as insertion, deletion, and searching. It also compares linked lists with arrays, highlights variations like circular and doubly linked lists, and outlines the corresponding operations for each type. Furthermore, it includes code snippets for implementing these operations in C++.
Mca ii dfs u-3 linklist,stack,queue
Mca ii dfs u-3 linklist,stack,queueRai University The document defines and describes stacks, queues, and linked lists. It defines a stack as a LIFO data structure that allows push and pop operations. A queue is defined as a FIFO data structure that allows enqueue and dequeue operations. Linked lists are collections of nodes that contain data and a pointer to the next node. The document discusses implementations of stacks, queues, and linked lists using arrays and linked nodes. It also covers priority queues, deques, and circular linked lists.
CSE240 Doubly Linked Lists
CSE240 Doubly Linked ListsGarrett Gutierrez This document discusses doubly linked lists. A doubly linked list is a list where each node contains a pointer to the next node and previous node. This allows traversal in both directions. The document explains how to implement a doubly linked list using a struct with next and previous pointers. It covers insertion, deletion, searching, and printing nodes in a doubly linked list by traversing forwards and backwards. Key operations like adding a node to the beginning, middle or end of the list are demonstrated along with deleting nodes and freeing memory.
Stacks,queues,linked-list
Stacks,queues,linked-listpinakspatel A stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (last in, first out) principle. Elements are inserted and removed from the top of the stack. Common stack operations include push to add an element and pop to remove the top element. Stacks can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Stacks are useful for operations like converting infix expressions to postfix and evaluating postfix expressions using a stack to hold operands. Queues follow the FIFO (first in, first out) principle with elements added to the rear and removed from the front. Common queue operations are enqueue to add and dequeue to remove elements. Queues can also be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Linked lists store elements in nodes with each node
Linked list
Linked listVONI The document discusses linked lists, including their definition as a dynamic linear data structure composed of connected nodes where each node contains a data element and a pointer, common operations on linked lists such as traversal, insertion, and deletion, and variations like single vs. double linked lists and circular lists. Algorithms for searching, inserting, and deleting nodes from a singly linked list are presented along with advantages of linked lists over arrays for dynamic data structures.
Unit 5 linked list
Unit 5 linked listDabbal Singh Mahara The document discusses linked lists and their implementation in C. It defines linked lists as dynamic data structures that store data in nodes linked together via pointers. The key operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion of nodes, as well as traversing and searching the list. It describes implementing linked lists as singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists. Functions are provided for basic linked list operations like insertion, deletion, display on singly linked lists, and implementations of stacks and queues using linked lists.
linked list
linked list Narendra Chauhan This document contains a presentation on linked lists. It includes:
1. An introduction to linked lists describing their representation using linked allocation and algorithms for inserting and deleting nodes.
2. Algorithms for inserting a node at the first, last, and ordered positions in a single linked list, as well as deleting a node and copying a linked list.
3. A section on linear linked list multiple choice questions.
Data structure , stack , queue
Data structure , stack , queueRajkiran Nadar The document discusses data structures including stacks, queues, and linked lists, emphasizing their importance for efficient data management in complex applications. It defines basic operations for each structure, highlights their implementations in C++, and outlines the associated algorithms for operations like push, pop, enqueue, and dequeue. The document also explains different types of linked lists and their operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal.
Linked list
Linked listTrupti Agrawal This document discusses linked lists and polynomials represented as linked lists. It provides details on singly linked lists, including how to implement insertion and deletion of nodes. It also describes how to represent stacks and queues as dynamically linked lists. Finally, it discusses representing polynomials using arrays or linked lists, and how to perform addition and multiplication of polynomials in each representation.
Doubly & Circular Linked Lists
Doubly & Circular Linked ListsAfaq Mansoor Khan The document discusses double and circular linked lists. It covers inserting and deleting nodes from doubly linked lists and circular linked lists. Specifically, it describes how to insert nodes at different positions in a doubly linked list, such as at the front, after a given node, at the end, and before a given node. It also explains how to delete nodes from a doubly linked list. For circular linked lists, it outlines how to insert nodes in an empty list, at the beginning, at the end, and between nodes. It also provides the steps to delete nodes from a circular linked list.
Sorting & Linked Lists
Sorting & Linked ListsJ.T.A.JONES The document discusses sorting algorithms, abstract data types (ADTs), and linked lists. It describes selection sort and insertion sort algorithms for sorting arrays. It then explains that linked lists are a more flexible data structure than arrays and defines a singly linked list as an ADT with nodes that point to the next node in the list. Functions for typical linked list operations like insertion, deletion, checking if empty, and printing the list are discussed.
linked list using c
linked list using cVenkat Reddy The document discusses linked lists and their advantages over arrays. It defines a linked list as a linear data structure composed of nodes, where each node contains data and a pointer to the next node. The key points are:
- Linked lists have dynamic sizes while arrays are fixed. Inserting and deleting from linked lists is more efficient as it doesn't require shifting elements.
- Linked lists don't allow random access so operations like sorting are less efficient, while arrays don't waste space if fully filled.
- The document then describes the basic operations on a singly linked list like creation, insertion, deletion and searching and provides algorithms to implement these operations.
linked list (c#)
linked list (c#)swajahatr The document discusses list data structures and their implementation using arrays and linked memory. It describes common list operations like insertion, removal, searching, and provides examples of how to implement them with arrays and linked lists. Key list operations include adding and removing elements from different positions, accessing elements by index or pointer, and traversing the list forward and backward. Linked lists offer more flexibility than arrays by not requiring predefined memory allocation.
Data Structures - Lecture 7 [Linked List]
Data Structures - Lecture 7 [Linked List]Muhammad Hammad Waseem - A linked list is a data structure where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node.
- It allows dynamic size and efficient insertion/deletion compared to arrays.
- A doubly linked list adds a pointer to the previous node, allowing traversal in both directions.
- A circular linked list connects the last node back to the first node, making it a continuous loop.
- Variations require changes to the node structure and functions like append/delete to handle the added previous/next pointers.
Data structure lecture 5
Data structure lecture 5Kumar Here are the key steps to insert a new node into a linked list:
1. Check for available memory (node)
2. Create the new node and set its data
3. If inserting at head, update head pointer; else insert after the given node by updating next pointers.
4. Return
Linked lists
Linked listsGowriKumar Chandramouli The document provides a detailed implementation of linked lists in C, including the structure definition and functions for initialization, insertion at various positions, searching for elements, and deletion. It showcases examples of function calls to manipulate the linked list, demonstrating operations like inserting at the beginning, end, and specific positions, as well as finding and deleting nodes. The main function illustrates how to create a linked list and use these operations in practice.
Linked list
Linked listRahulGandhi110 The document discusses various types of linked lists including circular linked lists, linked implementation of stacks and queues, and applications of linked lists. Circular linked lists form a closed loop where the last node points to the first node. Linked stacks and queues can be implemented using linked lists which allows dynamic memory allocation instead of fixed size arrays. Applications of linked lists include representing polynomials for arithmetic operations, adding long integers, and non-integer/heterogeneous lists.
linked list
linked listShaista Qadir The document presents an overview of linked lists, including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists, detailing their structure and functions. It outlines algorithms for insertion, deletion, and searching within these lists, illustrated with class definitions and operations for singly and doubly linked lists. Additionally, specific methods for adding and removing nodes are provided, alongside descriptions of how these structures can be utilized in programming.
Viewers also liked (20)
Splay Tree
Splay TreeDr Sandeep Kumar Poonia The document describes splay trees, a type of self-adjusting binary search tree. Splay trees differ from other balanced binary search trees in that they do not explicitly rebalance after each insertion or deletion, but instead perform a process called "splaying" in which nodes are rotated to the root. This splaying process helps ensure search, insert, and delete operations take O(log n) amortized time. The document explains splaying operations like zig, zig-zig, and zig-zag that rotate nodes up the tree, and analyzes how these operations affect the tree's balance over time through a concept called the "rank" of the tree.
Data Management (Data Mining Klasifikasi)
Data Management (Data Mining Klasifikasi)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen tersebut memberikan penjelasan mengenai konsep dasar data mining klasifikasi, proses klasifikasi menggunakan algoritma Naive Bayes, serta contoh kasus klasifikasi menggunakan atribut usia, pendapatan, pekerjaan, dan punya deposito atau tidak.
មេរៀនៈ Data Structure and Algorithm in C/C++
មេរៀនៈ Data Structure and Algorithm in C/C++Ngeam Soly This document provides an introduction to a lecture on data structures and algorithms. It discusses the lecturer's contact information and expectations for reading ahead of lectures. It then covers topics that will be discussed in the course, including programs and programming, introduction to programming, crafting programs effectively, what makes a good program, and why data structures and algorithms are important subjects. The document provides an overview of what will be covered in the course.
Data Structure
Data StructureKarthikeyan A K The binary search is faster than the sequential search. The complexity of binary search is O(log n) whereas the complexity of a sequential search is O(n). Stacks are used to evaluate algebraic or arithmetic expressions using prefix or postfix notations. Heap sort involves creating a max heap from the array and then replacing the root with the last element and rebuilding the heap for the remaining elements, repeating this process to sort the entire array.
Lecture 1 data structures and algorithms
Lecture 1 data structures and algorithmsAakash deep Singhal This document discusses data structures and their applications. It defines key terms like data, data item, entity, attribute, field, record, and file. It explains that a data structure is a logical organization of data that specifies the data elements and operations that can be performed on them. Common operations include traversing, searching, inserting, and deleting. The choice of data structure depends on how frequently certain operations will be performed. Real-life data manipulation requires storage, retrieval, and transformation of user data.
DATA STRUCTURES
DATA STRUCTURESbca2010 This document provides information about Dream Valley College for Girls Centre for Educational Excellence. It includes an index and presentation on data structures covering topics like arrays, linked lists, queues, trees, and graphs. The presentation was presented by Harish Sir and includes definitions, examples, and diagrams to explain each data structure concept.
Ap Power Point Chpt6
Ap Power Point Chpt6dplunkett The document discusses arrays in Java. It defines arrays as ordered lists that store multiple values of the same type. Arrays allow accessing elements using indexes, and declaring arrays involves specifying the type and size. The document covers key array concepts like initialization, bounds checking, passing arrays as parameters, multidimensional arrays, and sorting and searching arrays.
B tree &
B tree &memonayounas Deletion in a B-tree involves removing a key from any node while maintaining the properties of the B-tree. There are three main cases for deletion: 1) deleting from a leaf node with enough keys, 2) deleting from a leaf node with the minimum number of keys which may involve borrowing keys from a sibling, and 3) deleting from an internal node which may involve moving keys between subtrees or merging child nodes. The goal is to delete the target key while keeping all nodes with at least the minimum number of keys.
stack and queue array implementation in java.
stack and queue array implementation in java.CIIT Atd. This document discusses stack and queue data structures. It provides code examples in Java to demonstrate push and pop operations in a stack and enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue using arrays. Key aspects covered include LIFO and FIFO behavior, stack and queue operations, and sample code to implement stacks and queues in Java with output examples.
B trees and_b__trees
B trees and_b__treesRakhi Srivastava B-trees and B+-trees are common indexing structures used in relational database management systems. B-trees allow for rapid searching of data in large tables. They balance search trees through node splitting and ensure search efficiency even with millions of records. B+-trees are similar but only store data records in leaf nodes, improving search performance further. Both support efficient insertion and deletion through node splitting and merging as needed to maintain balance.
Chapter 15
Chapter 15Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University This document discusses phasor diagrams which are diagrams that use phasors to represent the amplitude and phase of sinusoidal quantities. Phasor diagrams allow engineers to add vectors that represent voltages and currents to show their relationship and calculate power. They provide a simple geometric method to analyze AC circuits and understand relationships between voltage, current, and power in sinusoidal steady state conditions.
04 ds and algorithm session_05
04 ds and algorithm session_05Niit Care The document discusses various sorting and searching algorithms, including quick sort, merge sort, linear search, and binary search. It provides details on implementing quick sort, including selecting a pivot, partitioning the list around the pivot, and recursively sorting the sublists. The worst-case time complexity of quick sort is O(n^2) if the pivot is poorly chosen, but it can be improved to O(n log n) on average by selecting the median element as the pivot. The document also introduces merge sort and its implementation.
07 ds and algorithm session_10
07 ds and algorithm session_10Niit Care The document discusses stacks and their implementation. It defines a stack as a LIFO data structure where elements can only be inserted or removed from the top. The basic stack operations are PUSH, which inserts an element onto the top of the stack, and POP, which removes the top element. Stacks can be used to check if parentheses in an arithmetic expression are correctly nested by scanning the expression and using a stack to match opening and closing parentheses.
Lec6 mod linked list
Lec6 mod linked listIbrahim El-Torbany The document discusses various topics related to dynamic linked lists including their meaning, traversal, insertion, and deletion operations. It describes implementing a list abstract data type using either an array or linked list as the underlying data structure. Key points covered include traversing a linked list using pointers, inserting and deleting nodes by allocating and deallocating memory dynamically, and the additional operations needed for a sorted linked list such as insert as first and remove first elements.
B tree long
B tree longNikhil Sharma The document discusses B-trees, which are self-balancing tree data structures that allow efficient insertion and deletion of data while keeping the tree height shallow. B-trees allow for efficient searching, insertion, and deletion of data in logarithmic time by allowing nodes to have more than two child nodes, and by splitting and merging nodes as needed to balance the tree during operations. The document covers the basic structure and properties of B-trees and explains the algorithms for insertion and deletion of keys through cases involving splitting, merging, redistribution and underflow of nodes.
Chap 13(dynamic memory allocation)
Chap 13(dynamic memory allocation)Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science and Technology University This document discusses dynamic memory allocation and linked lists. It describes functions like malloc, calloc, free, and realloc for allocating and releasing memory at runtime. It also explains the concepts of linked lists, where each node contains data and a pointer to the next node, allowing flexible growth and rearrangement but slower random access than arrays.
B tree
B treeRajendran The document discusses B-trees, which are self-balancing search trees used to store large datasets. B-trees overcome limitations of storing data in memory by keeping the tree partially balanced and stored on disk. The document outlines properties of B-trees including that internal nodes must have a minimum number of children based on the tree's order, and that inserting data may cause nodes to split and keys to propagate up the tree to maintain balance.
05 ds and algorithm session_07
05 ds and algorithm session_07Niit Care The document discusses implementing a singly-linked list to store prime numbers between 1 and 10,00,000. It explains that a linked list allows dynamic memory allocation as nodes are added, with each node containing a data field and link to the next node. To insert a new prime number, a node is allocated, its data field is set, and it is added to the end of the linked list by making the current last node's next pointer point to the new node. This allows storing an unknown number of prime numbers without predefined array size limits.
Linked Lists
Linked ListsHafiz Umair 1) Linked lists are a data structure that store elements in individual nodes that are connected to each other using pointers. This allows for dynamic memory allocation as opposed to static allocation in arrays.
2) The basic operations on linked lists include creation, insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, concatenation, and displaying the list. Insertion and deletion can be done at the beginning, middle, or end of the list.
3) Linked lists are useful for applications that require dynamic memory allocation, like stacks, queues, and storing objects that may vary in number, such as images to burn to a CD.
Ad
Similar to Data Structure (Dynamic Array and Linked List) (20)
Double linked list c8
Double linked list c8Omar Al-Sabek This document discusses the Pascal programming language and some of its key features including sets, records, files, pointers, linked lists, and units. It then focuses on describing the structure of a doubly linked list in Pascal which includes the data type, references to the next and previous elements, and examples of inserting and deleting elements from the list. Procedures are provided for inserting elements into the list in different locations and deleting elements from the start, end, or middle of the list.
Linked lists c7
Linked lists c7Omar Al-Sabek The document discusses linked lists and procedures for manipulating them. It defines linked lists as arrays with a non-constant size, where each element contains data and a reference to the next element. There are two types: single linked lists and double linked lists. Procedures are presented for inserting elements into and deleting elements from single linked lists in different positions.
Ppt of operations on one way link list
Ppt of operations on one way link listSukhdeep Kaur This document discusses various operations that can be performed on one-way linked lists including traversing, searching, inserting, deleting, copying, merging, and splitting linked lists. It provides algorithms and explanations for each operation using diagrams and pseudocode. Key points covered include inserting and deleting nodes from the beginning, end, or a particular position of a linked list, as well as merging two sorted linked lists into a single sorted list.
Ppt of operations on one way link list
Ppt of operations on one way link listSukhdeep Kaur This document discusses various operations that can be performed on one-way linked lists including traversing, searching, inserting, deleting, copying, merging, and splitting linked lists. It provides algorithms and explanations for each operation using diagrams and pseudocode. Key points covered include inserting and deleting nodes from the beginning, end, or a particular position of a linked list, as well as merging two sorted linked lists into a single sorted list.
single linked list
single linked listSathasivam Rangasamy This document discusses the implementation of a single linked list data structure. It describes the nodes that make up a linked list, which have an info field to store data and a next field pointing to the next node. The document outlines different ways to represent linked lists, including static arrays and dynamic pointers. It also provides algorithms for common linked list operations like traversing, inserting, and deleting nodes from the beginning, end, or a specified position within the list.
Team 9
Team 9Sathasivam Rangasamy This document discusses doubly linked lists and provides information about their structure and basic operations. It describes that a doubly linked list contains nodes with two pointer fields that link to both the previous and next nodes. The document outlines how to represent a doubly linked list with a head node and describes the insertion and deletion algorithms. It explains that insertion requires updating the forward and backward pointers of the new and existing nodes. Deletion locates the target node and changes the pointers of the predecessor and successor nodes to bypass the deleted node.
Data Structures_Linked List
Data Structures_Linked ListThenmozhiK5 The document discusses linked lists, which are a data structure made up of nodes that are connected to each other via links. Each node contains a data field and a link field pointing to the next node. The last node's link points to null to indicate the end of the list. Linked lists allow dynamic memory allocation and easy insertion/deletion of nodes. Common operations on linked lists include traversing the list, inserting nodes, deleting nodes, and searching for a node. Doubly linked lists are also discussed, where each node contains links to both the previous and next nodes.
Linked List Basics
Linked List BasicsKaustavRoy40 A linked list is a dynamic data structure composed of nodes that are linked using pointers. Each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. Linked lists allow for efficient insertion and removal of nodes and can grow and shrink dynamically as needed. The document discusses different types of linked lists including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists. It provides algorithms and diagrams for common linked list operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, merging lists, and more.
Presentation1.pptx
Presentation1.pptxKoteswari Kasireddy The document describes algorithms for common linked list operations:
1) Creating a linked list by adding nodes to the start pointer and linking each new node to the previous.
2) Traversing a linked list by using a current pointer to iterate through each node until the end is reached.
3) Inserting a new node at different positions - the beginning, end, or a specified position in between - by linking the new node accordingly in the list.
algorithms_in_linkedlist.pptx
algorithms_in_linkedlist.pptxKoteswari Kasireddy The document describes algorithms for common linked list operations:
1) Creating a linked list by adding nodes to the start pointer and linking each new node to the previous.
2) Traversing a linked list by using a current pointer to iterate through each node until the end is reached.
3) Inserting a new node at the beginning by linking it to the start pointer and making it the new start node.
algorithms_in_linkedlist (1).pdf
algorithms_in_linkedlist (1).pdfKoteswari Kasireddy The document describes algorithms for creating and manipulating linked lists. It includes algorithms for creating a linked list, traversing a linked list, inserting and deleting nodes at different positions, and searching a linked list. It also includes a brief description of garbage collection, explaining that it is the automatic reclamation of unused memory to avoid memory accumulation.
Ds006 linked list- delete from front
Ds006 linked list- delete from frontjyoti_lakhani This C++ program implements functions to perform operations on a singly linked list:
1. A create_node function allocates and returns a new node with the given value.
2. An insert_begin function inserts a new node at the beginning of the list, updating the start pointer.
3. A delete_begin function deletes the node at the beginning of the list, updating the start pointer and deallocating the node.
4. A display function traverses the list and prints out the values of each node.
linked list1.ppt linked list ppts and notes
linked list1.ppt linked list ppts and notesnisharaheja1986 The document provides an overview of linked lists, highlighting their structure, advantages over arrays, and memory management, including insertion and deletion operations. It details algorithms for traversing, counting, and searching linked lists, along with memory-related concepts such as garbage collection, overflow, and underflow. Procedures for inserting new nodes in various positions are also described, emphasizing the dynamic nature of linked lists compared to other data structures.
please i need help Im writing a program to test the merge sort alg.pdf
please i need help Im writing a program to test the merge sort alg.pdfezonesolutions The document contains Java and C code for implementing and testing a merge sort algorithm for linked lists. It includes classes for linked lists, nodes, and elements, as well as methods for inserting and deleting nodes, printing lists, and sorting operations. The test program prompts the user for integers, stores them in a linked list, and demonstrates the sorting functionality.
linkrd_list.pdf
linkrd_list.pdfISHAN194169 Linked lists are a data structure that store elements non-contiguously in memory. Each element, called a node, contains data and a pointer to the next node. There are several types of linked lists including singly linked lists where each node has a next pointer, doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers, and circular linked lists where the last node points to the first. Common operations on linked lists include traversing, inserting nodes, deleting nodes, and searching for elements. Insertion and deletion have lower time complexity than arrays since they only require updating pointers rather than shifting elements.
Linked Lists.pdf
Linked Lists.pdfKaynattariq1 The document provides a comprehensive guide on linked list data structures, including their definitions, types (single, double, and circular linked lists), and advantages over arrays. It details the basic operations involved such as insertion and deletion of nodes, along with the implementation in C++. Additionally, the document includes extensive explanations and steps for adding and deleting nodes in various scenarios.
linkedlist.pptx
linkedlist.pptxMeghaKulkarni27 Heap memory is a common pool of dynamic memory used for allocating objects and data structures during program execution. It is part of RAM and allows for longer-lived allocations compared to stack memory. When the heap is full, garbage collection clears unused objects to free up space. Linked lists are linear data structures composed of nodes containing a data field and a pointer to the next node. They allow for dynamic sizes and efficient insertions/deletions unlike arrays. Doubly linked lists include pointers to both the next and previous nodes, allowing traversal in both directions but requiring more space.
data structures and applications power p
data structures and applications power pMeghaKulkarni27 A linked list is a linear data structure where nodes are linked using pointers. Each node contains a data field for storing elements and a pointer field for linking to the next node. There are different types of linked lists including singly linked lists where each node has a pointer to the next node, doubly linked lists where each node has a pointer to both the next and previous nodes, and circular linked lists where the last node is linked to the first node. Common operations on linked lists include insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, and sorting of nodes. Linked lists have advantages over arrays for dynamic memory allocation and efficient insertion/deletion but have disadvantages for random access and memory usage.
Bca data structures linked list mrs.sowmya jyothi
Bca data structures linked list mrs.sowmya jyothiSowmya Jyothi 1. Linked lists are a linear data structure where each element contains a data field and a pointer to the next element. This allows flexible insertion and deletion compared to arrays.
2. Each node of a singly linked list contains a data field and a next pointer. Traversal follows the next pointers from head to tail. Doubly linked lists add a back pointer for bidirectional traversal.
3. Common operations on linked lists include traversal, search, insertion at head/specific point, and deletion by adjusting pointers. Memory for new nodes comes from a free list, and deleted nodes return there.
Engineering.CSE.DataStructure.Linkedlist.notes
Engineering.CSE.DataStructure.Linkedlist.noteslimev72215 The document discusses linked lists in data structures, explaining their representation and operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal. It outlines different types of linked lists (singly, doubly, circular) and highlights their advantages and disadvantages compared to arrays. Additionally, it delves into memory management techniques like garbage collection and overflow/underflow scenarios in linked lists.
Ad
More from Adam Mukharil Bachtiar (20)
Materi 8 - Data Mining Association Rule.pdf
Materi 8 - Data Mining Association Rule.pdfAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini menjelaskan metode data mining association rule, termasuk penggunaan nilai support dan confidence untuk mengekstraksi hubungan antar item. Algoritma yang dibahas adalah Apriori dan FP-Growth, dengan implementasi langkah-langkah untuk mengidentifikasi strong association rules. Penjelasan meliputi pembuatan frequent itemsets dan penerapan conditional pattern base untuk membentuk pola yang signifikan.
Clean Code - Formatting Code
Clean Code - Formatting CodeAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen tersebut memberikan tips untuk membuat formatting kode program yang baik agar mudah dibaca dan dipahami. Terdapat dua jenis formatting, yaitu vertical dan horizontal formatting. Secara vertical, kode perlu diatur dengan memperhatikan konsep-konsep, jarak antar konsep, kerapatan kode yang berkaitan, dan letak deklarasi dan pemanggilan fungsi. Secara horizontal, perlu memperhatikan pemberian jarak, penyamaan baris, dan pengindentasian untuk membedakan struktur program.
Clean Code - Clean Comments
Clean Code - Clean CommentsAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas pentingnya komentar dalam kode pemrograman dan memberikan tips untuk menulis komentar yang efektif. Tips tersebut mencakup penggunaan komentar untuk legalitas, informasi, peringatan, dan dokumentasi, serta menghindari komentar yang berlebihan atau menyesatkan. Penulis menekankan bahwa komentar seharusnya tidak digunakan untuk menjelaskan kode yang sudah jelas dan lebih baik menggunakan alat versioning untuk mencatat perubahan kode.
Clean Method
Clean MethodAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini menjelaskan prinsip-prinsip untuk membuat metode yang bersih dan efisien dalam pemrograman, termasuk pentingnya ukuran kecil metode dan pemisahan logika. Beberapa tips mencakup penggunaan blok dan indentasi yang tepat, penerapan aturan stepdown, dan penghindaran parameter berlebihan. Selain itu, dokumen menekankan pentingnya menghindari efek samping dalam metode dan perlunya menangani kesalahan dengan menggunakan exception.
Clean Code and Design Pattern - Meaningful Names
Clean Code and Design Pattern - Meaningful NamesAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen tersebut memberikan tips-tips untuk membuat nama variabel, fungsi, kelas, dan paket yang baik dalam pembuatan kode program. Beberapa tips utama adalah menggunakan nama yang jelas maksudnya, hindari penggunaan encoding, gunakan kata benda untuk nama kelas dan verba untuk nama metode, serta tambahkan konteks yang bermakna.
Model Driven Software Development
Model Driven Software DevelopmentAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas tentang model driven software development dengan penekanan pada penggunaan diagram UML untuk memodelkan kebutuhan perangkat lunak. Berbagai perspektif pemodelan seperti use case, activity, dan class diagram dijelaskan secara detail untuk mendukung analisis dan perancangan sistem. Selain itu, terdapat tips dan contoh dalam menyusun user story serta analisis fungsional perangkat lunak.
Scrum: How to Implement
Scrum: How to ImplementAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini menjelaskan implementasi metode scrum dalam pengembangan perangkat lunak, yang merupakan bagian dari siklus hidup pengembangan perangkat lunak (SDLC). Scrum membagi proyek menjadi sprint, dimana tim berkolaborasi untuk menghasilkan produk yang dapat diluncurkan, dengan fokus pada backlog dan aturan kolaborasi. Proses termasuk perencanaan sprint, pengelolaan backlog, dan tinjauan hasil untuk meningkatkan efektivitas pengembangan.
Pengujian Perangkat Lunak
Pengujian Perangkat LunakAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang pengujian perangkat lunak, termasuk definisi pengujian perangkat lunak, tujuan pengujian, jenis pengujian seperti manual testing, automated testing, unit testing, integration testing, serta metode pengujian seperti white box testing dan black box testing.
Data Mining Clustering
Data Mining ClusteringAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas tentang data mining, khususnya teknik clustering, yang mengelompokkan data berdasarkan kesamaan karakteristik. Proses ini melibatkan algoritma k-means, yang mencakup langkah-langkah penting seperti memilih centroid, menghitung jarak antar data, dan menentukan cluster terdekat. Selain itu, dihitung juga nilai variasi antar cluster dan dalam cluster sebagai acuan untuk menghentikan iterasi.
Data Mining Klasifikasi (Updated 30 Desember 2020)
Data Mining Klasifikasi (Updated 30 Desember 2020)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas dasar-dasar data mining klasifikasi, terutama dalam konteks supervised learning yang digunakan untuk memprediksi kelas data baru. Dikenalkan beberapa algoritma seperti Naïve Bayes, K-NN, dan ID3, beserta proses perhitungan yang diperlukan untuk klasifikasi data. Penjelasan rinci tentang langkah-langkah dan contoh penerapan setiap algoritma juga diuraikan.
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Dynamic Programming
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Dynamic ProgrammingAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen tersebut membahas algoritma program dinamis untuk menentukan lintasan terpendek antara dua simpul dalam sebuah graf. Metode yang digunakan adalah program dinamis mundur dimana permasalahan dibagi menjadi beberapa tahap dan dihitung secara mundur untuk menentukan nilai optimal pada setiap tahap. Hasil akhir adalah terdapat tiga lintasan terpendek dengan panjang 11 antara simpul 1 dan 10.
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Divide and Conquer
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Divide and ConquerAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Teks tersebut membahas strategi algoritma Divide and Conquer untuk memecahkan masalah. Strategi ini membagi masalah menjadi submasalah kecil, memecahkan submasalah tersebut secara rekursif, lalu menggabungkan hasilnya untuk mendapatkan solusi masalah awal. Dua contoh masalah yang dijelaskan adalah mencari nilai maksimum dan minimum dalam tabel, serta mencari pasangan titik terdekat dalam himpunan titik.
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Greedy
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma GreedyAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas strategi algoritma greedy sebagai pendekatan untuk menyelesaikan permasalahan optimasi, menyoroti karakteristik, kelebihan, dan kelemahan dari metode ini. Beberapa contoh penerapan algoritma greedy seperti penukaran uang, knapsack 1/0, dan pelayanan antrian disajikan untuk menjelaskan penggunaannya dalam mencari solusi optimal. Meskipun seringkali memberikan solusi hampiran yang baik, algoritma greedy tidak selalu menjamin solusi paling optimal.
Analisis Algoritma - Penerapan Strategi Algoritma Brute Force
Analisis Algoritma - Penerapan Strategi Algoritma Brute ForceAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas penerapan strategi algoritma brute force dalam dua masalah yaitu exhaustive search dan 1/0 knapsack. Untuk masalah exhaustive search, digunakan teknik enumerasi untuk menemukan sirkuit hamilton dengan bobot minimum, sedangkan untuk 1/0 knapsack, enumerasi digunakan untuk memilih objek dengan keuntungan maksimum tanpa melebihi kapasitas knapsack. Contoh yang diberikan menunjukkan langkah-langkah detail dan solusi optimal untuk kedua masalah tersebut.
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Brute Force
Analisis Algoritma - Strategi Algoritma Brute ForceAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas algoritma brute force sebagai strategi dasar dalam pemecahan masalah, dengan karakteristik yang cenderung sederhana dan mudah diimplementasikan. Meskipun memiliki kekurangan seperti lambat dan tidak kreatif, brute force dapat digunakan untuk beberapa masalah penting seperti pencarian dan pengurutan. Beberapa contoh penerapannya juga disertakan dalam dokumen.
Analisis Algoritma - Kelas-kelas Dasar Efisiensi Algoritma
Analisis Algoritma - Kelas-kelas Dasar Efisiensi AlgoritmaAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas analisis efisiensi algoritma dengan mengelompokkannya ke dalam kelas-kelas efisiensi dasar, termasuk kelas algoritma polinomial dan eksponensial. Kelas efisiensi dasar dijelaskan berdasarkan kompleksitas waktu pelaksanaan algoritma, contohnya meliputi algoritma konstan, logaritmik, linear, dan eksponensial. Selain itu, dijelaskan juga konsep masalah yang dapat dipecahkan secara polinomial dan yang tidak, serta contoh praktis seperti masalah travelling salesman.
Analisis Algoritma - Teorema Notasi Asimptotik
Analisis Algoritma - Teorema Notasi AsimptotikAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas analisis algoritma dengan fokus pada notasi asimptotik, khususnya big oh, untuk menghitung efisiensi waktu. Teorema dan aturan perhitungan dijelaskan, termasuk cara menangani berbagai jenis instruksi dan pengulangan dalam algoritma. Contoh aplikasi teorema dan aturan perhitungan untuk menghitung kompleksitas waktu juga disediakan.
Analisis Algoritma - Notasi Asimptotik
Analisis Algoritma - Notasi AsimptotikAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas analisis algoritma dengan fokus pada notasi asimptotik yang digunakan untuk menilai efisiensi waktu. Tiga jenis notasi asimptotik yang dijelaskan adalah Big O, Big Omega, dan Big Theta, masing-masing menunjukkan tingkat pertumbuhan fungsi. Contoh dan definisi formal disertakan untuk menjelaskan cara penggunaan notasi tersebut dalam analisis algoritma.
Activity Diagram
Activity DiagramAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini menjelaskan tentang pemodelan process view menggunakan activity diagram dalam UML, yang mencakup berbagai notasi dan simbol, seperti initial state, final state, dan swimlanes. Selain itu, dijelaskan juga tentang penggambaran objek, penggunaan signals, dan notasi untuk mengelola aksi dalam diagram aktivitas. Informasi juga mencakup pengenalan konsep interrupt dan flow final untuk mengendalikan alur aktivitas.
UML dan Use Case View
UML dan Use Case ViewAdam Mukharil Bachtiar Dokumen ini membahas tentang penggunaan UML dan use case view dalam pemodelan perangkat lunak dalam OOAD. UML menggambarkan sistem dari berbagai perspektif, termasuk fungsionalitas, interaksi antar bagian, serta organisasi dan desain sistem. Use case view mendeskripsikan fungsionalitas sistem dari sudut pandang aktor, dengan diagram dan deskripsi yang jelas mengenai kondisi dan alur eksekusi use case.
Recently uploaded (20)
Migrating to Azure Cosmos DB the Right Way
Migrating to Azure Cosmos DB the Right WayAlexander (Alex) Komyagin In this session we cover the benefits of a migration to Cosmos DB, migration paths, common pain points and best practices. We share our firsthand experiences and customer stories. Adiom is the trusted partner for migration solutions that enable seamless online database migrations from MongoDB to Cosmos DB vCore, and DynamoDB to Cosmos DB for NoSQL.
Open Source Software Development Methods
Open Source Software Development MethodsVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Open Source Software Development Methods
What is data visualization and how data visualization tool can help.pdf
What is data visualization and how data visualization tool can help.pdfVarsha Nayak An open source data visualization tool enhances this process by providing flexible, cost-effective solutions that allow users to customize and scale their visualizations according to their needs. These tools enable organizations to make data-driven decisions with complete freedom from proprietary software limitations. Whether you're a data scientist, marketer, or business leader, understanding how to utilize an open source data visualization tool can significantly improve your ability to communicate insights effectively.
How Insurance Policy Management Software Streamlines Operations
How Insurance Policy Management Software Streamlines OperationsInsurance Tech Services Insurance policy management software transforms complex, manual insurance operations into streamlined, efficient digital workflows, enhancing productivity, accuracy, customer service, and profitability for insurers. Visit https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/policy-management-software for more details!
Code and No-Code Journeys: The Coverage Overlook
Code and No-Code Journeys: The Coverage OverlookApplitools Explore practical ways to expand visual and functional UI coverage without deep coding or heavy maintenance in this session. Session recording and more info at applitools.com
Agile Software Engineering Methodologies
Agile Software Engineering MethodologiesGaurav Sharma Software Engineering Process, Notation & Tools Introduction
Software Testing & it’s types (DevOps)
Software Testing & it’s types (DevOps)S Pranav (Deepu) NTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE TESTING
• Definition:
• Software testing is the process of evaluating and
verifying that a software application or system meets
specified requirements and functions correctly.
• Purpose:
• Identify defects and bugs in the software.
• Ensure the software meets quality standards.
• Validate that the software performs as intended in
various scenarios.
• Importance:
• Reduces risks associated with software failures.
• Improves user satisfaction and trust in the product.
• Enhances the overall reliability and performance of
the software
Advanced Token Development - Decentralized Innovation
Advanced Token Development - Decentralized Innovationarohisinghas720 The world of blockchain is evolving at a fast pace, and at the heart of this transformation lies advanced token development. No longer limited to simple digital assets, today’s tokens are programmable, dynamic, and play a crucial role in driving decentralized applications across finance, governance, gaming, and beyond.
MOVIE RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM, UDUMULA GOPI REDDY, Y24MC13085.pptx
MOVIE RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM, UDUMULA GOPI REDDY, Y24MC13085.pptxMaharshi Mallela Movie recommendation system is a software application or algorithm designed to suggest movies to users based on their preferences, viewing history, or other relevant factors. The primary goal of such a system is to enhance user experience by providing personalized and relevant movie suggestions.
Artificial Intelligence Applications Across Industries
Artificial Intelligence Applications Across IndustriesSandeepKS52 Artificial Intelligence is a rapidly growing field that influences many aspects of modern life, including transportation, healthcare, and finance. Understanding the basics of AI provides insight into how machines can learn and make decisions, which is essential for grasping its applications in various industries. In the automotive sector, AI enhances vehicle safety and efficiency through advanced technologies like self-driving systems and predictive maintenance. Similarly, in healthcare, AI plays a crucial role in diagnosing diseases and personalizing treatment plans, while in financial services, it helps in fraud detection and risk management. By exploring these themes, a clearer picture of AI's transformative impact on society emerges, highlighting both its potential benefits and challenges.
wAIred_RabobankIgniteSession_12062025.pptx
wAIred_RabobankIgniteSession_12062025.pptxSimonedeGijt In today's world, artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the way we learn.
This talk will explore how we can use AI tools to enhance our learning experiences, by looking at some (recent) research that has been done on the matter.
But as we embrace these new technologies, we must also ask ourselves:
Are we becoming less capable of thinking for ourselves?
Do these tools make us smarter, or do they risk dulling our critical thinking skills?
This talk will encourage us to think critically about the role of AI in our education. Together, we will discover how to use AI to support our learning journey while still developing our ability to think critically.
Step by step guide to install Flutter and Dart
Step by step guide to install Flutter and DartS Pranav (Deepu) Flutter is basically Google’s portable user
interface (UI) toolkit, used to build and
develop eye-catching, natively-built
applications for mobile, desktop, and web,
from a single codebase. Flutter is free, open-
sourced, and compatible with existing code. It
is utilized by companies and developers
around the world, due to its user-friendly
interface and fairly simple, yet to-the-point
commands.
Looking for a BIRT Report Alternative Here’s Why Helical Insight Stands Out.pdf
Looking for a BIRT Report Alternative Here’s Why Helical Insight Stands Out.pdfVarsha Nayak The search for an Alternative to BIRT Reports has intensified as companies face challenges with BIRT's steep learning curve, limited visualization capabilities, and complex deployment requirements. Organizations need reporting solutions that offer intuitive design interfaces, comprehensive analytics features, and seamless integration capabilities – all while maintaining the reliability and performance that enterprise environments demand.
Reimagining Software Development and DevOps with Agentic AI
Reimagining Software Development and DevOps with Agentic AIMaxim Salnikov Key announcements about Developer Productivity from Microsoft Build 2025
Milwaukee Marketo User Group June 2025 - Optimize and Enhance Efficiency - Sm...
Milwaukee Marketo User Group June 2025 - Optimize and Enhance Efficiency - Sm...BradBedford3 Inspired by the Adobe Summit hands-on lab, Optimize Your Marketo Instance Performance, review the recording from June 5th to learn best practices that can optimize your smart campaign and smart list processing time, inefficient practices to try to avoid, and tips and tricks for keeping your instance running smooth!
You will learn:
How smart campaign queueing works, how flow steps are prioritized, and configurations that slow down smart campaign processing.
Best practices for smart list and smart campaign configurations that yield greater reliability and processing efficiencies.
Generally recommended timelines for reviewing instance performance: walk away from this session with a guideline of what to review in Marketo and how often to review it.
This session will be helpful for any Marketo administrator looking for opportunities to improve and streamline their instance performance. Be sure to watch to learn best practices and connect with your local Marketo peers!
Who will create the languages of the future?
Who will create the languages of the future?Jordi Cabot Will future languages be created by language engineers?
Can you "vibe" a DSL?
In this talk, we will explore the changing landscape of language engineering and discuss how Artificial Intelligence and low-code/no-code techniques can play a role in this future by helping in the definition, use, execution, and testing of new languages. Even empowering non-tech users to create their own language infrastructure. Maybe without them even realizing.
Wondershare PDFelement Pro 11.4.20.3548 Crack Free Download
Wondershare PDFelement Pro 11.4.20.3548 Crack Free DownloadPuppy jhon ➡ 🌍📱👉COPY & PASTE LINK👉👉👉 ➤ ➤➤ https://drfiles.net/
Wondershare PDFelement Professional is professional software that can edit PDF files. This digital tool can manipulate elements in PDF documents.
Data Structure (Dynamic Array and Linked List)
- 1. Dynamic Array and Linked List Adam M.B.
- 4. Array which can be managed dynamically in memory (its size). To order the place in memory, it uses POINTER. Description
- 5. Declaration Type Pengenal = ↑Simpul Simpul = TipeData Atau NamaVariabel : ↑TipeData
- 6. Example (1) Kamus: Bilangan : ↑integer Nama : ↑string
- 7. Example (2) Kamus: Type Point = ↑Data Data = Record < Nim : integer, Nama : string, Nilai : real > EndRecord DataMhs : point
- 9. Definition • Alloc is statement that can be used to order place in memory while program is running. • Dealloc is statement that can be used to delete place which had been ordered while program is running.
- 10. Ilustration in Memory Alloc(DataMhs) Still Empty DataMhs Nil
- 11. OPERATION
- 12. Case Kamus: Type Point = ↑Data Data = Record < NamaMhs : string, Jurusan : string > EndRecord T1,T2: point
- 14. Copy Pointer (Cont’d) T1.NamaMhs ‘Adam’ T1.Jurusan ‘Teknik Informatika’ T2 T1
- 15. Copy Pointer (Cont’d) T2 T1 T2 T1
- 16. Copy Value T1 T2 T1 T2
- 18. LINKED LIST
- 19. DEFINITION
- 20. Data structure that is prepared sequentially, dynamically, and infinite. Linked list is connected by pointer. Description
- 21. Array VS Linked List ARRAY LINKED LIST Static Dynamic Insert and Delete are finite Insert and Delete are infinite Random Access Sequential Access Delete element is only delete value Delete element is truly delete space
- 22. • Single Linked List • Double Linked List • Circular Linked List Types of Linked List
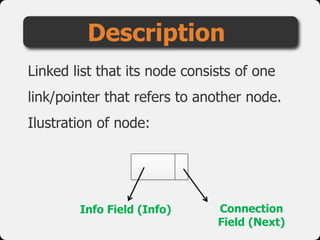
- 24. Linked list that its node consists of one link/pointer that refers to another node. Ilustration of node: Description Info Field (Info) Connection Field (Next)
- 25. Declaration Kamus: Type NamaPointer = ↑Simpul Simpul = Record < InfoField : TipeData, ConnectionField : NamaPointer > EndRecord NamaVarPointer : NamaPointer
- 26. Example Kamus: Type Point = ↑Simpul Simpul = Record < Info : integer, Next : Point > EndRecord Awal,Akhir : Point
- 27. OPERATION
- 28. • Creation • Insertion • Delete • Traversal • Searching • Sorting • Destroy
- 29. Pointer (awal and akhir) is given nil as their value. Creation awal akhir awal nil akhir nil
- 30. • If list is empty (awal = nil). Front Insertion baru baru 1 baru 1 awal akhir alloc(baru) baru.next nil baru.info 1 awal baru akhir baru
- 31. • If list isn’t empty (awal ≠ nil). For example, there is list that has two nodes: Front Insertion (cont’d) akhirawal 2 3 One node will be inserted in front of list: 1baru alloc(baru) baru.info 1
- 32. New node will be inserted before the node that was refered by awal. Front Insertion (cont’d) baru 1 awal 2 akhir 3 baru↑.next awal
- 33. After new node was inserted, move awal to new node. Front Insertion (cont’d) awal 2 3 baru 1 akhir awal baru
- 34. The last result for front insertion if linked list wasn’t empty: Front Insertion (cont’d) baru 1 awal 2 3 akhir
- 35. Procedure SisipDepanSingle(Input elemen : tipedata, I/O awal, akhir : nama_pointer) {I.S. : data yang akan disisipkan (elemen), pointer penunjuk awal dan pointer penunjuk akhir sudah terdifinisi} {F.S. : menghasilkan satu simpul yang disisipkan di depan pada single linked list} Kamus : baru : nama_pointer Algoritma : alloc(baru) baru↑.info elemen If (awal = nil) Then baru↑.next nil akhir baru Else baru↑.next awal EndIf awal baru EndProcedure
- 36. • If list is empty (awal = nil) the process is same as front insertion if linked list is empty. Back Insertion
- 37. • If list isn’t empty (awal ≠ nil). For example, there is list that has two nodes: Back Insertion (cont’d) awal 3 2 akhir New node that will be inserted: baru 1 alloc(baru) baru.next nil baru.info 1
- 38. New node will be inserted after the node that was refered by akhir. Back Insertion (cont’d) baru 1 akhirawal 3 2 akhir.next baru
- 39. Move akhir to new node. Back Insertion (cont’d) akhir baru akhirawal 3 2 baru 1
- 40. The last result for back insertion if linked list wasn’t empty: Back Insertion (cont’d) awal 3 2 baru 1 akhir
- 41. Procedure SisipBelakangSingle(Input elemen : tipedata, I/O awal, akhir : nama_pointer) {I.S. : data yang akan disisipkan (elemen), pointer penunjuk awal dan pointer penunjuk akhir sudah terdifinisi} {F.S. : menghasilkan satu simpul yang disisipkan di belakang pada single linked list} Kamus : baru : nama_pointer Algoritma : alloc(baru) baru↑.info elemen baru↑.next nil If (awal = nil) Then awal baru Else akhir↑.next baru EndIf akhir baru EndProcedure
- 42. • If list is empty (awal = nil) the process is same as front insertion if linked list is empty. Middle Insertion
- 43. • If list isn’t empty (awal ≠ nil). Middle Insertion (cont’d) awal 2 54 akhir 3 New node that will be inserted after 4: baru 1 alloc(baru) baru.info 1
- 44. Search node 4 using sequential search and bantu pointer. Middle Insertion (cont’d) bantu baru 1 awal 2 54 akhir 3 bantu
- 45. Connect the connection field from new node to the neighbour node of node that was refered by bantu. Middle Insertion (cont’d) baru.next bantu↑.next baru 1 awal 2 54 akhir 3 bantu
- 46. After new node was connected with node 4 then refer the connection field of node that was refered by bantu to new node. Middle Insertion (cont’d) bantu.next baru bantuawal 2 baru 1 4 akhir 3 5
- 47. The last result for middle insertion if linked list wasn’t empty: Middle Insertion (cont’d) bantu baru 1 2 akhir 5 awal 43
- 48. Procedure SisipTengahSingle(Input elemen : tipedata, I/O awal, akhir : nama_pointer) {I.S. : data yang akan disisipkan (elemen), pointer penunjuk awal dan pointer penunjuk akhir sudah terdifinisi} {F.S. : menghasilkan satu simpul yang disisipkan di tengah pada single linked list} Kamus : baru,bantu : nama_pointer ketemu : boolean datasisip : tipedata Algoritma : If (awal = nil) Then alloc(baru) baru↑.info elemen baru↑.next nil
- 49. awal baru akhir baru Else Input(datasisip) bantu awal ketemu false While (not ketemu and bantu ≠ nil) do If (datasisip = bantu↑.info) Then ketemu true Else bantu bantu↑.next EndIf EndWhile
- 50. If (ketemu) Then alloc(baru) baru↑.info elemen If (bantu = akhir) Then sisip_belakang_single(elemen,awal,akhir) Else baru↑.next bantu↑.next bantu↑.next baru EndIf Else Output(“Data yang akan disisipkan tidak ada”); EndIf EndIf EndProcedure
- 51. • Delete one node in beggining of linked list if linked list has only one node (awal = akhir). Front Deletion awal akhir 1
- 52. If deletion happens in linked list with one node then linked list will be empty. Front Deletion (cont’d) awal akhir phapus elemen 1phapus phapus awal elemen phapus .info dealloc(phapus) awal nil akhir nil 1 awal akhir
- 53. • If linked list has more than one node (awal ≠ akhir). For example, linked list has two nodes. Front Deletion (cont’d) awal 2 3 akhir
- 54. Front Deletion (cont’d) phapus awal 2 3 akhir elemen awal 2 3phapus akhir phapus awal elemen phapus.info awal awal.next dealloc(phapus)
- 55. The last result for front deletion if linked list has more than one node: Front Deletion (cont’d) phapus awal 3 akhir 2
- 56. Procedure HapusDepanSingle(Output elemen : tipedata, I/O awal, akhir : nama_pointer) {I.S. : pointer penunjuk awal dan pointer penunjuk akhir sudah terdifinisi} {F.S. : menghasilkan single linked list yang sudah dihapus satu simpul di depan} Kamus : phapus : nama_pointer Algoritma : phapus awal elemen baru↑.info If (awal = akhir) Then awal nil akhir nil Else awal awal ↑.next EndIf dealloc(phapus) EndProcedure
- 57. • Delete one node in back of linked list if linked list has only one node (awal = akhir). This process is same as front deletion if linked list has only one node. Back Deletion
- 58. • If linked list has more than one node (awal ≠ akhir). For example, linked list has three nodes. Back Deletion (cont’d) awal 1 32 akhir
- 59. Back Deletion (cont’d) phapus awal 1 3 akhir 2 elemen phapus phapusakhirawal 1 32 phapus awal elemen akhir.info phapus phapus.next phapus phapus.next akhir phapus
- 60. Back Deletion (cont’d) awal 1 3 phapus 2 akhir akhir.next nil dealloc(phapus)
- 61. The last result for back deletion if linked list has more than one node: Back Deletion (cont’d) phapus phapusakhir 3 awal 12
- 62. Procedure HapusBelakangSingle(Output elemen : tipedata, I/O awal, akhir : nama_pointer) {I.S. : pointer penunjuk awal dan pointer penunjuk akhir sudah terdifinisi} {F.S. : menghasilkan single linked list yang sudah dihapus satu simpul di belakang} Kamus : phapus : nama_pointer Algoritma : phapus awal elemen baru↑.info If (awal = akhir) Then awal nil akhir nil
- 63. Else while (phapus↑.next ≠ akhir) do phapus phapus↑.next endwhile akhir phapus phapus phapus↑.next akhir↑.next nil EndIf dealloc(phapus) EndProcedure
- 64. • Delete one node in middle of linked list if linked list has only one node (awal = akhir). This process is same as front deletion if linked list has only one node. Middle Deletion
- 65. • If linked list has more than one node (awal ≠ akhir). For example, linked list has four nodes and user want to delete third node. Middle Deletion (cont’d) awal 2 54 akhir 3
- 66. Search the third node start from the first node. If node is found then save the info of this node to the variable elemen. Middle Deletion (cont’d) phapus posisihapus=2awal 2 54 akhir 3 posisihapus=1 posisihapus=3 phapus elemen elemenphapus.info
- 67. Because the connection field of previous node must be connected to the next node of node that will be deleted so we need pointer bantu that refer the node that will be deleted. Middle Deletion (cont’d) bantuawal 2 54 phapus akhir 3 posisihapus=3
- 68. Connect the connection field of the node that was referred by pointer bantu to the neighbour node. Delete the node that was referred by pointer phapus. Middle Deletion (cont’d) awal 2 54 phapus akhir 3 posisihapus=3bantu bantu.next phapus.next dealloc(phapus)
- 69. The last result for middle deletion if linked list has more than one node: Middle Deletion (cont’d) 5 akhir 2 phapus posisihapus=1posisihapus=2 posisihapus=3 phapus bantuawal 43 43 5 akhir awal
- 70. Operation that visiting all nodes in linked list start from the first node until last node. Traversal awal 2 54 akhir 3 For example, shown the process to output data: • Place one pointer bantu in the first node awa l 2 54 akhir 3 bantu
- 71. The value in info field will be output to screen from the node that was referred by bantu then pointer bantu will move to the next node until all nodes were visited (bantu = nil). Traversal awal 2 54 akhir 3 bantu bantu bantu bantu 3 4 2 5Screen Output:
- 72. Contact Person: Adam Mukharil Bachtiar Informatics Engineering UNIKOM Jalan Dipati Ukur Nomor. 112-114 Bandung 40132 Email: [email protected] Blog: http://adfbipotter.wordpress.com Copyright © Adam Mukharil Bachtiar 2012
