Database Query Using SQL_ip.docx
0 likes708 views
The document provides information on various SQL functions. It discusses functions for sorting query results, performing calculations on aggregate data, grouping data, and filtering groups. Date and string functions are also covered, along with numeric and mathematical functions. Common functions include ORDER BY for sorting, SUM, AVG, COUNT for aggregates, GROUP BY for grouping, and HAVING for filtering groups. NOW() and SYSDATE() are described as functions for returning the current date and time.
1 of 23
Download to read offline






















Ad
Recommended
Chapter 02 functions -class xii



Chapter 02 functions -class xiiPraveen M Jigajinni Functions allow programmers to organize and reuse code. There are three types of functions: built-in functions, modules, and user-defined functions. User-defined functions are created using the def keyword and can take parameters and arguments. Functions can return values and have different scopes depending on if a variable is local or global. Recursion is when a function calls itself, and is useful for breaking down complex problems into simpler sub-problems. Common recursive functions calculate factorials, Fibonacci numbers, and generate the Pascal's triangle.
Functions in python



Functions in pythoncolorsof Functions allow programmers to organize code into reusable blocks. There are built-in functions and user-defined functions. Functions make code easier to develop, test and reuse. Variables inside functions can be local, global or nonlocal. Parameters pass data into functions, while functions can return values. Libraries contain pre-defined functions for tasks like mathematics and string manipulation.
String in c programming



String in c programmingDevan Thakur A string is a data type used in programming, such as an integer and floating point unit, but is used to represent text rather than numbers. It is comprised of a set of characters that can also contain spaces and numbers. For example, the word "hamburger" and the phrase "I ate 3 hamburgers" are both strings.
Array in c programming



Array in c programmingMazharul Islam This document discusses arrays in C programming. It defines an array as a collection of the same type of data elements stored in contiguous memory locations that are accessed via an index. It provides the syntax for declaring a 1-dimensional array, which specifies the type, array name, and number of elements. An example declares and initializes an integer array of size 5. The document also shows examples of summing the elements of a hardcoded and user-input array using indexing and loops.
Function & Recursion



Function & RecursionMeghaj Mallick Functions and recursion are programming concepts. A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. Functions have a prototype, call, and body. Recursion is a technique where a function calls itself to solve a problem. It breaks the problem into smaller subproblems until it reaches a base case. Recursion uses the call stack to remember the state each time the function calls itself. Tail recursion is when the recursive call is the last thing executed, while head recursion calls itself first.
Function in c program



Function in c programumesh patil The document discusses functions in C programming. It defines functions as self-contained blocks of code that perform a specific task. Functions make a program modular and easier to debug. There are four main types of functions: functions with no arguments and no return value, functions with no arguments but a return value, functions with arguments but no return value, and functions with both arguments and a return value. Functions are called by their name and can pass data between the calling and called functions using arguments.
Python Modules



Python ModulesNitin Reddy Katkam Python modules allow code reuse and organization. A module is a Python file with a .py extension that contains functions and other objects. Modules can be imported and their contents accessed using dot notation. Modules have a __name__ variable that is set to the module name when imported but is set to "__main__" when the file is executed as a script. Packages are collections of modules organized into directories, with each directory being a package. The Python path defines locations where modules can be found during imports.
C++ project



C++ projectSonu S S This document describes a C++ program that calculates employee wages. It contains sections for acknowledgements, introduction, system requirements, source code, output, and conclusions. The program allows the user to enter information for multiple employees, including name, phone number, hours worked, and hourly wage. It then calculates and displays each employee's pay for the week. The program uses arrays to store employee data and functions for the menu, data entry, and report display.
Array in C



Array in CKamal Acharya This document discusses one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays. It defines arrays as data structures that can hold multiple values of the same type stored consecutively in memory. One-dimensional arrays use a single set of indexes, while multi-dimensional arrays have two or more indexes to access elements. The document provides syntax examples and demonstrates how to initialize, read from, and display one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays. It also lists some example programs involving arrays.
File handling in Python



File handling in PythonMegha V The document discusses file handling in Python. It explains that a file is used to permanently store data in non-volatile memory. It describes opening, reading, writing, and closing files. It discusses opening files in different modes like read, write, append. It also explains attributes of file objects like name, closed, and mode. The document also covers reading and writing text and binary files, pickle module for serialization, and working with CSV files and the os.path module.
Strings in C



Strings in CKamal Acharya Strings are arrays of characters that are null-terminated. They can be manipulated using functions like strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp(). The document discusses initializing and reading strings, passing strings to functions, and using string handling functions to perform operations like copying, concatenating, comparing, and reversing strings. It also describes arrays of strings, which are 2D character arrays used to store multiple strings. Examples are provided to demonstrate reading and sorting arrays of strings.
User defined functions in C



User defined functions in CHarendra Singh User defined / Pre-defined functions in C
Function declaration, Function Call, Function definition, Types of functions, Categories of functions
Python tuples and Dictionary



Python tuples and DictionaryAswini Dharmaraj Tuples are immutable sequences like lists but cannot be modified after creation, making them useful for storing fixed data like dictionary keys; they are created using parentheses and accessed using indexes and slices like lists but elements cannot be added, removed, or reassigned. Dictionaries are mutable mappings of unique keys to values that provide fast lookup of values by key and can be used to represent polynomials by mapping powers to coefficients.
Threading in C#



Threading in C#Medhat Dawoud This document discusses multithreading in C#. It introduces threads and multithreading, describing how operating systems allow multitasking and how threads work. It explains that the .NET Framework supports multithreading using the System.Threading namespace and Thread class. It describes properties and methods of the Thread class, potential problems like deadlocks that can occur with multithreading, and solutions like synchronization and locking to prevent issues.
Storage classes in c++



Storage classes in c++Jaspal Singh The document discusses different storage classes in C++ including automatic, external, static, register, and mutable. It provides the syntax and examples of each:
- Automatic variables are declared with auto and have function block scope and lifetime.
- External variables use extern and have whole program global visibility.
- Static variables are declared with static and have whole program lifetime but local visibility.
- Register variables are intended for fast access and declared with register but storage is implementation-defined.
- Mutable variables allow changing class member values in const member functions and are declared with mutable.
Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)



Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)PyData NumPy is a Python library used for working with multidimensional arrays and matrices for scientific computing. It allows fast operations on arrays through optimized C code and is the foundation of the Python scientific computing stack. NumPy arrays can be created in many ways and support operations like indexing, slicing, broadcasting, and universal functions. NumPy provides many useful features for linear algebra, Fourier transforms, random number generation and more.
List in Python



List in PythonSiddique Ibrahim A list in Python is a mutable ordered sequence of elements of any data type. Lists can be created using square brackets [] and elements are accessed via indexes that start at 0. Some key characteristics of lists are:
- They can contain elements of different types
- Elements can be modified, added, or removed
- Common list methods include append(), insert(), remove(), pop(), and sort()
Python - An Introduction



Python - An IntroductionSwarit Wadhe Python An Introduction, A presentation Developed by Swarit Wadhe. This Slide Will Give you basic information about python (Origin, Codes and difference from other languages).
I hope you'll find this helpfull and if you do please share it with your fellows.
Python programming : Classes objects



Python programming : Classes objectsEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd A class is a code template for creating objects. Objects have member variables and have behaviour associated with them. In python a class is created by the keyword class.
An object is created using the constructor of the class. This object will then be called the instance of the class.
Pointers in c++



Pointers in c++Vineeta Garg Pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. It allows dynamic memory allocation and access of memory locations. There are three ways to pass arguments to functions in C++ - pass by value, pass by reference, and pass by pointer. Pass by value copies the value, pass by reference copies the address, and pass by pointer passes the address of the argument. Pointers can also point to arrays or strings to access elements. Arrays of pointers can store multiple strings. References are alternative names for existing variables and any changes made using the reference affect the original variable. Functions can return pointers or references.
Data Structure and Algorithms Arrays



Data Structure and Algorithms ArraysManishPrajapati78 This slide explains some basics concepts of array and operation performed on arrays like searching and sorting.
Functions & Recursion



Functions & RecursionNishant Munjal Functions allow programmers to organize code into self-contained blocks that perform tasks. A function is defined with a name, parameters, and code block. Functions can call other functions or recurse by calling themselves. Recursion involves defining a function that calls itself repeatedly until a base case is reached. Examples of recursive functions include calculating factorials and solving the Tower of Hanoi puzzle by moving disks from one rod to another according to rules.
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithm



Supervised Machine Learning AlgorithmPyingkodi Maran This document provides an overview of supervised machine learning algorithms. It explains that supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data so it can predict the correct output for new input data. Some examples of supervised learning tasks include image classification, disease prediction, and spam detection. Classification algorithms are used for predicting categorical outputs, like dog vs cat images. Regression algorithms predict continuous outputs, like housing prices. Common classification algorithms mentioned are random forest, decision trees, logistic regression, and support vector machines. Linear regression is also discussed as a basic regression algorithm that finds a linear relationship between variables.
Procedures/functions of rdbms



Procedures/functions of rdbmsjain.pralabh The document discusses stored procedures and functions in Oracle databases. It describes how procedures are compiled code stored in the database that can be called from client environments. Procedures allow encapsulating common operations like inserting records or updating salaries. The document provides examples of creating procedures and functions, specifying arguments, debugging errors, and managing dependencies.
Data Structures in Python



Data Structures in PythonDevashish Kumar Data Structures in Python, second in the series of Introduction to Python. Upcoming series will cover Functions and OOPs concept in Python.
Functions in C.pptx



Functions in C.pptxAshwini Raut Functions are fundamental building blocks of C programs, allowing for modular, structured, and efficient code organization.
1 D Arrays in C++



1 D Arrays in C++poonam.rwalia An array is a collection of variables of the same type that are referenced using a common name and contiguous memory locations. One-dimensional arrays allow storing multiple variables of the same type under a single variable name. Linear/sequential search compares each element to the search key while binary search divides the array in half at each step to find the search key faster than linear search.
Windows Server 2008 Active Directory



Windows Server 2008 Active Directoryanilinvns Active Directory is a database that stores information about a network's users, computers, groups, and other network resources. It allows for centralized management of these resources.
A domain controller is a server that responds to authentication requests on the Windows domain. It authenticates users' credentials when they log into the domain network.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open standard protocol that Active Directory supports to make user and resource information widely accessible for management and querying across the network.
SQL.pptx



SQL.pptxMrHello6 The document discusses aggregate functions in SQL such as SUM, AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN. It provides examples of using these functions to calculate totals, averages, counts and find maximum and minimum values from columns in tables. It also covers the use of the GROUP BY clause to perform aggregate calculations on grouped data and the HAVING clause to filter groups.
Introduction to Oracle Functions--(SQL)--Abhishek Sharma



Introduction to Oracle Functions--(SQL)--Abhishek Sharmaअभिषेक शर्मा Functions make query results easier to understand and manipulate data values. There are two categories of functions: single row/scalar functions that return one value per row, and group/aggregate functions that operate on sets of values to return a single result. The GROUP BY clause groups rows based on columns and is used with aggregate functions to return summary results for each group.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Array in C



Array in CKamal Acharya This document discusses one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays. It defines arrays as data structures that can hold multiple values of the same type stored consecutively in memory. One-dimensional arrays use a single set of indexes, while multi-dimensional arrays have two or more indexes to access elements. The document provides syntax examples and demonstrates how to initialize, read from, and display one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays. It also lists some example programs involving arrays.
File handling in Python



File handling in PythonMegha V The document discusses file handling in Python. It explains that a file is used to permanently store data in non-volatile memory. It describes opening, reading, writing, and closing files. It discusses opening files in different modes like read, write, append. It also explains attributes of file objects like name, closed, and mode. The document also covers reading and writing text and binary files, pickle module for serialization, and working with CSV files and the os.path module.
Strings in C



Strings in CKamal Acharya Strings are arrays of characters that are null-terminated. They can be manipulated using functions like strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp(). The document discusses initializing and reading strings, passing strings to functions, and using string handling functions to perform operations like copying, concatenating, comparing, and reversing strings. It also describes arrays of strings, which are 2D character arrays used to store multiple strings. Examples are provided to demonstrate reading and sorting arrays of strings.
User defined functions in C



User defined functions in CHarendra Singh User defined / Pre-defined functions in C
Function declaration, Function Call, Function definition, Types of functions, Categories of functions
Python tuples and Dictionary



Python tuples and DictionaryAswini Dharmaraj Tuples are immutable sequences like lists but cannot be modified after creation, making them useful for storing fixed data like dictionary keys; they are created using parentheses and accessed using indexes and slices like lists but elements cannot be added, removed, or reassigned. Dictionaries are mutable mappings of unique keys to values that provide fast lookup of values by key and can be used to represent polynomials by mapping powers to coefficients.
Threading in C#



Threading in C#Medhat Dawoud This document discusses multithreading in C#. It introduces threads and multithreading, describing how operating systems allow multitasking and how threads work. It explains that the .NET Framework supports multithreading using the System.Threading namespace and Thread class. It describes properties and methods of the Thread class, potential problems like deadlocks that can occur with multithreading, and solutions like synchronization and locking to prevent issues.
Storage classes in c++



Storage classes in c++Jaspal Singh The document discusses different storage classes in C++ including automatic, external, static, register, and mutable. It provides the syntax and examples of each:
- Automatic variables are declared with auto and have function block scope and lifetime.
- External variables use extern and have whole program global visibility.
- Static variables are declared with static and have whole program lifetime but local visibility.
- Register variables are intended for fast access and declared with register but storage is implementation-defined.
- Mutable variables allow changing class member values in const member functions and are declared with mutable.
Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)



Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)PyData NumPy is a Python library used for working with multidimensional arrays and matrices for scientific computing. It allows fast operations on arrays through optimized C code and is the foundation of the Python scientific computing stack. NumPy arrays can be created in many ways and support operations like indexing, slicing, broadcasting, and universal functions. NumPy provides many useful features for linear algebra, Fourier transforms, random number generation and more.
List in Python



List in PythonSiddique Ibrahim A list in Python is a mutable ordered sequence of elements of any data type. Lists can be created using square brackets [] and elements are accessed via indexes that start at 0. Some key characteristics of lists are:
- They can contain elements of different types
- Elements can be modified, added, or removed
- Common list methods include append(), insert(), remove(), pop(), and sort()
Python - An Introduction



Python - An IntroductionSwarit Wadhe Python An Introduction, A presentation Developed by Swarit Wadhe. This Slide Will Give you basic information about python (Origin, Codes and difference from other languages).
I hope you'll find this helpfull and if you do please share it with your fellows.
Python programming : Classes objects



Python programming : Classes objectsEmertxe Information Technologies Pvt Ltd A class is a code template for creating objects. Objects have member variables and have behaviour associated with them. In python a class is created by the keyword class.
An object is created using the constructor of the class. This object will then be called the instance of the class.
Pointers in c++



Pointers in c++Vineeta Garg Pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. It allows dynamic memory allocation and access of memory locations. There are three ways to pass arguments to functions in C++ - pass by value, pass by reference, and pass by pointer. Pass by value copies the value, pass by reference copies the address, and pass by pointer passes the address of the argument. Pointers can also point to arrays or strings to access elements. Arrays of pointers can store multiple strings. References are alternative names for existing variables and any changes made using the reference affect the original variable. Functions can return pointers or references.
Data Structure and Algorithms Arrays



Data Structure and Algorithms ArraysManishPrajapati78 This slide explains some basics concepts of array and operation performed on arrays like searching and sorting.
Functions & Recursion



Functions & RecursionNishant Munjal Functions allow programmers to organize code into self-contained blocks that perform tasks. A function is defined with a name, parameters, and code block. Functions can call other functions or recurse by calling themselves. Recursion involves defining a function that calls itself repeatedly until a base case is reached. Examples of recursive functions include calculating factorials and solving the Tower of Hanoi puzzle by moving disks from one rod to another according to rules.
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithm



Supervised Machine Learning AlgorithmPyingkodi Maran This document provides an overview of supervised machine learning algorithms. It explains that supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data so it can predict the correct output for new input data. Some examples of supervised learning tasks include image classification, disease prediction, and spam detection. Classification algorithms are used for predicting categorical outputs, like dog vs cat images. Regression algorithms predict continuous outputs, like housing prices. Common classification algorithms mentioned are random forest, decision trees, logistic regression, and support vector machines. Linear regression is also discussed as a basic regression algorithm that finds a linear relationship between variables.
Procedures/functions of rdbms



Procedures/functions of rdbmsjain.pralabh The document discusses stored procedures and functions in Oracle databases. It describes how procedures are compiled code stored in the database that can be called from client environments. Procedures allow encapsulating common operations like inserting records or updating salaries. The document provides examples of creating procedures and functions, specifying arguments, debugging errors, and managing dependencies.
Data Structures in Python



Data Structures in PythonDevashish Kumar Data Structures in Python, second in the series of Introduction to Python. Upcoming series will cover Functions and OOPs concept in Python.
Functions in C.pptx



Functions in C.pptxAshwini Raut Functions are fundamental building blocks of C programs, allowing for modular, structured, and efficient code organization.
1 D Arrays in C++



1 D Arrays in C++poonam.rwalia An array is a collection of variables of the same type that are referenced using a common name and contiguous memory locations. One-dimensional arrays allow storing multiple variables of the same type under a single variable name. Linear/sequential search compares each element to the search key while binary search divides the array in half at each step to find the search key faster than linear search.
Windows Server 2008 Active Directory



Windows Server 2008 Active Directoryanilinvns Active Directory is a database that stores information about a network's users, computers, groups, and other network resources. It allows for centralized management of these resources.
A domain controller is a server that responds to authentication requests on the Windows domain. It authenticates users' credentials when they log into the domain network.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open standard protocol that Active Directory supports to make user and resource information widely accessible for management and querying across the network.
Similar to Database Query Using SQL_ip.docx (20)
SQL.pptx



SQL.pptxMrHello6 The document discusses aggregate functions in SQL such as SUM, AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN. It provides examples of using these functions to calculate totals, averages, counts and find maximum and minimum values from columns in tables. It also covers the use of the GROUP BY clause to perform aggregate calculations on grouped data and the HAVING clause to filter groups.
Introduction to Oracle Functions--(SQL)--Abhishek Sharma



Introduction to Oracle Functions--(SQL)--Abhishek Sharmaअभिषेक शर्मा Functions make query results easier to understand and manipulate data values. There are two categories of functions: single row/scalar functions that return one value per row, and group/aggregate functions that operate on sets of values to return a single result. The GROUP BY clause groups rows based on columns and is used with aggregate functions to return summary results for each group.
Introduction to oracle functions



Introduction to oracle functionsNitesh Singh Functions in Oracle can be used to manipulate data values and are categorized as single-row/scalar functions and group/aggregate functions. Single-row functions operate on each row and return one value per row, while group functions operate on sets of values to return one result. The GROUP BY clause is used to group or categorize data and can be used with aggregate functions to return summary results for each group.
SQL-AGG-FUN.pdfiiiijuyyttfffgyyuyyyyyhhh



SQL-AGG-FUN.pdfiiiijuyyttfffgyyuyyyyyhhhNaveeN547338 Aggregate functions operate on a collection of values from a column and return a single value. The main aggregate functions are SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX, and COUNT. COUNT returns the number of rows, SUM adds values, AVG calculates the average, MIN returns the minimum value, and MAX returns the maximum value. The GROUP BY clause groups data by one or more columns and the HAVING clause allows filtering groups based on aggregate functions.
Aggregate Functions,Final



Aggregate Functions,Finalmukesh24pandey The document discusses various aggregate functions used in SQL such as SUM, COUNT, AVG, MIN, and MAX. It provides examples of how to use these functions to retrieve aggregated data from tables, including the use of GROUP BY and HAVING clauses. Aggregate functions summarize data over multiple rows, returning a single value. COUNT(*) counts all rows while other functions like COUNT ignore NULL values.
Aggregate Function - Database



Aggregate Function - DatabaseShahadat153031 Shahadat Hossain presented on aggregate functions in SQL. Aggregate functions take a collection of values as input and return a single value. Common aggregate functions include MAX(), MIN(), AVG(), SUM(), and COUNT(). Each function operates on a single column and returns a single value. SUM() and AVG() operate on numeric data, while MIN(), MAX(), and COUNT() can operate on numeric or non-numeric data. Examples demonstrated how to use each function to return values like the total salary, average salary, minimum salary, and number of records that meet a condition.
Data Base Management Slides SQL with example



Data Base Management Slides SQL with exampleAmeerHamza708060 This document discusses how to use group functions in SQL to aggregate data and summarize information. Group functions such as MAX, MIN, SUM, AVG, COUNT operate on sets of rows and return one result per group. The GROUP BY clause is used to divide rows into groups, and the HAVING clause filters groups. Examples demonstrate finding minimum/maximum salaries, averages grouped by department, and sums grouped by multiple columns using functions like ROLLUP and CUBE.
Data Manipulation Language.pptx



Data Manipulation Language.pptxEllenGracePorras This document provides an overview of SQL (Structured Query Language). It discusses SQL functions including data manipulation language (DML) and data definition language (DDL). DML commands like SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE and INSERT are covered. The SELECT statement syntax and use of clauses like WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY and JOINs are explained. Aggregate functions like COUNT, AVG, SUM etc and scalar functions are also summarized. Examples are provided throughout to illustrate the concepts and syntax.
Unit 3-Select Options and Aggregate Functions in SQL (1).pptx



Unit 3-Select Options and Aggregate Functions in SQL (1).pptxHAMEEDHUSSAINBU21CSE Select statement is used to fetch data from one or more tables. It can use predicates like WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, and ORDER BY. The WHERE clause filters rows based on conditions, GROUP BY organizes rows into groups, HAVING applies conditions to groups, and ORDER BY sorts the results. Aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG, MAX, MIN perform calculations on multiple rows and return a single value.
SQL || overview and detailed information about Sql



SQL || overview and detailed information about Sqlgourav kottawar This document provides an overview of the SQL language. It explains that SQL allows users to access and manipulate databases. The core functionality of SQL includes executing queries, retrieving data, inserting/updating/deleting records, and creating/modifying database structures. It also describes common SQL statements like SELECT, WHERE, DISTINCT, BETWEEN, aggregate functions, and string functions.
DBMS: Week 07 - Advanced SQL Queries in MySQL



DBMS: Week 07 - Advanced SQL Queries in MySQLRashidFaridChishti DBMS: Week 07 - Advanced SQL Queries in MySQL
ORACLE NOTES



ORACLE NOTESSachin Shukla 1. The document discusses various SQL commands for creating, manipulating, and querying database tables. It covers commands like CREATE TABLE, INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, ALTER TABLE, COMMENT, and more.
2. Mathematical functions like COUNT, MAX, MIN, ROUND, TRUNC are described along with logical and comparison operators.
3. The document provides examples of using operators, functions, joins and grouping with detailed explanations.
Lab3 aggregating data



Lab3 aggregating dataBalqees Al.Mubarak Group functions operate on sets of rows to aggregate data and return a single result per group. Common group functions include AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN, and SUM. The GROUP BY clause is used to split rows into groups and is required when non-aggregate columns are selected. The HAVING clause allows filtering groups based on conditions and is analogous to the WHERE clause for rows. Nesting group functions allows aggregating aggregates, like finding the maximum average salary.
PHP mysql Aggregate functions



PHP mysql Aggregate functionsMudasir Syed Aggregate functions summarize data from multiple rows into a single value. They operate on a single column and return a single value. Common aggregate functions include SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX, and COUNT. SUM returns the sum of numeric column values. AVG returns the average of numeric column values. MIN and MAX return the minimum and maximum values in a column. COUNT returns the number of rows.
Sql query [select, sub] 4![Sql query [select, sub] 4](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/sqlqueryselectsub4-111119075704-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Sql query [select, sub] 4](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/sqlqueryselectsub4-111119075704-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Sql query [select, sub] 4](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/sqlqueryselectsub4-111119075704-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Sql query [select, sub] 4](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/sqlqueryselectsub4-111119075704-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Sql query [select, sub] 4Dr. C.V. Suresh Babu The document provides an overview of Data Query Language (DQL) syntax for SELECT statements including:
- Selecting columns from tables
- Using column aliases
- Filtering rows with the WHERE clause
- Working with NULL values
- Sorting results with the ORDER BY clause
- Grouping rows with the GROUP BY clause and aggregate functions
- Filtering groups with the HAVING clause
- Sorting on multiple columns
- Nested subqueries
SQL WORKSHOP::Lecture 5



SQL WORKSHOP::Lecture 5Umair Amjad This document discusses how to aggregate data using group functions in SQL. It describes the available group functions like AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, and how to use them. It explains how to group data using the GROUP BY clause and include or exclude grouped rows using the HAVING clause. Examples are provided to illustrate grouping data by one or more columns and restricting groups with the HAVING clause.
5. Group Functions



5. Group FunctionsEvelyn Oluchukwu This document discusses group functions in SQL, which operate on groups of rows and return results. It covers common group functions like COUNT, AVG, SUM, MIN, MAX, STDDEV and VARIANCE. It explains how to use the GROUP BY clause to group data by columns and the HAVING clause to include or exclude grouped rows. Examples are provided for counting rows, getting averages, and filtering groups. Nested groups and the order of operations are also discussed.
Ad
More from VandanaGoyal21 (9)
sql_data.pdf



sql_data.pdfVandanaGoyal21 - A database is an organized collection of data stored together to serve applications. Most databases store data in tables which can be managed using RDBMS software like MySQL.
- MySQL is an open source and free RDBMS that uses SQL and allows storing, modifying, and querying data across various platforms. It provides features like security, connectivity, and transaction control.
- SQL commands allow defining the database structure using DDL, manipulating data using DML, and controlling transactions with TCL. Common queries include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE. Functions and clauses like WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY etc. filter and organize query results.
sample project-binary file.docx



sample project-binary file.docxVandanaGoyal21 This document defines several functions for a library management system that uses pickle to read from and write to a binary file called "lib.dat". The functions allow a user to insert book records by prompting for inputs, display all records by reading the file, search by accession number, book name or publisher, delete a record by accession number, and update a record. A main menu loop calls the different functions based on user input and allows continuing the program.
STACK.docx



STACK.docxVandanaGoyal21 The document defines functions for common stack operations like isEmpty, Push, Pop, and Show. It uses a list to represent the stack and tracks the top index. The main section runs an interactive menu where the user can push, pop, and show the stack.
Computer Networks.docx



Computer Networks.docxVandanaGoyal21 1. Computer networks allow for the interconnection of independent computers to share information and resources. ARPANET, developed in 1967, was one of the first computer networks and connected four nodes through the use of IMPs (Interface Message Processors).
2. Computer networks provide advantages like central storage of data, sharing of information and resources, reliability, and reduced costs. However, they also present disadvantages such as requiring specific setups and introducing security and cost issues.
3. Common network topologies include bus, ring, and star configurations. A bus topology connects all nodes to a single cable or backbone but a failure of one node can shutdown the entire network. Ring topologies connect all nodes in a closed loop but also
Computer Networks.docx



Computer Networks.docxVandanaGoyal21 1. Computer networks allow for the interconnection of independent computers to share information and resources.
2. Early computer networks included ARPANET in 1967, which connected four nodes, and the presentation of TCP in 1973 to achieve reliable data delivery.
3. Computer networks provide advantages like central data storage, information and resource sharing, reliability, and reduced costs. Disadvantages include setup costs and lack of security.
functions.docx



functions.docxVandanaGoyal21 1. A variable's scope determines where it is visible within a program. Local variables are only visible within their defined function, while global variables are visible program-wide.
2. Mutable objects like lists allow their values to change when passed to functions, while immutable objects like integers do not.
3. Functions can return single values or multiple values as tuples. If no return statement is specified, a function implicitly returns None.
Functions.docx



Functions.docxVandanaGoyal21 Functions are reusable blocks of code that perform a specific task. They help reduce complexity, improve reusability and maintainability of code. There are built-in functions predefined in modules and user-defined functions. Built-in functions include type conversion, math operations etc. User-defined functions are created using the def keyword and defined with a name, parameters and indented block of code. Functions are called by their name with actual parameters. This transfers program control to the function block, executes code, then returns control to calling block.
CLASS 10 IT PRACTICAL FILE.pdf



CLASS 10 IT PRACTICAL FILE.pdfVandanaGoyal21 This document provides instructions and examples for various practical exercises involving digital documentation, spreadsheets, and relational database management systems. It includes templates, image cropping, drawing objects, mail merge, styles, consolidation, scenarios, macros, primary keys, and definitions of data, information, and databases. The exercises guide the student through completing tasks like creating templates, inserting images, applying styles, mail merge, subtotals, goal seek, and creating database tables.
WEB APPLICATIONS 1.pdf



WEB APPLICATIONS 1.pdfVandanaGoyal21 This document discusses assistive technologies and accessibility features in Microsoft Windows XP that help users with disabilities. It covers features like Sticky Keys, Filter Keys, Toggle Keys, and Sound Sentry that assist users with physical and auditory impairments. High contrast, cursor options, and mouse keys help users with vision impairments. Networking allows sharing of resources and information between connected computers, while the internet is a worldwide network connecting millions of smaller networks. Common internet connections include dial-up, DSL, cable, 3G, WiFi and WiMAX. Data is transferred over the internet through packets that are examined and reassembled at the destination.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Exploring Ocean Floor Features for Middle School



Exploring Ocean Floor Features for Middle SchoolMarie This 16 slide science reader is all about ocean floor features. It was made to use with middle school students.
You can download the PDF at thehomeschooldaily.com
Thanks! Marie
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024



BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS BRINGS T0 YOU A FUN-FILLED, SEAT EDGE BUSINESS QUIZ
DIVE INTO THE PRELIMS OF BIZCOM 2024
QM: GOWTHAM S
BCom (2022-25)
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS
Artificial intelligence Presented by JM.



Artificial intelligence Presented by JM.jmansha170 AI (Artificial Intelligence) :
"AI is the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence, such as learning, decision-making, and problem-solving."
Important Points about AI:
1. Learning – AI can learn from data (Machine Learning).
2. Automation – It helps automate repetitive tasks.
3. Decision Making – AI can analyze and make decisions faster than humans.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP) – AI can understand and generate human language.
5. Vision & Recognition – AI can recognize images, faces, and patterns.
6. Used In – Healthcare, finance, robotics, education, and more.
Owner By:
Name : Junaid Mansha
Work : Web Developer and Graphics Designer
Contact us : +92 322 2291672
Email : [email protected]
LDMMIA Reiki Yoga Next Week Grad Updates



LDMMIA Reiki Yoga Next Week Grad UpdatesLDM & Mia eStudios A short update and next week. I am writing both Session 9 and Orientation S1.
As a Guest Student,
You are now upgraded to Grad Level.
See Uploads for “Student Checkin” & “S8”. Thx.
Thank you for attending our workshops.
If you are new, do welcome.
Grad Students: I am planning a Reiki-Yoga Master Course (As a package). I’m Fusing both together.
This will include the foundation of each practice. Our Free Workshops can be used with any Reiki Yoga training package. Traditional Reiki does host rules and ethics. Its silent and within the JP Culture/Area/Training/Word of Mouth. It allows remote healing but there’s limits As practitioners and masters. We are not allowed to share certain secrets/tools. Some content is designed only for “Masters”. Some yoga are similar like the Kriya Yoga-Church (Vowed Lessons). We will review both Reiki and Yoga (Master tools) in the Course upcoming.
Session Practice, For Reference:
Before starting a session, Make sure to check your environment. Nothing stressful. Later, You can decorate a space as well.
Check the comfort level, any needed resources (Yoga/Reiki/Spa Props), or Meditation Asst?
Props can be oils, sage, incense, candles, crystals, pillows, blankets, yoga mat, any theme applies.
Select your comfort Pose. This can be standing, sitting, laying down, or a combination.
Monitor your breath. You can add exercises.
Add any mantras or affirmations. This does aid mind and spirit. It helps you to focus.
Also you can set intentions using a candle.
The Yoga-key is balancing mind, body, and spirit.
Finally, The Duration can be long or short.
Its a good session base for any style.
Next Week’s Focus:
A continuation of Intuition Development. We will review the Chakra System - Our temple. A misguided, misused situation lol. This will also serve Attunement later.
For Sponsor,
General updates,
& Donations:
Please visit:
https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptx



june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptxroger malina art science is over -talk by roger malina for jack madden group
Optimization technique in pharmaceutical product development.pptx



Optimization technique in pharmaceutical product development.pptxUrmiPrajapati3 Optimization techniques in pharmaceutical product development
Unit- 4 Biostatistics & Research Methodology.pdf



Unit- 4 Biostatistics & Research Methodology.pdfKRUTIKA CHANNE Blocking and confounding (when a third variable, or confounder, influences both the exposure and the outcome) system for Two-level factorials (a type of experimental design where each factor (independent variable) is investigated at only two levels, typically denoted as "high" and "low" or "+1" and "-1")
Regression modeling (statistical model that estimates the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables using a line): Hypothesis testing in Simple and Multiple regression models
Introduction to Practical components of Industrial and Clinical Trials Problems: Statistical Analysis Using Excel, SPSS, MINITAB®️, DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS, R - Online Statistical Software to Industrial and Clinical trial approach
Different pricelists for different shops in odoo Point of Sale in Odoo 17



Different pricelists for different shops in odoo Point of Sale in Odoo 17Celine George Price lists are a useful tool for managing the costs of your goods and services. This can assist you in working with other businesses effectively and maximizing your revenues. Additionally, you can provide your customers discounts by using price lists.
How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18



How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18Celine George Efficient maintenance management is crucial for keeping equipment and work centers running smoothly in any business. Odoo 18 provides a Maintenance module that helps track, schedule, and manage maintenance requests efficiently.
SEXUALITY , UNWANTED PREGANCY AND SEXUAL ASSAULT .pptx



SEXUALITY , UNWANTED PREGANCY AND SEXUAL ASSAULT .pptxPoojaSen20 SEXUALITY AND ITS TYPES , UNWANTED PREGANCY AND SEXUAL ASSAULT
Diptera: The Two-Winged Wonders, The Fly Squad: Order Diptera.pptx



Diptera: The Two-Winged Wonders, The Fly Squad: Order Diptera.pptxArshad Shaikh Diptera, commonly known as flies, is a large and diverse order of insects that includes mosquitoes, midges, gnats, and horseflies. Characterized by a single pair of wings (hindwings are modified into balancing organs called halteres), Diptera are found in almost every environment and play important roles in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and food sources. Some species, however, are significant pests and disease vectors, transmitting diseases like malaria, dengue, and Zika virus.
THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION included definition, characteristics, nurse patient...



THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION included definition, characteristics, nurse patient...parmarjuli1412 The document provides an overview of therapeutic communication, emphasizing its importance in nursing to address patient needs and establish effective relationships. THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION included some topics like introduction of COMMUNICATION, definition, types, process of communication, definition therapeutic communication, goal, techniques of therapeutic communication, non-therapeutic communication, few ways to improved therapeutic communication, characteristics of therapeutic communication, barrier of THERAPEUTIC RELATIONSHIP, introduction of interpersonal relationship, types of IPR, elements/ dynamics of IPR, introduction of therapeutic nurse patient relationship, definition, purpose, elements/characteristics , and phases of therapeutic communication, definition of Johari window, uses, what actually model represent and its areas, THERAPEUTIC IMPASSES and its management in 5th semester Bsc. nursing and 2nd GNM students
Hemiptera & Neuroptera: Insect Diversity.pptx



Hemiptera & Neuroptera: Insect Diversity.pptxArshad Shaikh *Order Hemiptera:*
Hemiptera, commonly known as true bugs, is a large and diverse order of insects that includes cicadas, aphids, leafhoppers, and shield bugs. Characterized by their piercing-sucking mouthparts, Hemiptera feed on plant sap, other insects, or small animals. Many species are significant pests, while others are beneficial predators.
*Order Neuroptera:*
Neuroptera, also known as net-winged insects, is an order of insects that includes lacewings, antlions, and owlflies. Characterized by their delicate, net-like wing venation and large, often prominent eyes, Neuroptera are predators that feed on other insects, playing an important role in biological control. Many species have aquatic larvae, adding to their ecological diversity.
Rose Cultivation Practices by Kushal Lamichhane.pdf



Rose Cultivation Practices by Kushal Lamichhane.pdfkushallamichhame This includes the overall cultivation practices of Rose prepared by:
Kushal Lamichhane (AKL)
Instructor
Shree Gandhi Adarsha Secondary School
Kageshowri Manohara-09, Kathmandu, Nepal
Adam Grant: Transforming Work Culture Through Organizational Psychology



Adam Grant: Transforming Work Culture Through Organizational PsychologyPrachi Shah This presentation explores the groundbreaking work of Adam Grant, renowned organizational psychologist and bestselling author. It highlights his key theories on giving, motivation, leadership, and workplace dynamics that have revolutionized how organizations think about productivity, collaboration, and employee well-being. Ideal for students, HR professionals, and leadership enthusiasts, this deck includes insights from his major works like Give and Take, Originals, and Think Again, along with interactive elements for enhanced engagement.
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big Cycle



Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big CycleDadang Solihin A complete and practical understanding of the Big Debt Cycle. A much more practical understanding of how supply and demand really work compared to the conventional economic thinking. A complete and practical understanding of the Overall Big Cycle, which is driven by the Big Debt Cycle and the other major cycles, including the big political cycle within countries that changes political orders and the big geopolitical cycle that changes world orders.
Respiratory System , Urinary System



Respiratory System , Urinary SystemRushiMandali Human Anatomy and Physiology II Unit 3 B pharm Sem 2
Respiratory system
Anatomy of respiratory system with special reference to anatomy
of lungs, mechanism of respiration, regulation of respiration
Lung Volumes and capacities transport of respiratory gases,
artificial respiration, and resuscitation methods
Urinary system
Anatomy of urinary tract with special reference to anatomy of
kidney and nephrons, functions of kidney and urinary tract,
physiology of urine formation, micturition reflex and role of
kidneys in acid base balance, role of RAS in kidney and
disorders of kidney
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024



BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
Database Query Using SQL_ip.docx
- 1. Database Query Using SQL Lets do practical on DATABASE…
- 2. SORTING OUTPUT By default records will come in the output in the same order in which it was entered. Tosee the output rows in sorted or arranged in ascending or descending order SQL provide ORDER BY clause. By default output will be ascending order(ASC) to see output in descending order we use DESC clause with ORDER BY . Select * from emp order by name; (ascending order) Select * from emp order by salary desc; Select * from emp order by dept asc, salary desc;
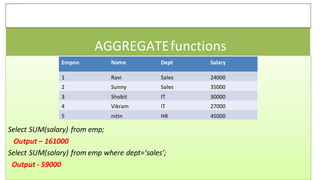
- 3. AGGREGATEfunctions Aggregate function is used to perform calculation on group of rows and return the calculated summary like sum of salary,averageof salary etc. Available aggregatefunctions are – 1. SUM() 2. AVG() 3. COUNT() 4. MAX() 5. MIN() 6. COUNT(*)
- 4. AGGREGATEfunctions Select SUM(salary) from emp; Output – 161000 Select SUM(salary) from emp where dept=‘sales’; Output - 59000 Empno Name Dept Salary 1 Ravi Sales 24000 2 Sunny Sales 35000 3 Shobit IT 30000 4 Vikram IT 27000 5 nitin HR 45000
- 5. AGGREGATEfunctions Empno Name Dept Salary 1 Ravi Sales 24000 2 Sunny Sales 35000 3 Shobit IT 30000 4 Vikram IT 27000 5 nitin HR 45000 Select AVG(salary) from emp; Output – 32200 Select AVG(salary) from emp where dept=‘sales’; Output - 29500
- 6. AGGREGATEfunctions Select COUNT(name) from emp; Empno Name Dept Salary 1 Ravi Sales 24000 2 Sunny Sales 35000 3 Shobit IT 30000 4 Vikram IT 27000 5 nitin HR 45000 Output – 5 Select COUNT(salary) from emp where dept=‘HR’; Output - 1 Select COUNT(DISTINCT dept)from emp; Output - 3
- 7. AGGREGATEfunctions Empno Name Dept Salary 1 Ravi Sales 24000 2 Sunny Sales 35000 3 Shobit IT 30000 4 Vikram IT 27000 5 nitin HR 45000 Select MAX(Salary) from emp; Output – 45000 Select MAX(salary) from emp where dept=‘Sales’; Output - 35000
- 8. AGGREGATEfunctions Empno Name Dept Salary 1 Ravi Sales 24000 2 Sunny Sales 35000 3 Shobit IT 30000 4 Vikram IT 27000 5 nitin HR 45000 Select MIN(Salary) from emp; Output – 24000 Select MIN(salary) from emp where dept=‘IT’; Output - 27000
- 9. AGGREGATEfunctions Empno Name Dept Salary 1 Ravi Sales 24000 2 Sunny Sales 35000 3 Shobit IT 30000 4 Vikram IT 27000 5 nitin HR 45000 6 Krish HR Select COUNT(*)from emp; Output – 6 Select COUNT(salary) from emp; Output - 5
- 10. count(*) Vs count() Count(*) function is used to count the number of rows in query output whereas count() is used to count values present in any column excludingNULL values. Note: All aggregatefunction ignores the NULL values.
- 11. GROUP BY GROUP BY clause is used to divide the table into logical groups and we can perform aggregate functions in those groups. In this case aggregate function will return output for each group. For example if we want sum of salary of each department we have to divide table records.
- 12. Aggregate functions by default takes the entire table as a single group that’s why we are getting the sum(), avg(), etc output for the entire table. Now suppose organizationwants the sum() of all the job separately,or wants to find the average salary of every job. In this case we have to logically divide our table into groups based on job, so that every group will be passed to aggregate function for calculation and aggregate function will return the result for every group.
- 13. Group by clause helps up to divide the table into logical groups based on any column value. In those logically divided records we can apply aggregate functions.For.E.g. SELECT SUM(SAL) FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPT; SELECT JOB,SUM(SAL) FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPT; SELECT JOB,SUM(SAL),AVG(SAL),MAX(SAL),COUNT(*) EMPLOYEE_COUNTFROM EMP; NOTE :- when we are using GROUP BY we can use only aggregate function and the column on which we are grouping in the SELECT list because they will form a group other than any column will gives you an error because they will be not the part of the group. For e.g. SELECT ENAME,JOB,SUM(SAL) FROM EMP GROUP BY JOB; Error -> because Ename is not a group expression
- 14. HAVING with GROUP BY • If we wantto filter or restrict some rowsfrom the output produced by GROUP BYthen we use HAVING clause. It is used to put condition of group of rows. With having clause we can use aggregatefunctions also. • WHERE is used before the GROUP BY.With WHEREwe cannot use aggregatefunction. • E.g. • SELECT DEPT,AVG(SAL)FROM EMP GROUP BYDEPT HAVINGJOB IN (‘HR’,’SALES’ ) • SELECT DEPT,MAX(SAL),MIN(SAL),COUNT(*)FROM EMP GROUP BYDEPT HAVING COUNT(*)>2 • SELECT DEPT,MAX(SAL),MIN(SAL)FROM EMP WHERE SAL>=2000 GROUP BYDEPT HAVING DEPT IN(‘IT’,’HR’)
- 15. MYSQL FUNCTIONS A function is built – in code for specific purpose that takesvalue and returns a single value. Valuespassed to functions are known as arguments/parameters. There are various categories of function in MySQL:- 1) String Function 2) Mathematical function 3) Date and time function
- 16. Function Description Example CHAR() Return character for given ASCII Code Select Char(65); Output- A CONCAT() Return concatenated string Select concat(name, ‘ works in ‘, dept,’ department ’); LOWER()/ LCASE() Return string in small letters Select lower(‘INDIA’); Output- india Select lower(name) from emp; SUBSTRING(S, P,N) / MID(S,P,N) Return N character of string S, beginning from P Select SUBSTRING(‘LAPTOP’,3,3); Output – PTO Select SUBSTR(‘COMPUTER’,4,3); Output – PUT UPPER()/ UCASE() Return string in capital letters Select Upper(‘india’); Output- INDIA LTRIM() Removes leading space Select LTRIM(‘ Apple’); Output- ‘Apple’ RTRIM Remove trailing space Select RTRIM(‘Apple ‘); Output- ‘Apple’ String Function
- 17. Function Description Example TRIM() Remove spaces from beginning and ending Select TRIM(‘ Apple ‘); Output-’Apple’ Select* fromemp where trim(name) = ‘Suyash’; INSTR() It search one string in another string and returns position, if not found 0 SelectINSTR(‘COMPUTER’,’PUT’); Output-4 Select INSTR(‘PYTHON’,’C++’); Output – 0 LENGTH() Returns number of character in string Selectlength(‘python’); Output- 7 Select name, length(name) fromemp LEFT(S,N) Return N characters of S from beginning SelectLEFT(‘KV NO1 TEZPUR’,2); Output-KV String Function
- 18. RIGHT(S,N) Return N characters of S from ending Select RIGHT(‘KV NO1 ’,3); Output- NO1
- 19. Function Description Example MOD(M,N) Return remainderM/N SelectMOD(11,5); Output- 1 POWER(B,P) Return B to power P SelectPOWER(2,5); Output-32 ROUND(N,D) Return number rounded to D place after decimal SelectROUND(11.589,2); Output- 11.59 SelectROUND(12.999,2); Output- 13.00 SelectROUND(267.478,-2) OUTPUT- 300 SIGN(N) Return -1 for –ve number 1 for ve + number Selectsign(-10) Output : -1 Selectsign(10); Output : 1 SQRT(N) Returns square rootof N SelectSQRT(144);Output: 12 TRUNCATE(M, N) Return number upto N place after decimal without rounding it SelectTruncate(15.789,2);Output: 15.79 Numeric Function
- 20. Function Description Example CURDATE()/ CURRENT_DATE()/ CURRENT_DATE Return the current date Selectcurdate(); Select current_date(); DATE() Return date part from datetime expression Select date(‘2018-08-15 12:30’); Output: 2018-08-15 MONTH() Return month fromdate Selectmonth(‘2018-08-15’);Output: 08 YEAR() Return year fromdate Selectyear(‘2018-08-15’);Output: 2018 DAYNAME() Return weekday name Select dayname(‘2018-12-04’); Output: Tuesday DAYOFMONTH() Return value from1-31 Select dayofmonth(‘2018-08-15’) Output: 15 DAYOFWEEK() Return weekday index, for Sunday-1, Monday-2, .. Select dayofweek(‘2018-12-04’); Output: 3 Date and Time Function
- 21. DAYOFYEAR() Return value from1-366 Select dayofyear(‘2018-02-10’) Output: 41
- 22. Date and Time Function Function Description Example NOW() Return both current date and time Select now(); at which the function executes SYSDATE() Return both current date and time Select sysdate() Difference Between NOW() and SYSDATE(): NOW() function return the date and time at which function was executed even if we execute multiple NOW() function with select. whereas SYSDATE() will always return date and time at which each SYDATE() function started execution. For example. mysql> Select now(), sleep(2), now(); Output: 2018-12-04 10:26:20, 0, 2018-12-04 10:26:20 mysql> Select sysdate(), sleep(2), sysdate(); Output: 2018-12-04 10:27:08, 0, 2018-12-04 10:27:10





