Embedded system design using arduino
- 1. Santosh Kumar Verma Department of Computer Science and Information Technology Jaypee Institute of Information Technology, Noida
- 2. Content 1. Introduction of µp and µc 2. Introduction of 8051 µc 3. Introduction of Arduino 4. Atmega328 : Basics and internal Architecture 5. Atmega328 : Instruction Set 6. Arduino programming interface 7. Analog/Digital components and its application with arduino 8. References
- 3. Do you know computer organization? Arithmetic Logic Unit Memory OutputInput Control Unit
- 4. - How does it work? - Map it’s units in personal computer – Input Output Memory ALU Software – System software & Application software
- 5. Introduction to Microprocessor ARITHMATIC LOGIC UNIT CONTROL UNIT MEMORY INPUT OUTPUT MICROCOMPUTER MICROPROCESSOR
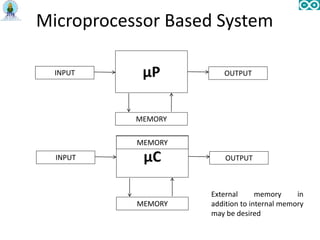
- 6. Microprocessor Based System INPUT µP OUTPUT MEMORY INPUT µC OUTPUT MEMORY External memory in addition to internal memory may be desired MEMORY
- 7. Address, Data and Control Bus • Bus - defined pathway for transfer of digital information between different units. • To write data to memory or output device. - µp needs to send . Address of memory location or port address of device. . Data . Write control signal • To read data from memory or Input device - µp needs to send . Address and . Read Control Signal - Memory/device sends – data.
- 8. Thus three pathways (buses) for 3 types of digital information. Address Bus - From µp to devices - Unidirectional. Data Bus - From µp to devices & devices to µp - Bidirectional Control - From µp to devices & from devices to µp [Interrupt, DMA] - Bidirectional Now let us redraw the computer organization diagram
- 9. Address Bus I/O Device I/O Device I/O Device Memory µp Control Bus Data Bus
- 10. Microcontroller A microcontroller is a complete computer system, including a CPU, memory, a clock oscillator, and I/O on a single integrated circuit chip. [1] ANALOG INPUTS http://www.freescale.com/files/microcontrollers/doc/ref_manual/M68HC05TB.pdf, p. 25
- 11. General Facilities 8 bit CPU On chip clock oscillator 4 KB of ROM (Program memory) 128 bytes RAM (Data Memory) 21 Special Function Registers(SFR) 32 I/O lines (Ports P0 to P3) 64 KB address space for external data memory 64 KB address space for program memory
- 12. 2- 16 bit timer/counter 5 source interrupt structure Full duplex serial port Bit addressability Bit processing capability MCS-51 compatible chips 8031 – Romless version – 4KB ROM not available 8751 – EPROM version – 4KB EPROM 8052- (8 KB ROM + 256 byte Data memory)
- 14. • The 8051 was one of the very early microcontrollers (~1980). • One of the early Arduino-like project was based on the 8051, in the form of "8052 Basic" board. • Atmel, Mentor Graphics, Intel, Honeywell, and Maxim (Dallas Semiconductor), and may more have a variety of 8051 chips.
- 15. • Introduced in 2005 as a project for students at the Interaction Design Institute Ivrea in Ivrea, Italy, Arduino is a single board microcontroller. • An Arduino board consists of an Atmel 8-bit AVR microcontroller with complementary components to facilitate programming and incorporation into other circuits [2]. • Arduino can sense the environment by receiving input from a variety of sensors and can affect its surroundings by controlling lights, motors, and other actuators. • The boards can be assembled or purchased preassembled; the open-source IDE can be downloaded for free. • The Arduino programming language is very simple and follows C like syntax. • Arduino projects can be stand-alone or they can communicate with software running on a computer (e.g. Processing).
- 16. • Other similar microcontrollers platforms are: Parallax Basic Stamp, Netmedia's BX-24, Phidgets, MIT's Handyboard, and many more. • All these platforms have an easy-to-use package. Why Arduino? Arduino also simplifies the process of working with microcontrollers, but it offers some advantage:
- 17. 1. Inexpensive - Arduino boards are relatively inexpensive compared to other microcontroller platforms. 2. Cross-platform - The Arduino software runs on Windows, Macintosh OSX, and Linux operating systems. Most microcontroller systems are limited to Windows. 3. Simple, clear programming environment - The Arduino programming environment is easy-to-use. 4. Open source and extensible software- The Arduino software is published as open source tools. The language can be expanded through C++ libraries. 5. Open source and extensible hardware -The Arduino is based on Atmel's ATMEGA8 and ATMEGA168 microcontrollers.
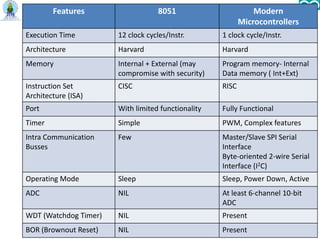
- 18. Features 8051 Modern Microcontrollers Execution Time 12 clock cycles/Instr. 1 clock cycle/Instr. Architecture Harvard Harvard Memory Internal + External (may compromise with security) Program memory- Internal Data memory ( Int+Ext) Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) CISC RISC Port With limited functionality Fully Functional Timer Simple PWM, Complex features Intra Communication Busses Few Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface Byte-oriented 2-wire Serial Interface (I2C) Operating Mode Sleep Sleep, Power Down, Active ADC NIL At least 6-channel 10-bit ADC WDT (Watchdog Timer) NIL Present BOR (Brownout Reset) NIL Present
- 19. THE GOOGLE TRENDS FOR ARDUINO RELATIVE TO OTHER EMBEDDED TERMS
- 20. ATmega328 data sheet pp. 2, 5 http://www.adafruit.com/index.php?main_page=popup_image&pID=50
- 21. Pin number Pin name Special function Source:http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/product_card.asp?PN=ATmega328P Note the limitations! p. 316
- 22. http://www.atmel.com/Images/Atmel-8271-8-bit-AVR-Microcontroller-ATmega48A-48PA-88A-88PA-168A-168PA-328-328P_datasheet.pdf High Performance, Low Power AVR® 8-Bit Microcontroller – Advanced RISC Architecture – 131 Powerful Instructions – Most Single Clock Cycle Execution – 32 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers – Up to 20 MIPS Throughput at 20 MHz High Endurance Non-volatile Memory Segments – 4/8/16/32K Bytes of In-System Programmable Flash program memory (ATmega48PA/88PA/168PA/328P) – 256/512/512/1K Bytes EEPROM – 512/1K/1K/2K Bytes Internal SRAM – Data retention: 20 years at 85°C/100 years at 25°C(1)
- 23. Peripheral Features – Two 8-bit Timer/Counters – One 16-bit Timer/Counter – Real Time Counter with Separate Oscillator – Six PWM Channels – 6-channel 10-bit ADC – Programmable Serial USART – Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface Special Microcontroller Features – Internal Calibrated Oscillator – External and Internal Interrupt Sources – Six Sleep Modes: Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power- save, Power-down, Standby, and Extended Standby
- 24. I/O and Packages – 23 Programmable I/O Lines Operating Voltage: – 1.8 - 5.5V for ATmega48PA/88PA/168PA/328P Temperature Range: – -40°C to 85°C Speed Grade: – 0 - 20 MHz @ 1.8 - 5.5V Low Power Consumption at 1 MHz, 1.8V, 25°C for ATmega48PA/88PA/168PA/328P: – Active Mode: 0.2 mA – Power-down Mode: 0.1 μA – Power-save Mode: 0.75 μA
- 29. Absolute Maximums ATmega328 data sheet p. 316
- 30. Microcontroller Ports and Pins The communication channels through which information flows into or out of the microcontroller Ex. PORTB Pins PB0 – PB7 May not be contiguous Often bi-directional C See next slides!
- 31. Port Pin Data Directionality • Input – When you want to take information from the external world (sensors) into the MCU • Output – When you want to change the state of something outside the MCU (turn a motor on or off, etc.) • Pins default to input direction on power-up or reset. • Your program can set or change the directionality of a pin at any time
- 33. Setting the Pin Data Direction • Arduino – pinMode(pin_no., dir) • Ex. Make Arduino pin 3 (PD3) an output – pinMode(3, OUTPUT); – pinMode(PIN_D3, OUTPUT); // with me106.h – Note: one pin at a time • Suppose you wanted Arduino pins 3, 5, and 7 (PD3, PD5, and PD7) to be outputs? • Is there a way to make them all outputs at the same time?
- 34. Pin Used as an Output • Turn on an LED, which is connected to pin Arduino pin 0 (PD0) – What should the data direction be for pin 0 (PD0)? • pinMode(____, ____); – Turn on the LED • digitalWrite(0,HIGH); – Turn off the LED • digitalWrite(0,LOW); ATmega328 Arduino pin 0 (PD0)
- 35. • Recall the question: – Is there a way change the data direction for a set of pins all at the same time? • All the work of MCU happens through registers (special memory locations) – Registers on the Atmega328 are 8-bits wide • The data direction register (DDRx) handles the data directions for pins in PORTx Source:http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/product_card.asp?PN=ATmega328P p. 93 Pin Used as an Output
- 36. Data Direction Register • If the bit is zero -> pin will be an input – Making a bit to be zero == ‘clearing the bit’ • If the bit is one -> pin will be an output – Making a bit to be one == ‘setting the bit’ • To change the data direction for a set of pins belonging to PORTx at the same time: 1. Determine which bits need to be set and cleared in DDRx 2. Store the binary number or its equivalent (in an alternate base, such as hex) into DDRx
- 37. Example 1 • Arduino approach • Alternate approach Make Arduino pins 3, 5, and 7 (PD3, PD5, and PD7) to be outputs pinMode(3, OUTPUT); pinMode(5, OUTPUT); pinMode(7, OUTPUT); DDRD = 0b10101000; or DDRD = 0xA8; Or if me106.h is used: pinMode(PIN_D3, OUTPUT); pinMode(PIN_D5, OUTPUT); pinMode(PIN_D7, OUTPUT);
- 38. Example 2 • Arduino approach • Alternate approach Make pins Arduino pins 0 and 1 (PD0 and PD1) inputs, and turn on the LEDs connected to it. pinMode(0, INPUT); pinMode(1, INPUT); digitalWrite(0, HIGH); digitalWrite(1, HIGH); DDRD = 0; // all PORTD pins inputs PORTD = 0b00000011; or PORTD = 0x03; Or if me106.h is used: pinMode(PIN_D0, INPUT); pinMode(PIN_D1, INPUT); digitalWrite(PIN_D0, HIGH); digitalWrite(PIN_D1, HIGH);
- 39. OFFICIAL BOARDS
- 40. Arduino Duemilanove http://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardDuemilanove http://arduino.cc/en/uploads/Main/ArduinoDuemilanove.jpg Pin 13 LED USB connector Barrel jack Digital pins header Reset button ATmega328 MCU Analog pins header Power-ground header See the handout: Arduino_ATmega328_pin_mapping_and_schematic
- 41. Arduino Uno R3 http://www.adafruit.com/index.php?main_page=popup_image&pID=50 ATmega16u2 replaces FT232RL for USB-serial comms See: http://learn.adafruit.com/arduino-tips-tricks-and-techniques/arduino-uno-faq
- 42. Arduino Due Atmel SAM3X8E processor (32 bit ARM Cortex M3 architecture, 84MHz) http://www.adafruit.com/index.php?main_page=popup_image&pID=1076 See: http://arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardDue Note: 3.3 V !!
- 43. Arduino Duemilanove/Uno Features Microcontroller ATmega168/328 Operating Voltage 5V Input Voltage (recommended) 7-12V Input Voltage (limits) 6-20V Digital I/O Pins 14 (of which 6 provide PWM output) Analog Input Pins 6 DC Current per I/O Pin 40 mA DC Current for 3.3V Pin 50 mA Flash Memory 16 KB (ATmega168) or 32 KB (ATmega328) of which 2 KB used by bootloader SRAM 1 KB (ATmega168) or 2 KB (ATmega328) EEPROM 512 bytes (ATmega168) or 1 KB (ATmega328) Clock Speed 16 MHz http://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardDuemilanove
- 44. • The Arduino Duemilanove can be programmed with the Arduino software. • The Arduino integrated development environment (IDE) is written in Java, and is derived from the IDE for the Processing programming language. • It includes a code editor with features such as syntax highlighting, brace matching, and automatic indentation, and is also capable of compiling and uploading programs to the board with a single click. A program or code written for Arduino is called a "sketch".[3] • Arduino programs are written in C or C++. About Arduino Programming
- 45. Getting Started w/ Arduino on Windows 1. Get an Arduino board and USB cable 2. Download the Arduino environment 3. Connect the board with PC 4. Install the drivers 5. Launch the Arduino application 6. Open the blink example 7. Select your board like UNO etc. 8. Select your serial port 9. Upload the program
- 47. Sample Program of LED BLINK • An arduino program == ‘sketch’ – Must have: • setup() • loop() – setup() • configures pin modes and registers – loop() • runs the main body of the program forever – like while(1) {…} – Where is main() ? • Arduino simplifies things • Does things for you /* Blink - turns on an LED for DELAY_ON msec, then off for DELAY_OFF msec, and repeats BJ Furman rev. 1.1 Last rev: 22JAN2011 */ #define LED_PIN 13 // LED on digital pin 13 #define DELAY_ON 1000 #define DELAY_OFF 1000 void setup() { // initialize the digital pin as an output: pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); } // loop() method runs forever, // as long as the Arduino has power void loop() { digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // set the LED on delay(DELAY_ON); // wait for DELAY_ON msec digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // set the LED off delay(DELAY_OFF); // wait for DELAY_OFF msec }
- 48. main() { init(); setup(); while (1) loop(); } Structure of an Arduino Program in C language /* Blink - turns on an LED for DELAY_ON msec, then off for DELAY_OFF msec, and repeats BJ Furman rev. 1.1 Last rev: 22JAN2011 */ #define LED_PIN 13 // LED on digital pin 13 #define DELAY_ON 1000 #define DELAY_OFF 1000 void setup() { // initialize the digital pin as an output: pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); } // loop() method runs forever, // as long as the Arduino has power void loop() { digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // set the LED on delay(DELAY_ON); // wait for DELAY_ON msec digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // set the LED off delay(DELAY_OFF); // wait for DELAY_OFF msec }
- 50. Projects Using Arduino 1. Line follower/Path follower 2. Obstacles Avoider 3. Automatic car parking 4. Driverless car 5. Quad copter 6. Water-level detection in soil 7. Surveillance System 8. Dancing/ Funny Robot 9. Smart phone Garage Door Opener 10. Intrusion alarm 11. Thermostat 12. Balance multirotor motor using arduino & acceleromter 13. Email notifier 14. LED Matrix Control 15. Maze Solver Robot
- 51. 1. http://www.freescale.com/files/microcontrollers/doc/ref_manual/M68HC0 5TB.pdf, p. 25 2. Arduino, “Avalable at http://www.arduino.cc,” 2010. 3. "Programming Arduino Getting Started with Sketches“ : http://www.amazon.com/Programming-Arduino-Getting-Started- Sketches/dp/0071784225/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=136449413 8&sr=1-1&keywords=arduino+sketches). McGraw-Hill. Nov 8, 2011. Retrieved 2013-03-28. 4. C. L. Dym, A. M. Agogino, D. D. Frey, and L. J. Leifer, “Engineering design thinking, teaching, and learning,” Journal of Engineering Education, vol. 94, pp. 103–120, 2005. [Online]. Available: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.72.1593 5. http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/product_card.asp?PN=ATmega328 6. J. Provost, “Why the arduino won and why it’s here to stay,” Tech.Rep. 7. http://learn.adafruit.com/arduino-tips-tricks-and-techniques/arduino-uno- faq






![Thus three pathways (buses) for 3 types of digital
information.
Address Bus - From µp to devices
- Unidirectional.
Data Bus - From µp to devices & devices to µp
- Bidirectional
Control - From µp to devices & from devices to µp
[Interrupt, DMA]
- Bidirectional
Now let us redraw the computer organization diagram](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedsystemdesignusingarduino-161008064345/85/Embedded-system-design-using-arduino-8-320.jpg)

![Microcontroller
A microcontroller is a complete computer system, including
a CPU, memory, a clock oscillator, and I/O on a single
integrated circuit chip. [1]
ANALOG
INPUTS
http://www.freescale.com/files/microcontrollers/doc/ref_manual/M68HC05TB.pdf, p. 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedsystemdesignusingarduino-161008064345/85/Embedded-system-design-using-arduino-10-320.jpg)




![• Introduced in 2005 as a project for students at the Interaction Design
Institute Ivrea in Ivrea, Italy, Arduino is a single board microcontroller.
• An Arduino board consists of an Atmel 8-bit AVR microcontroller with
complementary components to facilitate programming and incorporation
into other circuits [2].
• Arduino can sense the environment by receiving input from a variety of
sensors and can affect its surroundings by controlling lights, motors, and
other actuators.
• The boards can be assembled or purchased preassembled; the open-source
IDE can be downloaded for free.
• The Arduino programming language is very simple and follows C like
syntax.
• Arduino projects can be stand-alone or they can communicate with
software running on a computer (e.g. Processing).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedsystemdesignusingarduino-161008064345/85/Embedded-system-design-using-arduino-15-320.jpg)



























![• The Arduino Duemilanove can be programmed with the
Arduino software.
• The Arduino integrated development environment (IDE) is
written in Java, and is derived from the IDE for the
Processing programming language.
• It includes a code editor with features such as syntax
highlighting, brace matching, and automatic indentation,
and is also capable of compiling and uploading programs
to the board with a single click. A program or code written
for Arduino is called a "sketch".[3]
• Arduino programs are written in C or C++.
About Arduino Programming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedsystemdesignusingarduino-161008064345/85/Embedded-system-design-using-arduino-44-320.jpg)






![1. http://www.freescale.com/files/microcontrollers/doc/ref_manual/M68HC0
5TB.pdf, p. 25
2. Arduino, “Avalable at http://www.arduino.cc,” 2010.
3. "Programming Arduino Getting Started with Sketches“ :
http://www.amazon.com/Programming-Arduino-Getting-Started-
Sketches/dp/0071784225/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=136449413
8&sr=1-1&keywords=arduino+sketches). McGraw-Hill. Nov 8, 2011.
Retrieved 2013-03-28.
4. C. L. Dym, A. M. Agogino, D. D. Frey, and L. J. Leifer, “Engineering
design thinking, teaching, and learning,” Journal of Engineering
Education, vol. 94, pp. 103–120, 2005. [Online]. Available:
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.72.1593
5. http://www.atmel.com/dyn/products/product_card.asp?PN=ATmega328
6. J. Provost, “Why the arduino won and why it’s here to stay,” Tech.Rep.
7. http://learn.adafruit.com/arduino-tips-tricks-and-techniques/arduino-uno-
faq](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedsystemdesignusingarduino-161008064345/85/Embedded-system-design-using-arduino-51-320.jpg)
































































































![Présentation_gestion[1] [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/prsentationgestion1autosaved-250608153959-37fabfd3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
