Functional Programming in Javascript - IL Tech Talks week
- 1. Functional Programming in Javascript Yoav Rubin @yoavrubin
- 2. Today • About functional programming • A little about Javascript • Deep dive into the combination of the two – Inner functions and closures – Higher order functions – Decomplecting calls patterns
- 3. What will you gain? • Inner functions and closures – Improving performance via memoization – A different perspective on objects • Higher order functions – Avoiding mistakes due to the leaky abstraction of arrays – Composing functions from functions • Decomplecting calls patterns – Regaining the ability to use recursion – A look behind the scenes of streams
- 4. Today • About functional programming • A little about Javascript • Deep dive into the combination of the two – Inner functions and closures – Higher order functions – Decomplecting calls patterns
- 5. About functional programming • All agree – it’s a programming paradigm • There’s no agreed upon definition – See Gilad Bracha’s talk: http://www.infoq.com/presentations/functional-pros-cons
- 6. My definition • Thinking the software using data and functions – Analysis, modeling • Data and functions focused development – Data transformation instead of mutable object state • Core ideas – Data is immutable – Functions are first class citizens
- 7. Why functional programming • Higher level of programming – Faster to develop – Simpler to test MUST • A good software person should know more then one paradigm – Because problems are getting tougher
- 8. Today • About functional programming • A little about Javascript • Deep dive into the combination of the two – Inner functions and closures – Higher order functions – Decomplecting calls patterns
- 9. A little about Javascript
- 10. Objects are maps • An object is a set of key-value pairs • Values can be anything and may change • Pairs can be added and removed
- 11. key1 value1 key2 value2 key3 value3 key5 key4 { } { } { } key6
- 12. key1 value1 key2 value2 key3 value3 key5 key4 { } { } { } key6 Keys whose values are members
- 13. key1 value1 key2 value2 key3 value3 key5 key4 { } { } { } key6 Keys whose values are methods
- 14. Arrays • Arrays are objects are maps • Fields whose keys are integers gain “special treatment”
- 15. key1 value1 key2 value2 Integer key2 value4 key3 key4 Integer key3 value5 Integer key1 value3 { } { }
- 16. key1 value1 key2 value2 Integer key2 value4 key3 key4 Fields whose values are members Integer key3 value5 Integer key1 value3 { } { }
- 17. key1 value1 key2 value2 Integer key2 value4 key3 key4 Integer key3 Fields whose values are methods value5 Integer key1 value3 { } { }
- 18. key1 value1 key2 value2 Integer key2 value4 key3 key4 Integer key3 value5 Integer key1 value3 { } { } Fields whose keys are integers
- 19. Functions • Functions are objects are maps • Can also be executed
- 20. key1 value1 key2 value2 (…) {…} key3 key4 Fields whose keys are members { } { }
- 21. key1 value1 key2 value2 (…) {…} key3 key4 Fields whose values are methods { } { }
- 22. key1 value1 key2 value2 (…) {…} key3 key4 { } { } What gets executed
- 23. Functions are objects • Can be defined anywhere • Can be assigned to a variable – Or act as a value in an object (or in an array) • Can be sent as an argument to a function • Can be returned as a return value from a function
- 24. Today • About functional programming • A little about Javascript • Deep dive into the combination of the two – Inner functions and closures – Higher order functions – Decomplecting calls patterns
- 25. Inner functions and closures • A function can be defined inside another function • The inner function can access anything found at the outer function
- 26. Recursive Fibonacci function fib(n){ if (n < 2) return n; return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } fib(10) results in 177 calls to fib n (time complexity - O(2 ) )
- 27. Fibonacci using inner function function fastFib(n){ var memo = [0,1]; var fib = function(n){ var result = memo[n]; if(result !== undefined) return result; result = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); memo[n] = result; return result; } return fib(n); } fastFib(10) results in 19 calls to the fib function (time complexity - O(n)) An inner function
- 28. FastFib Memo The Fib function • Calculate if value is not in the cache • Maintain the cache This pattern is nicknamed memoization
- 29. Closure • Computation done in an inner function can access data found in the outer function • Such an access creates a construct called closure
- 30. Closures remain alive even when the execution of the outer function was finished
- 31. Fibonacci using closure function fastFibMaker(){ var memo = [0,1]; var fib = function(n){ var result = memo[n]; if (result !== undefined) return result; result = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); memo[n] = result; return result; } return fib; } var theFib = fastFibMaker(); // returns a function theFib (10); // 19 calls to fib theFib (10); // 1 call to fib
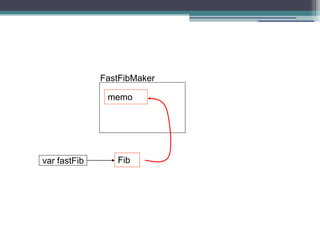
- 33. FastFibMaker memo Fib var fastFib
- 34. key1 value1 key2 value2 (…) {…} key3 key4 What gets executed { } { } X=… Y=…
- 36. Today • About functional programming • A little about Javascript • Deep dive into the combination of the two – Inner functions and closures – Higher order functions – Decomplecting calls patterns
- 37. Higher order functions • Receive function, return value • Receive value, return function
- 38. Higher order functions • Receive function, return value • Receive value, return function
- 39. Receive function, return value • The receiving function provides the syntactic skeleton of the computation • The sent function provides the semantics for the calculation • Implementation of the “Strategy design pattern”
- 40. Where do we see it?
- 41. Working with arrays • One of the most common things we do in code • Especially, in conjunction with looping • The common looping patterns have equivalent higher order methods in arrays
- 42. Building a value out of an array var i, res = seed; for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++) res = someFunc(res, arr[i]);
- 43. Building a value out of an array var i, res = seed; for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++) res = someFunc(res, arr[i]); This is just the same as res = arr.reduce(someFunc, seed);
- 44. Creating an array out of an array var i, res = []; for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++) res.push(someFunc(arr[i]));
- 45. Creating an array out of an array var i, res = []; for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++) res.push(someFunc(arr[i])); This is just the same as res = arr.map(someFunc);
- 46. Selecting items from an array var i, res = []; for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++){ if (pred(arr[i])) res.push(arr[i]); } This is just the same as res = arr.filter(someFunc);
- 47. Selecting items from an array var i, res = []; for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++){ if (pred(arr[i])) res.push(arr[i]); } This is just the same as res = arr.filter(pred);
- 48. Few more variations • Array.forEach(someFunc) – To execute someFunc on every item in the array • Array.some(predFunc) – Checks whether at least one of the elements of the array fulfils predFunc • Array.every(predFunc) – Checks whether all of the elements of the array fulfils predFunc
- 49. And combination of these var i, tmp, res = seed; for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(pred(arr[i])){ tmp = mapFn(arr[i]); res = redFn(res, tmp); } } var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFunc);
- 50. And combination of these var i, tmp, res = seed; for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(pred(arr[i])){ tmp = mapFn(arr[i]); res = redFn(res, tmp); } } var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);
- 51. Boilerplatting var i, tmp, res = seed; for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(pred(arr[i])){ tmp = mapFn(arr[i]); res = redFn(res, tmp); } } var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed); That’s just boilerplate code !!!
- 52. What can bite you here? var i, tmp, res = seed; for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(pred(arr[i])){ tmp = mapFn(arr[i]); res = redFn(res, tmp); } } What will happen if you copy & paste the loop’s code without copying the declaration of i ? var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);
- 53. What can bite you here? var i, tmp, res = seed; for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(pred(arr[i])){ tmp = mapFn(arr[i]); res = redFn(res, tmp); } } Once in a while you’ll have an off by one error var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);
- 55. What can bite you here? var i, tmp, res = seed; for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(pred(arr[i])){ tmp = mapFn(arr[i]); res = redFn(res, tmp); } } What if there’s a hole ? var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);
- 57. Same same but different arr = [1,2,3] arr[4] = 4 var res = 0; for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ res += arr[i]; } arr.reduce(add, 0) NaN 10
- 58. Just *don’t* do it • Array is a leaky abstraction in Javascript – It is not a continuum of memory – It is just a map • Using array’s methods makes your code resilient to – Copy paste mistakes – Off by one errors – Holes in the array
- 59. Looping over an array is a code smell in Javascript
- 60. Higher order functions • Receive function, return value • Receive value, return function
- 61. Receive value, return function • Composing a new function – Keep the received value in a closure – Return a new function that uses that value
- 62. Fanning out
- 64. Fan out • Receives several functions • Return a fun-out function that – For a given input – Returns all the results of applying the previously given functions on that input
- 65. Fan out function fanOutMaker(/* fns*/){ var fns = arguments; return function(/* arguments */){ var res = []; for (var i=0,l=fns.length;i<l;i++){ res.push(fns[i].apply(null, arguments)); } return res; } }
- 66. Fan out function fanOutMaker(/* fns*/){ var fns = arguments; return function(/* arguments */){ var res = []; for (var i=0,l=fns.length;i<l;i++){ res.push(fns[i].apply(null, arguments)); } return res; } } Not the same
- 67. Fan out function fanOutMaker(/* fns*/){ var fns = arguments; return function(/* arguments */){ var res = []; for (var i=0,l=fns.length;i<l;i++){ res.push(fns[i].apply(null, arguments)); } return res; } } Call each of the closured fns with current argument
- 68. Today • About functional programming • A little about Javascript • Deep dive into the combination of the two – Inner functions and closures – Higher order functions – Decomplecting calls patterns
- 70. Reclaiming recursion • We were taught that recursion works in theory – But only there • Some languages provide built-in tail call optimization – Javascript doesn’t • We can do it by ourselves
- 71. Why would you want recursion • Handling recursive structures – Data formats - Json (or Xml) – DOM • Data digestion (especially in node.js) – Graph processing • Sometimes there are tools that do it • Sometimes you need to make the tools
- 72. Decomplecting calls patterns • A function call is built of: – Saying what computation should be done • What’s the function, what are the arguments – Telling it to be executed now
- 73. function someFunc(arg1, arg2){ //do something // return something } someFunc ( a1, a2 )
- 74. function someFunc(arg1, arg2){ //do something // return something } someFunc ( a1, a2 ) What computation should be done
- 75. function someFunc(arg1, arg2){ //do something // return something } someFunc ( a1, a2 ) Do it now
- 76. How to separate? • Wrap the call to someFunc with a function that executes it function(){ return someFunc(a1,a2); } Let’s call it ‘continuation’ We can invoke the continuation with different mechanisms
- 77. How to separate? • Wrap the call to someFunc with a function that executes it function(){ return someFunc(a1,a2); } • Let’s call it ‘continuation’ • We can invoke the continuation with different mechanisms to solve different problems
- 78. • Controlling recursion • To inWfinhitay,t s kteipn bdy ostfe pproblems
- 79. What kind of problems • Controlling recursion • To infinity, step by step
- 80. function factorial (n) { if(n<2) return n; return n*factorial(n-1); } • What’s the problem here? – Can’t control the depth of the recursion – How can we make it better?
- 81. function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n === num) return accum; n += 1; return fact(accum*n, n); } return fact(1, 1); } • What have we changed?
- 82. function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n === num) return accum; n += 1; return fact(accum*n, n); } return fact(1, 1); } • What have we changed? – Using inner function to compute the factorial – Moved the recursive call to be in a tail position
- 83. function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n === num) return accum; n += 1; return fact(accum*n, n); } return fact(1, 1); } • What have we changed? – Using inner function to compute the factorial – Moved the recursive call to be in a tail position • Still, we can’t control the recursion depth
- 84. Where’s the problem ? function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n === num) return accum; n += 1; return fact(accum*n, n); } return fact(1, 1); }
- 85. Where’s the problem ? function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n === num) return accum; n += 1; return fact(accum*n, n); } return fact(1, 1); }
- 86. Where’s the problem ? function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n === num) return accum; n += 1; return fact(accum*n, n); } return fact(1, 1); } We define the calculation and say that it should be performed now
- 87. Separate the definition of the call from executing it function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n===num) return accum; n +=1; return function() { return fact(accum*n, n);}; } return function() {return fact(1, 1);}; } • What have we changed? Made a continuation out of the recursive call Still need a mechanism to invoke the continuation
- 88. Separate the definition of the call from executing it function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n===num) return accum; n +=1; return function() { return fact(accum*n, n);}; } return function() {return fact(1, 1);}; } • What have we changed? – Made a continuation out of the recursive call – Still need a mechanism to invoke the continuation
- 89. function trampoline (f) { while(isFunction(f)) f = f(); return f; }
- 90. Separate the definition of the call from executing it function factorial (num) { function fact(accum, n){ if(n===num) return accum; n += 1; return function() { return fact(accum*n, n);}; } return function(){ return fact(1, 1);}; } Trampoline (factorial(…)) • What have we changed? function trampoline (f) { while(isFunction(f)) f = f(); return f; } – Used trampoline as a mechanism to invoke the continuation
- 91. factorial(5) trampoline with f(fact(1, 1)) Trampoline if isFunction(f) – invoke it otherwise return what it got f(fact(2, 2)) f(fact(6,3)) fact(1,1) fact(2,2) fact(6,3) … fact(120,5) Return value is a function Returning 120 from trampoline f(fact(24,4)) 120 Function call Return value is a value
- 92. The recipe • Move the recursive call to be in a tail position – Helper function and accum – Call the helper function to start • Wrap the recursive call in a continuation – function() {return <the-recursive-call>;} – Also the first call to the helper function • Have trampoline around • Call trampoline with the initial continuation
- 93. What is it good for? • Controlling recursion • To infinity, step by step
- 94. To infinity, step by step • Trampoline computed all the intermediate results till it got to the stop condition – Immediately called the continuation • Instead, we can make the user control when to call the continuation, and when to stop calling it
- 95. How about • Each computation will return an intermediate result and the continuation • Put these two in an object – Call the result ‘first’ • As it is the first result in the stream starting from this object – Call the continuation rest • As it is the way to get to the rest of the stream
- 96. function factorialStream () { function fact(accum, n){ n += 1; return { first: accum, rest: function(){return fact(accum*n, n));} }; return fact(1, 1); }
- 97. function factorialStream () { function fact(accum, n){ n += 1; return { first: accum, rest: function(){return fact(accum*n, n));} }; return fact(1, 1); } .rest() { first: 2, { first: 6, { first: 24, … rest:F2 } rest:F3 } rest:F4 } .rest() .rest() factorialStream() { first: 1, rest:F1 }
- 99. Infinite and lazy streams • What can you do with a stream – Find specific values – Make new streams out of streams • map • filter – Make streams out of values • Repeating , cycling – Combine streams • interleaving
- 100. Find the n’th element function dropN(strm, n){ while (n-- > 0 && strm){ strm = strm.rest(); } return strm; } function nth(strm, n) { return dropN(strm, n-1).first; }
- 101. Infinite and lazy streams • Streams can be passed around and materialize a computation only when needed • See more in this repo: https//:github.com/yoavrubin/streams
- 102. Summary – key takeaways • In Javascript functions are objects are maps • Closures are your friends • Don’t loop over arrays • Don’t fear recursion
- 103. Thank You @yoavrubin


























![Fibonacci using inner function
function fastFib(n){
var memo = [0,1];
var fib = function(n){
var result = memo[n];
if(result !== undefined) return result;
result = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
memo[n] = result;
return result;
}
return fib(n);
}
fastFib(10) results in 19 calls to the fib function (time
complexity - O(n))
An inner
function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-27-320.jpg)



![Fibonacci using closure
function fastFibMaker(){
var memo = [0,1];
var fib = function(n){
var result = memo[n];
if (result !== undefined) return result;
result = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
memo[n] = result;
return result;
}
return fib;
}
var theFib = fastFibMaker(); // returns a function
theFib (10); // 19 calls to fib
theFib (10); // 1 call to fib](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-31-320.jpg)









![Building a value out of an array
var i, res = seed;
for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++)
res = someFunc(res, arr[i]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-42-320.jpg)
![Building a value out of an array
var i, res = seed;
for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++)
res = someFunc(res, arr[i]);
This is just the same as
res = arr.reduce(someFunc, seed);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-43-320.jpg)
![Creating an array out of an array
var i, res = [];
for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++)
res.push(someFunc(arr[i]));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-44-320.jpg)
![Creating an array out of an array
var i, res = [];
for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++)
res.push(someFunc(arr[i]));
This is just the same as
res = arr.map(someFunc);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-45-320.jpg)
![Selecting items from an array
var i, res = [];
for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++){
if (pred(arr[i]))
res.push(arr[i]);
}
This is just the same as
res = arr.filter(someFunc);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-46-320.jpg)
![Selecting items from an array
var i, res = [];
for (i=0 ; i<arr.length ;i ++){
if (pred(arr[i]))
res.push(arr[i]);
}
This is just the same as
res = arr.filter(pred);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-47-320.jpg)

![And combination of these
var i, tmp, res = seed;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(pred(arr[i])){
tmp = mapFn(arr[i]);
res = redFn(res, tmp);
}
}
var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFunc);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-49-320.jpg)
![And combination of these
var i, tmp, res = seed;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(pred(arr[i])){
tmp = mapFn(arr[i]);
res = redFn(res, tmp);
}
}
var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-50-320.jpg)
![Boilerplatting
var i, tmp, res = seed;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(pred(arr[i])){
tmp = mapFn(arr[i]);
res = redFn(res, tmp);
}
}
var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);
That’s just boilerplate code !!!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-51-320.jpg)
![What can bite you here?
var i, tmp, res = seed;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(pred(arr[i])){
tmp = mapFn(arr[i]);
res = redFn(res, tmp);
}
}
What will happen if you
copy & paste the loop’s
code without copying the
declaration of i ?
var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-52-320.jpg)
![What can bite you here?
var i, tmp, res = seed;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(pred(arr[i])){
tmp = mapFn(arr[i]);
res = redFn(res, tmp);
}
}
Once in a while
you’ll have an
off by one error
var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-53-320.jpg)

![What can bite you here?
var i, tmp, res = seed;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(pred(arr[i])){
tmp = mapFn(arr[i]);
res = redFn(res, tmp);
}
}
What if there’s
a hole ?
var res = arr.filter(pred).map(mapFn).reduce(redFn, seed);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-55-320.jpg)

![Same same but different
arr = [1,2,3]
arr[4] = 4
var res = 0;
for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
res += arr[i];
}
arr.reduce(add, 0)
NaN
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-57-320.jpg)







![Fan out
function fanOutMaker(/* fns*/){
var fns = arguments;
return function(/* arguments */){
var res = [];
for (var i=0,l=fns.length;i<l;i++){
res.push(fns[i].apply(null, arguments));
}
return res;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-65-320.jpg)
![Fan out
function fanOutMaker(/* fns*/){
var fns = arguments;
return function(/* arguments */){
var res = [];
for (var i=0,l=fns.length;i<l;i++){
res.push(fns[i].apply(null, arguments));
}
return res;
}
}
Not the same](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-66-320.jpg)
![Fan out
function fanOutMaker(/* fns*/){
var fns = arguments;
return function(/* arguments */){
var res = [];
for (var i=0,l=fns.length;i<l;i++){
res.push(fns[i].apply(null, arguments));
}
return res;
}
}
Call each of the closured fns
with current argument](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpjs-iltechtalks-140909045639-phpapp02/85/Functional-Programming-in-Javascript-IL-Tech-Talks-week-67-320.jpg)













































































































