Introduction to Java Programming- Java Programming Tutorials for beginners
- 2. Java is ... Old - maybe not old enough 2
- 3. 3 1.0 What is Java ? – Java is a programming language and a platform. – Java is a high level, robust, object-oriented and secure programming language. – Platform: Any hardware or software environment in which a program runs, is known as a platform. ■ Since Java has a runtime environment (JRE) and API, it is called a platform.
- 4. 4 Java Example //File name : simple.java import java.io.*; class Simple { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("Hello Java"); } }
- 5. 5 Java Applications ■ We know that Java is the “King of all programming languages”. ■ Since its foundation, this language has become a backbone for billions of devices and applications. ■ This language is continually ranked first in the rankings of software developers as the best choice of programming languages. ■ Java is used in the majority of applications, from mobile phones to enterprise servers and computing platforms.
- 6. 6 Java Applications ■ Currently, about 3 billion mobile phones are implemented in Java, as well as about 125 million TV sets and each Blu-ray player use Java. ■ Every big organization uses Java in one way or another. ■ More than 64,000 companies are using Java in the United States. ■ For example, Google uses Java to build and develop Google Docs applications. ■ According to Sun, 3 billion devices run Java. – There are many devices where Java is currently used.
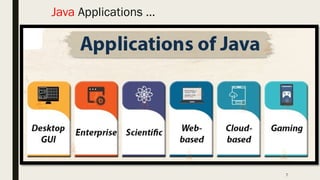
- 8. 8 Java Applications ■ You would be wondering why Java is so popular and where it is exactly used. ■ Below is the Java applications list: 1) Desktop GUI Applications 2) Mobile Applications 3) Enterprise Applications 4) Scientific Applications 5) Web-based Applications 6) Embedded Systems 7) Big Data Technologies 8) Distributed Applications 9) Cloud-based Applications 10) Web servers and Application servers 11) Software Tools 12) Gaming Applications
- 9. 9 Java Applications … 1. Desktop GUI (Graphical User Interface) Applications ■ Desktop applications can be easily developed using Java. – We use APIs like AWT, Swing, JavaFX to build these applications. ■ AWT (Abstract Windowing Toolkit) is an interface used to develop window-based applications in Java. – It is “not totally Java-based” as it uses window user interface functionalities such as a menu, button, list, etc. ■ Swing is a GUI widget toolkit, which uses AWT and provides certain advanced components like trees, tables, scroll panes, tabbed panels and, lists. – Swing is” totally java-based” and uses Swing packages of Java to develop applications. It responds to all the mouse-click events, key entries, etc., ■ JavaFX is a modern way to develop a desktop application in Java, it is graph-based and totally different from AWT and Swings. ■ Examples of desktop GUI applications are Acrobat Reader, ThinkFree, Media Player, Antiviruses, etc.
- 10. 10 Java Applications … 2. Mobile Applications ■ A mobile application is an application created for mobile phones and tablets. – In today’s era, the majority of phones and smart devices have Android OS and Android development is not possible without Java. – Java Micro Edition (Java ME or J2ME) is a popular cross-platform framework that is used to build applications that run across all feature phones and smartphones. ■ Moreover, Java is compatible with AndroidStudio and Kotlin. ■ Now, you must be thinking why only for Android mobile app development? – The reason is that Java compiler compiles the Java classes into bytecode and this bytecode runs on Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM), which is a specialized virtual machine (VM) for Android. ■ Examples of mobile applications are Photo and video gallery apps, Simple Calendar, Netflix, Tinder, QRReader, Google Earth, Uber, etc.
- 11. 11 Java Applications … 3. Enterprise Applications ■ An enterprise application is a large software system which operates in a corporate environment, to satisfy the needs of an organization, rather than of individual users. ■ Java becomes the first choice for the development of enterprise applications because of its robust features that match the requirements for the same. – In today’s era, most of the enterprise organizations are based on the applications of Java only because it is the most secure, powerful, scalable language. ■ Oracle Corporation claims that “about 97% of enterprise applications use Java for development of large-scale software”. ■ Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) is an API that is used to provide the tools necessary to develop large-scale, multi-tiered, scalable, reliable, distributed and secured network applications in enterprises.
- 12. 12 Java Applications … 3. Enterprise Applications … ■ Java fulfills the most essential need of these enterprises, which is security, as Java runs inside the JVM (Java Virtual Machine), which verifies the bytecode coming from the external systems, which ultimately prevents the security breaches. – This is the reason why most of the banking applications are developed on the Java platform. ■ Moreover, Java improves the performance of these applications, as it comes with strong memory management, which automatically deletes the unused memory. ■ Applications of Java can easily be made scalable in order to increase the number of users on the enterprise application site. ■ Companies like Naukri, Jabong, Google, Myntra, Flipkart, Trivago, ibibo, TripAdvisor, Spotify, Uber, TCS, Infosys, HCL, Wipro, Pinterest, eBay, etc. use Java. ■ Examples of enterprise applications are Business corporations, schools, banks, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Resource Management) systems, clubs, charities, governments, interest-based user groups, etc.
- 13. 13 Java Applications … 4. Scientific Applications ■ A scientific application is an application that affects real-world activities using mathematics. – Java supports the development of scientific applications, because of its powerful features. ■ Java becomes the best choice for writing scientific applications involving scientific calculations and mathematical operations. – It provides a fast, secure and highly portable environment to these applications, which is the basic requirement for these applications. ■ It has powerful mathematical calculations which have to give the same results on different platforms, this makes the choice for the developers to opt Java for scientific applications. ■ MATLAB (Mathematical Laboratory) which is one of the most popular scientific applications, uses Java for developing both front-end (interactive user-interface) and back-end (a core part of the system). ■ The front-end and back-end of the scientific applications are both based on Java. – For the front-end, Java provides struts, JSP (Java Server Pages), servlets. – For the back-end, core Java can be used in servlets. ■ Examples of scientific applications are applications related to research, science, medical science, space, aeronautics, etc.
- 14. 14 Java Applications … 5. Web-based Applications ■ A web application is a client-server program that is delivered on the Internet through a browser interface. ■ Java supports the development of web-applications with the help of servlets, struts, JSP (Java Server Pages) and JSF (Java Server Faces), Spring, Hibernate and web-servers like Apache Tomcat, Apache HTTP web-server, Resin, adobe JRun, etc. – With the help of these technologies, we can develop any kind of web-based application. ■ Servlets and JSPs are the server-side components that help to develop the business logic of the web application. – JSP is an extension of the Servlet as it has more features as compared to the servlet. ■ E-commerce web applications also use Java with the help of open-source eCommerce platforms, such as Broadleaf. ■ Java provides easy coding and high security which enables the development of a large number of applications for health, social security, education, and insurance. ■ Examples of web-based applications are irctc.co.in, online forms, shopping carts, Gmail, Google Sheets, Google Slides and many more.
- 15. 15 Java Applications … 6. Embedded Systems ■ An embedded system, also known as an integrated system, is a combination of many small computing units that assemble together to perform dedicated functions for the larger systems. ■ Embedded systems are present everywhere. – Don’t believe it? Most of us use them without knowing. ■ For example, a motor system, entertainment and multimedia in a car, E-commerce, wireless communication, mobile computing and networking use an embedded system. ■ Embedded systems use Java for development. – Originally, Java was designed for the purpose of developing embedded systems. ■ Java shows how efficient its platform is, for which there is a need of just 130 KBs to use it on smart cards or sensors. – Java is fast which can be important when using low-power/low-speed processors, and its robustness which means handles exceptions safely. ■ SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards in our phones have been running a variant of the JVM (Java Card) for nearly 20 years. ■ Other devices like BlueRay Disc players, utility meters and televisions use Java technology. – According to Oracle Corporation, “100% of Blu-ray Disc Players and 125 million TV devices use Java”.
- 16. 16 Java Applications … 7. Big Data Technologies ■ The term big data is defined as “extremely large and complex datasets that may be analyzed to extract patterns, trends, and useful information. – It is one of the most popular topics in the world of the latest technology. – Java is the perspective of big data. – Today, many developers are switching their careers to Big Data Technology. ■ An open-source framework, called Hadoop, associated with big data, is written in Java. – Moreover, the Automatic Garbage Collection and strong memory management give it higher priority over the other programming languages. ■ Many prominent big data technologies like Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Mahout, etc. are the sub-projects of Java. – Also, the most powerful programming languages like Scala (Scalable Language), a pure object- oriented language, is based on Java. – Scala programs are easily convertible into bytecode; which can run on the JVM. ■ Hadoop and other big data technologies are also using Java in one way or the other. – For example, Apache’s Java-based HBase and Accumulo (open source), and ElasticSearch as well.
- 17. 17 Java Applications … 8. Distributed Applications ■ A distributed application is an application or software that executes or runs on multiple computers within a network. ■ Distributed applications or systems have many common requirements that occur especially because of the distributed and dynamic nature of the platforms they operate on. – Java offers options to realize these applications. ■ RMI (Remote Procedure Invocation) and CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) are the APIs to develop distributed applications. ■ The Jini (Java Intelligent Networking Infrastructure) gives an infrastructure to provide, register, and find distributed services based on its specifications. – An essential part of Jini is JavaSpaces, that supports distribution, persistence, and migration of objects in a distributed environment.
- 18. 18 Java Applications … 9. Cloud-based Applications ■ Cloud computing means on-demand delivery of IT resources via the Internet, including storage, servers, databases, networking, and software with a pay-as-you-go pricing model. – It provides a solution for IT infrastructure at a low cost, as we can save files on remote databases and retrieve them on demand. ■ No doubt you’re curious how Java programming fits into the cloud computing picture. ■ Java has long been the programming language that provides a structure for web applications, and now it has reached cloud applications, because of its distributed nature. ■ Java provides us with features that can help us build applications used in SaaS (Software-as-a-service), IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-service) and PaaS (Platform-as-a-service) development. ■ There are many Java cloud development tools. – For example, Oracle Java cloud service provides a platform to develop and configure the Oracle servers. ■ Java can serve the companies to build their applications remotely or help them share data with others, according to their needs.
- 19. 19 Java Applications … 10. Web Servers and Application Servers ■ A web server is a computer program that uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and other protocols, to store, process, and respond to client requests made over WWW (World Wide Web). – A web server is a system that runs websites and delivers web pages to users. ■ An application server (or app server) is a software framework that stores the business logic for an application program and handles all operations between the client-end and the back-end of organizations. – It is not limited to HTTP but can do a bunch of other stuff. ■ Java ecosystem contains multiple Java web servers and application servers. ■ Java provides web servers including Apache Tomcat, Simple, Jo!, Rimfaxe Web Server (RWS) Apache HTTP server, Resin, Adobe JRun, and Project Jigsaw. ■ WebLogic, GlassFish, WildFly, WebSphere, and JBoss EAP occupy commercial application server space.
- 20. 20 Java Applications … 11. Software Tools ■ A software tool is a set of computer programs that developers use to develop, analyze, maintain, debug, or support other applications and programs. – Many developers use Java to write and develop useful software tools. ■ Examples of software tools are Eclipse, IntelliJ Idea, and NetBeans IDE. 12. Gaming Applications ■ Java proves to be one of the best platforms for developing 2-Dimensional games. – Today almost every person has an Android phone that has Android games in it. – Android games cannot be built without Java. ■ Java supports jMonkeyEngine which is the most powerful open-source 3D-Engine and has the capacity to design 3-Dimensional games. ■ Android games use Java as a primary language because Java supports the Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) which is specially designed to run on the Android platform.
- 21. 21 Java Platforms / Editions ■ There are 4 platforms or editions of Java: 1) Java SE (Java Standard Edition) ■ It is a Java programming platform. – It includes Java programming APIs such as java.lang, java.io, java.net, java.util, java.sql, java.math etc. – It includes core topics like OOPs, String, Regex, Exception, Inner classes, Multithreading, I/O Stream, Networking, AWT, Swing, Reflection, Collection, etc. 2) Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) ■ It is an enterprise platform which is mainly used to develop web and enterprise applications. – It is built on the top of the Java SE platform. – It includes topics like Servlet, JSP, Web Services, EJB, JPA, etc.
- 22. 22 Java Platforms / Editions … 3) Java ME (Java Micro Edition) ■ It is a micro platform which is mainly used to develop mobile applications. 4) JavaFX ■ It is used to develop rich internet applications. – It uses a light-weight user interface API.
- 23. 23 1.1 History of Java ■ The history of Java is very interesting. – Java was originally designed for interactive television, but it was too advanced technology for the digital cable television industry at the time. – The history of java starts with Green Team. – Java team members (also known as Green Team), initiated this project to develop a language for digital devices such as set-top boxes, televisions, etc. – However, it was suited for internet programming. – Later, Java technology was incorporated by Netscape. ■ The principles for creating Java programming were "Simple, Robust, Portable, Platform- independent, Secured, High Performance, Multithreaded, Architecture Neutral, Object- Oriented, Interpreted and Dynamic". ■ James Gosling - founder of java – Currently, Java is used in internet programming, mobile devices, games, e-business solutions, etc.
- 24. 24 1.1 History of Java … ■ There are given the significant points that describe the history of Java. 1) James Gosling, Mike Sheridan, and Patrick Naughton initiated the Java language project in June 1991. ■ The small team of sun engineers called Green Team. 2) Originally designed for small, embedded systems in electronic appliances like set-top boxes. 3) Firstly, it was called "Greentalk" by James Gosling, and file extension was .gt. 4) After that, it was called Oak and was developed as a part of the Green project.
- 25. 25 1.1 History of Java … Why Java named "Oak"? 5) Why Oak? – Oak is a symbol of strength and chosen as a national tree of many countries like U.S.A., France, Germany, Romania, etc. 6) In 1995, Oak was renamed as "Java" because it was already a trademark by Oak Technologies.
- 26. 26 1.1 History of Java … Why Java Programming named "Java"? 7) Why had they chosen java name for java language? – The team gathered to choose a new name. – The suggested words were "dynamic", "revolutionary", "Silk", "jolt", "DNA", etc. – They wanted something that reflected the essence of the technology: revolutionary, dynamic, lively, cool, unique, and easy to spell and fun to say. – According to James Gosling, "Java was one of the top choices along with Silk". – Since Java was so unique, most of the team members preferred Java than other names. 8) Java is an island of Indonesia where first coffee was produced (called java coffee). 9) Notice that Java is just a name, not an acronym. 10) Initially developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (which is now a subsidiary of Oracle Corporation) and released in 1995. 11) In 1995, Time magazine called Java one of the Ten Best Products of 1995. 12) JDK 1.0 released in(January 23, 1996).
- 27. 27 1.2 Java Version History … ■ Many java versions have been released till now. – The current stable release of Java is Java SE 10. 1) JDK Alpha and Beta (1995) 2) JDK 1.0 (23rd Jan 1996) 3) JDK 1.1 (19th Feb 1997) 4) J2SE 1.2 (8th Dec 1998) 5) J2SE 1.3 (8th May 2000) 6) J2SE 1.4 (6th Feb 2002) 7) J2SE 5.0 (30th Sep 2004) 8) Java SE 6 (11th Dec 2006) 9) Java SE 7 (28th July 2011) 10) Java SE 8 (18th March 2014) 11) Java SE 9 (21st Sep 2017) 12) Java SE 10 (20th March 2018) 13) Java SE 11 (September 25, 2018) 14) Java SE 12 (March 19, 2019) 15) Java SE 13 (September 17, 2019) 16) Java SE 14 (March 17, 2020) 17) Java SE 15 (September 15, 2020)
- 28. 28 1.3 Features of Java ■ The primary objective of Java programming language creation was to make it portable, simple and secure programming language. – Apart from this, there are also some excellent features which play an important role in the popularity of this language. – The features of Java are also known as java buzzwords.
- 29. 29 1.3 Features of Java … ■ A list of most important features of Java language is given below. 1)Simple 2)Object-Oriented 3)Portable 4)Platform independent 5)Secured 6)Robust 7)Architecture neutral 8)Interpreted 9)High Performance 10)Multithreaded 11)Distributed 12)Dynamic
- 30. 30 1.3. Features of Java … 1.) Simple – Java is very easy to learn, and its syntax is simple, clean and easy to understand. – According to Sun, Java language is a simple programming language because: ■ Java syntax is based on C++ (so easier for programmers to learn it after C++). ■ Java has removed many complicated and rarely-used features, for example, explicit pointers, operator overloading, etc. ■ There is no need to remove unreferenced objects because there is an Automatic Garbage Collection in Java.
- 31. 31 1.3. Features of Java … 2.) Object-oriented – Java is an object-oriented programming language. ■ Everything in Java is an object. ■ Object-oriented means we organize our software as a combination of different types of objects that incorporates both data and behavior. – Object-oriented programming (OOPs) is a methodology that simplifies software development and maintenance by providing some rules. – Basic concepts of OOPs are: Object Class Inheritance Polymorphism Abstraction Encapsulation
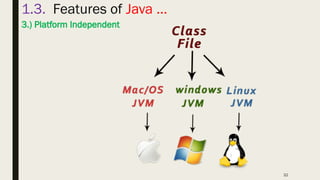
- 32. 32 1.3. Features of Java … 3.) Platform Independent
- 33. 33 1.3. Features of Java … 3.) Platform Independent – Java is platform independent because it is different from other languages like C, C++, etc. which are compiled into platform specific machines while Java is a write once, run anywhere language. ■ A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a program runs. – There are two types of platforms software-based and hardware-based. ■ Java provides a software-based platform. – The Java platform differs from most other platforms in the sense that it is a software-based platform that runs on the top of other hardware- based platforms.
- 34. 34 1.3. Features of Java … 3.) Platform Independent – It has two components: 1) Runtime Environment 2) API(Application Programming Interface) – Java code can be run on multiple platforms, for example, Windows, Linux, Sun Solaris, Mac/OS, etc. – Java code is compiled by the compiler and converted into bytecode. – This bytecode is a platform-independent code because it can be run on multiple platforms, i.e., Write Once and Run Anywhere(WORA).
- 35. 35 1.3. Features of Java … 4.) Secured
- 36. 36 1.3 Features of Java … 4.) Secured ■ Java is best known for its security. ■ With Java, we can develop virus-free systems. ■ Java is secured because: No explicit pointer Java Programs run inside a virtual machine sandbox Classloader: Classloader in Java is a part of the Java Runtime Environment(JRE) which is used to load Java classes into the Java Virtual Machine dynamically. It adds security by separating the package for the classes of the local file system from those that are imported from network sources. Bytecode Verifier: It checks the code fragments for illegal code that can violate access right to objects. Security Manager: It determines what resources a class can access such as reading and writing to the local disk. Java language provides these securities by default. Some security can also be provided by an application developer explicitly through SSL(Secure Sockets Layer) , JAAS (Java Authentication and Authorization Service), Cryptography, etc.
- 37. 37 1.3. Features of Java … 5.) Robust ■ Robust simply means strong. ■ Java is robust because: – It uses strong memory management. – There is a lack of pointers that avoids security problems. – There is automatic garbage collection in java which runs on the Java Virtual Machine to get rid of objects which are not being used by a Java application anymore. – There are exception handling and the type checking mechanism in Java. ■ All these points make Java robust.
- 38. 38 1.3. Features of Java … 6.) Interpreted – Java byte code is translated on the fly to native machine instructions and is not stored anywhere. – The development process is more rapid and analytical since the linking is an incremental and light weight process.
- 39. 39 1.3. Features of Java … 7.) Architecture-neutral – Java is architecture neutral because there are no implementation dependent features, for example, the size of primitive types is fixed. – In C programming, int data type occupies 2 bytes of memory for 32-bit architecture and 4 bytes of memory for 64-bit architecture. – However, it occupies 4 bytes of memory for both 32 and 64- bit architectures in Java.
- 40. 40 1.3. Features of Java … 8.) Portable – Java is portable because it facilitates you to carry the Java bytecode to any platform. – It doesn't require any implementation.
- 41. 41 1.3. Features of Java … 9.) High-performance – Java is faster than other traditional interpreted programming languages because Java bytecode is "close" to native code. – It is still a little bit slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++). – Java is an interpreted language that is why it is slower than compiled languages, e.g., C, C++, etc.
- 42. 42 1.3. Features of Java … 10.) Distributed – Java is distributed because it facilitates users to create distributed applications in Java. – RMI (Remote Method Invocation) and EJB are used for creating distributed applications. – This feature of Java makes us able to access files by calling the methods from any machine on the internet.
- 43. 43 1.3. Features of Java … 11.) Multi-threaded – A thread is like a separate program, executing concurrently. – We can write Java programs that deal with many tasks at once by defining multiple threads. – The main advantage of multi-threading is that it doesn't occupy memory for each thread. – It shares a common memory area. – Threads are important for multi-media, Web applications, etc.
- 44. 44 1.3. Features of Java … 12.) Dynamic – Java is a dynamic language. – It supports dynamic loading of classes. – It means classes are loaded on demand. ■ It also supports functions from its native languages, i.e., C and C++. – Java supports dynamic compilation and automatic memory management (garbage collection).
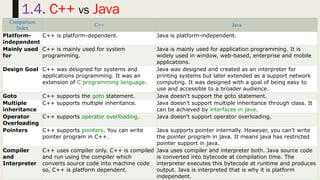
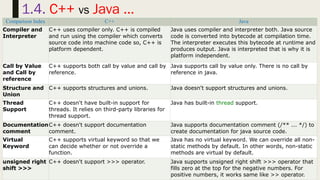
- 45. 45 1.4. C++ vs Java Comparison Index C++ Java Platform- independent C++ is platform-dependent. Java is platform-independent. Mainly used for C++ is mainly used for system programming. Java is mainly used for application programming. It is widely used in window, web-based, enterprise and mobile applications. Design Goal C++ was designed for systems and applications programming. It was an extension of C programming language. Java was designed and created as an interpreter for printing systems but later extended as a support network computing. It was designed with a goal of being easy to use and accessible to a broader audience. Goto C++ supports the goto statement. Java doesn't support the goto statement. Multiple inheritance C++ supports multiple inheritance. Java doesn't support multiple inheritance through class. It can be achieved by interfaces in java. Operator Overloading C++ supports operator overloading. Java doesn't support operator overloading. Pointers C++ supports pointers. You can write pointer program in C++. Java supports pointer internally. However, you can't write the pointer program in java. It means java has restricted pointer support in java. Compiler and Interpreter C++ uses compiler only. C++ is compiled and run using the compiler which converts source code into machine code so, C++ is platform dependent. Java uses compiler and interpreter both. Java source code is converted into bytecode at compilation time. The interpreter executes this bytecode at runtime and produces output. Java is interpreted that is why it is platform independent.
- 46. 46 1.4. C++ vs Java … Comparison Index C++ Java Compiler and Interpreter C++ uses compiler only. C++ is compiled and run using the compiler which converts source code into machine code so, C++ is platform dependent. Java uses compiler and interpreter both. Java source code is converted into bytecode at compilation time. The interpreter executes this bytecode at runtime and produces output. Java is interpreted that is why it is platform independent. Call by Value and Call by reference C++ supports both call by value and call by reference. Java supports call by value only. There is no call by reference in java. Structure and Union C++ supports structures and unions. Java doesn't support structures and unions. Thread Support C++ doesn't have built-in support for threads. It relies on third-party libraries for thread support. Java has built-in thread support. Documentation comment C++ doesn't support documentation comment. Java supports documentation comment (/** ... */) to create documentation for java source code. Virtual Keyword C++ supports virtual keyword so that we can decide whether or not override a function. Java has no virtual keyword. We can override all non- static methods by default. In other words, non-static methods are virtual by default. unsigned right shift >>> C++ doesn't support >>> operator. Java supports unsigned right shift >>> operator that fills zero at the top for the negative numbers. For positive numbers, it works same like >> operator.
- 47. 47 1.4. C++ vs Java … Comparison Index C++ Java Inheritance Tree C++ creates a new inheritance tree always. Java uses a single inheritance tree always because all classes are the child of Object class in java. The object class is the root of the inheritance tree in java. Hardware C++ is nearer to hardware. Java is not so interactive with hardware. Object- oriented C++ is an object-oriented language. However, in C language, single root hierarchy is not possible. Java is also an object-oriented language. However, everything (except fundamental types) is an object in Java. It is a single root hierarchy as everything gets derived from java.lang.Object. Note • Java doesn't support default arguments like C++. • Java does not support header files like C++. • Java uses the import keyword to include different classes and methods.
- 48. 48 1.5. First Java Program | Hello World Example ■ We can write a simple hello java program easily after installing the JDK. – To create a simple java program, you need to create a class that contains the main method. ■ Let's understand the requirement first. ■ The requirement for Java Hello World Example – For executing any java program, you need to – Install the JDK if you don't have installed it, download the JDK and install it. – Set path of the jdk/bin directory. – Create the java program – Compile and run the java program


![4
Java Example
//File name : simple.java
import java.io.*;
class Simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Hello Java");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02introductiontojavaprogramming-241126094017-77d07618/85/Introduction-to-Java-Programming-Java-Programming-Tutorials-for-beginners-4-320.jpg)