Introduction to MongoDB Basics from SQL to NoSQL
- 1. Introduction to Prof Mayur S Patil, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering, MIT Academy of Engineering, Alandi (D.)
- 2. Contents • Databases • Purpose of Databases • Types of Databases • Relational Model • Relational Databases • What is MongoDB? • Basics of MongoDB • CRUD Terms • Limitations • Current Trending
- 3. Databases • Data + Base • Add • Access • Update • Delete
- 4. Purpose of Databases • Easy to inject and retrieve data • Able to store and use sets of data • To get faster and accurate access of data through organized ways. • Query data in a database (ask it questions). • Relate data from two different tables together using JOINs. • Create meaningful reports from data in a database. • Information of a given type is always stored only once. • Fault-tolerant. • Concurrent; multiple users can use them at the same time without corrupting the data.
- 5. Applications: Early Phase: Airline, Accounting, Railway reservation. Now Trending: Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter. Search Engines: Bing, Google. Cloud Services: Amazon, Openstack. Big Data: Hadoop.
- 6. Types of Databases • Relational Databases: MySQL – Facebook, Twitter. PostGreSQL - SQLite – Browsers. • Non Relational Databases: MongoDB document CouchDB document ArangoDB Cassandra
- 7. Relational Model • The relational model (RM) for database management is an approach to managing data using a structure and language. • In the relational model of a database, all data is represented in terms of tuples and grouped into relations. • A database organized in terms of the relational model is a relational database.
- 8. Relational Databases • A database structured to recognize relations between stored items of information. • Data organization approach Tables Row Columns
- 9. RDBMS • Introduction • Systems that used relational databases known as RDBMS. • It used SQL. • DML – Update. • DDL – New things • DCL – Control Access • Advantages • Building a low-volume, medium-complexity suite of applications that will evolve over time. • Data volumes (duplicated) would be ridiculous if you didn’t do a reasonable amount of normalization. • You simply don’t see a cost/benefit advantage to moving away from proven legacy technology. • Limitations • Data Complexity • Broken Keys and Records • Developer Expertise • Hardware Performance
- 10. Introduction to MongoDB • MongoDB (from "humongous“ i.e. huge + Monstrous) is a scalable, high-performance, open source, schema-free, document-oriented database. - mongodb.org • It used NoSQL mechanism. • A record in MongoDB is a document. • The advantages of using documents are: • Documents (i.e. objects) correspond to native data types in many programming languages. • Data structure composed of field and value pairs.
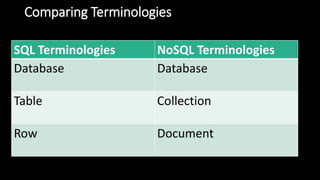
- 11. Comparing Terminologies SQL Terminologies NoSQL Terminologies Database Database Table Collection Row Document
- 12. Features of MongoDB • High Performance • I/O results • Faster keys • High Availability • Replica Set • Automatic Scaling • Sharding • Automatic balancing for changes in load and data distribution • Easy addition of new machines without down time • Scaling to one thousand nodes • No single points of failure • Automatic failover
- 13. • One or more shards, each shard holds a portion of the total • Each shard is backed by a replica set • Failure Management • One or more routers, each one acts as a server for one or more clients. • One or more clients, each one is (part of) the user's application and issues commands to a router via the mongo client library (driver) for its language. • mongod is server process and mongos is router process.
- 14. Basics of MongoDB • JSON •Stores data in Object format. •It supports nested looping i.e. objects within array. •Documents enclosed in circular braces. •Objects are enclosed in curly braces and separated by commas •JSON supports • Number, • Strings, • Objects • Arrays
- 15. Example db.things.save ( { a : 1, b : 1, fruit: ["apple", "grapes", "pear" ] } )
- 16. BSON •Its binary JSON i.e. format in which mongodb stores its data. •MDB drivers send and receive data as BSON from app. •On app side, MDB drivers maps BSON to native Data types in relative to programming language. •Why BSON: • Lightweight: Its space required to for data keeping is minimum • Traversable: Writing and reading indexes to MDB • Efficient: Encoding data to BSON and Decoding from BSON by drivers for app.
- 18. Working of MongoDB • MongoDB is a server process that runs on Linux, Windows and OS X • It can be run both as a 32 or 64-bit application. • Clients connect to the MongoDB process. • MongoDB stores its data in files (default location is /data/db/), and uses memory mapped files for data management for efficiency.
- 19. CRUD Terms Create Create Create Read Insert Insert Update Update Update Delete Delete Remove
- 20. Limitations • Joins: between two collections because it is difficult to scale out. • Transaction: because documents are stored in hierarchical manner so it is not possible to access those items atomically. • Naming Restrictions • Database Name Case Sensitivity • BSON Documents • BSON Document Size • Max connection number is hardcoded to 20k.
- 21. • Auto rollback is not for more than 300 MB; more than this manual intervention is needed. • To shard a collection, it must be smaller than 256 GB, or else it will likely fail to shard. • Map / Reduce are single-threaded. • Map / Reduce cannot output to sharded collections.
- 22. Trending •Adobe – AEM •Nokia – For Entertainment databases •Facebook – Customer Data •Google – Google Cloud Platform •Ebay – Media Metadata
- 23. THANKS !














![Example
db.things.save
(
{
a : 1, b : 1,
fruit:
["apple", "grapes", "pear" ]
}
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontomongodb-160411190501/85/Introduction-to-MongoDB-Basics-from-SQL-to-NoSQL-15-320.jpg)







