Introduction to Programming and QBasic Tutorial
Download as pptx, pdf3 likes3,754 views
This document introduces programming and the QBasic programming language. It discusses what programming is, the program life cycle, levels of programming languages from machine language to natural languages. It also covers flowcharting, variables, strings, input/output, and basic programming structures like IF/THEN statements. The document uses examples in QBasic to demonstrate concepts like printing output, taking user input, and making conditional comparisons. It provides an overview of key programming concepts for beginners to get started with QBasic.
1 of 22
Downloaded 136 times





















Ad
Recommended
Qbasic
QbasicFercie Caseria QBASIC is a simple BASIC programming language introduced in the 1980s. It has a direct mode for executing single commands and a program mode for writing and running programs with line numbers. QBASIC programs use commands like PRINT, LET, REM, CLS, and END. Variables can be numeric or alphanumeric, and constants can be numeric or strings enclosed in quotes. Programs are made up of statements executed in order, following syntax rules.
Introduction to qbasic
Introduction to qbasicRicha Karthikeyan QBasic is an introduction to basic programming concepts using a simple programming language. It discusses that computers require a language to communicate, dividing languages into low-level and high-level forms. QBasic is presented as a popular version of the high-level BASIC language, suitable for beginners to learn simple commands like PRINT, INPUT, and END. Examples are provided to demonstrate printing text, taking user input, and creating a basic program to print a greeting.
Qbasic tutorial
Qbasic tutorialjovelleluzon This is all about QBasic and it will used as your guide/tutorial in on how to make a program. :D :D THANKS FOR VIEWING THE PRESENTATION. XD<3><3
Communicative competence
Communicative competenceDrew F Communicative competence refers to an individual's knowledge and ability to use language appropriately in social contexts. It was proposed by Hymes as an expansion of Chomsky's notions of linguistic competence and performance. Hymes argued that communicative competence includes not just knowledge of grammar but also sociocultural knowledge necessary for effective communication. It encompasses grammatical, sociolinguistic, discourse and strategic competencies. Later theorists like Canale and Swain, and Bachman further developed and categorized the dimensions of communicative competence.
Materials Evaluation
Materials EvaluationMaryJane162 Materials evaluation involves measuring the potential value of learning materials using judgments about their effects on users. It considers criteria like appeal, credibility, validity, ability to interest and motivate learners, and value for short and long-term learning. Effective materials also align with principles of second language acquisition, such as achieving impact, making learners feel at ease, developing confidence, perceived relevance, self-investment, developmental and psychological readiness, attention to linguistic features, communicative opportunities, and accounting for differences in learning styles and attitudes.
Coursebook evaluation
Coursebook evaluationNoura Al-Budeiwi Teachers can evaluate coursebooks. They use them frequently and make sure to adapt them to learners' needs. All what teachers need is to learn to set criteria and understand how and what to assess of a coursebook. Please, write your comment and share your own opinion of the topic. Your contribution matters.
Types of Syllabus
Types of SyllabusAsif Afridy Riadh What is syllabus and 6 types of syllabuses are discusses here. By this ppt you be able to understand how many kinds of syllabuses are there and how they are performed in the classroom for learning L2 languages. Syllabus design is very much essential for foreign language learning in terms of different strategies. In this PowerPoint presentation the definition and examples are discusses very well so that acquisition will easy for learners.
Programming : QBASIC
Programming : QBASICvnuvalcrepollo This slideshow is all about QBASIC PROGRAMMING. This slideshow contains Introduction ,Interface,Features,Rules,Data,Types of Mode,Keywords,Commands and Reminders about QBASIC plus a Simple Activity!
Societal multilingualism
Societal multilingualismWinda Widia This document discusses societal multilingualism. It defines multilingualism as the knowledge or use of more than one language by an individual or community. It describes characteristics of multilingual communities, including that individuals may not have perfect command of multiple languages and instead demonstrate selective functionality. The document also discusses concepts like speech communities, language choice based on domains, patterns of language use, diglossia, code switching, code mixing, and implications for language teaching.
Computer languages
Computer languagesAqdasNoor its about computer languages like how many languages computer have and how to operate computers with programming languages.
CALL - Computer Assisted Language Learning
CALL - Computer Assisted Language LearningDilip Barad This document discusses the history and development of Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL). It describes three main phases of CALL's development: [1] Behavioristic CALL from the 1960s-1980s focused on drills and repetition; [2] Communicative CALL from the late 1970s-1980s emphasized communication; and [3] Integrative CALL from the 1990s onward integrated language skills into projects using multimedia. The document also outlines some CALL methods and tools as well as references for further reading on the topic.
Introduction of Sociolinguistics and describes Language variation, Linguistic...
Introduction of Sociolinguistics and describes Language variation, Linguistic...Sardarsinh Solanki Introduction of Sociolinguistics and describes Language variation, Linguistic relativity, and Languages in contact
2nd material linguistics design language features 2014
2nd material linguistics design language features 2014Ayu Juwita This document discusses key features of human language that distinguish it from animal communication systems. It covers two modes of language: spoken and written. It then examines four unique properties of human language: arbitrariness, duality, creativity, and displacement. Arbitrariness refers to the arbitrary relationship between words and their meanings. Duality refers to language having two layers - sounds that combine to form meaningful units. Creativity comes from language's recursiveness allowing new meanings. Displacement allows referring to things not present in space or time. The document asks cases about a president wondering about many local languages versus one national language, and why English is used internationally. It also defines lingua franca, vernacular, pidgin,
Programming Fundamental Presentation
Programming Fundamental Presentationfazli khaliq This presentation for the introduction of Programming languages
i.e High level language, Middle level language and Low level Language.
Qbasic
QbasicShubham Gupta The document provides an overview of using the QBASIC programming language. It discusses what QBASIC is, how to write simple programs in QBASIC using commands like PRINT, INPUT, LET, CLS, and how to run and save programs. It also covers basic programming concepts like variables, constants, operators, and input/output.
Corpus Tools for Language Teaching
Corpus Tools for Language TeachingCALPER This document summarizes a workshop on using language corpora for teaching. It began with an introduction to the goals of reviewing corpora uses and exploring corpus-based activities. Examples of corpora like MICASE and BYU were provided. Corpora can show word frequencies, clusters, collocations and examples of words in context. Benefits include exposing learners to authentic language patterns. Specific applications for teaching vocabulary, grammar and pragmatics were discussed. The workshop concluded with demonstrations of corpus searches and an activity for participants to design their own corpus-based lesson.
Task-based Language Teaching
Task-based Language Teaching Patrmartin Task-based language teaching (TBLT) is an approach that uses tasks as the core unit of planning and instruction in language teaching. It draws on principles of communicative language teaching, where real communication activities that use language for meaningful tasks promote learning. In TBLT, the focus is on process, communication, meaning, and interacting purposefully through activities and tasks that simulate real-life experiences. A task is defined as an activity or goal carried out using language. Lessons following TBLT are designed around objectives and sequenced tasks. The teacher takes on roles of selecting, preparing, and providing feedback on tasks while students take on participant, monitor, risk-taker, and innovator roles.
Best Practices for Teaching English to Young Learners by Joan Shin
Best Practices for Teaching English to Young Learners by Joan ShinVenezuela TESOL Workshop offered to English Language teachers in Venezuela as part of the Methodology of the ELT Tour 2011-2 organized by VenTESOL and sponsored by the US Embassy
Fundamentals of CLIL
Fundamentals of CLILYamith José Fandiño Parra A comprehensive introduction to Content Language Integrated Learning - CLIL created to help pre and in-service EFL teachers understand the basics of this approach.
Introduction to programming
Introduction to programmingGwyneth Calica Want to know how programming works? how it helps the human being with their everyday work? well you can easily find the answers to those questions that are in your minds. Programming, well it is a kind of software that can make games, applications, movies and a lot more. For a start, programming can help us students with our home works and such stuffs. and now, we can learn more about the different languages used in programming, program life cycle, rules and symbols used and its level. Let us discover how programming works!
A.content based instruction (cbi)
A.content based instruction (cbi)diah Cwek Tauruz Content-based instruction (CBI) uses content area subjects to teach language skills. Students can acquire content knowledge through comprehensible input which also increases their language abilities. CBI has advantages like making language learning more interesting and motivating while also teaching valuable study skills. However, disadvantages include potentially confusing learners about language learning and difficulties finding leveled texts.
Introduction to MS Office
Introduction to MS Officecristy nazareno Microsoft Word is a word processing program that allows users to create documents. It features a ribbon interface with tabs for formatting options like fonts, paragraph styles, page layout, and more. The ribbon replaces traditional menus and toolbars. Key features in Word include formatting text with different fonts, sizes, colors, and styles. Users can also align, cut, copy and paste text. Formatting and editing tools are found primarily on the Home tab of the ribbon.
Direct method by m.hasnnain
Direct method by m.hasnnainMuhammad Haseeb The Direct Method is an approach to teaching foreign languages that uses the target language exclusively and avoids translation or explaining grammar rules. It was developed in the 1860s based on observations of how children acquire their first language. Key principles include using real-world examples and demonstrations rather than explanations, emphasizing oral skills and questions/answers, and avoiding grammar explanations. Techniques include reading aloud, conversations, dictation, and map tasks. While it aims to mimic natural language acquisition, critics argue it is difficult to implement fully and may not be suitable for large classes.
Introduction to computer programming
Introduction to computer programmingNSU-Biliran Campus This document provides an introduction to computer programming. It discusses that a computer program is a list of instructions that the computer follows to accept input, process it, and present results. Programming is both an art and a science. Programs fall into application programs, which perform functions for users, and operating systems, which manage computer resources. A programmer uses a text editor to write source code in a programming language, which is then translated into machine-readable object code by compilers, interpreters, or assemblers. The document then describes the basic parts of a computer and operating system functions. It also discusses high-level programming languages and provides a basic example program in C.
SKILL BASED SYLLABUS
SKILL BASED SYLLABUSAillen Goleña The document discusses skill-based syllabus in language teaching. It defines skills as specific ways of using language that combine structural and functional ability. A skill-based syllabus groups language competencies like grammar, vocabulary and discourse into generalized behaviors like listening for main ideas or writing paragraphs. The primary purpose is to teach skills useful for language use. Examples include guessing vocabulary from context and reading for the main idea. Skill-based syllabus is most useful when learners need to master specific language uses.
The audio lingual method
The audio lingual methodomarswan The document outlines the Audio-Lingual method of foreign language teaching. It was developed in the US during World War 2 to train military personnel. It is based on behaviorist psychology and the idea that language is acquired through habit formation and imitation. Teachers use drills and repetition of dialogues to help students master the target language system. While it was effective for its time, the method was later criticized for its lack of creativity and focus on memorization over understanding.
Linguistic Imperialism
Linguistic ImperialismAiden Yeh The document discusses the theory of linguistic imperialism proposed by Robert Phillipson. Linguistic imperialism refers to the dominance of English asserted through establishing structural and cultural inequalities between English and other languages. Phillipson argues that English dominance is maintained in former colonies and increasingly in Europe through policies promoting English be taught monolingually from an early age with native English speakers. This can endanger other languages and local cultural identity over time. The document also examines arguments used to promote English learning.
Teaching speaking brown
Teaching speaking brownshohreh12345 The document discusses various techniques for teaching speaking skills, including both direct and indirect approaches. It emphasizes using tasks that focus on meaningful communication over language practice. Specific techniques mentioned include conversation practice, transactional activities like ordering from a catalog, and individual oral dialogue journals. Principles for designing speaking techniques include using a variety that cover accuracy and fluency, providing meaningful contexts, feedback, and opportunities for student initiation of oral communication. The document also discusses teaching pronunciation and considerations around error correction.
QBASIC
QBASICnivi88 QBasic is a simple programming language developed by Microsoft as the successor to BASIC for beginners to learn programming fundamentals. It was designed for the MS-DOS operating system and provides an intuitive integrated development environment for writing, compiling, and running programs. While less powerful than other languages, QBasic remains a valuable educational tool for newcomers to learn programming basics due to its extensive documentation and tutorials available online.
Qbasic introduction
Qbasic introductionChristian Joseph Opiana This document provides an overview of the QBasic programming language and its features. It discusses how QBasic was created in 1963 and is an interpreter that reads and executes code line by line. The document also covers QBasic commands like PRINT, INPUT, IF/THEN, variables, constants, and how to get input from the user. It provides examples of expressions, data types, and how to evaluate logical statements in QBasic.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Societal multilingualism
Societal multilingualismWinda Widia This document discusses societal multilingualism. It defines multilingualism as the knowledge or use of more than one language by an individual or community. It describes characteristics of multilingual communities, including that individuals may not have perfect command of multiple languages and instead demonstrate selective functionality. The document also discusses concepts like speech communities, language choice based on domains, patterns of language use, diglossia, code switching, code mixing, and implications for language teaching.
Computer languages
Computer languagesAqdasNoor its about computer languages like how many languages computer have and how to operate computers with programming languages.
CALL - Computer Assisted Language Learning
CALL - Computer Assisted Language LearningDilip Barad This document discusses the history and development of Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL). It describes three main phases of CALL's development: [1] Behavioristic CALL from the 1960s-1980s focused on drills and repetition; [2] Communicative CALL from the late 1970s-1980s emphasized communication; and [3] Integrative CALL from the 1990s onward integrated language skills into projects using multimedia. The document also outlines some CALL methods and tools as well as references for further reading on the topic.
Introduction of Sociolinguistics and describes Language variation, Linguistic...
Introduction of Sociolinguistics and describes Language variation, Linguistic...Sardarsinh Solanki Introduction of Sociolinguistics and describes Language variation, Linguistic relativity, and Languages in contact
2nd material linguistics design language features 2014
2nd material linguistics design language features 2014Ayu Juwita This document discusses key features of human language that distinguish it from animal communication systems. It covers two modes of language: spoken and written. It then examines four unique properties of human language: arbitrariness, duality, creativity, and displacement. Arbitrariness refers to the arbitrary relationship between words and their meanings. Duality refers to language having two layers - sounds that combine to form meaningful units. Creativity comes from language's recursiveness allowing new meanings. Displacement allows referring to things not present in space or time. The document asks cases about a president wondering about many local languages versus one national language, and why English is used internationally. It also defines lingua franca, vernacular, pidgin,
Programming Fundamental Presentation
Programming Fundamental Presentationfazli khaliq This presentation for the introduction of Programming languages
i.e High level language, Middle level language and Low level Language.
Qbasic
QbasicShubham Gupta The document provides an overview of using the QBASIC programming language. It discusses what QBASIC is, how to write simple programs in QBASIC using commands like PRINT, INPUT, LET, CLS, and how to run and save programs. It also covers basic programming concepts like variables, constants, operators, and input/output.
Corpus Tools for Language Teaching
Corpus Tools for Language TeachingCALPER This document summarizes a workshop on using language corpora for teaching. It began with an introduction to the goals of reviewing corpora uses and exploring corpus-based activities. Examples of corpora like MICASE and BYU were provided. Corpora can show word frequencies, clusters, collocations and examples of words in context. Benefits include exposing learners to authentic language patterns. Specific applications for teaching vocabulary, grammar and pragmatics were discussed. The workshop concluded with demonstrations of corpus searches and an activity for participants to design their own corpus-based lesson.
Task-based Language Teaching
Task-based Language Teaching Patrmartin Task-based language teaching (TBLT) is an approach that uses tasks as the core unit of planning and instruction in language teaching. It draws on principles of communicative language teaching, where real communication activities that use language for meaningful tasks promote learning. In TBLT, the focus is on process, communication, meaning, and interacting purposefully through activities and tasks that simulate real-life experiences. A task is defined as an activity or goal carried out using language. Lessons following TBLT are designed around objectives and sequenced tasks. The teacher takes on roles of selecting, preparing, and providing feedback on tasks while students take on participant, monitor, risk-taker, and innovator roles.
Best Practices for Teaching English to Young Learners by Joan Shin
Best Practices for Teaching English to Young Learners by Joan ShinVenezuela TESOL Workshop offered to English Language teachers in Venezuela as part of the Methodology of the ELT Tour 2011-2 organized by VenTESOL and sponsored by the US Embassy
Fundamentals of CLIL
Fundamentals of CLILYamith José Fandiño Parra A comprehensive introduction to Content Language Integrated Learning - CLIL created to help pre and in-service EFL teachers understand the basics of this approach.
Introduction to programming
Introduction to programmingGwyneth Calica Want to know how programming works? how it helps the human being with their everyday work? well you can easily find the answers to those questions that are in your minds. Programming, well it is a kind of software that can make games, applications, movies and a lot more. For a start, programming can help us students with our home works and such stuffs. and now, we can learn more about the different languages used in programming, program life cycle, rules and symbols used and its level. Let us discover how programming works!
A.content based instruction (cbi)
A.content based instruction (cbi)diah Cwek Tauruz Content-based instruction (CBI) uses content area subjects to teach language skills. Students can acquire content knowledge through comprehensible input which also increases their language abilities. CBI has advantages like making language learning more interesting and motivating while also teaching valuable study skills. However, disadvantages include potentially confusing learners about language learning and difficulties finding leveled texts.
Introduction to MS Office
Introduction to MS Officecristy nazareno Microsoft Word is a word processing program that allows users to create documents. It features a ribbon interface with tabs for formatting options like fonts, paragraph styles, page layout, and more. The ribbon replaces traditional menus and toolbars. Key features in Word include formatting text with different fonts, sizes, colors, and styles. Users can also align, cut, copy and paste text. Formatting and editing tools are found primarily on the Home tab of the ribbon.
Direct method by m.hasnnain
Direct method by m.hasnnainMuhammad Haseeb The Direct Method is an approach to teaching foreign languages that uses the target language exclusively and avoids translation or explaining grammar rules. It was developed in the 1860s based on observations of how children acquire their first language. Key principles include using real-world examples and demonstrations rather than explanations, emphasizing oral skills and questions/answers, and avoiding grammar explanations. Techniques include reading aloud, conversations, dictation, and map tasks. While it aims to mimic natural language acquisition, critics argue it is difficult to implement fully and may not be suitable for large classes.
Introduction to computer programming
Introduction to computer programmingNSU-Biliran Campus This document provides an introduction to computer programming. It discusses that a computer program is a list of instructions that the computer follows to accept input, process it, and present results. Programming is both an art and a science. Programs fall into application programs, which perform functions for users, and operating systems, which manage computer resources. A programmer uses a text editor to write source code in a programming language, which is then translated into machine-readable object code by compilers, interpreters, or assemblers. The document then describes the basic parts of a computer and operating system functions. It also discusses high-level programming languages and provides a basic example program in C.
SKILL BASED SYLLABUS
SKILL BASED SYLLABUSAillen Goleña The document discusses skill-based syllabus in language teaching. It defines skills as specific ways of using language that combine structural and functional ability. A skill-based syllabus groups language competencies like grammar, vocabulary and discourse into generalized behaviors like listening for main ideas or writing paragraphs. The primary purpose is to teach skills useful for language use. Examples include guessing vocabulary from context and reading for the main idea. Skill-based syllabus is most useful when learners need to master specific language uses.
The audio lingual method
The audio lingual methodomarswan The document outlines the Audio-Lingual method of foreign language teaching. It was developed in the US during World War 2 to train military personnel. It is based on behaviorist psychology and the idea that language is acquired through habit formation and imitation. Teachers use drills and repetition of dialogues to help students master the target language system. While it was effective for its time, the method was later criticized for its lack of creativity and focus on memorization over understanding.
Linguistic Imperialism
Linguistic ImperialismAiden Yeh The document discusses the theory of linguistic imperialism proposed by Robert Phillipson. Linguistic imperialism refers to the dominance of English asserted through establishing structural and cultural inequalities between English and other languages. Phillipson argues that English dominance is maintained in former colonies and increasingly in Europe through policies promoting English be taught monolingually from an early age with native English speakers. This can endanger other languages and local cultural identity over time. The document also examines arguments used to promote English learning.
Teaching speaking brown
Teaching speaking brownshohreh12345 The document discusses various techniques for teaching speaking skills, including both direct and indirect approaches. It emphasizes using tasks that focus on meaningful communication over language practice. Specific techniques mentioned include conversation practice, transactional activities like ordering from a catalog, and individual oral dialogue journals. Principles for designing speaking techniques include using a variety that cover accuracy and fluency, providing meaningful contexts, feedback, and opportunities for student initiation of oral communication. The document also discusses teaching pronunciation and considerations around error correction.
Viewers also liked (19)
QBASIC
QBASICnivi88 QBasic is a simple programming language developed by Microsoft as the successor to BASIC for beginners to learn programming fundamentals. It was designed for the MS-DOS operating system and provides an intuitive integrated development environment for writing, compiling, and running programs. While less powerful than other languages, QBasic remains a valuable educational tool for newcomers to learn programming basics due to its extensive documentation and tutorials available online.
Qbasic introduction
Qbasic introductionChristian Joseph Opiana This document provides an overview of the QBasic programming language and its features. It discusses how QBasic was created in 1963 and is an interpreter that reads and executes code line by line. The document also covers QBasic commands like PRINT, INPUT, IF/THEN, variables, constants, and how to get input from the user. It provides examples of expressions, data types, and how to evaluate logical statements in QBasic.
Qbasic Tutorial
Qbasic TutorialJoy Hilary Yambao This is all about the program QBASIC and what are the different characteristics and rules of the program.
Qbasic program
Qbasic programFercie Caseria QBASIC is a simple BASIC programming language introduced in the 1980s. It has several features that make it user-friendly, like using simple English commands and allowing variables to be easily named. A QBASIC program consists of lines with line numbers and commands. Common commands include PRINT to display output, LET to assign values to variables, and REM for remarks. QBASIC can run in either direct mode for single line commands or program mode to store and run multi-line programs.
The Knowledge of QBasic
The Knowledge of QBasicEnelrah Vanna Dela Cruz It is all you need to know about Qbasic. This gives knowledge where did Qbasic was founded, who founded it, what does Qbasic mean, What is its use, and how to solve problems using Qbasic.
QBASIC: A Tool For Modern Programming
QBASIC: A Tool For Modern ProgrammingGifty Belle Manaois This document provides an overview of the QBASIC programming language and its commands. It discusses QBASIC's interpreter-based execution model and use of line numbers. It also covers basic QBASIC concepts like constants, variables, and commands for printing, clearing screens, and running programs. The document then examines specific commands in more detail, such as PRINT, INPUT, IF/THEN, ELSE, and ELSEIF. It provides examples of how to use expressions, variables, and conditional logic in QBASIC programs.
Ch02 mis-imp-concepts
Ch02 mis-imp-conceptsSR NAIDU This document provides an overview of management information systems (MIS). It defines key terms like management, information, systems, and information systems. It then discusses what MIS are, how they have evolved to provide the right information to managers, and the different types of information systems that serve various management levels. The document also examines organizational structures that MIS support, like virtual organizations, and outlines challenges for information systems like ensuring strategic and global alignment of information architecture.
Lec monitor
Lec monitorProtik Roy ier, computer in education, dhaka university, educational technology, introduction to computer, bangladesh education , protik ray, education computer
Lecture 1 mis
Lecture 1 missukhalalton1 Management information systems (MIS) blend knowledge from management and computers to provide information for decision making through integrated hardware, software, data bases, and decision models. MIS has evolved over four phases from the 1950s focus on data processing to today's use of expert systems. While computers make MIS more efficient and effective, human users remain central to decision making with this user-machine combination.
Lect 30 dbms_fundamentals
Lect 30 dbms_fundamentalsProtik Roy ier, computer in education, dhaka university, educational technology, introduction to computer, bangladesh education , protik ray, education computer
Management information system Unit 1
Management information system Unit 1Sharda University Greater Noida Management Information System (MIS) provides information to support decision-making and management in an organization. The goals of an MIS include enhancing communication, delivering information efficiently, supporting data collection and analysis, and aiding strategic objectives. An MIS contains interconnected sub-systems that capture, store, process, and distribute data, information and knowledge across different levels and functions of a business. It integrates transaction processing systems, office automation systems, decision support systems and other applications to provide timely, relevant information to management.
Lecture 11 bmbs management information system qs
Lecture 11 bmbs management information system qsMuhammad Ovais 1) Batch processing involves collecting transaction data over time and processing it in batches, while real-time processing involves processing individual transactions as they occur.
2) Networking provides benefits like improved communication and data sharing in a corporate environment.
3) A closed loop control system automatically corrects deviations from the set standard, while an open loop system does not provide feedback or correction.
Mis 001
Mis 001Kinshook Chaturvedi The document discusses the definitions and types of information systems. It defines information systems as a set of manual and/or computerized components for gathering, storing, processing, and converting business data into useful decision-oriented information. Information systems can be computerized, manual, business-oriented, or non-business oriented. The document also discusses different generations of information systems from manual to expert systems, as well as common myths, information needs at different management levels, and requirements for a good information system.
Ch01
Ch01Taha Khan This document summarizes the key points from the introduction chapter of the textbook "Information Systems: Creating Business Value". It discusses the importance of knowledge work and knowledge workers in modern businesses. It defines key terms like data, information, information systems, and different types of IS. It also explains how factors like globalization and the internet are impacting businesses and their need for timely access to data and information.
Management information system
Management information systemRanjeeta Swarnakar This document discusses different types of systems and management information systems (MIS). It defines a system as a set of interrelated elements that work towards a common goal. There are five types of systems described: open systems that interact with their environment; closed systems that are isolated from external factors; physical systems that can be touched; abstract systems that are conceptual; and information systems that collect or provide data. The document also outlines four types of MIS - transaction processing systems, information providing systems, decision support systems, and programmed decision making systems - that deliver various levels of data and analysis to managers.
Laudon mis12 ppt01
Laudon mis12 ppt01Norazila Mat 1) Information systems are essential for businesses today and have transformed operations through increased wireless technology, web technologies, and cloud computing. They provide opportunities for globalization and new products/services.
2) An information system collects, processes, stores, and distributes information to support decision making, coordination, and control. It has organizational, management, and technology dimensions.
3) Investing in information technology alone does not guarantee returns; firms must also invest in complementary assets like efficient processes and incentives to derive full value from new technologies.
MIS Chapter 1
MIS Chapter 1Dara Som The presentations cover the chapter objectives and list the objectives at the beginning of each presentation. They can be customized for class needs. Some figures from the chapters are included and a complete set of images can be found in the instructor resources.
Mis lecture ppt
Mis lecture pptVandana Agrawal The document provides information on management information systems (MIS). It defines key terms like data, information, database and file. It describes the stages in converting data to information like capturing, verifying, classifying etc. It discusses classification and types of information. It then introduces MIS, describes its purpose and scope, expectations from MIS and types of MIS reports. The document further discusses functional MIS systems, subsystems and elements of information systems. [END SUMMARY]
Management Information System (Full Notes)
Management Information System (Full Notes)Harish Chand This document provides a summary of key topics related to Management Information Systems (MIS). It discusses the importance of information systems for businesses and defines different types of systems, including Transaction Processing Systems, Knowledge Work Systems, Management Information Systems, and Decision Support Systems. It also outlines some of the challenges of implementing effective information systems, such as realizing digital transformation and addressing globalization.
Ad
Similar to Introduction to Programming and QBasic Tutorial (20)
Computer programming k 12
Computer programming k 12lemonmichelangelo This document provides an overview of the QBasic programming language and its features. It discusses how QBasic was created in 1963 and is an interpreter that reads and executes code line by line. The document also covers QBasic commands like PRINT, INPUT, IF/THEN, variables, constants, and how to get input from the user. It provides examples of expressions, data types, and how to evaluate logical statements in QBasic.
Basic Computer Programming
Basic Computer ProgrammingAllen de Castro This document provides an introduction to basic computer programming concepts including:
- Programs are sets of step-by-step instructions that direct a computer to perform tasks and produce outputs. Programming languages provide rules and instructions for computers.
- The programming process involves identifying problems, planning solutions with flowcharts or pseudocode, coding the program, testing it, and documenting it.
- There are different levels of programming languages from low-level machine languages to high-level languages like Visual Basic that resemble English. Procedural languages use sequential statements while object-oriented languages are event-driven.
- Basic commands in QBasic are introduced like PRINT, CLS, INPUT, IF/THEN/ELSE
programming.ppt
programming.pptAdrianVANTOPINA This document provides an overview of programming concepts including what programming is, programming languages, how to write programs, and key elements of programs such as variables, commands/syntax, loops, decisions, and functions. It defines programming as a series of instructions for a computer to accomplish a task. It explains that programming languages allow writing programs and different languages have different rules. The document outlines the steps to write a program including using pseudocode or flowcharts, translating to a programming language, testing, and debugging. It also defines and provides examples of common programming elements.
Learn Programming with Livecoding.tv http://goo.gl/tIgO1I
Learn Programming with Livecoding.tv http://goo.gl/tIgO1Ilivecoding.tv This document provides an introduction to programming concepts. It defines programming as a series of instructions for a computer to accomplish a task. It explains that programs must be written in a programming language the computer understands. It also discusses pseudocode, flowcharts, variables, loops, decisions, functions, debugging, and other core programming topics. Examples are provided throughout to illustrate key points. The document concludes with self-check questions to test understanding of the material.
Basic computer-programming-2
Basic computer-programming-2lemonmichelangelo This document contains information about QBasic including:
1) QBasic is a version of the BASIC programming language that was developed for beginners. BASIC stands for Beginner's All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code.
2) In QBasic, data can be constants like numbers or strings, or variables that can change value. Variables are used to store numeric or alphanumeric values.
3) QBasic has two modes - direct mode for quick calculations and program mode for storing programs with line numbers to run later.
4) The document also describes other QBasic concepts like using INPUT to get user input, IF/THEN statements, operators, and a simple guessing game program example.
Programming
ProgrammingLeo Simon Anfone This document provides an overview of programming concepts such as what programming is, programming languages, how to write programs, and key elements of programs like variables, functions, loops, and decisions. Specifically:
- Programming involves writing instructions for a computer to accomplish tasks, using programming languages that the computer can understand. Programs must be compiled or interpreted before running.
- Pseudocode and flowcharts are used to plan programs by listing steps in plain English or using graphic symbols. Variables store data, and functions perform sub-tasks. Loops and decisions allow programs to repeat actions and make choices.
- Debugging fixes errors by testing programs step-by-step. Key symbols represent starting, input/output,
Assembly Language Programming
Assembly Language ProgrammingNiropam Das This document discusses assembly language programming concepts and provides examples of assembly language programs for the 8086 processor. It covers variables, assignment, input/output, and control flow. It also provides examples of complete assembly language programs that display characters, read keyboard input, and print strings. The document concludes with sample programming exercises involving operations like addition, subtraction, and conditional branching.
COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
COMPUTER PROGRAMMINGarisamae1114 This document provides information and examples on using basic programming commands like INPUT, IF/THEN, ELSE in QBASIC. It explains how to get input from the user, compare values, and perform different actions based on conditional statements. It also includes 3 exercises for readers to practice these commands: 1) An IF/THEN program to check a condition, 2) An IF/THEN/ELSE program with multiple conditions, and 3) An IF/THEN/ELSE/END IF program that asks for user input and prints different outputs. The document was prepared by two students for their computer programming class and adviser.
The basics of c programming
The basics of c programmingMuhammed Thanveer M This document provides an introduction to the basics of C programming. It explains that C is a compiled programming language commonly used to create computer programs and operating systems. The document then walks through a simple C program line-by-line to demonstrate how it works, covering key concepts like functions, variables, and input/output functions like printf and scanf. It provides examples of printing output, accepting user input, and performing basic math operations in C.
C language industrial training report
C language industrial training reportRaushan Pandey Utkarsh Kapoor expresses gratitude to various people who helped and supported him in completing another chapter of his life. He thanks his industrial supervisor Mr. Setu Maheshwari for guiding him during his training. He also thanks his colleagues for their kindness and help. Finally, he thanks his parents for their sacrifice and inspiration in allowing him to pursue his studies.
Algorithms and flowcharts
Algorithms and flowchartsSamuel Igbanogu This document discusses algorithms, flowcharts, pseudocode, and decision structures. It begins by defining algorithms and their purpose in problem solving. It then explains flowchart symbols and how to represent algorithms visually using flowcharts. Several examples are provided of writing pseudocode, detailed algorithms, and corresponding flowcharts to solve problems. The document also covers decision structures like if-then-else statements and relational operators. It provides examples of algorithms using nested if statements. Finally, it presents an example of determining an employee bonus based on overtime worked and absences.
Input-output
Input-outputneda marie maramo The document discusses input-output (I/O) architecture in computer systems. It explains that I/O devices have different characteristics than memory devices and can operate at different speeds than the CPU. It describes the general components of an I/O structure, including I/O controllers that interface between devices and the system bus. It also discusses the need for handshaking between CPUs and I/O devices to ensure reliable data transfer given their asynchronous nature.
Python Programming - II. The Basics
Python Programming - II. The BasicsRanel Padon Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
A tutorial on C++ Programming
A tutorial on C++ ProgrammingProf. Erwin Globio This document provides an introduction to C programming concepts including basic syntax, variables, operators, control flow statements like if/else, functions, and modular programming. It also covers string handling functions in C++ like strcpy(), strcat(), strcmp(), and strlen(). Key points include:
- C++ programs begin execution in the main() function
- cout is used for console output
- Comments begin with // and /* */
- If statements control program flow based on conditions
- Strings are arrays of characters terminated with null character
- Functions like gets() and strcpy() can be used to input and copy strings
Flowcharts and Introduction to computers
Flowcharts and Introduction to computersssuser2023c6 Flowcharts are visual representations of processes, workflows, or systems that use symbols, shapes, and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps involved in completing a task or achieving a goal. They are widely used in various fields, including programming, business management, engineering, and education, to simplify complex processes, identify potential inefficiencies, and communicate ideas effectively. The structure of a flowchart typically consists of standardized symbols such as ovals to denote start and end points, rectangles to represent processes or tasks, diamonds for decision points, and arrows to indicate the flow of information or actions. This method of diagramming makes it easier for teams and individuals to understand the logical progression of steps and to pinpoint bottlenecks or redundancies in a system. Flowcharts are particularly valuable in software development for mapping algorithms, debugging programs, and documenting workflows. Moreover, in business, they aid in process optimization and decision-making by providing a clear and concise overview of operations. Their simplicity and versatility make them an essential tool for both beginners and professionals looking to analyze and improve processes systematically. Flowcharts are visual representations of processes, workflows, or systems that use symbols, shapes, and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps involved in completing a task or achieving a goal. They are widely used in various fields, including programming, business management, engineering, and education, to simplify complex processes, identify potential inefficiencies, and communicate ideas effectively. The structure of a flowchart typically consists of standardized symbols such as ovals to denote start and end points, rectangles to represent processes or tasks, diamonds for decision points, and arrows to indicate the flow of information or actions. This method of diagramming makes it easier for teams and individuals to understand the logical progression of steps and to pinpoint bottlenecks or redundancies in a system. Flowcharts are particularly valuable in software development for mapping algorithms, debugging programs, and documenting workflows. Moreover, in business, they aid in process optimization and decision-making by providing a clear and concise overview of operations. Their simplicity and versatility make them an essential tool for both beginners and professionals looking to analyze and improve processes systematically. Flowcharts are visual representations of processes, workflows, or systems that use symbols, shapes, and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps involved in completing a task or achieving a goal. They are widely used in various fields, including programming, business management, engineering, and education, to simplify complex processes, identify potential inefficiencies, and communicate ideas effectively. The structure of a flowchart typically consists of standardized symbols such as
Flowchart presentation that can be useful
Flowchart presentation that can be usefulssuser2023c6 Flowcharts are visual representations of processes, workflows, or systems that use symbols, shapes, and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps involved in completing a task or achieving a goal. They are widely used in various fields, including programming, business management, engineering, and education, to simplify complex processes, identify potential inefficiencies, and communicate ideas effectively. The structure of a flowchart typically consists of standardized symbols such as ovals to denote start and end points, rectangles to represent processes or tasks, diamonds for decision points, and arrows to indicate the flow of information or actions. This method of diagramming makes it easier for teams and individuals to understand the logical progression of steps and to pinpoint bottlenecks or redundancies in a system. Flowcharts are particularly valuable in software development for mapping algorithms, debugging programs, and documenting workflows. Moreover, in business, they aid in process optimization and decision-making by providing a clear and concise overview of operations. Their simplicity and versatility make them an essential tool for both beginners and professionals looking to analyze and improve processes systematically.Flowcharts are visual representations of processes, workflows, or systems that use symbols, shapes, and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps involved in completing a task or achieving a goal. They are widely used in various fields, including programming, business management, engineering, and education, to simplify complex processes, identify potential inefficiencies, and communicate ideas effectively. The structure of a flowchart typically consists of standardized symbols such as ovals to denote start and end points, rectangles to represent processes or tasks, diamonds for decision points, and arrows to indicate the flow of information or actions. This method of diagramming makes it easier for teams and individuals to understand the logical progression of steps and to pinpoint bottlenecks or redundancies in a system. Flowcharts are particularly valuable in software development for mapping algorithms, debugging programs, and documenting workflows. Moreover, in business, they aid in process optimization and decision-making by providing a clear and concise overview of operations. Their simplicity and versatility make them an essential tool for both beginners and professionals looking to analyze and improve processes systematically.Flowcharts are visual representations of processes, workflows, or systems that use symbols, shapes, and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps involved in completing a task or achieving a goal. They are widely used in various fields, including programming, business management, engineering, and education, to simplify complex processes, identify potential inefficiencies, and communicate ideas effectively. The structure of a flowchart typically consists of standardized symbols such as o
QBASIC: A Tool For Modern Programming
QBASIC: A Tool For Modern ProgrammingGifty Belle Manaois This document provides an overview of the QBASIC programming language and its commands. It discusses QBASIC's interpreter-based execution model and use of line numbers. It also covers basic QBASIC concepts like constants, variables, and commands for printing, clearing screens, assigning values, and more. Examples are given to demonstrate how to use commands like PRINT, INPUT, IF/THEN, ELSE, and ELSEIF to conditionally output text based on expressions. The document is intended as an introduction to programming in QBASIC.
Learning R while exploring statistics
Learning R while exploring statisticsDorothy Bishop This document provides instructions for learning R through an exercise on illusory correlation. It describes how to:
1. Download R and R Studio, an interface for R.
2. Learn basic R operations like assigning variables, using help functions, and writing scripts.
3. Generate simulated correlated data for two variables X and Y by using the mvrnorm function from the MASS package to specify the number of cases, means, and covariance matrix with a specified correlation between the two variables.
Basic programming
Basic programmingNicole Danielle Mallari The document discusses computers and programming basics. It covers computer hardware components like the system unit, CPU, memory and peripheral devices. It also discusses software topics like operating systems, programming languages, and QBasic. QBasic is an introductory programming language that uses basic commands like PRINT, CLS, INPUT and arithmetic expressions. The document provides examples of using these commands and expressions in simple QBasic programs.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptx
june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptxroger malina art science is over -talk by roger malina for jack madden group
Diptera: The Two-Winged Wonders, The Fly Squad: Order Diptera.pptx
Diptera: The Two-Winged Wonders, The Fly Squad: Order Diptera.pptxArshad Shaikh Diptera, commonly known as flies, is a large and diverse order of insects that includes mosquitoes, midges, gnats, and horseflies. Characterized by a single pair of wings (hindwings are modified into balancing organs called halteres), Diptera are found in almost every environment and play important roles in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and food sources. Some species, however, are significant pests and disease vectors, transmitting diseases like malaria, dengue, and Zika virus.
How to Create Time Off Request in Odoo 18 Time Off
How to Create Time Off Request in Odoo 18 Time OffCeline George Odoo 18 provides an efficient way to manage employee leave through the Time Off module. Employees can easily submit requests, and managers can approve or reject them based on company policies.
How to Create a Stage or a Pipeline in Odoo 18 CRM
How to Create a Stage or a Pipeline in Odoo 18 CRMCeline George In Odoo, the CRM (Customer Relationship Management) module’s pipeline is a visual representation of a company's sales process that helps sales teams track and manage their interactions with potential customers.
Forestry Model Exit Exam_2025_Wollega University, Gimbi Campus.pdf
Forestry Model Exit Exam_2025_Wollega University, Gimbi Campus.pdfChalaKelbessa This is Forestry Exit Exam Model for 2025 from Department of Forestry at Wollega University, Gimbi Campus.
The exam contains forestry courses such as Dendrology, Forest Seed and Nursery Establishment, Plantation Establishment and Management, Silviculture, Forest Mensuration, Forest Biometry, Agroforestry, Biodiversity Conservation, Forest Business, Forest Fore, Forest Protection, Forest Management, Wood Processing and others that are related to Forestry.
POS Reporting in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 Slides
POS Reporting in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 SlidesCeline George To view all the available reports in Point of Sale, navigate to Point of Sale > Reporting. In this section, you will find detailed reports such as the Orders Report, Sales Details Report, and Session Report, as shown below.
Module 4 Presentation - Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Y...
Module 4 Presentation - Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Y...GeorgeDiamandis11 Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Youth Work
Parenting Teens: Supporting Trust, resilience and independence
Parenting Teens: Supporting Trust, resilience and independencePooky Knightsmith For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/
SESSION OVERVIEW:
Parenting Teens: Supporting Trust, Resilience & Independence
The teenage years bring new challenges—for teens and for you. In this practical session, we’ll explore how to support your teen through emotional ups and downs, growing independence, and the pressures of school and social life.
You’ll gain insights into the teenage brain and why boundary-pushing is part of healthy development, along with tools to keep communication open, build trust, and support emotional resilience. Expect honest ideas, relatable examples, and space to connect with other parents.
By the end of this session, you will:
• Understand how teenage brain development affects behaviour and emotions
• Learn ways to keep communication open and supportive
• Explore tools to help your teen manage stress and bounce back from setbacks
• Reflect on how to encourage independence while staying connected
• Discover simple strategies to support emotional wellbeing
• Share experiences and ideas with other parents
How to Manage Allocations in Odoo 18 Time Off
How to Manage Allocations in Odoo 18 Time OffCeline George Allocations in Odoo 18 Time Off allow you to assign a specific amount of time off (leave) to an employee. These allocations can be used to track and manage leave entitlements for employees, such as vacation days, sick leave, etc.
Hemiptera & Neuroptera: Insect Diversity.pptx
Hemiptera & Neuroptera: Insect Diversity.pptxArshad Shaikh *Order Hemiptera:*
Hemiptera, commonly known as true bugs, is a large and diverse order of insects that includes cicadas, aphids, leafhoppers, and shield bugs. Characterized by their piercing-sucking mouthparts, Hemiptera feed on plant sap, other insects, or small animals. Many species are significant pests, while others are beneficial predators.
*Order Neuroptera:*
Neuroptera, also known as net-winged insects, is an order of insects that includes lacewings, antlions, and owlflies. Characterized by their delicate, net-like wing venation and large, often prominent eyes, Neuroptera are predators that feed on other insects, playing an important role in biological control. Many species have aquatic larvae, adding to their ecological diversity.
IDSP(INTEGRATED DISEASE SURVEILLANCE PROGRAMME...
IDSP(INTEGRATED DISEASE SURVEILLANCE PROGRAMME...SweetytamannaMohapat IDSP is a disease surveillance program in India that aims to strengthen/maintain decentralized laboratory-based IT enabled disease surveillance systems for epidemic prone diseases to monitor disease trends, and to detect and respond to outbreaks in the early phases swiftly.....
"Hymenoptera: A Diverse and Fascinating Order".pptx
"Hymenoptera: A Diverse and Fascinating Order".pptxArshad Shaikh Hymenoptera is a diverse order of insects that includes bees, wasps, ants, and sawflies. Characterized by their narrow waists and often social behavior, Hymenoptera play crucial roles in ecosystems as pollinators, predators, and decomposers, with many species exhibiting complex social structures and communication systems.
LDMMIA Reiki Yoga S8 Free Workshop Grad Level
LDMMIA Reiki Yoga S8 Free Workshop Grad LevelLDM & Mia eStudios Available for Weekend June 6th. Uploaded Wed Evening June 4th.
Topics are unlimited and done weekly. Make sure to catch mini updates as well. TY for being here. More upcoming this summer.
A 8th FREE WORKSHOP
Reiki - Yoga
“Intuition” (Part 1)
For Personal/Professional Inner Tuning in. Also useful for future Reiki Training prerequisites. The Attunement Process. It’s all about turning on your healing skills. See More inside.
Your Attendance is valued.
Any Reiki Masters are Welcomed
More About:
The ‘Attunement’ Process.
It’s all about turning on your healing skills. Skills do vary as well. Usually our skills are Universal. They can serve reiki and any relatable Branches of Wellness.
(Remote is popular.)
Now for Intuition. It’s silent by design. We can train our intuition to be bold or louder. Intuition is instinct and the Senses. Coded in our Workshops too.
Intuition can include Psychic Science, Metaphysics, & Spiritual Practices to aid anything. It takes confidence and faith, in oneself.
Thank you for attending our workshops.
If you are new, do welcome.
Grad Students: I am planning a Reiki-Yoga Master Course. I’m Fusing both together.
This will include the foundation of each practice. Both are challenging independently. The Free Workshops do matter. They can also be downloaded or Re-Read for review.
My Reiki-Yoga Level 1, will be updated Soon/for Summer. The cost will be affordable.
As a Guest Student,
You are now upgraded to Grad Level.
See, LDMMIA Uploads for “Student Checkin”
Again, Do Welcome or Welcome Back.
I would like to focus on the next level. More advanced topics for practical, daily, regular Reiki Practice. This can be both personal or Professional use.
Our Focus will be using our Intuition. It’s good to master our inner voice/wisdom/inner being. Our era is shifting dramatically. As our Astral/Matrix/Lower Realms are crashing; They are out of date vs 5D Life.
We will catch trickster
energies detouring us.
(See Presentation for all sections, THX AGAIN.)
la storia dell'Inghilterra, letteratura inglese
la storia dell'Inghilterra, letteratura ingleseLetiziaLucente presentazione su alcuni aspetti della storia dell'Inghilterra, argomenti di letteratura inglese.
Artificial intelligence Presented by JM.
Artificial intelligence Presented by JM.jmansha170 AI (Artificial Intelligence) :
"AI is the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence, such as learning, decision-making, and problem-solving."
Important Points about AI:
1. Learning – AI can learn from data (Machine Learning).
2. Automation – It helps automate repetitive tasks.
3. Decision Making – AI can analyze and make decisions faster than humans.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP) – AI can understand and generate human language.
5. Vision & Recognition – AI can recognize images, faces, and patterns.
6. Used In – Healthcare, finance, robotics, education, and more.
Owner By:
Name : Junaid Mansha
Work : Web Developer and Graphics Designer
Contact us : +92 322 2291672
Email : [email protected]
TV Shows and web-series quiz | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 13TH MARCH 2025
TV Shows and web-series quiz | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 13TH MARCH 2025Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science HOW YOU DOIN'?
Cool, cool, cool...
Because that's what she said after THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS' TV SHOW quiz.
Grab your popcorn and be seated.
QM: THARUN S A
BCom Accounting and Finance (2023-26)
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS.
Gibson "Secrets to Changing Behaviour in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NISO...
Gibson "Secrets to Changing Behaviour in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NISO...National Information Standards Organization (NISO) This presentation was provided by Jennifer Gibson of the Dryad, during the first session of our 2025 NISO training series "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communications." Session One was held June 5, 2025.
How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18
How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18Celine George Efficient maintenance management is crucial for keeping equipment and work centers running smoothly in any business. Odoo 18 provides a Maintenance module that helps track, schedule, and manage maintenance requests efficiently.
Stewart Butler - OECD - How to design and deliver higher technical education ...
Stewart Butler - OECD - How to design and deliver higher technical education ...EduSkills OECD Stewart Butler, Labour Market Economist at the OECD presents at the webinar 'How to design and deliver higher technical education to develop in-demand skills' on 3 June 2025. You can check out the webinar recording via our website - https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/ .
You can check out the Higher Technical Education in England report via this link 👉 - https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/higher-technical-education-in-england-united-kingdom_7c00dff7-en.html
You can check out the pathways to professions report here 👉 https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/pathways-to-professions_a81152f4-en.html
TV Shows and web-series quiz | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 13TH MARCH 2025
TV Shows and web-series quiz | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 13TH MARCH 2025Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
Gibson "Secrets to Changing Behaviour in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NISO...
Gibson "Secrets to Changing Behaviour in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NISO...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
Introduction to Programming and QBasic Tutorial
- 1. INTRODUCTION to Programming and QBasic By: Nyrhon Von V. Bautista and Mhon Vincent S. Saldivar JGMNHS G9-SSC-Lavoisier
- 2. Programming???? A brief background • Programming is a set of step by step instructions that tells or direct the computer what to do. It sequences the tasks a user wants to be done and produces the results or output needed. • The set of rules or instructions that tells the computer what to perform is done through a programming languange. In this tutorial we will use the QBASIC programming language. • A programmer is the person who designs a program.
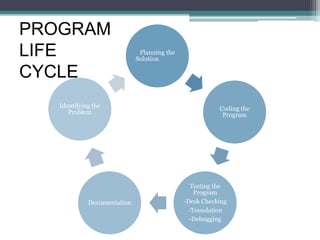
- 3. Planning the Solution Coding the Program Testing the Program -Desk Checking -Translation -Debugging Documentation Identifying the Problem PROGRAM LIFE CYCLE
- 4. Did you know that the first programmed word is “HELLO WORLD” LEVELS OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES Machine Language or First Generation Programming Language -this is considered to be the lowest level of programming language. Assembly Language or Second Generation of Programming Language -instead of using 1s and 0s assembly language uses MNEMONIC Codes. Mnemonic codes are abbreviations that easy to remember High Level Language or Third Generation Programming Language -this language transformed programming in the early 1960’s. Very High Level Languages or Fourth Generation Languages -Fourth generation languages (4GL) simplifies further the third level generation languages. Natural Languages - These languages are considered to be the fifth Generation languages. These programming languages are called Natural Languages because of their resemblance to English Language.
- 5. Procedural Languages Programming languages which are considered procedural that uses a series of instructions or statements which are sequential from the beginning to the end. Examples of Procedural Languages: BASIC – Beginner’s All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code COBOL – Common Business Oriented Language PASCAL FORTRAN- Formula Translator C PL1 – Programming Language One
- 6. Non-procedural Languages These Programming languages are considered as object- oriented programming languages. It is different from procedural language since statements are not executed line per line instead a series of instructions are executed as a whole when an event occurs. Examples of Non-procedural Languages VISUAL BASIC C++ JAVA DELPHI
- 7. FLOWCHARTING Flowcharting is one of the processes used in designing or planning the solution to a problem. It is a graphical representation to the solution of a problem. It uses shapes to show instructions and arrow lines and heads to display the flow. It uses the shapes OVAL, PARALLELOGRAM, RECTANGLE, DIAMOND,CIRCLE & PENTAGON
- 8. Oval Terminal Symbol Parallelogram Input/Output Rectangle Process Diamond Decision Hexagon Initialization/Preparation Arrow Lines & Arrow Heads Direction Annotation Circle On Page Connector Pentagon Odd-Page connector
- 9. Qbasic Tutorial After launching the QBasic interpreter (see before you start), you might see a window requesting a list of "parameters." If this window comes up, press the Enter key to continue. You should now see the QBasic interpreter, which has a blue background and displays a dialog box at the center. (If the interpreter fills the entire screen, then you may want to press "Alt + Enter," to make it smaller.) Press the Esc key to hide the dialog box. QBasic interpreter - main screen
- 10. Type the following (including the quotation marks) in the QBasic interpreter: PRINT "Hello World!" <press Enter> Now press F5 to run the program. You should now see a black screen, with Hello World at the top, and Press any key to continue at the bottom. Press a key on the keyboard to return to the main screen. (The figure below displays the "output screen.") Basic interpreter - output screen If you run the program again, the interpreter adds another Hello World. QBasic adds Hello World each time the program is run.
- 11. Deleting the program To erase the current program:Go to the "File" menu. Click "New." The interpreter asks if you want to save the program. Select "No" (or if you'd rather keep the program, select "Yes"). Strings There are certain types of data (or information) called "strings." Strings contain a sequence of characters (letters, numbers, and symbols) enclosed in quotation marks. For example, "Hello World!" is a string. The following are also strings: "0123456789" "This is a string" "abc123" "1 + 1 = 2"
- 12. Commands There are also special functions called "commands" (also called "instructions"). A "command" tells the QBasic interpreter to do something. The PRINT command tells the QBasic interpreter to print something to the screen. In this case, the interpreter printed"Hello World!". TIP: Instead of typing PRINT, you can enter a question mark. For example: ?"Hello World!" With the PRINT command, you can also print numbers to the screen. Delete the current program (unless you already have) and write the following:PRINT 512 (or ?512) <press Enter> Press F5 to run the program. The program outputs:512
- 13. More about the PRINT command You can use multiple print statements in your program.PRINT "Hello" PRINT "World" Output:Hello World To place World onto the previous line, place a semi-colon after PRINT "Hello".PRINT "Hello"; PRINT "World" Output:HelloWorld Also, if you put a comma instead of a semi-colon on the first line, the program will insert spaces between the two words.PRINT "Hello", PRINT "World" Output:Hello World
- 14. Variables This chapter discusses an important topic in programming, "variables." Please read this section thoroughly. A variable is a piece of data kept in the computer's memory (RAM). The location of a variable in RAM is called the"address." How a variable is stored in RAM The following program prints the variable X to the screen:print X Since the variable hasn't been assigned a number, the value of the variable is 0. So, the output of the program is:0 This next program sets X to 15, and then prints the variable: X = 15 print X This time, the output is:15 In the above example, the number 15 was stored in the computer's RAM at a certain memory address. Then the PRINTcommand accessed (or looked at) that address when it printed "15" to the screen.
- 15. Expressions If you pass an expression to a variable, the expression is evaluated and the variable is set to that value.x = 500 + (10 * 7) PRINT x Output:570 You can also use variables as expressions.rate = 50 time = 2 distance = rate * time PRINT distance Output:100 Plus, you can have both variables and numbers in an expression.X = 100 Y = X * 7 PRINT Y Output:700 TIP: The following increases X by 1: X = X + 1
- 16. Strings If you add a dollar sign ($) to the end of a variable, the variable is a string.X$ = "Hello World!" PRINT X$ Output:Hello World! If you try to set a string to a non-string variable, an error occurs.X = "Hello World!" The QBasic interpreter says "Type mismatch" when you try to run the above program. A string can be added to the end of an existing variable string.X$ = "Hello" X$ = X$ + "World" PRINT X$ Output:HelloWorld You can also add variable strings together.a$ = "String1" b$ = "String2" c$ = "String3" d$ = a$ + b$ + c$ PRINT d$ Output:String1String2String3
- 17. Retrieving keyboard input from the user One way to receive input from the keyboard is with the INPUT command. The INPUT command allows the user to enter either a string or a number, which is then stored in a variable.INPUT data$ PRINT data$ When this program is executed, the INPUT command displays a question mark, followed by a blinking cursor. And when you enter text, the program stores that text into the variable data$, which is printed to the screen. TIP: If you place a string and a semi-colon between INPUT and the variable, the program will print the string. INPUT "Enter some text:"; data$ To receive a number, use a non-string variable.INPUT number PRINT number If you enter text instead of a number, the QBasic interpreter displays an error message ("Redo from start").
- 18. To receive a number, use a non-string variable.INPUT number PRINT number If you enter text instead of a number, the QBasic interpreter displays an error message ("Redo from start"). Below is another example of the INPUT command:PRINT "Enter some text:" INPUT text$ PRINT "Now enter a number:" INPUT num PRINT text$ PRINT num TIP: You can have the question mark displayed on the previous line by using a semi-colon. PRINT "Enter some text:"; INPUT text$
- 19. The IF and THEN commands The IF and THEN commands are used to compare an expression and then perform some task based on that expression. x = 5 IF x = 5 THEN PRINT "x equals 5" Since X does equal 5 in this case, the program outputs:x equals 5 Expression signs You can also enter the following statements, instead of the equals sign:x < 5 (x is less than 5) x > 5 (x is greater than 5) Run the following:x = 16 IF (x > 5) THEN PRINT "x is greater than 5" Output:x is greater than 5
- 20. ELSE Using the ELSE command, you can have the program perform a different action if the statement is false.x = 3 IF x = 5 THEN PRINT "Yes" ELSE PRINT "No" Since X doesn't equal 5, the output is:No END IF END IF allows you to have multiple commands after the IF...THEN statement, but they must start on the line after theIF statement. END IF should appear right after the list of commands.x = 5 IF (x = 5) THEN INPUT a$ PRINT a$
- 21. END IF The following program uses ELSE with the END IF command:x = 16 IF (x = 5) THEN INPUT a$ PRINT a$ ELSE PRINT x * 2 END IF Output:32 TIP: There is a way to have multiple commands after IF...THENwithout using END IF. To do so, place a colon between each command. IF (x = 5) THEN INPUT a$: PRINT a$
- 22. THANK YOU FOR INQUIRIES Contact us. https://www.facebook.com/mhonarch https://www.facebook.com/eirelavlavun?fref=ts Or Email us at [email protected]