Introduction to R for Data Science :: Session 7 [Multiple Linear Regression in R]
- 1. Introduction to R for Data Science Lecturers dipl. ing Branko Kovač Data Analyst at CUBE/Data Science Mentor at Springboard Data Science Serbia [email protected] dr Goran S. Milovanović Data Scientist at DiploFoundation Data Science Serbia [email protected] [email protected]
- 2. MultipleLinear Regression in R • Dummy coding of categorical predictors • Multiple regression • Nested models and Partial F-test • Partial and Part Correlation • Multicolinearity • {Lattice} plots • Prediction, Confidence Intervals, Residuals • Influential Cases and the Influence Plot Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 3. ######################################################## # Introduction to R for Data Science # SESSION 7 :: 9 June, 2016 # Multiple Linear Regression in R # Data Science Community Serbia + Startit # :: Goran S. Milovanović and Branko Kovač :: ######################################################## #### read data library(datasets) library(broom) library(ggplot2) library(lattice) #### load data(iris) str(iris) MultipleRegression in R • Problems with simple linear regression: iris dataset Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 4. #### simple linearregression:SepalLength vs Petal Lenth # Predictorvs Criterion {ggplot2} ggplot(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Petal.Length)) + geom_point(size = 2, colour = "black") + geom_point(size = 1, colour = "white") + geom_smooth(aes(colour = "black"), method='lm') + ggtitle("Sepal Length vs Petal Length") + xlab("Sepal Length") + ylab("Petal Length") + theme(legend.position = "none") MultipleRegression in R • Problems with simple linear regression: iris dataset Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 5. # And now for something completelly different(but in R)... #### Problemswith linearregressionin iris # Predictorvs Criterion {ggplot2} - group separation ggplot(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Petal.Length, color = Species)) + geom_point(size = 2) + ggtitle("Sepal Length vs Petal Length") + xlab("Sepal Length") + ylab("Petal Length") MultipleRegression in R • Problems with simple linear regression: iris dataset Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 6. # Predictorvs Criterion {ggplot2} - separate regression lines ggplot(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Petal.Length, colour=Species)) + geom_smooth(method=lm) + geom_point(size = 2) + ggtitle("Sepal Length vs Petal Length") + xlab("Sepal Length") + ylab("Petal Length") MultipleRegression in R • Problems with simple linear regression: iris dataset Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
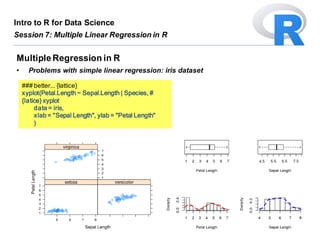
- 7. ### better... {lattice} xyplot(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length | Species, # {latice} xyplot data = iris, xlab = "Sepal Length", ylab = "Petal Length" ) MultipleRegression in R • Problems with simple linear regression: iris dataset Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 8. # Petal Length and SepalLength:Conditional Densities densityplot(~ Petal.Length | Species, # {latice} xyplot data = iris, plot.points=FALSE, xlab = "Petal Length", ylab = "Density", main = "P(Petal Length|Species)", col.line = 'red' ) densityplot(~ Sepal.Length | Species, # {latice} xyplot data = iris, plot.points=FALSE, xlab = "Sepal Length", ylab = "Density", main = "P(Sepal Length|Species)", col.line = 'blue' ) MultipleRegression in R • Problems with simple linear regression: iris dataset Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 9. # Linearregressionin subgroups species <- unique(iris$Species) w1 <- which(iris$Species == species[1]) # setosa reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris[w1,]) tidy(reg) w2 <- which(iris$Species == species[2]) # versicolor reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris[w2,]) tidy(reg) w3 <- which(iris$Species == species[3]) # virginica reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris[w3,]) tidy(reg) MultipleRegression in R • Simple linear regressions in sub-groups Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 10. #### Dummy Coding:Species in the iris dataset is.factor(iris$Species) levels(iris$Species) reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Species, data=iris) tidy(reg) glance(reg) # Neverforget whatthe regressioncoefficientfor a dummy variablemeans: # It tells us aboutthe effectof moving from the baselinetowardsthe respectivereferencelevel! # Here: baseline = setosa (cmp.levels(iris$Species)vs.the outputof tidy(reg)) # NOTE: watch for the order of levels! levels(iris$Species) # Levels: setosa versicolor virginica iris$Species <- factor(iris$Species, levels = c("versicolor", "virginica", "setosa")) levels(iris$Species) # baseline is now:versicolor reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Species, data=iris) tidy(reg)# The regression coefficents (!): figure out whathas happened! MultipleRegression in R • Dummy coding of categorical predictors Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 11. ### anotherway to do dummy coding rm(iris); data(iris) # ...justto fix the order of Species backto default levels(iris$Species) contrasts(iris$Species) = contr.treatment(3, base = 1) contrasts(iris$Species) # this probably whatyou rememberfrom your stats class... iris$Species <- factor(iris$Species, levels = c ("virginica","versicolor","setosa")) levels(iris$Species) contrasts(iris$Species) = contr.treatment(3, base = 1) # baseline is now:virginica contrasts(iris$Species) # considercarefully whatyou need to do MultipleRegression in R • Dummy coding of categorical predictors Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 12. ### Petal.Length ~ Species(Dummy Coding)+ Sepal.Length rm(iris); data(iris) # ...just to fix the order of Species backto default reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Species + Sepal.Length, data=iris) # BTW: since is.factor(iris$Species)==T,R does the dummy coding in lm() for you regSum <- summary(reg) regSum$r.squared regSum$coefficients # compare w. Simple LinearRegression reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris) regSum <- summary(reg) regSum$r.squared regSum$coefficients MultipleRegression in R • Multiple regression with dummy-coded categorical predictors Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 13. ### Comparingnestedmodels reg1 <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris) reg2 <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Species + Sepal.Length, data=iris) # reg1 is nested under reg2 # terminology:reg2 is a "full model" # this terminology will be used quite often in Logistic Regression # NOTE: Nested models # There is a set of coefficientsfor the nested model(reg1)such thatit # can be expressedin terms of the full model(reg2); in our case it is simple # HOME: - figure it out. anova(reg1, reg2) # partial F-test; Speciescertainly has an effect beyond Sepal.Length # NOTE: for partial F-test, see: # http://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~gsimon/B902301Page/CLASS02_24FEB10/PartialFtest.pdf MultipleRegression in R • Comparison of nested models Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 14. #### Multiple Regression - by the book # Following: http://www.r-tutor.com/elementary-statistics/multiple-linear-regression # (that's from yourreading list, to remind you...) data(stackloss) str(stackloss) # Data set description # URL: https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/datasets/html/stackloss.html stacklossModel = lm(stack.loss ~ Air.Flow + Water.Temp + Acid.Conc., data=stackloss) # let's see: summary(stacklossModel) glance(stacklossModel) # {broom} tidy(stacklossModel) # {broom} # predictnew data obs = data.frame(Air.Flow=72, Water.Temp=20, Acid.Conc.=85) predict(stacklossModel, obs) MultipleRegression in R • By the book: two or three continuous predictors… Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 15. # confidence intervals confint(stacklossModel, level=.95) # 95% CI confint(stacklossModel, level=.99) # 99% CI # 95% CI for Acid.Conc.only confint(stacklossModel, "Acid.Conc.", level=.95) # defaultregressionplots in R plot(stacklossModel) MultipleRegression in R • By the book: two or three continuous predictors… Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 16. # multicolinearity library(car) # John Fox's carpackage VIF <- vif(stacklossModel) VIF sqrt(VIF) # Variance Inflation Factor(VIF) # The increasein the ***variance***of an regression ceoff.due to colinearity # NOTE: sqrt(VIF)= how much larger the ***SE*** of a reg.coeff.vs. whatit would be # if there were no correlationswith the other predictors in the model # NOTE: lower_bound(VIF)= 1; no upperbound;VIF > 2 --> (Concerned== TRUE) Tolerance <- 1/VIF # obviously,tolerance and VIF are redundant Tolerance # NOTE: you can inspectmulticolinearity in the multiple regressionmode # by conductinga PrincipalComponentAnalysis overthe predictors; # when the time is right. MultipleRegression in R • Assumptions: multicolinearity Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 17. #### R for partial and part (semi-partial)correlations library(ppcor) # a good one;there are many ways to do this in R #### partialcorrelation in R dataSet <- iris str(dataSet) dataSet$Species <- NULL irisPCor <- pcor(dataSet, method="pearson") irisPCor$estimate # partialcorrelations irisPCor$p.value # results of significancetests irisPCor$statistic # t-test on n-2-k degrees offreedom ;k = num. of variablesconditioned # partial correlation between x and y while controlling forz partialCor <- pcor.test(dataSet$Sepal.Length, dataSet$Petal.Length, dataSet$Sepal.Width, method = "pearson") partialCor$estimate partialCor$p.value partialCor$statistic MultipleRegression in R • Partial Correlation in R Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 18. #### semi-partialcorrelation in R # NOTE: ... Semi-partialcorrelation is the correlation of two variables # with variation from a third or more othervariables removedonly # from the ***second variable*** # NOTE: The first variable <- rows, the secondvariable <-columns # cf. ppcor:An R Packagefor a FastCalculationto Semi-partialCorrelation Coefficients(2015) # SeonghoKim, BiostatisticsCore,Karmanos CancerInstitute,Wayne State University # URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4681537/ irisSPCor <- spcor(dataSet, method = "pearson") irisSPCor$estimate irisSPCor$p.value irisSPCor$statistic partCor <- spcor.test(dataSet$Sepal.Length, dataSet$Petal.Length, dataSet$Sepal.Width, method = "pearson") # NOTE: this is a correlation of dataSet$Sepal.Length w. dataSet$Petal.Length # when the variance ofdataSet$Petal.Length(2nd variable)due to dataSet$Sepal.Width # is removed! partCor$estimate partCor$p.value MultipleRegression in R • Part (semi-partial) Correlation in R Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R
- 19. # NOTE: In multiple regression,this is the semi-partial(or part) correlation # that you need to inspect: # assume a modelwith X1, X2, X3 as predictors,and Y as a criterion # You need a semi-partialof X1 and Y following the removalof X2 and X3 from Y # It goes like this: in Step 1, you perform a multiple regression Y ~ X2 + X3; # In Step 2, you take the residualsof Y, call them RY; in Step 3, you regress (correlate) # RY ~ X1: the correlation coefficientthat you get from Step 3 is the part correlation # that you're looking for. MultipleRegression in R • NOTE on semi-partial (part) correlation in multiple regression… Intro to R for Data Science Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R








![# Linearregressionin subgroups
species <- unique(iris$Species)
w1 <- which(iris$Species == species[1]) # setosa
reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris[w1,])
tidy(reg)
w2 <- which(iris$Species == species[2]) # versicolor
reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris[w2,])
tidy(reg)
w3 <- which(iris$Species == species[3]) # virginica
reg <- lm(Petal.Length ~ Sepal.Length, data=iris[w3,])
tidy(reg)
MultipleRegression in R
• Simple linear regressions in sub-groups
Intro to R for Data Science
Session 7: Multiple Linear Regression in R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrordatasciencesession7eng-160609234357/85/Introduction-to-R-for-Data-Science-Session-7-Multiple-Linear-Regression-in-R-9-320.jpg)










![Introduction to R for Data Science :: Session 7 [Multiple Linear Regression in R]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrordatasciencesession7eng-160609234357/85/Introduction-to-R-for-Data-Science-Session-7-Multiple-Linear-Regression-in-R-20-320.jpg)