Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) with Spring Framework is a powerful combination that simplifies database interactions in Java applications.
- 1. SQL and JDBC Peter Mork
- 2. Database Primer* All data values are simple No arrays, pointers, vectors, complex types All data are stored as 2D tables/relations Contains 0 or more rows/tuples Contains 1 or more columns/attributes All operations defined logically Order of tuples is irrelevant Keys used to identify unique tuples * SQL Instant Reference by Martin Gruber
- 3. SQL: What is it? Data Definition Language (DDL) CREATE relations, attributes, etc. Data Manipulation Language (DML) INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE data Data Control Language (DCL) GRANT, REVOKE privileges Data Query Language (DQL) SELECT data from relations
- 4. CREATE-ing Relations CREATE TABLE {name} ( {col1} {type1} [{cons1}], {col2} {type2} [{cons2}], ... ); col? = A name for the column type? = The column’s data-type cons? = An optional constraint on the column
- 5. Data types CHAR(len), VARCHAR(len): Strings of maximum length len FLOAT, REAL: Approximate numbers INT, INTEGER: Exact integers DECIMAL, DEC: Exact decimals DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP: Timestamp combines date and time
- 6. Constraints NOT NULL: No missing data allowed UNIQUE: Every value is unique or missing PRIMARY KEY: Every value is unique Plus other more sophisticated predicates
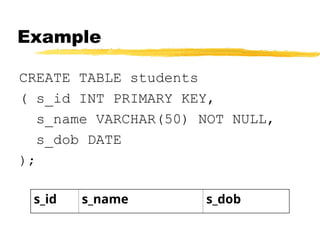
- 7. Example CREATE TABLE students ( s_id INT PRIMARY KEY, s_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, s_dob DATE ); s_id s_name s_dob
- 8. INSERT-ing New Values INSERT INTO {table} [ ( {col-a}, {col-b}, … ) ] VALUES ( {val-a}, {val-b}, … ); col-x = Optional column names val-x = A value for that column If no column names are given, the order in the CREATE statement is used.
- 9. Example INSERT INTO students VALUES ( 001, ‘Peter Mork’ ); Since no column names were specified: 001 is s_id ‘Peter Mork’ is s_name NULL is used for missing data s_id s_name s_dob 1 Peter Mork NULL
- 10. DELETE-ing Values DELETE FROM {table} [ WHERE {predicate} ]; Deletes all tuples from {table} that match {predicate} Use a primary key to isolate one tuple Example: DELETE FROM students WHERE s_id = 1;
- 11. SELECT-ing Results SELECT {attr-list} FROM {table-list} [ WHERE {pred-list} ]; Logically: Computes cross-product of all tables Discards results that don’t match predicates Returns listed attributes
- 12. Simple Example SELECT s_name FROM students WHERE s_dob > ‘1975-1-1’; This retrieves all students born since 1975.
- 13. SELECT Clause An attribute list is either: * (indicating all columns) A list of unique attribute names: Usually an attribute name will suffice Sometimes you need {table}.{attr} Can rename attributes using AS Example: SELECT students.s_id AS id, s_name, grades.grade
- 14. FROM Clause A table list is a list of unique table names: Usually a table name will suffice Multiple occurrences of the same table must be renamed using AS Example: FROM students, final_grades AS grades
- 15. WHERE Clause The predicate list contains Join predicates, which relate two columns from different tables Select predicates, which relate a column to a constant or another column in the same table Example: WHERE grade >= 3.0 AND students.s_id = grades.s_id;
- 16. Full Example SELECT students.s_id AS id, s_name, grades.grade FROM students, final_grades as grades WHERE grade >= 3.0 AND students.s_id = grades.s_id;
- 17. Sample Data s_id s_name s_dob 1 Alice NULL 2 Bob 1974-8-28 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 s_id course grade 1 544 3.5 1 521 3.8 1 531 3.9 2 544 3.6 2 551 2.9
- 18. Cross-Product Results students.s_id s_name s_dob grades.s_id course grade 1 Alice NULL 1 544 3.5 1 Alice NULL 1 521 3.8 1 Alice NULL 1 531 3.9 1 Alice NULL 2 544 3.6 1 Alice NULL 2 551 2.9 2 Bob 1974-8-28 1 544 3.5 2 Bob 1974-8-28 1 521 3.8 2 Bob 1974-8-28 1 531 3.9 2 Bob 1974-8-28 2 544 3.6 2 Bob 1974-8-28 2 551 2.9 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 1 544 3.5 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 1 521 3.8 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 1 531 3.9 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 2 544 3.6 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 2 551 2.9
- 19. Check Predicates students.s_id s_name s_dob grades.s_id course grade 1 Alice NULL 1 544 3.5 1 Alice NULL 1 521 3.8 1 Alice NULL 1 531 3.9 1 Alice NULL 2 544 3.6 1 Alice NULL 2 551 2.9 2 Bob 1974-8-28 1 544 3.5 2 Bob 1974-8-28 1 521 3.8 2 Bob 1974-8-28 1 531 3.9 2 Bob 1974-8-28 2 544 3.6 2 Bob 1974-8-28 2 551 2.9 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 1 544 3.5 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 1 521 3.8 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 1 531 3.9 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 2 544 3.6 3 Cindy 1973-10-19 2 551 2.9
- 20. Final Result id s_name Grade 1 Alice 3.5 1 Alice 3.8 1 Alice 3.9 2 Bob 3.6
- 21. Note This is the logical order of operations. The database system will not choose such a brain-damaged approach. Application developers/users do not need to know how to execute the query efficiently; access plans are chosen automatically by the database system.
- 22. Other capabilities Grouping and aggregation Uses GROUP BY keyword Aggregation functions include: COUNT SUM AVG More sophisticated predicates Nested queries
- 23. JDBC: What is it? API for database programs Collection of interfaces, and a few key classes Relies on vendor-supplied drivers (i.e., implementations of the interfaces)
- 24. Connectivity Protocols JDBC Driver registered with system Downloaded (linked at run-time by VM) Written in Java can be linked to an existing ODBC driver ODBC Driver registered with system Installed on host machine Written in C de facto standard
- 25. JDBC Classes Date, Time, Timestamp, Types Represent standard RDB types Mapped to Java type system DriverManager/DriverPropertyInfo Used to initialize driver Analogous to the System class
- 26. JDBC Interfaces Driver/Connection Used to communicate with database Statement (Callable, Prepared) Used to package SQL ResultSet Used to iterate through query result (cursor) DatabaseMetadata/ResultSetMetaData Contains data about the data
- 27. Steps to manipulate DB 1. Load driver 2. Connect to database 3. Manipulate data 4. Close database
- 28. 1. Load driver Explicitly: Class.forName(“driver name”) This creates a new instance of the driver Implicitly: Update the Java system settings (See Java docs for more info)
- 29. 2. Connect to database getConnection(db) getConnection(db, uid, pwd) getConnection(db, info) db = “jdbc:odbc:data-source-name” db = “jdbc:???://host:port/dbname”
- 30. Connection notes Properties is a sub-class of HashTable Used to package multiple parameters close() closes a connection (step 4) isClosed() tests a connection’s status
- 31. 3. Manipulate data createStatement establishes a framework for executing queries executeQuery returns a ResultSet executeUpdate returns an int execute can return either, but is usually used when there is no data to return
- 32. Which execute to execute? DDL and DCL queries are generally run using execute() DML queries are generally run using executeUpdate(); the return value represents the number of rows affected DQL queries are generally run using executeQuery(); a collection of tuples is returned
- 33. ResultSet A cursor that iterates through a collection of tuples Forward only! Each Statement object can have at most one active ResultSet
- 34. Metadata Metadata lets you know what the database looks like Information about the table names, field names, domains, etc. Metadata exists for both the Database (effectively constant) and for each ResultSet (depends on the query)
- 35. Important Metadata methods columnCount(): The number of fields in a ResultSet columnType(i): The type (as listed in Types) of column i. Note that columns are 1-indexed, not 0. The return value of columnType can be used to select the correct getXXX method to invoke on the ResultSet
- 36. Possible Uses of JDBC Leverage Java’s GUI tools to allow users to visualize the contents of a database Use Java to publish information stored in a database on the web Create tools to aid the database programmer in designing queries
- 37. Observations Java’s inherent speed problems can be offset by the power of an efficient database Many databases have awkward user interfaces Database queries are disk/network requests -- think multi-threading



![CREATE-ing Relations
CREATE TABLE {name}
( {col1} {type1} [{cons1}],
{col2} {type2} [{cons2}],
...
);
col? = A name for the column
type? = The column’s data-type
cons? = An optional constraint on the column](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javajdbcwithspring-250313105015-e3f6255b/85/Java-Database-Connectivity-JDBC-with-Spring-Framework-is-a-powerful-combination-that-simplifies-database-interactions-in-Java-applications-4-320.jpg)


![INSERT-ing New Values
INSERT INTO {table}
[ ( {col-a}, {col-b}, … ) ]
VALUES ( {val-a}, {val-b}, … );
col-x = Optional column names
val-x = A value for that column
If no column names are given, the order
in the CREATE statement is used.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javajdbcwithspring-250313105015-e3f6255b/85/Java-Database-Connectivity-JDBC-with-Spring-Framework-is-a-powerful-combination-that-simplifies-database-interactions-in-Java-applications-8-320.jpg)

![DELETE-ing Values
DELETE FROM {table}
[ WHERE {predicate} ];
Deletes all tuples from {table} that
match {predicate}
Use a primary key to isolate one tuple
Example:
DELETE FROM students
WHERE s_id = 1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javajdbcwithspring-250313105015-e3f6255b/85/Java-Database-Connectivity-JDBC-with-Spring-Framework-is-a-powerful-combination-that-simplifies-database-interactions-in-Java-applications-10-320.jpg)
![SELECT-ing Results
SELECT {attr-list}
FROM {table-list}
[ WHERE {pred-list} ];
Logically:
Computes cross-product of all tables
Discards results that don’t match predicates
Returns listed attributes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javajdbcwithspring-250313105015-e3f6255b/85/Java-Database-Connectivity-JDBC-with-Spring-Framework-is-a-powerful-combination-that-simplifies-database-interactions-in-Java-applications-11-320.jpg)

























