java1.pptjava is programming language, having core and advanced java
- 1. 1 Java
- 2. 2 Readings and References • References » "Collections", Java tutorial » http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/collections/index.html
- 3. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 3 Java 2 Collections • A collection is an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit • Very useful » store, retrieve and manipulate data » transmit data from one method to another » data structures and methods written by hotshots in the field • Joshua Bloch, who also wrote the Collections tutorial
- 4. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 4 Collections Framework • Unified architecture for representing and manipulating collections. • A collections framework contains three things » Interfaces » Implementations » Algorithms
- 5. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 5 Collections Framework Diagram •Interfaces, Implementations, and Algorithms •From Thinking in Java, page 462
- 6. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 6 Collection Interface • Defines fundamental methods » int size(); » boolean isEmpty(); » boolean contains(Object element); » boolean add(Object element); // Optional » boolean remove(Object element); // Optional » Iterator iterator(); • These methods are enough to define the basic behavior of a collection • Provides an Iterator to step through the elements in the Collection
- 7. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 7 Iterator Interface • Defines three fundamental methods » Object next() » boolean hasNext() » void remove() • These three methods provide access to the contents of the collection • An Iterator knows position within collection • Each call to next() “reads” an element from the collection » Then you can use it or remove it
- 8. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 8 Iterator Position
- 9. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 9 Example - SimpleCollection public class SimpleCollection { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection c; c = new ArrayList(); System.out.println(c.getClass().getName()); for (int i=1; i <= 10; i++) { c.add(i + " * " + i + " = "+i*i); } Iterator iter = c.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) System.out.println(iter.next()); } }
- 10. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 10 List Interface Context Collection List
- 11. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 11 List Interface • The List interface adds the notion of order to a collection • The user of a list has control over where an element is added in the collection • Lists typically allow duplicate elements • Provides a ListIterator to step through the elements in the list.
- 12. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 12 ListIterator Interface • Extends the Iterator interface • Defines three fundamental methods » void add(Object o) - before current position » boolean hasPrevious() » Object previous() • The addition of these three methods defines the basic behavior of an ordered list • A ListIterator knows position within list
- 13. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 13 Iterator Position - next(), previous()
- 14. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 14 ArrayList and LinkedList Context ArrayList LinkedList Collection List
- 15. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 15 List Implementations • ArrayList » low cost random access » high cost insert and delete » array that resizes if need be • LinkedList » sequential access » low cost insert and delete » high cost random access
- 16. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 16 ArrayList overview • Constant time positional access (it’s an array) • One tuning parameter, the initial capacity public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; }
- 17. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 17 ArrayList methods • The indexed get and set methods of the List interface are appropriate to use since ArrayLists are backed by an array » Object get(int index) » Object set(int index, Object element) • Indexed add and remove are provided, but can be costly if used frequently » void add(int index, Object element) » Object remove(int index) • May want to resize in one shot if adding many elements » void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)
- 18. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 18 LinkedList overview • Stores each element in a node • Each node stores a link to the next and previous nodes • Insertion and removal are inexpensive » just update the links in the surrounding nodes • Linear traversal is inexpensive • Random access is expensive » Start from beginning or end and traverse each node while counting
- 19. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 19 LinkedList entries private static class Entry { Object element; Entry next; Entry previous; Entry(Object element, Entry next, Entry previous) { this.element = element; this.next = next; this.previous = previous; } } private Entry header = new Entry(null, null, null); public LinkedList() { header.next = header.previous = header; }
- 20. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 20 LinkedList methods • The list is sequential, so access it that way » ListIterator listIterator() • ListIterator knows about position » use add() from ListIterator to add at a position » use remove() from ListIterator to remove at a position • LinkedList knows a few things too » void addFirst(Object o), void addLast(Object o) » Object getFirst(), Object getLast() » Object removeFirst(), Object removeLast()
- 21. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 21 Set Interface Context Collection Set
- 22. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 22 Set Interface • Same methods as Collection » different contract - no duplicate entries • Defines two fundamental methods » boolean add(Object o) - reject duplicates » Iterator iterator() • Provides an Iterator to step through the elements in the Set » No guaranteed order in the basic Set interface » There is a SortedSet interface that extends Set
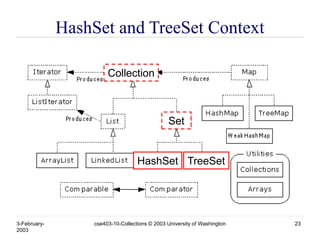
- 23. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 23 HashSet and TreeSet Context HashSet TreeSet Collection Set
- 24. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 24 HashSet • Find and add elements very quickly » uses hashing implementation in HashMap • Hashing uses an array of linked lists » The hashCode() is used to index into the array » Then equals() is used to determine if element is in the (short) list of elements at that index • No order imposed on elements • The hashCode() method and the equals() method must be compatible » if two objects are equal, they must have the same hashCode() value
- 25. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 25 TreeSet • Elements can be inserted in any order • The TreeSet stores them in order » Red-Black Trees out of Cormen-Leiserson-Rivest • An iterator always presents them in order • Default order is defined by natural order » objects implement the Comparable interface » TreeSet uses compareTo(Object o) to sort • Can use a different Comparator » provide Comparator to the TreeSet constructor
- 26. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 26 Map Interface Context Map
- 27. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 27 Map Interface • Stores key/value pairs • Maps from the key to the value • Keys are unique » a single key only appears once in the Map » a key can map to only one value • Values do not have to be unique
- 28. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 28 Map methods Object put(Object key, Object value) Object get(Object key) Object remove(Object key) boolean containsKey(Object key) boolean containsValue(Object value) int size() boolean isEmpty()
- 29. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 29 Map views • A means of iterating over the keys and values in a Map • Set keySet() » returns the Set of keys contained in the Map • Collection values() » returns the Collection of values contained in the Map. This Collection is not a Set, as multiple keys can map to the same value. • Set entrySet() » returns the Set of key-value pairs contained in the Map. The Map interface provides a small nested interface called Map.Entry that is the type of the elements in this Set.
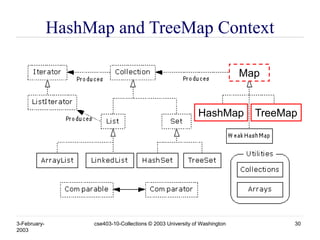
- 30. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 30 HashMap and TreeMap Context HashMap TreeMap Map
- 31. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 31 HashMap and TreeMap • HashMap » The keys are a set - unique, unordered » Fast • TreeMap » The keys are a set - unique, ordered » Same options for ordering as a TreeSet • Natural order (Comparable, compareTo(Object)) • Special order (Comparator, compare(Object, Object))
- 32. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 32 Bulk Operations • In addition to the basic operations, a Collection may provide “bulk” operations boolean containsAll(Collection c); boolean addAll(Collection c); // Optional boolean removeAll(Collection c); // Optional boolean retainAll(Collection c); // Optional void clear(); // Optional Object[] toArray(); Object[] toArray(Object a[]);
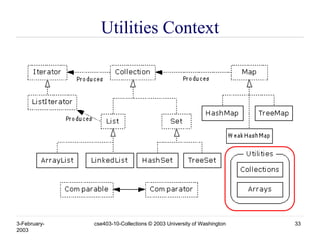
- 33. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 33 Utilities Context
- 34. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 34 Utilities • The Collections class provides a number of static methods for fundamental algorithms • Most operate on Lists, some on all Collections » Sort, Search, Shuffle » Reverse, fill, copy » Min, max • Wrappers » synchronized Collections, Lists, Sets, etc » unmodifiable Collections, Lists, Sets, etc
- 35. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 35 Appendix
- 36. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 36 Legacy classes • Still available • Don’t use for new development » unless you have to, eg, J2ME, J2EE in some cases • Retrofitted into Collections framework • Hashtable » use HashMap • Enumeration » use Collections and Iterators » if needed, can get an Enumeration with Collections.enumeration(Collection c)
- 37. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 37 More Legacy classes • Vector » use ArrayList • Stack » use LinkedList • BitSet » use ArrayList of boolean, unless you can’t stand the thought of the wasted space • Properties » legacies are sometimes hard to walk away from … » see next few pages
- 38. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 38 Properties class • Located in java.util package • Special case of Hashtable » Keys and values are Strings » Tables can be saved to/loaded from file
- 39. 3-February- 2003 cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 39 System properties • Java VM maintains set of properties that define system environment » Set when VM is initialized » Includes information about current user, VM version, Java environment, and OS configuration Properties prop = System.getProperties(); Enumeration e = prop.propertyNames(); while (e.hasMoreElements()) { String key = (String) e.nextElement(); System.out.println(key + " value is " + prop.getProperty(key)); }








![3-February-
2003
cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 9
Example - SimpleCollection
public class SimpleCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c;
c = new ArrayList();
System.out.println(c.getClass().getName());
for (int i=1; i <= 10; i++) {
c.add(i + " * " + i + " = "+i*i);
}
Iterator iter = c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java1-240722092932-3d32046e/85/java1-pptjava-is-programming-language-having-core-and-advanced-java-9-320.jpg)






![3-February-
2003
cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 16
ArrayList overview
• Constant time positional access (it’s an array)
• One tuning parameter, the initial capacity
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java1-240722092932-3d32046e/85/java1-pptjava-is-programming-language-having-core-and-advanced-java-16-320.jpg)













![3-February-
2003
cse403-10-Collections © 2003 University of Washington 32
Bulk Operations
• In addition to the basic operations, a Collection may
provide “bulk” operations
boolean containsAll(Collection c);
boolean addAll(Collection c); // Optional
boolean removeAll(Collection c); // Optional
boolean retainAll(Collection c); // Optional
void clear(); // Optional
Object[] toArray();
Object[] toArray(Object a[]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java1-240722092932-3d32046e/85/java1-pptjava-is-programming-language-having-core-and-advanced-java-32-320.jpg)







































































![GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdf](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/geography-studymaterial-250613053858-319e1b53-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

