Lambda Expression For anyone that needs Java Lambda notes
0 likes17 views
Java Lambda expression concept
1 of 20
Download to read offline








![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
public int getValue();
}
class ClsIntf implements FuncIntf
{
public int getValue()
{
return 20;
}
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = new ClsInft();
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-10-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
int getValue();
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = new ClsInft();
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-11-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
int getValue();
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = ;
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-12-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression Example1
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf {
int getValue();
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = () -> 20;
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue());
}
}
Lambda Expression () -> 20
================
• Implements the method getValue() in FuncIntf
• Returns an instance of the class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-13-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression with parameters - Example2
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf
{
int findSum(int a,int b);
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = (x,y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;};
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-14-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression with parameters type- Example3
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf
{
int findSum(int a,int b);
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = (int x, int y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;};
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-15-320.jpg)
![Lambda Expression with parameters type- Example4
Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
interface FuncIntf
{
int findSum(int a,int b);
}
class MyClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FuncIntf intfRef = (int x, int y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;}; //with return(with multiple statements)
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8));
FuncIntf intfRef1 = (int x,int y)-> (x+y); //without return(with only one statement)
System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef1.findSum(6,8));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-240707080146-84abf75f/85/Lambda-Expression-For-anyone-that-needs-Java-Lambda-notes-16-320.jpg)




Ad
Recommended
Lambdas, Collections Framework, Stream API



Lambdas, Collections Framework, Stream APIPrabu U The presentation starts with functional programming. Then collections framework is discussed. Finally the concepts of stream API is detailed
Lambdas in Java 8



Lambdas in Java 8Tobias Coetzee This document introduces lambda expressions in Java 8. It provides background on why lambda expressions were added to Java, including to allow for more functional programming and parallel processing. It covers the syntax of lambda expressions, when they should and should not be used, functional interfaces, method and constructor references, referencing external variables, debugging lambda expressions, and new lambda methods added in Java 8. The document also advertises exercises for the reader to complete to practice using lambda expressions.
Lambda Expressions Java 8 Features usage



Lambda Expressions Java 8 Features usageAsmaShaikh478737 Lambda expressions in Java 8 enable functional programming and allow code blocks to be treated as values. They provide a more readable and concise syntax than traditional anonymous classes. Lambdas improve APIs and support parallel processing. Functional programming separates code from objects and allows independent functions. Lambda expressions infer types from functional interfaces and can implement interfaces like Runnable more concisely than anonymous classes. Java 8 defines functional interfaces to have a single abstract method to be compatible with lambdas. Common functional interfaces include Predicate and Consumer. Streams and Optional are new classes that work with lambdas to support functional-style operations on collections and optional values.
Java 8 presentation



Java 8 presentationVan Huong Lambda expressions, default methods in interfaces, and the new date/time API are among the major new features in Java 8. Lambda expressions allow for functional-style programming by treating functionality as a method argument or anonymous implementation. Default methods add new capabilities to interfaces while maintaining backwards compatibility. The date/time API improves on the old Calendar and Date APIs by providing immutable and easier to use classes like LocalDate.
What's new in java 8



What's new in java 8Dian Aditya The document discusses new features in Java 8 including lambda expressions, default methods, streams, and static methods in interfaces. Lambda expressions allow for anonymous functions and method references provide shorthand syntax. Default methods enable adding new functionality to interfaces while maintaining binary compatibility. Streams support sequential and parallel aggregate operations on a sequence of elements. Static methods can now be defined in interfaces.
Functional Interfaces and Method References.pptx



Functional Interfaces and Method References.pptxMuhammadSalman701062 This document discusses functional interfaces and method references in Java. It covers the main functional interfaces in the java.util.function package like Function, Predicate, and Consumer. It explains how to compose functions using andThen() and how method references provide a compact way to refer to existing methods rather than defining anonymous methods. Examples are provided to demonstrate method references with Thread, Runnable, and filtering a list.
Charles Sharp: Java 8 Streams



Charles Sharp: Java 8 Streamsjessitron The document discusses Java 8 Streams, which provide a way to process data in a functional style. Streams allow operations like filter, map, and reduce to be performed lazily on collections, arrays, or I/O sources. The key aspects of streams are that they are lazy, support both sequential and parallel processing, and represent a sequence of values rather than storing them. The document provides examples of using intermediate operations like filter and map and terminal operations like forEach and collect. It also discusses spliterators, which drive streams and allow parallelization, and functional interfaces which are used with lambda expressions in streams.
Java moderno java para Jedis episodio I



Java moderno java para Jedis episodio IRoan Brasil Monteiro This document provides an overview of modern Java features including lambda expressions, method references, functional interfaces, streams API, default methods, Optional class, and date/time API. It defines lambda expressions as anonymous functions that can be passed as arguments or stored in variables. It provides examples of lambda syntax and explains functional interfaces. The document also demonstrates the streams API, describes how to use the Optional class to avoid null checks, and shows how to work with dates and times using classes like LocalDate from the new date/time API.
Functional programming in java 8 by harmeet singh



Functional programming in java 8 by harmeet singhHarmeet Singh(Taara) Cover Basic concept for Functional Programming in Java. Define new functional interfaces, lambda expressions, how to translate lambda expression, JVM deal with new byte code etc. This is not the perfect slides for functional programming, but trying cover simple basic functional programming.
Java findamentals1



Java findamentals1Todor Kolev The document discusses Java architecture and fundamentals. It can be summarized as:
1. Java's architecture consists of four main components: the Java programming language, Java class files, the Java API, and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
2. When a Java program is written and run, it uses these four technologies. The program is written in Java source code and compiled to class files, which are then run on the JVM along with the Java API library.
3. The JVM handles execution by using areas like the method area for bytecode storage, the Java stack for method calls and parameters, and the heap for object instantiation and garbage collection.
Java findamentals1



Java findamentals1Todor Kolev The document discusses Java architecture and fundamentals. It can be summarized as:
1. Java's architecture consists of four main components: the Java programming language, Java class files, the Java API, and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
2. When a Java program is written and run, it uses these four technologies. The program is written in Java source code and compiled to class files, which are then run on the JVM along with the Java API library.
3. The JVM handles execution by using areas like the method area for bytecode storage, the Java stack for method calls and parameters, and the heap for object instantiation and garbage collection.
Java findamentals1



Java findamentals1Todor Kolev The document discusses Java architecture and fundamentals. It can be summarized as:
1. Java's architecture consists of four main components: the Java programming language, Java class files, the Java API, and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
2. When a Java program is written and run, it uses these four technologies. The program is written in Java source code and compiled to class files, which are then run on the JVM along with the Java API library.
3. The JVM handles execution by using areas like the method area for bytecode storage, the Java stack for method calls and parameters, and the heap for object instantiation and garbage collection.
java150929145120-lva1-app6892 (2).pptx



java150929145120-lva1-app6892 (2).pptxBruceLee275640 The document provides an overview of new features in Java 8 including lambda expressions, functional interfaces, default and static interface methods, method references, stream API, and date/time API. Lambda expressions allow for anonymous functions and functional interfaces provide functional signatures. Default and static interface methods allow interfaces to define implementations. Method references provide shorthand syntax for lambda expressions. The stream API supports functional-style processing of collections through intermediate and terminal operations. The new date/time API replaces the Calendar class with more easily used and immutable classes like LocalDate.
Lambdas



Lambdasmalliksunkara This document discusses Java 8 features including defining methods in interfaces, functional programming concepts, lambda expressions, and the stream API. Key points include: interfaces can now define default and static methods; functional programming uses declarative code, avoids mutability, and handles concurrency; lambda expressions define anonymous methods; and the stream API processes data in parallel streams to leverage multi-core architectures.
20130329 introduction to linq



20130329 introduction to linqLearningTech LINQ allows querying different data sources using a common syntax. It includes LINQ to Objects, LINQ to XML, and LINQ to SQL. Queries can be written using query syntax or method syntax, which ultimately gets compiled to method syntax. Common LINQ methods include Where, Select, GroupBy, Join, Max, and Average. Query syntax is usually simpler and more readable than method syntax, though there is no semantic difference. The var type is implicitly typed based on the right side expression. Lambda expressions allow inline anonymous methods and are useful for certain LINQ queries only expressible in method syntax. Expression lambdas specify an expression on the right side of =>.
Java gets a closure



Java gets a closureTomasz Kowalczewski Presentation from Krakow Java Developers Day 2011 about future of Java - closures, defender methods etc.
JDK8 Lambda expressions demo



JDK8 Lambda expressions demoMouryaKumar Reddy Rajala This document provides an overview of lambda functions in Java, including their syntax, functional interfaces, type checking, local variables and closures, and method references. Lambda functions allow implementing functional interfaces concisely and can be passed around as arguments. They are anonymous and support multiple argument types. Common functional interfaces in Java 8 include Runnable and Callable. Method references provide an even more concise way to refer to existing methods rather than defining anonymous functions.
Java 8 Features



Java 8 FeaturesLeninkumar Koppoju Default methods and static methods allow interfaces to define new methods without breaking existing implementations. The lambda expressions feature introduces functional programming to Java through functional interfaces like Consumer and Function. The streams API provides a functional-style way to process and analyze collections through parallelization, optional return values, and collectors.
Java 8 lambda



Java 8 lambdaManav Prasad The document discusses lambda expressions in Java 8. It provides background on the lambda calculus and functional programming. Lambda expressions allow anonymous functions and are implemented using functional interfaces in Java 8. This enables a more functional style of programming. Lambda expressions can access variables from their enclosing scope and method references provide a concise way to pass existing methods. The streams API allows functional-style operations on collections and supports sequential and parallel processing.
Java 8 features



Java 8 featuresNexThoughts Technologies Java is Object Oriented Programming. Java 8 is the latest version of the Java which is used by many companies for the development in many areas. Mobile, Web, Standalone applications.
Java8 features



Java8 featuresMinal Maniar The document discusses lambda expressions in Java. It defines a lambda expression as a concise representation of an anonymous function that can be passed around. Lambda expressions allow for passing functions as arguments or returning them. They make code shorter and cleaner compared to anonymous classes. Functional interfaces are required for lambda expressions, where a functional interface defines a single abstract method that lambda expressions can implement.
Java8: what's new and what's hot



Java8: what's new and what's hotSergii Maliarov Java 8 was released in 2014 and introduced several new features including lambda expressions, functional interfaces, method references, and default methods in interfaces. It also included a new Stream API for functional-style data processing, a date/time API, and Project Nashorn for embedding JavaScript in Java applications. Future versions like Java 9 will focus on modularity, new APIs, and further improvements.
Insight into java 1.8, OOP VS FP



Insight into java 1.8, OOP VS FPSyed Awais Mazhar Bukhari ● Object Oriented Programming.
● Functional Programming.
● FP VS OOP
● Java 8 Recent API’s
● Default Methods for Interfaces
● Functional Interfaces
● Lambda expressions
● Method References
● Built-in Functional Interfaces
● Streams
● Why Lambdas?
Java 8 new features



Java 8 new featuresAniket Thakur The document discusses new features introduced in Java 8, including allowing static and default methods in interfaces, lambda expressions, and the Stream API. Key points include: interfaces can now contain static and default methods; lambda expressions provide a concise way to implement functional interfaces and allow passing code as a method argument; and the Stream API allows operations on sequences of data through intermediate and terminal operations.
Lambda Expressions in Java | Java Lambda Tutorial | Java Certification Traini...



Lambda Expressions in Java | Java Lambda Tutorial | Java Certification Traini...Edureka! **** Java Certification Training: https://www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training ****
This Edureka tutorial on “Lambda Expressions in Java” will introduce you to a new Java feature called Lambda Expressions. It will also talk about the functional interface in Java. Through this tutorial you will learn the following topics:
Java Lambda Expressions
Functional Interface
Lambda Parameters
Lambda as an Object
Lambda Value Capture
Method References as lambdas
Check out our Java Tutorial blog series: https://goo.gl/osrGrS
Check out our complete Youtube playlist here: https://goo.gl/gMFLx3
Functional Programming In Jdk8 



Functional Programming In Jdk8 Bansilal Haudakari The document provides an overview of functional programming concepts in Java 8. It discusses how functions are now first-class citizens in Java that can be passed as parameters and returned from other functions. Lambda expressions are introduced as anonymous functions that can be used to concisely represent implementations of functional interfaces. The document also discusses how lambda expressions are compiled using invokedynamic rather than by converting them to anonymous inner classes, and how this allows them to be more efficient. Finally, it covers additional Java 8 features like streams that further support a functional style of programming.
C#-LINQ-and-Lambda-Expression



C#-LINQ-and-Lambda-ExpressionSimplilearn This Lambda Expression C# Tutorial will acquaint you with a clear understanding of the fundamentals of LINQ C#. In this C# Tutorial for beginners, you will get a better understanding of are Lambda Expression C# tutorial. We will begin our session with a discussion on Linq. Then we will discuss the Lambda Expression and Async Lambda. After that, we will look into Lambda in the standard query operators with an implementation. Now we will dive into the Type Interface. Then we will discuss the Variable scope. After that, we will have a look at the Expression tree. Finally, we will wind up this session with a conclusion.
最新版美国威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证(UWSP毕业证书)原版定制



最新版美国威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证(UWSP毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea 鉴于此,定制威斯康星大学史蒂文分校学位证书提升履历【q薇1954292140】原版高仿威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证(UWSP毕业证书)可先看成品样本【q薇1954292140】帮您解决在美国威斯康星大学史蒂文分校未毕业难题,美国毕业证购买,美国文凭购买,【q微1954292140】美国文凭购买,美国文凭定制,美国文凭补办。专业在线定制美国大学文凭,定做美国本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制美国University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point completion letter。在线快速补办美国本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买美国学位证、威斯康星大学史蒂文分校Offer,美国大学文凭在线购买。
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
【复刻一套威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证成绩单信封等材料最强攻略,Buy University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
威斯康星大学史蒂文分校成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括威斯康星大学史蒂文分校课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
More Related Content
Similar to Lambda Expression For anyone that needs Java Lambda notes (20)
Java moderno java para Jedis episodio I



Java moderno java para Jedis episodio IRoan Brasil Monteiro This document provides an overview of modern Java features including lambda expressions, method references, functional interfaces, streams API, default methods, Optional class, and date/time API. It defines lambda expressions as anonymous functions that can be passed as arguments or stored in variables. It provides examples of lambda syntax and explains functional interfaces. The document also demonstrates the streams API, describes how to use the Optional class to avoid null checks, and shows how to work with dates and times using classes like LocalDate from the new date/time API.
Functional programming in java 8 by harmeet singh



Functional programming in java 8 by harmeet singhHarmeet Singh(Taara) Cover Basic concept for Functional Programming in Java. Define new functional interfaces, lambda expressions, how to translate lambda expression, JVM deal with new byte code etc. This is not the perfect slides for functional programming, but trying cover simple basic functional programming.
Java findamentals1



Java findamentals1Todor Kolev The document discusses Java architecture and fundamentals. It can be summarized as:
1. Java's architecture consists of four main components: the Java programming language, Java class files, the Java API, and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
2. When a Java program is written and run, it uses these four technologies. The program is written in Java source code and compiled to class files, which are then run on the JVM along with the Java API library.
3. The JVM handles execution by using areas like the method area for bytecode storage, the Java stack for method calls and parameters, and the heap for object instantiation and garbage collection.
Java findamentals1



Java findamentals1Todor Kolev The document discusses Java architecture and fundamentals. It can be summarized as:
1. Java's architecture consists of four main components: the Java programming language, Java class files, the Java API, and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
2. When a Java program is written and run, it uses these four technologies. The program is written in Java source code and compiled to class files, which are then run on the JVM along with the Java API library.
3. The JVM handles execution by using areas like the method area for bytecode storage, the Java stack for method calls and parameters, and the heap for object instantiation and garbage collection.
Java findamentals1



Java findamentals1Todor Kolev The document discusses Java architecture and fundamentals. It can be summarized as:
1. Java's architecture consists of four main components: the Java programming language, Java class files, the Java API, and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
2. When a Java program is written and run, it uses these four technologies. The program is written in Java source code and compiled to class files, which are then run on the JVM along with the Java API library.
3. The JVM handles execution by using areas like the method area for bytecode storage, the Java stack for method calls and parameters, and the heap for object instantiation and garbage collection.
java150929145120-lva1-app6892 (2).pptx



java150929145120-lva1-app6892 (2).pptxBruceLee275640 The document provides an overview of new features in Java 8 including lambda expressions, functional interfaces, default and static interface methods, method references, stream API, and date/time API. Lambda expressions allow for anonymous functions and functional interfaces provide functional signatures. Default and static interface methods allow interfaces to define implementations. Method references provide shorthand syntax for lambda expressions. The stream API supports functional-style processing of collections through intermediate and terminal operations. The new date/time API replaces the Calendar class with more easily used and immutable classes like LocalDate.
Lambdas



Lambdasmalliksunkara This document discusses Java 8 features including defining methods in interfaces, functional programming concepts, lambda expressions, and the stream API. Key points include: interfaces can now define default and static methods; functional programming uses declarative code, avoids mutability, and handles concurrency; lambda expressions define anonymous methods; and the stream API processes data in parallel streams to leverage multi-core architectures.
20130329 introduction to linq



20130329 introduction to linqLearningTech LINQ allows querying different data sources using a common syntax. It includes LINQ to Objects, LINQ to XML, and LINQ to SQL. Queries can be written using query syntax or method syntax, which ultimately gets compiled to method syntax. Common LINQ methods include Where, Select, GroupBy, Join, Max, and Average. Query syntax is usually simpler and more readable than method syntax, though there is no semantic difference. The var type is implicitly typed based on the right side expression. Lambda expressions allow inline anonymous methods and are useful for certain LINQ queries only expressible in method syntax. Expression lambdas specify an expression on the right side of =>.
Java gets a closure



Java gets a closureTomasz Kowalczewski Presentation from Krakow Java Developers Day 2011 about future of Java - closures, defender methods etc.
JDK8 Lambda expressions demo



JDK8 Lambda expressions demoMouryaKumar Reddy Rajala This document provides an overview of lambda functions in Java, including their syntax, functional interfaces, type checking, local variables and closures, and method references. Lambda functions allow implementing functional interfaces concisely and can be passed around as arguments. They are anonymous and support multiple argument types. Common functional interfaces in Java 8 include Runnable and Callable. Method references provide an even more concise way to refer to existing methods rather than defining anonymous functions.
Java 8 Features



Java 8 FeaturesLeninkumar Koppoju Default methods and static methods allow interfaces to define new methods without breaking existing implementations. The lambda expressions feature introduces functional programming to Java through functional interfaces like Consumer and Function. The streams API provides a functional-style way to process and analyze collections through parallelization, optional return values, and collectors.
Java 8 lambda



Java 8 lambdaManav Prasad The document discusses lambda expressions in Java 8. It provides background on the lambda calculus and functional programming. Lambda expressions allow anonymous functions and are implemented using functional interfaces in Java 8. This enables a more functional style of programming. Lambda expressions can access variables from their enclosing scope and method references provide a concise way to pass existing methods. The streams API allows functional-style operations on collections and supports sequential and parallel processing.
Java 8 features



Java 8 featuresNexThoughts Technologies Java is Object Oriented Programming. Java 8 is the latest version of the Java which is used by many companies for the development in many areas. Mobile, Web, Standalone applications.
Java8 features



Java8 featuresMinal Maniar The document discusses lambda expressions in Java. It defines a lambda expression as a concise representation of an anonymous function that can be passed around. Lambda expressions allow for passing functions as arguments or returning them. They make code shorter and cleaner compared to anonymous classes. Functional interfaces are required for lambda expressions, where a functional interface defines a single abstract method that lambda expressions can implement.
Java8: what's new and what's hot



Java8: what's new and what's hotSergii Maliarov Java 8 was released in 2014 and introduced several new features including lambda expressions, functional interfaces, method references, and default methods in interfaces. It also included a new Stream API for functional-style data processing, a date/time API, and Project Nashorn for embedding JavaScript in Java applications. Future versions like Java 9 will focus on modularity, new APIs, and further improvements.
Insight into java 1.8, OOP VS FP



Insight into java 1.8, OOP VS FPSyed Awais Mazhar Bukhari ● Object Oriented Programming.
● Functional Programming.
● FP VS OOP
● Java 8 Recent API’s
● Default Methods for Interfaces
● Functional Interfaces
● Lambda expressions
● Method References
● Built-in Functional Interfaces
● Streams
● Why Lambdas?
Java 8 new features



Java 8 new featuresAniket Thakur The document discusses new features introduced in Java 8, including allowing static and default methods in interfaces, lambda expressions, and the Stream API. Key points include: interfaces can now contain static and default methods; lambda expressions provide a concise way to implement functional interfaces and allow passing code as a method argument; and the Stream API allows operations on sequences of data through intermediate and terminal operations.
Lambda Expressions in Java | Java Lambda Tutorial | Java Certification Traini...



Lambda Expressions in Java | Java Lambda Tutorial | Java Certification Traini...Edureka! **** Java Certification Training: https://www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training ****
This Edureka tutorial on “Lambda Expressions in Java” will introduce you to a new Java feature called Lambda Expressions. It will also talk about the functional interface in Java. Through this tutorial you will learn the following topics:
Java Lambda Expressions
Functional Interface
Lambda Parameters
Lambda as an Object
Lambda Value Capture
Method References as lambdas
Check out our Java Tutorial blog series: https://goo.gl/osrGrS
Check out our complete Youtube playlist here: https://goo.gl/gMFLx3
Functional Programming In Jdk8 



Functional Programming In Jdk8 Bansilal Haudakari The document provides an overview of functional programming concepts in Java 8. It discusses how functions are now first-class citizens in Java that can be passed as parameters and returned from other functions. Lambda expressions are introduced as anonymous functions that can be used to concisely represent implementations of functional interfaces. The document also discusses how lambda expressions are compiled using invokedynamic rather than by converting them to anonymous inner classes, and how this allows them to be more efficient. Finally, it covers additional Java 8 features like streams that further support a functional style of programming.
C#-LINQ-and-Lambda-Expression



C#-LINQ-and-Lambda-ExpressionSimplilearn This Lambda Expression C# Tutorial will acquaint you with a clear understanding of the fundamentals of LINQ C#. In this C# Tutorial for beginners, you will get a better understanding of are Lambda Expression C# tutorial. We will begin our session with a discussion on Linq. Then we will discuss the Lambda Expression and Async Lambda. After that, we will look into Lambda in the standard query operators with an implementation. Now we will dive into the Type Interface. Then we will discuss the Variable scope. After that, we will have a look at the Expression tree. Finally, we will wind up this session with a conclusion.
Recently uploaded (20)
最新版美国威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证(UWSP毕业证书)原版定制



最新版美国威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证(UWSP毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea 鉴于此,定制威斯康星大学史蒂文分校学位证书提升履历【q薇1954292140】原版高仿威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证(UWSP毕业证书)可先看成品样本【q薇1954292140】帮您解决在美国威斯康星大学史蒂文分校未毕业难题,美国毕业证购买,美国文凭购买,【q微1954292140】美国文凭购买,美国文凭定制,美国文凭补办。专业在线定制美国大学文凭,定做美国本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制美国University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point completion letter。在线快速补办美国本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买美国学位证、威斯康星大学史蒂文分校Offer,美国大学文凭在线购买。
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
【复刻一套威斯康星大学史蒂文分校毕业证成绩单信封等材料最强攻略,Buy University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
威斯康星大学史蒂文分校成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括威斯康星大学史蒂文分校课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
ACEN presentation / huddle from June 2025



ACEN presentation / huddle from June 2025Mark Rauterkus ACEN is for externships for Audiology students. Learn more at:
https://audclinicaled.net/
Top HR interview question and answer.pdf



Top HR interview question and answer.pdfmbbseo1 Discover the top HR interview questions with expert tips on how to answer them. Perfect guide for job seekers to ace their next HR round.
A Guide for a Winning Interview June 2025



A Guide for a Winning Interview June 2025Bruce Bennett This webinar is an in-depth review of the interview process. Preparation is a key element to acing an interview. Learn the best approaches from the initial phone screen to the face-to-face meeting with the hiring manager. You will hear great answers to several standard questions, including the dreaded “Tell Me About Yourself”.
"Housefull 5" (.2025.) +Fu𝗅𝗅Mov𝗂e! Down𝗅oad Fre𝖾 𝟩𝟤𝟢𝗉, 𝟦𝟪𝟢𝗉 𝖧𝖣 & 𝟣𝟢𝟪𝟢𝗉



"Housefull 5" (.2025.) +Fu𝗅𝗅Mov𝗂e! Down𝗅oad Fre𝖾 𝟩𝟤𝟢𝗉, 𝟦𝟪𝟢𝗉 𝖧𝖣 & 𝟣𝟢𝟪𝟢𝗉deltaforcedxb7 Download Link ➤➤: https://rebrand.ly/656e26/ 👈👈
Download Link ➤➤: https://rebrand.ly/656e26/ 👈👈
"Housefull 5" (.2025.) +Fu𝗅𝗅Mov𝗂e! Down𝗅oad Fre𝖾 𝟩𝟤𝟢𝗉, 𝟦𝟪𝟢𝗉 𝖧𝖣 & 𝟣𝟢𝟪𝟢𝗉
Modern trends in Fruit Breedings , A new techniques of fruit Breedings



Modern trends in Fruit Breedings , A new techniques of fruit Breedings7300511143 Current trends in fruit Breedings covers e-classes, PhD Horticulture syllabus
👉 Top 11 IT Companies in Hinjewadi You Should Know About



👉 Top 11 IT Companies in Hinjewadi You Should Know Aboutvaishalitraffictail Hinjewadi, Pune, has emerged as a leading IT hub in India, hosting top tech giants and driving digital transformation across industries. With companies like Infosys, TCS, Wipro, and Cognizant establishing a strong presence, Hinjewadi offers excellent career opportunities, modern infrastructure, and a thriving tech ecosystem. This article explores the Top 11 IT Companies in Hinjewadi, highlighting their innovations, impact, and why they are key players in India's IT landscape.
Academic Preparation for Final Year Externship.pptx



Academic Preparation for Final Year Externship.pptxMark Rauterkus Preparation insights for Audiology graduate students approaching their externship. More than 40 slides to use as a template to cover important topics with budding professionals about to enter their professional clinic placements and externships.
最新版西班牙巴斯克大学毕业证(UPV毕业证书)原版定制



最新版西班牙巴斯克大学毕业证(UPV毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea 挂科无法毕业鉴于此购买文凭【q薇1954292140】一比一原版(UPV毕业证)巴斯克大学毕业证如何办理改成绩单GPA,文凭购买,毕业证办理,文凭办理只是基础业务。【q薇1954292140】一比一还原国外大学毕业证,定制国外大学学历,制作国外大学文凭,复刻国外大学毕业证书。学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【办理巴斯克大学成绩单Buy Universidad del País Vasco Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
巴斯克大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括巴斯克大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
Buy Universidad del País Vasco Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办?鉴于此,购买西班牙毕业证【q微1954292140】西班牙文凭购买,西班牙文凭购买,西班牙文凭定制,西班牙文凭补办。专业在线定制西班牙大学文凭,定做西班牙本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制西班牙Universidad del País Vasco completion letter。在线快速补办西班牙本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买西班牙学位证、巴斯克大学Offer,西班牙大学文凭在线购买。
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理巴斯克大学毕业证(UPV毕业证书)文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理巴斯克大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】西班牙学位证(UPV毕业证书)巴斯克大学毕业证书如何办理国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证
三.材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理巴斯克大学毕业证(UPV毕业证书)请加学历顾问【微信:1954292140】毕业证购买指大学文凭购买,毕业证办理和文凭办理。学院文凭定制,学校原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。经常操作的国家有美国毕业证,英国毕业证,澳洲毕业证,加拿大毕业证,以及德国毕业证,法国毕业证、荷兰毕业证、瑞士毕业证、日本毕业证、韩国毕业证、新西兰毕业证、新加坡毕业证、泰国毕业证、马来西亚毕业证等。包括了本科毕业证,硕士毕业证。
Revolutionizing Environmental Compliance with AI.pdf



Revolutionizing Environmental Compliance with AI.pdfDorian F Corliss In the face of rising regulatory pressures and growing environmental concerns, industrial sectors must evolve. Traditional compliance approaches are no longer sufficient for meeting today’s complex sustainability goals. Dorian Corliss, a veteran environmental compliance expert with over 20 years of experience and two emissions technology patents, is at the forefront of this transformation. By integrating artificial intelligence into power, wastewater, and landfill operations, he is setting a new standard for smart, sustainable, and scalable environmental management.
Using Social Media in Job Search June 2025



Using Social Media in Job Search June 2025Bruce Bennett The job search process has changed in the last several years & social media is a vital component. Learn where to find jobs and how to research your target companies using social media. In this informational session, see how to create a job search alert using LinkedIn and discover the uses of Twitter, Facebook, and other social media to find jobs.
最新版英国纽曼大学毕业证(Newman毕业证书)原版定制



最新版英国纽曼大学毕业证(Newman毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea 被学校开除?鉴于此购买文凭【q薇1954292140】在读证明+纽曼大学毕业证(Newman毕业证书)海外学历定制改成绩单GPA,文凭购买,毕业证办理,文凭办理只是基础业务。【q薇1954292140】一比一还原国外大学毕业证,定制国外大学学历,制作国外大学文凭,复刻国外大学毕业证书。学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【办理纽曼大学成绩单Buy Newman University, Birmingham Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
纽曼大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括纽曼大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
Buy Newman University, Birmingham Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办?鉴于此,购买英国毕业证【q微1954292140】英国文凭购买,英国文凭购买,英国文凭定制,英国文凭补办。专业在线定制英国大学文凭,定做英国本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制英国Newman University, Birmingham completion letter。在线快速补办英国本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买英国学位证、纽曼大学Offer,英国大学文凭在线购买。
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《英国毕业文凭证书快速办理纽曼大学学历学位证制作》【q微1954292140】《论文没过纽曼大学正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理Newman毕业证,改成绩单《Newman毕业证明办理纽曼大学毕业证书购买》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Newman University, Birmingham Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,纽曼大学Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
英国纽曼大学毕业证(Newman毕业证书)Newman文凭【q微1954292140】高仿真还原英国文凭证书和外壳,定制英国纽曼大学成绩单和信封。真实可查文凭Newman毕业证【q微1954292140】学位证和毕业证的区别纽曼大学offer/学位证毕业证书影本、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决纽曼大学学历学位认证难题。
How to Become a CPA USA and Boost Your Career



How to Become a CPA USA and Boost Your Careeripfcadwords Learn from the best renowned CPA USA Course provider and grow your career in leaps & bounce.
Ad
Lambda Expression For anyone that needs Java Lambda notes
- 2. Lambda Expression • It is an anonymous (that is, unnamed) method • A lambda expression results in a form of anonymous class. • This method is not executed on its own. Instead, it is used to implement a method defined by a functional interface. • Lambda expressions are also commonly referred to as closures Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 3. Lambda Expression Fundamentals • The lambda expression introduces a new syntax element and operator into the Java language • lambda operator or the arrow operator • Lambda operator divides the lambda expression into two parts. • The left side specifies any parameters required by the lambda expression. • On the right side is the lambda body, which specifies the actions of the lambda expression • Syntax: (param1,param2) -> body Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 4. Lambda Expression Fundamentals • lambda expression consist of three components: ▪ Argument-list: It can be empty or non-empty as well. ▪ Arrow-token: It is used to link arguments-list and body of expression. ▪ Body: It contains expressions and statements for lambda expression. Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 5. Lambda Expression • No Parameter Syntax () -> { //Body of no parameter lambda } • One Parameter Syntax (param1) -> { //Body of no parameter lambda } Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 6. Lambda Expression Multiple parameter Syntax (param1, param2) -> { //Body of no parameter lambda } Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
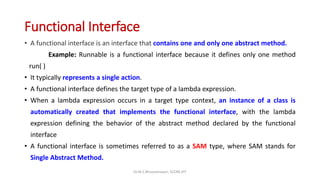
- 7. Functional Interface • A functional interface is an interface that contains one and only one abstract method. Example: Runnable is a functional interface because it defines only one method run( ) • It typically represents a single action. • A functional interface defines the target type of a lambda expression. • When a lambda expression occurs in a target type context, an instance of a class is automatically created that implements the functional interface, with the lambda expression defining the behavior of the abstract method declared by the functional interface • A functional interface is sometimes referred to as a SAM type, where SAM stands for Single Abstract Method. Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 8. Lambda Expression Fundamentals • Java defines two types of lambda bodies. ▪ single expression ▪ block of code Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT Normal Method ============= int findSum() { return 20; } Lambda Expression ================ () -> 20
- 9. Lambda Expression • In order for a lambda expression to be used in a target type context, the type of the abstract method and the type of the lambda expression must be compatible • Rules ▪ The type and number of the lambda expression’s parameters must be compatible with the method’s parameters; ▪ The return types must be compatible; and ▪ Any exceptions thrown by the lambda expression must be acceptable to the method Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 10. Lambda Expression Example1 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { public int getValue(); } class ClsIntf implements FuncIntf { public int getValue() { return 20; } } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = new ClsInft(); System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue()); } }
- 11. Lambda Expression Example1 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { int getValue(); } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = new ClsInft(); System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue()); } }
- 12. Lambda Expression Example1 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { int getValue(); } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = ; System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue()); } }
- 13. Lambda Expression Example1 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { int getValue(); } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = () -> 20; System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.getValue()); } } Lambda Expression () -> 20 ================ • Implements the method getValue() in FuncIntf • Returns an instance of the class
- 14. Lambda Expression with parameters - Example2 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { int findSum(int a,int b); } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = (x,y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;}; System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8)); } }
- 15. Lambda Expression with parameters type- Example3 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { int findSum(int a,int b); } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = (int x, int y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;}; System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8)); } }
- 16. Lambda Expression with parameters type- Example4 Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT interface FuncIntf { int findSum(int a,int b); } class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { FuncIntf intfRef = (int x, int y)-> {int c=x+y;return c;}; //with return(with multiple statements) System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef.findSum(6,8)); FuncIntf intfRef1 = (int x,int y)-> (x+y); //without return(with only one statement) System.out.println("Value is:"+intfRef1.findSum(6,8)); } }
- 17. Thread Implementation without Lambda class MyThread implements Runnable{ public void run() { try { for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Child Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(500); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Child interrupted."); } System.out.println("Exiting child thread."); } } Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 18. Thread Implementation without Lambda Runnable rintf=new MyThread() Thread th1=new Thread(rintf) th1.start() Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT
- 19. Thread Implementation using Lambda Thread th1=new Thread(() -> { try { for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Child Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(500); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Child interrupted."); } System.out.println("Exiting child thread."); }); th1.start(); Dr.M.S.Bhuvaneswari, SCORE,VIT







