Lecture20 user definedfunctions.ppt
- 1. USER DEFINED FUNCTIONS IN ‘C’ Prakash Khaire Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar
- 2. Introduction Strength of ‘C’ language is C functions ● They are easy to define and use ● We are very much familiar with main(), printf() & ● scanf() function Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 3. In this chapter, you will see… ● How a function is designed ? ● How a function is integrated into a program ? ● How two or more functions are put together / ● How they communicate with one another ? Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 4. Definition - function ●A set of statements working together with common goal is known as function. ●Also known as subprograms which are used to compute a value or perform a specific task. ●They can’t run independently and are always called by the main() program or by some other function. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 5. Categories of fucntions ●In ‘C’ language, functions are classified into the following two categories ●Library functions ●User-Defined functions ●scanf(), printf(), getch(), strlen(), strcmp(), strcat(), sqrt(), pow() are this are library functions. ●main() is user-defined functions Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 6. User Defined Functions ●User defined functions are self-contained blocks of statements which are written by the user to compute or perform a task. ●They can be called by the main program repeatedly as per the requirement. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 7. Uses of functions They are very much useful when a block of ● statements has to be written/executed again and again. They are useful when program size are too large ● and complex. It works like top-down modular programming technique to ● solve a problem. They are also used to reduce the difficulties during ● debugging a program. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 8. Uses of functions ●The length of a source program can be reduced by using functions at appropriate places. ●It is easy to locate and isolate a faulty function for further investigations. ●A function can be used by many other programs. Thus C programmer can build their own library. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 9. Top-down modular programming using functions Main program Function A Function B Function C B B 1 1 Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 10. A MULTI-FUNCTION PROGRAM void main() { printline(); printf(“I love my parents !!!”); printline(); } void printline() { int I; for(i=0;i<40;i++) printf(“-”); printf(“n”); } Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 11. ELEMENTS OF USER DEFINED FUNCTION Some similarities between functions and ● variables ●Both functions names and variables are considered as identifiers and therefore they must follow the rules for identifiers ●Like variables, functions have type associated with them ●Like variables, function names and their types must be declared and defined before they are used in program Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, Lecturer B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 12. ELEMENTS OF USER-DEFINED FUNCTION ●In order to make use of user-defined functions, we need to establish three elements that are related to functions. ●Function definition ●Function Call ●Function declaration Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 13. FUNCTION DEFINITION ●The function definition is an independent program module that is specially written or implement the requirements of the function. ●To use this block or function, we need to invoke it at the required place in the program, known as the functions ●The program that calls the function is referred to as the calling program or calling functions Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
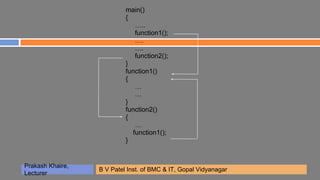
- 14. main() { ….. function1(); …. …. function2(); } function1() { … … } function2() { … function1(); } Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 15. FLOW OF FUNCTION ● When the program is executed (that is, run) execution always begins at the first statement in the function main no matter where it is placed in the program. ● Other functions are executed only when they are called. ● Function prototypes appear before any function definition, so the compiler translates these first. The compiler can then correctly translate a function call. ● A function call statement results in the transfer of control to the first statement in the body of the called function. ● After the last statement of the called function is executed, the control is passed back to the point immediately following the function call. ● A value-returning function returns a value. Therefore, for value-returning functions, after executing the function when the control goes back to the caller, the value that the function returns replaces the function call statement. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 16. FUNCTION DEFINITION A function definition includes the following ● elements ●Function name ●Function type ●List of parameters ●Local variable declarations ●A return statement Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 17. A general format of function definition Function header datatype functionName(parameter list) 1. function type { 2. function name local variable declarations; 3. formal parameter list executable statement1; executable statement2; function body … … return statement returns the value - optional } Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 18. A general format of function definition ●If no return data type is specified than by default ‘C’ will assume that it is an integer type. ●If the function is not going to return any value then we have to specify the return type as void. ●Function name follows the rules of identifier. Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 19. A general format of function definition ●Parameter list are list of variables that will receive the data sent by the calling program. ●int sum(int a, int b) { ………………… } ●float mul(float x, float y) { ………………. } Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 20. Calling a function ●A function is called by the calling program using the function name with the required number of arguments in parenthesis. ●The function call comes in assignment statement or in an output statement. ●printf(“%d”,sum(a,b)); ●ans = sum(a,b); A function is called using its name with required number of ● arguments in paranthesis. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 21. Formal and Actual Arguments int sum(int, int); //declaration //function definition void main() int sum(int x, int y) { int a=5, b=6,ans; { formal arguments int val; ans =sum(a , b);//calling function arguments actual val = x +y; return val; printf(“Answer : %d”,ans); } } The argument listed in the function calling The arguments used in the function declaration are statement are referred to as actual arguments referred as formal arguments Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMC B VIT, Gopalof BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Prakash Khaire, Lecturer & Patel Inst. Vidyanagar Lecturer
- 22. Formal and Actual Arguments ●The argument listed in the ●The agrument used in the function calling statement function declaration are are referred to as actual referred as formal arguments. arguments. ●They are the actual values ●They are simply formal passed to a function to variables that accepts or compute a value or to receive the values supplied perform a task. by the calling program. Prakash Khaire, B VPrakash Khaire, of BMC V PatelGopal BMC & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Patel Inst. B & IT, Inst. of Vidyanagar ● Lecturer Lecturer
- 23. Rules of call a function ●Function is called by the main() or any other function ●When the return type of the function is omitted, then by default the return type will be int. ●A function can return a value any stage of its execution by using more than one return statements. ●The return statement is omitted if it does not return a value directly to the calling program. ●Arguments listed can be omitted, but not the paranthesis () following the function. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 24. Function Declaration or prototype To match the number and data type of the actual and formal ● arguments in the calling and called function respectively. To check this compiler will verify the function declaration or prototype. ● ●data_type function_name(data_type var1, data_type var2,…..,data_type varn); ●Example ● int sum(int, int); The prototype declaration is always written above the main() function ● definition. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer
- 25. Return values and their types ●We can pass n numbers of values to the called function, but the called function can only return one value per call. ●The return statement can take one of the following form ●return; ●return(expression); ●The plain return does not return any value ●return statement with expression returns the value of the expression ●There can be more than one return statement if there is use of conditional statement. Prakash Khaire, Prakash Khaire, B V Patel Inst. of BMCBMCGopal Vidyanagar B V Patel Inst. of & IT, & IT, Gopal Vidyanagar Lecturer Lecturer