MongoDB's index and query optimize
- 2. What is an index?A set of references to your documents, efficiently ordered by key{x:0.5,y:0.5}{x:2,y:0.5}{x:5,y:2}{x:-4,y:10}{x:3,y:’f’}
- 3. What is an index?A set of references to your documents, efficiently ordered by key{x:1}{x:0.5,y:0.5}{x:2,y:0.5}{x:5,y:2}{x:-4,y:10}{x:3,y:’f’}
- 4. What is an index?A set of references to your documents, efficiently ordered by key{y:1}{x:0.5,y:0.5}{x:2,y:0.5}{x:5,y:2}{x:-4,y:10}{x:3,y:’f’}
- 5. How is an index stored?B-tree{x:2}{x:3}3<=x<44<=x<5{x:0.5}2<=x<5{x:5}0<=x<1x>=5x<0{x:-4}{x:1}
- 6. What if I have multiple indices?{c:1}{a:3}{c:2}{c:3}{b:’x’}{d:null}{a:3,b:’x’,c:[1,2,3]}{a:1}{c:1}{b:1}{d:1}
- 7. How does a simple query work?Tree traversal{x:2}{x:3}3<=x<44<=x<5{x:0.5}2<=x<5{x:5}0<=x<1x>=5x<0{x:-4}{x:1}
- 8. Simple document lookup db.c.findOne( {_id:2} ), using index {_id:1}db.c.find( {x:2} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:{$in:[2,3]}} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {‘x.a’:1} ), using index {‘x.a’:1}Matches {_id:1,x:{a:1}}db.c.find( {x:{a:1}} ), using index {x:1}Matches {_id:1,x:{a:1}}, but not {_id:2,x:{a:1,b:2}}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {$where:“this.x == this.y”} ), using index {x:1}?Indices cannot be used for $where type queries, but if there are non-where elements in the query then indices can be used for the non-where elements.
- 9. How does a range query work?Tree traversal + scan: find({x:{$gte:3,$lte:5}}){x:2}{x:3}{x:4}3<=x<44<=x<5{x:0.5}2<=x<5{x:5}0<=x<1{x:6}x>=5x<0{x:-4}{x:1}
- 10. Document range scandb.c.find( {x:{$gt:2}} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:{$gt:2,$lt:5}} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:/^a/} ), using index {x:1}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {x:/a/} ), using index {x:1}?The letter ‘a’ can appear anywhere in a matching string, so lexicographic ordering on strings won’t help. However, we can use the index to find the range of documents where x is string (eg not a number) or x is the regular expression /a/.
- 11. Other operationsdb.c.count( {x:2} ) using index {x:1}db.c.distinct( {x:2} ) using index {x:1}db.c.update( {x:2}, {x:3} ) using index {x:1}db.c.remove( {x:2} ) using index {x:1}QUESTION: What about db.c.update( {x:2}, {$inc:{x:3}} ), using index {x:1}?Older versions of mongoDB didn’t support modifiers on indexed fields, but we now support this.
- 12. Missing fieldsdb.c.find( {x:null} ), using index {x:1}Matches {_id:5}Matches {_id:5,x:null}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {x:{$exists:true}} ), using index {x:1}?The index is not currently used, though we will fix this in MongoDB 1.6.
- 13. Array matchingAll the following match {_id:6,x:[2,10]} and use index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:2} )db.c.find( {x:10} )db.c.find( {x:{$gt:5}} )db.c.find( {x:[2,10]} )db.c.find( {x:{$in:[2,5]}} )QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {x:{$all:[2,10]}} )?The index will be used to look up all documents matching {x:2}.
- 14. What is a compound index?{x:2,y:3}{x:1,y:5}{x:2,y:9}{x:3,y:1}{x:1,y:1}
- 15. How are bounds determined for a compound index?find( {x:{$gte:2,$lte:4},y:6} ){x:3,y:1}{x:2,y:6}{x:3,y:7}{x:3.5,y:6}{x:2,y:3}{x:4,y:6}{x:1,y:5}{x:5,y:6}{x:1,y:1}
- 16. How does an ordered range query work?Simple range scan if index already ensures desired ordering: find( {x:2} ).sort( {y:1} ){x:2,y:3}{x:1,y:5}{x:2,y:9}{x:3,y:1}{x:1,y:1}
- 17. How does an ordered range query work?Otherwise, in-memory sort of matching documents: find( {x:2} ).sort( {y:1} ){x:2,y:3}{x:2,y:9}{x:1,y:5}{x:2,y:3}{x:2,y:9}…{x:3,y:1}{x:1}
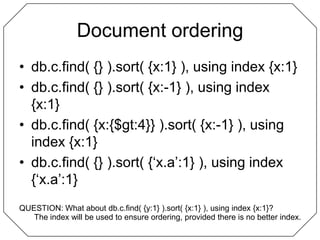
- 18. Document orderingdb.c.find( {} ).sort( {x:1} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {} ).sort( {x:-1} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:{$gt:4}} ).sort( {x:-1} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {} ).sort( {‘x.a’:1} ), using index {‘x.a’:1}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {y:1} ).sort( {x:1} ), using index {x:1}?The index will be used to ensure ordering, provided there is no better index.
- 19. Compound indices and orderingdb.c.find( {x:10,y:20} ), using index {x:1,y:1}db.c.find( {x:10,y:20} ), using index {x:1,y:-1}db.c.find( {x:{$in:[10,20]},y:20} ), using index {x:1,y:1}db.c.find().sort( {x:1,y:1} ), using index {x:1,y:1}db.c.find().sort( {x:-1,y:1} ), using index {x:1,y:-1}db.c.find( {x:10} ).sort( {y:1} ), using index {x:1,y:1}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {y:10} ).sort( {x:1} ), using index {x:1,y:1}?The index will be used to ensure ordering, provided no better index is available.
- 20. What if we negate a query?find({x:{$ne:2}}){x:2}{x:1}{x:2}{x:3}{x:1}
- 21. When indices are less helpfuldb.c.find( {x:{$ne:1}} )db.c.find( {x:{$mod:[10,1]}} )Uses index {x:1} to scan numbers onlydb.c.find( {x:{$not:/a/}} )db.c.find( {x:{$gte:0,$lte:10},y:5} ) using index {x:1,y:1}Currently must scan all elements from {x:0,y:5} to {x:10,y:5}, but some improvements may be possibledb.c.find( {$where:’this.x = 5’} )QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {x:{$not:/^a/}} ), using index {x:1}?The index is not used currently, but will be used in mongoDB 1.6
- 22. How is an index chosen?find( {x:2,y:3} ){x:2,y:1}{y:3,x:1}{x:2,y:3}{x:2,y:9}{y:3,x:2}{y:9,x:2}{x:1,y:3}{y:1,x:2}{x:1}{y:1}√{x:2,y:3}{x:2,y:1}{x:2,y:9}{y:3,x:2}{y:3,x:1}
- 23. Query pattern matchingVery simple algorithm, few complaints so farfind({x:1})find({x:2})find({x:100})find({x:{$gt:4}})find({x:{$gte:6}})find({x:1,y:2})find({x:{$gt:4,$lte:10}})find({x:{$gte:6,$lte:400}})find({x:1}).sort({y:1})
- 24. Query optimizerIn charge of picking which index to use for a query/count/update/delete/etcUsually it does a good job, but if you know what you’re doing you can override itdb.c.find( {x:2,y:3} ).hint( {y:1} )Use index {y:1} and avoid trying {x:1}As your data changes, different indices may be chosen. Ordering requirements should be made explicit using sort().QUESTION: How can you force a full collection scan instead of using indices?db.c.find( {x:2,y:3} ).hint( {$natural:1} ) to bypass indices
- 25. Geospatial indicesdb.c.find( {a:[50,50]} ) using index {a:’2d’}db.c.find( {a:{$near:[50,50]}} ) using index {a:’2d’}Results are sorted closest - farthestdb.c.find( {a:{$within:{$box:[[40,40],[60,60]]}}} ) using index {a:’2d’}db.c.find( {a:{$within:{$center:[[50,50],10]}}} ) using index {a:’2d’}db.c.find( {a:{$near:[50,50]},b:2} ) using index {a:’2d’,b:1}QUESTION: Most queries can be performed with or without an index. Is this true of geospatial queries?No. A geospatial query requires an index.
- 26. How does an insert work?Tree traversal and insert, split if necessary{x:3.5}{x:2}{x:3}{x:4}3<=x<44<=x<5{x:0.5}2<=x<5{x:5}0<=x<1{x:6}x>=5x<0{x:-4}{x:1}
- 27. What if my keys are increasing?You’ll always insert on the right{x:2}{x:3}{x:4}3<=x<44<=x<5{x:0.5}2<=x<5{x:5}0<=x<1{x:6}x>=5x<0{x:7}{x:-4}{x:8}{x:1}{x:9}
- 28. Why is RAM important?RAM is basically used as a LIFO disk cacheWhole index in RAMPortion of index in RAM
- 29. Creating an index{_id:1} index created automaticallyFor non-capped collectionsdb.c.ensureIndex( {x:1} )Can create an index at any time, even when you already have plenty of data in your collectionCreating an index will block mongoDB unless you specify background index creationdb.c.ensureIndex( {x:1}, {background:true} )Background index creation is a still impacts performance – run at non peak times if you’re concernedQUESTION: Can an index be removed during background creation?Not at this time.
- 30. Unique key constraintsdb.c.ensureIndex( {x:1}, {unique:true} )Don’t allow {_id:10,x:2} and {_id:11,x:2}Don’t allow {_id:12} and {_id:13} (both match {x:null}What if duplicates exist before index is created?Normally index creation fails and the index is removeddb.ensureIndex( {x:1}, {unique:true,dropDups:true} )QUESTION: In dropDups mode, which duplicates will be removed?The first document according to the collection’s “natural order” will be preserved.
- 31. Cleaning up an indexdb.system.indices.find( {ns:’db.c’} )db.c.dropIndex( {x:1} )db.c.dropindices()db.c.reIndex()Rebuilds all indices, removing index cruft that has built up over large numbers of updates and deletes. Index cruft will not exist in mongoDB 1.6, so this command will be deprecated.QUESTION: Why would you want to drop an index?See next slide…
- 32. Limits and tradeoffsMax 40 indices per collectionLogically equivalent indices are not prevented (eg {x:1} and {x:-1})indices can improve speed of queries, but make inserts slowerA more specific index {a:1,b:1,c:1} can be more helpful than less specific index {a:1} but the more specific index will be larger, thus harder to fit in RAMQUESTION: Do indices make updates slower? How about deletes?It depends – finding your document might be faster, but if any indexed fields are changed the indices must be updated.
- 33. Mongod log outputquery test.c ntoreturn:1 reslen:69 nscanned:100000 { i: 99999.0 } nreturned:1 157msquery test.$cmd ntoreturn:1 command: { count: "c", query: { type: 0.0, i: { $gt: 99000.0 } }, fields: {} } reslen:64 256msquery:{ query: {}, orderby: { i: 1.0 } } ... query test.c ntoreturn:0 exception 1378ms ... User Exception 10128:too much key data for sort() with no index. add an index or specify a smaller limitquery test.c ntoreturn:0 reslen:4783 nscanned:100501 { query: { type: 500.0 }, orderby: { i: 1.0 } } nreturned:101 390msOccasionally may see a slow operation as a result of disk activity or mongo cleaning things up – some messages about slow ops are spuriousKeep this in mind when running the same op a massive number of times, and it appears slow very rarely
- 34. ProfilingRecord same info as with log messages, but in a database collection> db.system.profile.find(){"ts" : "Thu Jan 29 2009 15:19:32 GMT-0500 (EST)" , "info" : "query test.$cmd ntoreturn:1 reslen:66 nscanned:0 <br>query: { profile: 2 } nreturned:1 bytes:50" , "millis" : 0}...> db.system.profile.find( { info: /test.foo/ } )> db.system.profile.find( { millis : { $gt : 5 } } )> db.system.profile.find().sort({$natural:-1})Enable explicitly using levels (0:off, 1:slow ops (>100ms), 2:all ops)> db.setProfilingLevel(2);{"was" : 0 , "ok" : 1}> db.getProfilingLevel()2> db.setProfilingLevel( 1 , 10 ); // slow means > 10msProfiling impacts performance, but not severely
- 35. Query explain> db.c.find( {x:1000,y:0} ).explain(){ "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "x" : 1000 }, { "x" : 1000 } ] ], "nscanned" : 10, "nscannedObjects" : 10, "n" : 10, "millis" : 0, "oldPlan" : { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "x" : 1000 }, { "x" : 1000 } ] ] }, "allPlans" : [ { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "x" : 1000 }, { "x" : 1000 } ] ] }, { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor y_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "y" : 0 }, { "y" : 0 } ] ] }, { "cursor" : "BasicCursor", "indexBounds" : [ ] } ]}
- 36. Example 1> db.c.findOne( {i:99999} ){ "_id" : ObjectId("4bb962dddfdcf5761c1ec6a3"), "i" : 99999 }query test.c ntoreturn:1 reslen:69 nscanned:100000 { i: 99999.0 } nreturned:1 157ms> db.c.find( {i:99999} ).limit(1).explain(){ "cursor" : "BasicCursor", "indexBounds" : [ ], "nscanned" : 100000, "nscannedObjects" : 100000, "n" : 1, "millis" : 161, "allPlans" : [ { "cursor" : "BasicCursor", "indexBounds" : [ ] } ]}> db.c.ensureIndex( {i:1} );> for( i = 0; i < 100000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {i:i} ); }
- 37. Example 2> db.c.count( {type:0,i:{$gt:99000}} )499query test.$cmd ntoreturn:1 command: { count: "c", query: { type: 0.0, i: { $gt: 99000.0 } }, fields: {} } reslen:64 256ms> db.c.find( {type:0,i:{$gt:99000}} ).limit(1).explain(){ "cursor" : "BtreeCursor type_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "type" : 0 }, { "type" : 0 } ] ], "nscanned" : 49502, "nscannedObjects" : 49502, "n" : 1, "millis" : 349,...> db.c.ensureIndex( {type:1,i:1} );> for( i = 0; i < 100000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {type:i%2,i:i} ); }
- 38. Example 3> db.c.find().sort( {i:1} )error: { "$err" : "too much key data for sort() with no index. add an index or specify a smaller limit"}> db.c.find().sort( {i:1} ).explain()JS Error: uncaught exception: error: { "$err" : "too much key data for sort() with no index. add an index or specify a smaller limit"}> db.c.ensureIndex( {i:1} );> db.c.find().sort( {i:1} ).limit( 1000 ); //alternatively> for( i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {i:i} ); }
- 39. Example 4> db.c.find( {type:500} ).sort( {i:1} ){ "_id" : ObjectId("4bba4904dfdcf5761c2f917e"), "i" : 500, "type" : 500 }{ "_id" : ObjectId("4bba4904dfdcf5761c2f9566"), "i" : 1500, "type" : 500 }...query test.c ntoreturn:0 reslen:4783 nscanned:100501 { query: { type: 500.0 }, orderby: { i: 1.0 } } nreturned:101 390ms> db.c.find( {type:500} ).sort( {i:1} ).explain(){ "cursor" : "BtreeCursor i_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "i" : { "$minElement" : 1 } }, { "i" : { "$maxElement" : 1 } } ] ], "nscanned" : 1000000, "nscannedObjects" : 1000000, "n" : 1000, "millis" : 5388,...> db.c.ensureIndex( {type:1,i:1} );> for( i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {i:i,type:i%1000} ); }
- 40. Questions?Get involved www.mongodb.orgDownloads, user group, chat roomFollow @mongodbUpcoming events www.mongodb.org/display/DOCS/EventsSF MongoDB office hours Mondays 4-6pm at Epicenter CaféSF MongoDBmeetupMay 17 at Engine YardCommercial support [email protected]





![What if I have multiple indices?{c:1}{a:3}{c:2}{c:3}{b:’x’}{d:null}{a:3,b:’x’,c:[1,2,3]}{a:1}{c:1}{b:1}{d:1}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-6-320.jpg)

![Simple document lookup db.c.findOne( {_id:2} ), using index {_id:1}db.c.find( {x:2} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:{$in:[2,3]}} ), using index {x:1}db.c.find( {‘x.a’:1} ), using index {‘x.a’:1}Matches {_id:1,x:{a:1}}db.c.find( {x:{a:1}} ), using index {x:1}Matches {_id:1,x:{a:1}}, but not {_id:2,x:{a:1,b:2}}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {$where:“this.x == this.y”} ), using index {x:1}?Indices cannot be used for $where type queries, but if there are non-where elements in the query then indices can be used for the non-where elements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-8-320.jpg)




![Array matchingAll the following match {_id:6,x:[2,10]} and use index {x:1}db.c.find( {x:2} )db.c.find( {x:10} )db.c.find( {x:{$gt:5}} )db.c.find( {x:[2,10]} )db.c.find( {x:{$in:[2,5]}} )QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {x:{$all:[2,10]}} )?The index will be used to look up all documents matching {x:2}.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-13-320.jpg)




![Compound indices and orderingdb.c.find( {x:10,y:20} ), using index {x:1,y:1}db.c.find( {x:10,y:20} ), using index {x:1,y:-1}db.c.find( {x:{$in:[10,20]},y:20} ), using index {x:1,y:1}db.c.find().sort( {x:1,y:1} ), using index {x:1,y:1}db.c.find().sort( {x:-1,y:1} ), using index {x:1,y:-1}db.c.find( {x:10} ).sort( {y:1} ), using index {x:1,y:1}QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {y:10} ).sort( {x:1} ), using index {x:1,y:1}?The index will be used to ensure ordering, provided no better index is available.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-19-320.jpg)

![When indices are less helpfuldb.c.find( {x:{$ne:1}} )db.c.find( {x:{$mod:[10,1]}} )Uses index {x:1} to scan numbers onlydb.c.find( {x:{$not:/a/}} )db.c.find( {x:{$gte:0,$lte:10},y:5} ) using index {x:1,y:1}Currently must scan all elements from {x:0,y:5} to {x:10,y:5}, but some improvements may be possibledb.c.find( {$where:’this.x = 5’} )QUESTION: What about db.c.find( {x:{$not:/^a/}} ), using index {x:1}?The index is not used currently, but will be used in mongoDB 1.6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-21-320.jpg)



![Geospatial indicesdb.c.find( {a:[50,50]} ) using index {a:’2d’}db.c.find( {a:{$near:[50,50]}} ) using index {a:’2d’}Results are sorted closest - farthestdb.c.find( {a:{$within:{$box:[[40,40],[60,60]]}}} ) using index {a:’2d’}db.c.find( {a:{$within:{$center:[[50,50],10]}}} ) using index {a:’2d’}db.c.find( {a:{$near:[50,50]},b:2} ) using index {a:’2d’,b:1}QUESTION: Most queries can be performed with or without an index. Is this true of geospatial queries?No. A geospatial query requires an index.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-25-320.jpg)








![Query explain> db.c.find( {x:1000,y:0} ).explain(){ "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "x" : 1000 }, { "x" : 1000 } ] ], "nscanned" : 10, "nscannedObjects" : 10, "n" : 10, "millis" : 0, "oldPlan" : { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "x" : 1000 }, { "x" : 1000 } ] ] }, "allPlans" : [ { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "x" : 1000 }, { "x" : 1000 } ] ] }, { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor y_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "y" : 0 }, { "y" : 0 } ] ] }, { "cursor" : "BasicCursor", "indexBounds" : [ ] } ]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-35-320.jpg)
![Example 1> db.c.findOne( {i:99999} ){ "_id" : ObjectId("4bb962dddfdcf5761c1ec6a3"), "i" : 99999 }query test.c ntoreturn:1 reslen:69 nscanned:100000 { i: 99999.0 } nreturned:1 157ms> db.c.find( {i:99999} ).limit(1).explain(){ "cursor" : "BasicCursor", "indexBounds" : [ ], "nscanned" : 100000, "nscannedObjects" : 100000, "n" : 1, "millis" : 161, "allPlans" : [ { "cursor" : "BasicCursor", "indexBounds" : [ ] } ]}> db.c.ensureIndex( {i:1} );> for( i = 0; i < 100000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {i:i} ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-36-320.jpg)
![Example 2> db.c.count( {type:0,i:{$gt:99000}} )499query test.$cmd ntoreturn:1 command: { count: "c", query: { type: 0.0, i: { $gt: 99000.0 } }, fields: {} } reslen:64 256ms> db.c.find( {type:0,i:{$gt:99000}} ).limit(1).explain(){ "cursor" : "BtreeCursor type_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "type" : 0 }, { "type" : 0 } ] ], "nscanned" : 49502, "nscannedObjects" : 49502, "n" : 1, "millis" : 349,...> db.c.ensureIndex( {type:1,i:1} );> for( i = 0; i < 100000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {type:i%2,i:i} ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-37-320.jpg)

![Example 4> db.c.find( {type:500} ).sort( {i:1} ){ "_id" : ObjectId("4bba4904dfdcf5761c2f917e"), "i" : 500, "type" : 500 }{ "_id" : ObjectId("4bba4904dfdcf5761c2f9566"), "i" : 1500, "type" : 500 }...query test.c ntoreturn:0 reslen:4783 nscanned:100501 { query: { type: 500.0 }, orderby: { i: 1.0 } } nreturned:101 390ms> db.c.find( {type:500} ).sort( {i:1} ).explain(){ "cursor" : "BtreeCursor i_1", "indexBounds" : [ [ { "i" : { "$minElement" : 1 } }, { "i" : { "$maxElement" : 1 } } ] ], "nscanned" : 1000000, "nscannedObjects" : 1000000, "n" : 1000, "millis" : 5388,...> db.c.ensureIndex( {type:1,i:1} );> for( i = 0; i < 1000000; ++i ) { db.c.save( {i:i,type:i%1000} ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbsindexandqueryoptimize-110916002139-phpapp02/85/MongoDB-s-index-and-query-optimize-39-320.jpg)
