Notes DATA STRUCTURE - queue
- 1. QUEUE
- 2. Course Objectives At the end of the lesson students are expected to be able to: • Understand queue concepts and applications. • Understand queue structure and operations that can be done on queue. • Understand and know how to implement queue using array and linked list : linear array, circular array, linear link list and circular list.
- 3. 1.0 Introduction to Queue
- 4. Introduction to Queue • New items enter at the back, or rear, of the queue • Items leave from the front of the queue • First-in, first-out (FIFO) property – The first item inserted into a queue is the first item to leave – Middle elements are logically inaccessible
- 5. Introduction to Queue • Important in simulation & analyzing the behavior of complex systems
- 6. Queue Applications • Real-World Applications – Cashier lines in any store – Check out at a bookstore – Bank / ATM – Call an airline
- 7. Queue Applications • Computer Science Applications – Print lines of a document – Printer sharing between computers – Recognizing palindromes – Shared resource usage (CPU, memory access, …)
- 8. Queue Applications • Simulation – A study to see how to reduce the wait involved in an application
- 9. Queue implementation Remove/ Add/ A B C Enqueue Dequeue Front/Head Back/Rear Basic Structure of a Queue: •Data structure that hold the queue •head •rear
- 10. Queue implementation Add/ A B C D Enqueue Head Rear Insert D into Queue (enQueue) : D is inserted at rear Remove/ Dequeue A B C D Head Rear Delete from Queue (deQueue) : A is removed
- 11. Queue operations • Queue operations – Create an empty queue – Destroy a queue – Determine whether a queue is full – Add a new item to the queue (enQueue) – Determine whether a queue is empty – Remove the item that was added earliest(deQueue) – Retrieve at Front(getFront) – Retrieve at Back the item that was added earliest(getRear)
- 12. Queue Implementation Implementation: – Array-based (Linear or Circular) – Pointer-based : Link list (Linear or Circular)
- 13. 2.0 Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear)
- 14. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) • Number of elements in Queue are fixed during declaration. • Need isFull() operation to determine whether a queue is full or not.
- 15. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) • Queue structure need at least 3 elements: 1) Element to store items in Queue 2) Element to store index at head 3) Element to store index at rear
- 16. Create Queue Operation • Declare – front & back are indexes in the array – Initial condition: front =0 & back = -1 – Size of an array in queue Queue 0 0 1 2 3 Max size -1 front back
- 17. Create Queue operation Example Code 1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; #define max 5 int front = 0, back = -1; Create Queue char item[max], newitem; item 0 0 1 2 3 4 -1 front back Front refer to index 0 Continue…
- 18. enQueue operation void enQueue(){ cout<<"nt#################n"; cout<<"nt1. enQueuen"; //check queue is full if(back == max - 1){ cout<<"ntQueue Is Full, Cannot Add Item In Queuen"; }else{ cout<<"nttEnter Item:"; cin>>newitem; back++; item[back]=newitem; cout<<endl; enQueue } } item back++ 0 0 1 2 3 4 0 front A back back = -1+1 back = 0 Front refer to index 0 From back/rear item[back] = newitem Continue…
- 19. enQueue operation item back++ 0 0 1 2 3 4 1 front A B back back = 0 +1 back = 1 Front refer to index 0 From back/rear item[back] = newitem item back++ 0 0 1 2 3 4 2 front A B C back back = 1 +1 Front refer to index 0 back = 2 From back/rear item[back] = newitem Continue…
- 20. enQueue operation item back++ 0 0 1 2 3 4 3 front A B C D back back = 2 +1 back = 3 Front refer to index 0 From back/rear item[back] = newitem item back++ 0 0 1 2 3 4 4 front A B C D E back back = 3 +1 back = 4 Front refer to index 0 From back/rear item[back] = newitem Continue…
- 21. deQueue operation void deQueue(){ cout<<"nt#################n"; cout<<"nt2.deQueuen"; if(back < front){ cout<<"ntThere is no data to remove from queuen"; }else{ char itemdeleted; itemdeleted=item[front]; deQueue item[front] = NULL; cout<<"ntItem Remove From Queue:"<<itemdeleted<<endl; front++; } cout<<endl; item } 0 0 1 2 3 4 4 front A B C D E back back = 3 + 1 itemdeleted = item[front] Front refer to index 0 back = 4 front = 0 From front/head item[front] = NULL Continue…
- 22. deQueue operation front++ item 1 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL B C D E back front = 0 + back = 3 + 1 1 back = 4 front = 1 Front refer to index 1 item 1 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL B C D E back back = 3 + 1 Front refer to index 1 back = 4 itemdeleted = item[front] From front/head front = 1 item[front] = NULL front++ item 2 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL C D E back front = 1 + back = 3 + 1 1 back = 4 front = 2 Front refer to index 2 Continue…
- 23. deQueue operation item 2 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL C D E back back = 3 + 1 Front refer to index 2 back = 4 From front/head itemdeleted = item[front] item[front] = NULL front = 2 front++ item 3 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL NULL D E back front = 2 + back = 3 + 1 1 back = 4 front = 3 Front refer to index 3 Continue…
- 24. deQueue operation item 3 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL NULL D E back back = 3 + 1 Front refer to index 3 back = 4 itemdeleted = item[front] From front/head front = 3 item[front] = NULL front++ item 4 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL NULL NULL E back front = 3 + back = 3 + 1 1 back = 4 front = 4 Front refer to index 4 Continue…
- 25. deQueue operation item 4 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL NULL NULL E back back = 3 + 1 Front refer to index 4 back = 4 itemdeleted = item[front] From front/head front = 4 item[front] = NULL front++ item 5 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL back front = 4 + back = 3 + 1 1 back = 4 front = 5 Continue…
- 26. Retrieve at front(getFront) operation void getFront(){ cout<<"nt#################n"; cout<<"nt3.getFrontn"; if(back < front){ cout<<"ntThere is no data to at frontn"; }else{ cout<<"ntItem At Front:"<<item[front]<<endl; } } Continue…
- 27. Retrieve at back(getRear) operation void getRear(){ cout<<"nt#################n"; cout<<"nt4.getRearn"; if(back < front){ cout<<"ntThere is no data to at rearn"; }else{ cout<<"ntItem At Rear:"<<item[back]<<endl; } } Continue…
- 28. destroyQueue operation void destroyQueue(){ delete [] item; } Continue…
- 29. displayQueue operation void displayQueue(){ cout<<"ntDisplay Item In Queuen"; if(back < front){ cout<<"ntThere is no data in queue to be displayedn"; }else{ cout<<"t"; for(int i=0; i < max; i++ ){ cout<<"t"<<item[i]; } cout<<endl; } } Continue…
- 30. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) int main() { int selection; menu: cout<<"nPlease Choose Your Selectionn"; cout<<"n1tenQueuen"; cout<<"n2tdeQueuen"; cout<<"n3tGetFrontn"; cout<<"n4tGetRearn"; cout<<"n5tDestroyQueuen"; cout<<"n6tDisplayn"; cout<<"ntSelection is:"; cin>>selection; Continue…
- 31. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) switch(selection){ case 1: enQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 2: deQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 3: getFront(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; Continue…
- 32. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) case 4: getRear(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 5: destroyQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 6: displayQueue(); goto menu; break; default:cout<<"ntWrong Selectionn"; } return 0; }
- 33. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) • Problem: Rightward-Drifting: • After a sequence of additions & removals, items will drift towards the end of the array • enQueue operation cannot be performed on the queue below, since back = max – 1. front++ item 5 0 1 2 3 4 4 front NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL back front = 4 + back = 3 + 1 1 back = 4 front = 5
- 34. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) • Rightward drifting solutions – Shift array elements after each deletion • Shifting dominates the cost of the implementation
- 35. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) – Use a circular array: When Front or Back reach the end of the array, wrap them around to the beginning of the array • Problem: – Front & Back can't be used to distinguish between queue-full & queue- empty conditions
- 36. Queue Implementation Using Array(Linear) • Solution: – Use a counter – Count == 0 means empty queue – Count == MAX_QUEUE means full queue
- 37. 3.0 Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
- 38. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) • Number of elements in Queue are fixed during declaration. • Need isFull() operation to determine whether a queue is full or not.
- 39. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) • Queue structure need at least 3 elements: 1) Element to store items in Queue 2) Element to store index at head 3) Element to store index at rear 4) Element to store index in counter
- 40. Create Queue Operation • Declare – front & back are indexes in the array – count to store index – Initial condition: front =0 , back = -1, count = 0 – Size of an array in queue
- 41. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) – The Wrap-around effect is obtained by using modulo arithmetic (%-operator) front = 0 7 0 6 1 5 2 4 3 back = -1 count = 0
- 42. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) – enQueue • Increment back, using modulo arithmetic • Insert item • Increment count – deQueue • Increment front using modulo arithmetic • Decrement count – Disadvantage • Overhead of maintaining a counter or flag
- 43. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) Example Code 2: queue #include <iostream> front = 0 using namespace std; 7 0 6 1 #define max 8 char queue[max], newitem; 5 2 int front = 0, back = -1, count = 0; 4 3 back = -1 count = 0 Continue…
- 44. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) void enQueue(){ cout<<"nt#### enQueue Circular ####n"; if(count == max){ cout<<"ntQueue Circular Is Full!!!n"; }else{ cout<<"ntfront:"<<front<<"t"<<"back:"<<back<<"tcount:"<<count<<“tmax:”<<max<<"n"; cout<<"ntEnter Item:"; front = 0 7 0 back = 0 cin>>newitem; A back = (back + 1)% max; 6 1 back = (-1 + 1) % 8 back = 0 % 8 queue[back] = newitem; back = 0 5 2 count++; 0 queue[0] = A 8√ 0 4 3 } } count = 0 + 1 0 count = 1 count = 1 0 Continue…
- 45. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 0, count = 1 queue front = 0 7 0 A back = 1 6 1 back = (0 + 1) % 8 B back = 1 % 8 back = 1 5 2 0 queue[1] = B 8√ 1 4 3 count = 1 + 1 0 count = 2 1 count = 2 Continue…
- 46. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 1, count = 2 queue front = 0 7 0 A 6 1 back = (1 + 1) % 8 B back = 2 % 8 C back = 2 5 2 back = 2 0 queue[2] = C 8√ 2 4 3 count = 2 + 1 0 count = 3 2 count = 3 Continue…
- 47. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 2, count = 3 queue front = 0 7 0 A 6 1 back = (2 + 1) % 8 B back = 3 % 8 back = 3 C 5 2 0 queue[3] = D D 8√ 3 4 3 count = 3 + 1 0 count = 4 3 count = 4 back = 3 Continue…
- 48. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 3, count = 4 queue front = 0 7 0 A 6 1 back = (3 + 1) % 8 B back = 4 % 8 back = 4 C 5 2 0 queue[4] = E E D 8√ 4 4 3 count = 4 + 1 0 count = 5 4 count = 5 back = 4 Continue…
- 49. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 4, count = 5 queue front = 0 7 0 A 6 1 back = (4 + 1) % 8 B back = 5 % 8 back = 5 F C 5 2 0 queue[5] = F E D 8√ 5 back = 5 4 3 count = 5 + 1 0 count = 6 5 count = 6 Continue…
- 50. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 5, count = 6 queue front = 0 back = 6 7 0 A 6 1 back = (5 + 1) % 8 G B back = 6 % 8 back = 6 F C 5 2 0 queue[6] = G E D 8√ 6 4 3 count = 6 + 1 0 count = 7 6 count = 7 Continue…
- 51. enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 0, back = 6, count = 7 queue back = 7 front = 0 7 0 H A 6 1 back = (6 + 1) % 8 G B back = 7 % 8 back = 7 F C 5 2 0 queue[7] = H E D 8√ 7 4 3 count = 7 + 1 0 count = 8 7 count = 8 Continue…
- 52. deQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) void deQueue(){ cout<<"nt#### deQueue Circular ####n"; if(count == 0){ cout<<"ntQueue Circular Is Empty, No Data To Be Deleted!!!n"; }else{ queue back = 7 queue[front] = NULL; 7 0 front=(front + 1) % max; H front = 1 6 1 count--; queue[0] = NULL G B front = (0 + 1) % 8 front = 1 % 8 F C } 5 2 0 front = 1 E D } 8√ 1 4 3 count = 8 - 1 0 count = 7 1 count = 7 Continue…
- 53. deQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular) From previous slide: front = 1, back = 7 , count = 7 queue back = 7 7 0 H 6 1 queue[1] = NULL G front = (1 + 1) % 8 front = 2% 8 F C 5 2 0 front = 2 E D front = 2 8√ 2 4 3 count = 7 - 1 0 count = 6 2 count = 6 Continue…
- 54. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) void displayQueue(){ cout<<"nt#### Display Queue Circular ####n"; cout<<"ntfront:"<<front<<"t"<<"back:"<<back<<"tcount:"<<count<<“tmax:”<<max<<"n"; if(count == 0){ cout<<"ntQueue Circular Is Empty, No Data To Be Displayn"; }else{ cout<<"ntItem In Queue Circularn"; for(int i = 0; i < max; i++){ cout<<"t"<<queue[i]; } } } Continue…
- 55. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) int main(){ int selection; menu: cout<<"nnPlease Choose Your Selectionn"; cout<<"n1tenQueue Circularn"; cout<<"n2tdeQueue Circularn"; cout<<"n3tDisplay Queuen"; cout<<"ntSelection is:"; cin>>selection; Continue…
- 56. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) switch(selection){ case 1: enQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 2: deQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 3: displayQueue(); goto menu; break; Continue…
- 57. Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular) default:cout<<"ntWrong Selectionn"; } return 0; }
- 58. 4.0 Queue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear)
- 59. Queue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) Pointer-Based Implementation • More straightforward than array-based • Need Two external pointer (Front & Back) which front to trace deQueue operation and back to trace deQueue operation.
- 60. Create Queue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) Example Code 1: #include <iostream> using namespace std; struct nodeQueue{ char name; int age; name age next nodeQueue *next; Compiler get the initial illustrated structure of node }; Continue…
- 61. Create Queue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) nodeQueue *back_ptr = NULL; NULL nodeQueue *front_ptr=NULL; back_ptr NULL front_ptr Continue…
- 62. enQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) void enQueue(){ 0110 //create new node 0110 Ali 29 NULL nodeQueue *newnode; newnode newnode = new nodeQueue; cout<<"nt####enQueue####n"; //assign data field for name and age cout<<"Enter Name:"; cin>>newnode->name; cout<<"Enter Age:"; cin>>newnode->age; newnode->next = NULL; Continue…
- 63. enQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) //insert newnode into queue Insertion to an empty queue //check whether queue is empty if((front_ptr == NULL) && (back_ptr == NULL)){ 0110 front_ptr = newnode; 0110 Ali 29 NULL back_ptr = newnode; newnode name age next }else{ 0110 0110 back_ptr->next = newnode; front_ptr back_ptr back_ptr = newnode; } Continue…
- 64. enQueue Implementation Using Linked Insertion to a non empty queue List(Linear) 0111 0111 Tina 30 NULL newnode name age next 0110 0110 Ali 29 NULL 0110 front_ptr back_ptr name age next back_ptr->next = newnode; back_ptr=newnode; Continue…
- 65. enQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) Insertion to a non empty queue 0110 0111 0110 Ali 29 0111 Tina 30 NULL 0111 front_ptr back_ptr name age next name age next Continue…
- 66. deQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) Continue…
- 67. void deQueue(){ cout<<"nt####deQueue####n"; //check whether queue is empty if((front_ptr == NULL) && (back_ptr == NULL)){ cout<<"ntQueue Is Empty!!!n"; }else{ nodeQueue *temp; temp = front_ptr; if(front_ptr->next == NULL){ front_ptr = NULL; back_ptr = NULL; If the queue contains one item only delete temp; }else{ front_ptr = front_ptr->next; delete temp; } } } Continue…
- 68. deQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) If the queue contains one item only to be deleted nodeQueue *temp; temp = front_ptr; 0110 0110 Ali 29 NULL 0110 front_ptr back_ptr name age next 0110 if(front_ptr->next == NULL){ temp front_ptr = NULL; NULL NULL back_ptr = NULL; front_ptr back_ptr delete temp; }else{ …} Continue…
- 69. deQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) If the queue contains more than one item nodeQueue *temp; temp = front_ptr; 0110 0111 0110 Ali 29 0111 Tina 30 NULL 0111 front_ptr name age next name age next back_ptr 0110 temp Continue…
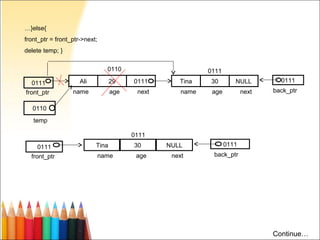
- 70. …}else{ front_ptr = front_ptr->next; delete temp; } 0110 0111 0111 Ali 29 0111 Tina 30 NULL 0111 front_ptr name age next name age next back_ptr 0110 temp 0111 0111 Tina 30 NULL 0111 front_ptr name age next back_ptr Continue…
- 71. displayQueue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) void displayQueue(){ cout<<"nt####Display Queue####n"; if((front_ptr == NULL) && (back_ptr == NULL)){ cout<<"ntQueue Is Empty!!!n"; cout<<"ntfront_ptr :"<<front_ptr<<"tback_ptr :"<<back_ptr<<endl; }else{ nodeQueue *cursor; cursor=front_ptr; cout<<"ntThe Elements In Queue Aren"; cout<<"ntfront_ptr :"<<front_ptr<<"tback_ptr :"<<back_ptr<<endl; int node=1; while(cursor){ cout<<"ntNode :"<<node++<<"tName :"<<cursor->name<<"tAge :"<<cursor- >age<<"tcursor-next:"<<cursor->next<<endl; cursor=cursor->next; } } Continue…
- 72. Queue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) int main() { int selection; menu: cout<<"nnMenu Selectionn"; cout<<"n1tenQueuen"; cout<<"n2tdeQueuen"; cout<<"n3tDisplay Queuen"; cout<<"ntSelection is:"; cin>>selection; Continue…
- 73. Queue Implementation Using Linked List(Linear) switch(selection){ case 1: enQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 2: deQueue(); displayQueue(); goto menu; break; case 3: displayQueue(); goto menu; break; default:cout<<"ntWrong Selectionn"; } return 0; } Continue…

















![Create Queue operation
Example Code 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define max 5
int front = 0, back = -1;
Create Queue
char item[max], newitem;
item
0 0 1 2 3 4 -1
front back
Front refer to index 0
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-17-320.jpg)
![enQueue operation
void enQueue(){
cout<<"nt#################n";
cout<<"nt1. enQueuen";
//check queue is full
if(back == max - 1){
cout<<"ntQueue Is Full, Cannot Add Item In Queuen";
}else{
cout<<"nttEnter Item:";
cin>>newitem;
back++;
item[back]=newitem;
cout<<endl; enQueue
}
} item back++
0 0 1 2 3 4 0
front A back
back = -1+1
back = 0
Front refer to index 0 From back/rear
item[back] = newitem
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-18-320.jpg)
![enQueue operation
item back++
0 0 1 2 3 4 1
front A B back
back = 0 +1
back = 1
Front refer to index 0 From back/rear
item[back] = newitem
item back++
0 0 1 2 3 4 2
front A B C back
back = 1 +1
Front refer to index 0 back = 2
From back/rear
item[back] = newitem
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-19-320.jpg)
![enQueue operation
item back++
0 0 1 2 3 4 3
front A B C D back
back = 2 +1
back = 3
Front refer to index 0
From back/rear
item[back] = newitem
item back++
0 0 1 2 3 4 4
front A B C D E back
back = 3 +1
back = 4
Front refer to index 0
From back/rear
item[back] = newitem
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-20-320.jpg)
![deQueue operation
void deQueue(){
cout<<"nt#################n";
cout<<"nt2.deQueuen";
if(back < front){
cout<<"ntThere is no data to remove from queuen";
}else{
char itemdeleted;
itemdeleted=item[front]; deQueue
item[front] = NULL;
cout<<"ntItem Remove From Queue:"<<itemdeleted<<endl;
front++;
}
cout<<endl; item
} 0 0 1 2 3 4 4
front A B C D E back
back = 3 + 1
itemdeleted = item[front] Front refer to index 0 back = 4
front = 0
From front/head
item[front] = NULL Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-21-320.jpg)
![deQueue operation
front++ item
1 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL B C D E back
front = 0 + back = 3 + 1
1 back = 4
front = 1
Front refer to index 1
item
1 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL B C D E back
back = 3 + 1
Front refer to index 1 back = 4
itemdeleted = item[front]
From front/head
front = 1
item[front] = NULL
front++ item
2 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL C D E back
front = 1 + back = 3 + 1
1 back = 4
front = 2
Front refer to index 2 Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-22-320.jpg)
![deQueue operation
item
2 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL C D E back
back = 3 + 1
Front refer to index 2 back = 4
From front/head
itemdeleted = item[front] item[front] = NULL
front = 2
front++ item
3 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL NULL D E back
front = 2 + back = 3 + 1
1 back = 4
front = 3
Front refer to index 3
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-23-320.jpg)
![deQueue operation
item
3 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL NULL D E back
back = 3 + 1
Front refer to index 3 back = 4
itemdeleted = item[front] From front/head
front = 3 item[front] = NULL
front++ item
4 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL NULL NULL E back
front = 3 + back = 3 + 1
1 back = 4
front = 4
Front refer to index 4
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-24-320.jpg)
![deQueue operation
item
4 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL NULL NULL E back
back = 3 + 1
Front refer to index 4 back = 4
itemdeleted = item[front] From front/head
front = 4 item[front] = NULL
front++ item
5 0 1 2 3 4 4
front NULL NULL NULL NULL NULL back
front = 4 + back = 3 + 1
1 back = 4
front = 5
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-25-320.jpg)
![Retrieve at front(getFront) operation
void getFront(){
cout<<"nt#################n";
cout<<"nt3.getFrontn";
if(back < front){
cout<<"ntThere is no data to at frontn";
}else{
cout<<"ntItem At Front:"<<item[front]<<endl;
}
}
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-26-320.jpg)
![Retrieve at back(getRear) operation
void getRear(){
cout<<"nt#################n";
cout<<"nt4.getRearn";
if(back < front){
cout<<"ntThere is no data to at rearn";
}else{
cout<<"ntItem At Rear:"<<item[back]<<endl;
}
}
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-27-320.jpg)
![destroyQueue operation
void destroyQueue(){
delete [] item;
}
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-28-320.jpg)
![displayQueue operation
void displayQueue(){
cout<<"ntDisplay Item In Queuen";
if(back < front){
cout<<"ntThere is no data in queue to be displayedn";
}else{
cout<<"t";
for(int i=0; i < max; i++ ){
cout<<"t"<<item[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-29-320.jpg)













![Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
Example Code 2:
queue
#include <iostream> front = 0
using namespace std; 7 0
6 1
#define max 8
char queue[max], newitem;
5 2
int front = 0, back = -1, count = 0;
4 3
back = -1 count = 0
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-43-320.jpg)
![Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
void enQueue(){
cout<<"nt#### enQueue Circular ####n";
if(count == max){
cout<<"ntQueue Circular Is Full!!!n";
}else{
cout<<"ntfront:"<<front<<"t"<<"back:"<<back<<"tcount:"<<count<<“tmax:”<<max<<"n";
cout<<"ntEnter Item:"; front = 0
7 0 back = 0
cin>>newitem;
A
back = (back + 1)% max; 6 1
back = (-1 + 1) % 8
back = 0 % 8
queue[back] = newitem;
back = 0 5 2
count++; 0 queue[0] = A
8√ 0 4 3
} } count = 0 + 1
0 count = 1
count = 1
0 Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-44-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 0, count = 1 queue
front = 0
7 0
A back = 1
6 1
back = (0 + 1) % 8 B
back = 1 % 8
back = 1 5 2
0 queue[1] = B
8√ 1 4 3
count = 1 + 1
0 count = 2
1 count = 2
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-45-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 1, count = 2
queue front = 0
7 0
A
6 1
back = (1 + 1) % 8 B
back = 2 % 8
C
back = 2 5 2 back = 2
0 queue[2] = C
8√ 2 4 3
count = 2 + 1
0 count = 3
2 count = 3
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-46-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 2, count = 3
queue
front = 0
7 0
A
6 1
back = (2 + 1) % 8 B
back = 3 % 8
back = 3 C
5 2
0 queue[3] = D D
8√ 3 4 3
count = 3 + 1
0 count = 4
3 count = 4 back = 3
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-47-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 3, count = 4
queue
front = 0
7 0
A
6 1
back = (3 + 1) % 8 B
back = 4 % 8
back = 4 C
5 2
0 queue[4] = E E D
8√ 4 4 3
count = 4 + 1
0 count = 5
4 count = 5 back = 4
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-48-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 4, count = 5
queue
front = 0
7 0
A
6 1
back = (4 + 1) % 8 B
back = 5 % 8
back = 5 F C
5 2
0 queue[5] = F E D
8√ 5 back = 5 4 3
count = 5 + 1
0 count = 6
5 count = 6
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-49-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 5, count = 6
queue
front = 0
back = 6 7 0
A
6 1
back = (5 + 1) % 8 G B
back = 6 % 8
back = 6 F C
5 2
0 queue[6] = G E D
8√ 6 4 3
count = 6 + 1
0 count = 7
6 count = 7
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-50-320.jpg)
![enQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 0, back = 6, count = 7
queue
back = 7 front = 0
7 0
H A
6 1
back = (6 + 1) % 8 G B
back = 7 % 8
back = 7 F C
5 2
0 queue[7] = H E D
8√ 7 4 3
count = 7 + 1
0 count = 8
7 count = 8
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-51-320.jpg)
![deQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
void deQueue(){
cout<<"nt#### deQueue Circular ####n";
if(count == 0){
cout<<"ntQueue Circular Is Empty, No Data To Be Deleted!!!n";
}else{ queue
back = 7
queue[front] = NULL;
7 0
front=(front + 1) % max; H front = 1
6 1
count--; queue[0] = NULL G B
front = (0 + 1) % 8
front = 1 % 8 F C
} 5 2
0 front = 1 E D
} 8√ 1 4 3
count = 8 - 1
0 count = 7
1 count = 7
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-52-320.jpg)
![deQueue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
From previous slide: front = 1, back = 7 , count = 7
queue
back = 7
7 0
H
6 1
queue[1] = NULL G
front = (1 + 1) % 8
front = 2% 8 F C
5 2
0 front = 2 E D front = 2
8√ 2 4 3
count = 7 - 1
0 count = 6
2 count = 6
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-53-320.jpg)
![Queue Implementation Using Array(Circular)
void displayQueue(){
cout<<"nt#### Display Queue Circular ####n";
cout<<"ntfront:"<<front<<"t"<<"back:"<<back<<"tcount:"<<count<<“tmax:”<<max<<"n";
if(count == 0){
cout<<"ntQueue Circular Is Empty, No Data To Be Displayn";
}else{
cout<<"ntItem In Queue Circularn";
for(int i = 0; i < max; i++){
cout<<"t"<<queue[i];
}
}
}
Continue…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-fp305-12queue-121217190516-phpapp01/85/Notes-DATA-STRUCTURE-queue-54-320.jpg)