Operators in Python Arithmetic Operators
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes524 views
The document details various types of operators in Python, categorizing them into arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, bitwise, boolean, membership, and identity operators. It explains their functions with examples, operator precedence, and the use of comments for better code readability. Additionally, the document covers basic input and output operations necessary for data processing.
1 of 12
Downloaded 13 times

![Arithmetic Operators
• These operators perform basic arithmetic operations like addition,
subtraction, multiplication, division etc. and these operators are
binary operators that means these operators acts on two operands.
And there are 7 binary arithmetic operators available in Python.
Operator Meaning Example Result
+ Addition 10 + 7 12
- Subtraction 10.0 - 1.5 8.5
* Multiplication 30 * 3 900
/ Float Division 5 / 2 2.5
// Integer Division 5 // 2 2
** Exponentiation 3 ** 2 9
% Remainder 10 % 3 1
Operator Priority
Parenthesis (( ), [ ]) First
Exponentiation (**) Second
Multiplication (*), Division (/, //), Modulus (%) Third
Addition (+), Subtraction (-) Fourth
Assignment Fifth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinpython-240511093649-fe31fe50/85/Operators-in-Python-Arithmetic-Operators-2-320.jpg)









Ad
Recommended
Input output statement in C
Input output statement in CMuthuganesh S The document discusses input/output functions in C programming. It describes the scanf() function for input, which reads data from variables using format specifiers in a control string. It also describes printf() for output, which prints values to the screen using format specifiers. Additional functions getchar() and putchar() are discussed for reading and writing single characters respectively.
Type checking
Type checkingrawan_z Type checking involves assigning type expressions to each part of a program according to a type system's logical rules. This allows compilers to determine if a program's types conform or catch errors. Type checking can take the form of type synthesis, which builds up an expression's type from its parts, or type inference, which determines a construct's type from its use. Resolving names is also important for type checking.
Identification test for animal and plant poison
Identification test for animal and plant poisonSimranjit kaur The document provides an identification test for various plant and animal poisons, explaining that poisonous plants can cause harm or death due to toxic substances present in them. It includes specific examples of plants such as Croton tiglium, Atropa belladonna, and Cannabis sativa, detailing their poisonous parts, contents, and methods for conducting presumptive tests for their toxins. Additionally, it discusses the nature of animal venoms and outlines testing procedures for snake and scorpion venoms.
Exclusive gates
Exclusive gatesshubhajitCHATTERJEE2 This document discusses exclusive gates, including exclusive OR (XOR) and exclusive NOR (XNOR) gates. It defines XOR and XNOR gates, provides their symbols, and describes their truth tables. It also shows how XOR and XNOR gates can be implemented using basic logic gates like NAND. Finally, it lists some common applications of XOR and XNOR gates such as in arithmetic operations, parity checkers, encryption, and error detection.
Css Ppt
Css PptHema Prasanth This document provides an overview of various CSS topics including comments, colors, text formatting, positioning, and cross-browser compatibility. It explains concepts like using hexadecimal color codes, text properties like alignment and decoration, positioning elements with static, relative, absolute and fixed positioning, and strategies for aligning elements and dealing with browser inconsistencies.
15 bitwise operators
15 bitwise operatorsRavindra Rathore - Bitwise operators operate on individual bits of integer values and perform operations like AND, OR, XOR, and NOT.
- Negative integers are stored in two's complement form.
- Bitwise operators include & for AND, | for OR, ^ for XOR, ~ for NOT, << for left shift, >> for right shift, and >>> for unsigned right shift.
Css types internal, external and inline (1)
Css types internal, external and inline (1)Webtech Learning The document discusses the three types of CSS - internal, external, and inline. Internal CSS is defined within the HTML document using <style> tags. External CSS is defined in a separate .css file and linked using <link> tags. Inline CSS is defined directly in HTML elements using the style attribute. IDs and classes are also discussed as ways to target elements with CSS selectors.
Forensic audio
Forensic audioTejasvi Bhatia This document discusses forensic audio analysis and speaker identification. It covers:
1. How sound is produced through vibration of the vocal cords and interpreted by the brain.
2. The process of speaker identification which determines the identity of an unknown speaker by comparing their speech signals to a database of known speakers. This can be open-set where the speaker may not be in the database, or closed-set where they are known to be there.
3. Problems that can occur in forensic speaker examination including low quality recordings, disguised voices, health issues and non-cooperative suspects. Good quality samples with minimal noise are important for accurate analysis.
Linked list
Linked listMuhammad Qasim A linked list is a linear data structure made up of nodes that each contain data and a pointer to the next node, forming a chain. Advantages include dynamic memory allocation and ease of insertion and deletion, while disadvantages involve memory overhead from pointers and sequential access requirement. Types of linked lists include singly, doubly, and circular, and they are commonly used in implementing data structures such as stacks and queues.
Niveles de ejecución en linux
Niveles de ejecución en linuxruberush El documento describe los diferentes niveles de ejecución (runlevels) en Linux. Los niveles más bajos (0-2) se usan para mantenimiento y recuperación, mientras que los niveles 3-5 ofrecen servicios de red y capacidades multiusuario, con el nivel 5 agregando soporte gráfico. El nivel de ejecución predeterminado se puede configurar editando el archivo /etc/inittab.
Firing Marks
Firing MarksKetan Patil Firing marks left on bullets and cartridge cases can be used to identify the firearm used. There are several types of marks including:
1. Rifling marks on the bullet from the grooves in the barrel. These marks are unique to each gun.
2. Firing pin marks on the primer from the firing pin striking it. Imperfections in the firing pin can be transferred.
3. Breech face marks on the cartridge from the cartridge striking the breech face on firing. Imperfections are imprinted.
4. Extractor and ejector marks on the cartridge case from the mechanisms removing the spent case from the firearm.
Python-Functions.pptx
Python-Functions.pptxKarudaiyar Ganapathy Functions allow programmers to organize and reuse code. They take in parameters and return values. Parameters act as variables that represent the information passed into a function. Arguments are the actual values passed into the function call. Functions can have default parameter values. Functions can return values using the return statement. Python passes arguments by reference, so changes made to parameters inside functions will persist outside the function as well. Functions can also take in arbitrary or keyword arguments. Recursion is when a function calls itself within its own definition. It breaks problems down into sub-problems until a base case is reached. The main types of recursion are direct, indirect, and tail recursion. Recursion can make code more elegant but uses more memory than iteration.
Python strings
Python stringsMohammed Sikander This document discusses various string operations in Python including: finding the length of a string; accessing and slicing characters; the difference between strings and lists; converting case; checking character types; splitting strings; finding substrings; reading and printing strings; concatenation and repetition; iterating through strings with for loops; and common string methods like isalpha, isdigit, lower, upper, title, join, split, count, find, index. It also provides examples of problems involving anagrams, pangrams, unique characters, and removing duplicates from strings.
Datatypes in python
Datatypes in pythoneShikshak The document discusses various Python datatypes. It explains that Python supports built-in and user-defined datatypes. The main built-in datatypes are None, numeric, sequence, set and mapping types. Numeric types include int, float and complex. Common sequence types are str, bytes, list, tuple and range. Sets can be created using set and frozenset datatypes. Mapping types represent a group of key-value pairs like dictionaries.
Keyboard presentation.pdf
Keyboard presentation.pdfarturoraymundo A keyboard is a standard input device that sends unique signals to a computer when keys are pressed. These signals are called scan codes and they indicate which physical key was pressed. The computer receives the scan codes and uses its software and operating system to interpret the signals and translate them into letters, numbers, or other characters based on the keyboard layout. The interpretation of key presses is handled by the computer's software and operating system rather than just the hardware.
Python programming | Fundamentals of Python programming
Python programming | Fundamentals of Python programming KrishnaMildain Python is a versatile, high-level programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991, named after 'Monty Python's Flying Circus'. It is widely used in various fields, including data science, artificial intelligence, web development, and more, supported by popular frameworks like Django and TensorFlow. The language features dynamic typing and object-oriented capabilities, with built-in functions for user input and output.
Flowcharts and algorithms
Flowcharts and algorithmsStudent The document explains algorithms as a finite set of sequential instructions for problem-solving, highlighting their characteristics such as finiteness, definiteness, effectiveness, and input/output requirements. It compares algorithms to flowcharts, which provide a visual representation of the algorithms, and discusses their advantages and disadvantages. The document also includes examples illustrating how to create algorithms and corresponding flowcharts for converting measurements and calculating areas.
Queues
QueuesLovely Professional University The document provides an overview of queues as data structures, explaining their classification into primitive and non-primitive types and detailing the operations of inserting and deleting elements (enqueue and dequeue). It describes various types of queues, including circular queues, deques, and priority queues, along with their implementations and applications in computing. Additionally, it highlights the importance of queues in handling processes in operating systems and real-life scenarios like waiting lines.
Forensic Analysis of Bare Footprint .pptx
Forensic Analysis of Bare Footprint .pptxPawanMandal8 The document discusses the Gunn method used for partial print analysis, particularly in comparing known and questioned bare footprints. It references specific measurements such as instep width and heel and ball width. It also mentions the concept of the 'Greek ideal,' where the second toe is the longest toe.
Java Tokens
Java TokensMadishetty Prathibha The document provides an overview of Java and its object-oriented programming features, including the definition and significance of tokens such as keywords, identifiers, and constants. It discusses the structure of Java programs, types of operators, and various forms of comments used in coding. The content aims to enhance understanding of Java syntax and its foundational concepts.
Java compilation
Java compilationMike Kucera The document summarizes the process of compiling Java code from writing it in an IDE to running the bytecode on a JVM. It discusses how code is compiled incrementally in an IDE, generated into bytecode, dynamically loaded and interpreted with just-in-time compilation into native code for performance. It also overview's IBM's involvement in Java development and optimization.
PYTHON - TKINTER - GUI - PART 1.ppt
PYTHON - TKINTER - GUI - PART 1.pptPriyaSoundararajan1 This document is a tutorial on using Tkinter, the standard GUI library for Python, detailing its features, basic concepts, and various widget functionalities. It explains how to create windows, manage layouts with geometry methods (pack, grid, place), and utilize widgets like buttons and checkbuttons. Additionally, it covers event handling, text entry, and canvas drawing, providing syntax examples and common parameters for each widget type.
Oops practical file
Oops practical fileAnkit Dixit This document contains 22 code programs submitted by Ankit Dixit to his instructor Ms. Achhardeep Kaur for her class. The programs demonstrate various C++ concepts like conditional statements, loops, functions, arrays, pointers, structures, classes and objects. Example programs include checking if a number is even or odd, finding the greatest of three numbers, generating the Fibonacci series, and calculating the area of a rectangle using a class.
Introduction to Python
Introduction to Python Mohammed Sikander This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses Python's design philosophy emphasizing readability. It also covers printing messages, reading input, variables and data types, operators, and basic syntax like comments and identifiers. Arithmetic, relational, logical and bitwise operators are explained along with examples.
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS- Logic Gates
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS- Logic GatesTrinity Dwarka The document discusses fundamental concepts of logic gates used in digital circuits, detailing three primary gates (AND, OR, NOT) and their respective functions represented through symbols and truth tables. It also introduces NAND, NOR, exclusive OR, and exclusive NOR gates, explaining how they operate based on input combinations. The content is geared towards learners in the field of digital electronics.
Lexical analyzer
Lexical analyzerFarzana Aktar The presentation introduces lexical analysis, which is the process of converting input strings into tokens for easier parsing. It describes the role of a lexical analyzer as the first phase of a compiler, focusing on reading characters, generating tokens, and optimizing the syntax analysis process. The conclusion emphasizes that lexical analyzers enhance compiler efficiency and portability.
List in Python
List in PythonSiddique Ibrahim A list in Python is a mutable ordered sequence of elements of any data type. Lists can be created using square brackets [] and elements are accessed via indexes that start at 0. Some key characteristics of lists are:
- They can contain elements of different types
- Elements can be modified, added, or removed
- Common list methods include append(), insert(), remove(), pop(), and sort()
Stacks Implementation and Examples
Stacks Implementation and Examplesgreatqadirgee4u The document summarizes lecture 2 of the CIS-122 Data Structures course. It covers applications of stacks like arithmetic expressions, recursion, quicksort, and towers of Hanoi. It also discusses stack implementations using arrays and linked lists and provides examples of infix to postfix conversion and evaluating arithmetic expressions using a stack.
Operators and Expressions in C++
Operators and Expressions in C++Praveen M Jigajinni This document discusses operators and expressions in C++. It begins by defining operators as symbols that represent operations and operands as the objects involved in those operations. It then covers various types of operators in C++ like arithmetic, relational, logical, and conditional operators. It provides examples of using each operator and notes order of precedence. The document also discusses expressions, noting they are combinations of operators, constants, and variables. It provides examples of integer, real, relational, and logical expressions. Finally, it discusses mathematical functions available in the C++ standard library header file math.h that can be used in arithmetic expressions.
Python Programming | JNTUK | UNIT 1 | Lecture 5
Python Programming | JNTUK | UNIT 1 | Lecture 5FabMinds This document provides an overview of the topics covered in Unit 1 of a Python programming syllabus. It includes introductions to computer science topics, computer systems, installing Python, basic syntax, data types, variables, arithmetic operators, expressions, comments, and understanding error messages. Example code and explanations of operators like arithmetic, assignment, comparison, logical, membership, identity, and bitwise are also provided.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Linked list
Linked listMuhammad Qasim A linked list is a linear data structure made up of nodes that each contain data and a pointer to the next node, forming a chain. Advantages include dynamic memory allocation and ease of insertion and deletion, while disadvantages involve memory overhead from pointers and sequential access requirement. Types of linked lists include singly, doubly, and circular, and they are commonly used in implementing data structures such as stacks and queues.
Niveles de ejecución en linux
Niveles de ejecución en linuxruberush El documento describe los diferentes niveles de ejecución (runlevels) en Linux. Los niveles más bajos (0-2) se usan para mantenimiento y recuperación, mientras que los niveles 3-5 ofrecen servicios de red y capacidades multiusuario, con el nivel 5 agregando soporte gráfico. El nivel de ejecución predeterminado se puede configurar editando el archivo /etc/inittab.
Firing Marks
Firing MarksKetan Patil Firing marks left on bullets and cartridge cases can be used to identify the firearm used. There are several types of marks including:
1. Rifling marks on the bullet from the grooves in the barrel. These marks are unique to each gun.
2. Firing pin marks on the primer from the firing pin striking it. Imperfections in the firing pin can be transferred.
3. Breech face marks on the cartridge from the cartridge striking the breech face on firing. Imperfections are imprinted.
4. Extractor and ejector marks on the cartridge case from the mechanisms removing the spent case from the firearm.
Python-Functions.pptx
Python-Functions.pptxKarudaiyar Ganapathy Functions allow programmers to organize and reuse code. They take in parameters and return values. Parameters act as variables that represent the information passed into a function. Arguments are the actual values passed into the function call. Functions can have default parameter values. Functions can return values using the return statement. Python passes arguments by reference, so changes made to parameters inside functions will persist outside the function as well. Functions can also take in arbitrary or keyword arguments. Recursion is when a function calls itself within its own definition. It breaks problems down into sub-problems until a base case is reached. The main types of recursion are direct, indirect, and tail recursion. Recursion can make code more elegant but uses more memory than iteration.
Python strings
Python stringsMohammed Sikander This document discusses various string operations in Python including: finding the length of a string; accessing and slicing characters; the difference between strings and lists; converting case; checking character types; splitting strings; finding substrings; reading and printing strings; concatenation and repetition; iterating through strings with for loops; and common string methods like isalpha, isdigit, lower, upper, title, join, split, count, find, index. It also provides examples of problems involving anagrams, pangrams, unique characters, and removing duplicates from strings.
Datatypes in python
Datatypes in pythoneShikshak The document discusses various Python datatypes. It explains that Python supports built-in and user-defined datatypes. The main built-in datatypes are None, numeric, sequence, set and mapping types. Numeric types include int, float and complex. Common sequence types are str, bytes, list, tuple and range. Sets can be created using set and frozenset datatypes. Mapping types represent a group of key-value pairs like dictionaries.
Keyboard presentation.pdf
Keyboard presentation.pdfarturoraymundo A keyboard is a standard input device that sends unique signals to a computer when keys are pressed. These signals are called scan codes and they indicate which physical key was pressed. The computer receives the scan codes and uses its software and operating system to interpret the signals and translate them into letters, numbers, or other characters based on the keyboard layout. The interpretation of key presses is handled by the computer's software and operating system rather than just the hardware.
Python programming | Fundamentals of Python programming
Python programming | Fundamentals of Python programming KrishnaMildain Python is a versatile, high-level programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991, named after 'Monty Python's Flying Circus'. It is widely used in various fields, including data science, artificial intelligence, web development, and more, supported by popular frameworks like Django and TensorFlow. The language features dynamic typing and object-oriented capabilities, with built-in functions for user input and output.
Flowcharts and algorithms
Flowcharts and algorithmsStudent The document explains algorithms as a finite set of sequential instructions for problem-solving, highlighting their characteristics such as finiteness, definiteness, effectiveness, and input/output requirements. It compares algorithms to flowcharts, which provide a visual representation of the algorithms, and discusses their advantages and disadvantages. The document also includes examples illustrating how to create algorithms and corresponding flowcharts for converting measurements and calculating areas.
Queues
QueuesLovely Professional University The document provides an overview of queues as data structures, explaining their classification into primitive and non-primitive types and detailing the operations of inserting and deleting elements (enqueue and dequeue). It describes various types of queues, including circular queues, deques, and priority queues, along with their implementations and applications in computing. Additionally, it highlights the importance of queues in handling processes in operating systems and real-life scenarios like waiting lines.
Forensic Analysis of Bare Footprint .pptx
Forensic Analysis of Bare Footprint .pptxPawanMandal8 The document discusses the Gunn method used for partial print analysis, particularly in comparing known and questioned bare footprints. It references specific measurements such as instep width and heel and ball width. It also mentions the concept of the 'Greek ideal,' where the second toe is the longest toe.
Java Tokens
Java TokensMadishetty Prathibha The document provides an overview of Java and its object-oriented programming features, including the definition and significance of tokens such as keywords, identifiers, and constants. It discusses the structure of Java programs, types of operators, and various forms of comments used in coding. The content aims to enhance understanding of Java syntax and its foundational concepts.
Java compilation
Java compilationMike Kucera The document summarizes the process of compiling Java code from writing it in an IDE to running the bytecode on a JVM. It discusses how code is compiled incrementally in an IDE, generated into bytecode, dynamically loaded and interpreted with just-in-time compilation into native code for performance. It also overview's IBM's involvement in Java development and optimization.
PYTHON - TKINTER - GUI - PART 1.ppt
PYTHON - TKINTER - GUI - PART 1.pptPriyaSoundararajan1 This document is a tutorial on using Tkinter, the standard GUI library for Python, detailing its features, basic concepts, and various widget functionalities. It explains how to create windows, manage layouts with geometry methods (pack, grid, place), and utilize widgets like buttons and checkbuttons. Additionally, it covers event handling, text entry, and canvas drawing, providing syntax examples and common parameters for each widget type.
Oops practical file
Oops practical fileAnkit Dixit This document contains 22 code programs submitted by Ankit Dixit to his instructor Ms. Achhardeep Kaur for her class. The programs demonstrate various C++ concepts like conditional statements, loops, functions, arrays, pointers, structures, classes and objects. Example programs include checking if a number is even or odd, finding the greatest of three numbers, generating the Fibonacci series, and calculating the area of a rectangle using a class.
Introduction to Python
Introduction to Python Mohammed Sikander This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses Python's design philosophy emphasizing readability. It also covers printing messages, reading input, variables and data types, operators, and basic syntax like comments and identifiers. Arithmetic, relational, logical and bitwise operators are explained along with examples.
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS- Logic Gates
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS- Logic GatesTrinity Dwarka The document discusses fundamental concepts of logic gates used in digital circuits, detailing three primary gates (AND, OR, NOT) and their respective functions represented through symbols and truth tables. It also introduces NAND, NOR, exclusive OR, and exclusive NOR gates, explaining how they operate based on input combinations. The content is geared towards learners in the field of digital electronics.
Lexical analyzer
Lexical analyzerFarzana Aktar The presentation introduces lexical analysis, which is the process of converting input strings into tokens for easier parsing. It describes the role of a lexical analyzer as the first phase of a compiler, focusing on reading characters, generating tokens, and optimizing the syntax analysis process. The conclusion emphasizes that lexical analyzers enhance compiler efficiency and portability.
List in Python
List in PythonSiddique Ibrahim A list in Python is a mutable ordered sequence of elements of any data type. Lists can be created using square brackets [] and elements are accessed via indexes that start at 0. Some key characteristics of lists are:
- They can contain elements of different types
- Elements can be modified, added, or removed
- Common list methods include append(), insert(), remove(), pop(), and sort()
Stacks Implementation and Examples
Stacks Implementation and Examplesgreatqadirgee4u The document summarizes lecture 2 of the CIS-122 Data Structures course. It covers applications of stacks like arithmetic expressions, recursion, quicksort, and towers of Hanoi. It also discusses stack implementations using arrays and linked lists and provides examples of infix to postfix conversion and evaluating arithmetic expressions using a stack.
Similar to Operators in Python Arithmetic Operators (20)
Operators and Expressions in C++
Operators and Expressions in C++Praveen M Jigajinni This document discusses operators and expressions in C++. It begins by defining operators as symbols that represent operations and operands as the objects involved in those operations. It then covers various types of operators in C++ like arithmetic, relational, logical, and conditional operators. It provides examples of using each operator and notes order of precedence. The document also discusses expressions, noting they are combinations of operators, constants, and variables. It provides examples of integer, real, relational, and logical expressions. Finally, it discusses mathematical functions available in the C++ standard library header file math.h that can be used in arithmetic expressions.
Python Programming | JNTUK | UNIT 1 | Lecture 5
Python Programming | JNTUK | UNIT 1 | Lecture 5FabMinds This document provides an overview of the topics covered in Unit 1 of a Python programming syllabus. It includes introductions to computer science topics, computer systems, installing Python, basic syntax, data types, variables, arithmetic operators, expressions, comments, and understanding error messages. Example code and explanations of operators like arithmetic, assignment, comparison, logical, membership, identity, and bitwise are also provided.
Operators in python
Operators in pythonPrabhakaran V M This document discusses different types of operators in Python programming. It defines operators as symbols that represent operations that can be performed on operands or values. The main types of operators covered are: arithmetic operators for mathematical operations, relational operators for comparisons, logical operators for Boolean logic, assignment operators for assigning values, and special operators like identity and membership. Examples are provided to demonstrate the usage of each operator type.
operators and expressions in c++
operators and expressions in c++sanya6900 Operators in C++ represent specific tasks or operations that are applied to operands. There are several types of operators including arithmetic, relational, logical, increment/decrement, and conditional operators. Arithmetic operators perform basic math operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on operands. Relational operators compare operands and return true or false based on the comparison. Logical operators combine relational expressions and include logical AND, logical OR, and logical NOT. The increment/decrement operators increment or decrement operands by 1. The conditional operator returns one of two results based on a condition. Precedence rules determine the order in which operations are performed.
Python programming language introduction unit
Python programming language introduction unitmichaelaaron25322 The document provides an overview of Python programming focusing on types, operators, expressions, and control flow. It details standard data types such as numbers, strings, and booleans, along with various operators including arithmetic, relational, and logical operators. Additionally, it outlines control structures for decision making and looping, illustrating their usage with example code snippets.
Grade XI - Computer science Data Handling in Python
Grade XI - Computer science Data Handling in Pythonvidyuthno1 This document serves as an introduction to data handling in Python for Class 11, covering data types, variables, operators, and expressions. It explains core data types such as numbers, strings, lists, and dictionaries, along with mutable and immutable types, variable assignments, and operator functionalities. Additionally, it discusses debugging processes, built-in exceptions in Python, and highlights mathematical operations using the math module.
Types of Operators in C
Types of Operators in CThesis Scientist Private Limited The document explains various types of operators in the C programming language, including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment and decrement, conditional, bitwise, and special operators. It includes detailed descriptions of each operator type, their purposes, and examples of their usage. Additionally, the document covers operator precedence and type modifiers, highlighting how these concepts apply to data types in C.
Operators expressions-and-statements
Operators expressions-and-statementsCtOlaf The document discusses various operators in C# including arithmetic, logical, bitwise, comparison, and assignment operators. It provides examples of using each operator type and discusses operator precedence. Key points covered include the different categories of operators in C#, how they work, precedence rules, and examples of using each type of operator to perform calculations and comparisons in C# code.
1 Standard Data types.pptx
1 Standard Data types.pptxssuser8e50d8 This document discusses Python data types and operators. It describes mutable and immutable data types in Python and provides examples. It then defines and provides examples of different types of operators in Python including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, bitwise, boolean, and membership operators. Finally, it discusses operator precedence and provides a table showing operator precedence from highest to lowest.
Operators
OperatorsKamran The document discusses various C# operators including unary operators, binary operators, and ternary operators. It provides examples and explanations of increment/decrement, bitwise, logical, comparison, and assignment operators. It also covers operator precedence and uses the Math class for common mathematical functions.
hlukj6;lukm,t.mnjhgjukryopkiu;lyk y2.ppt
hlukj6;lukm,t.mnjhgjukryopkiu;lyk y2.pptPraveenaFppt The document provides an overview of various types of operators in Python, including arithmetic, comparison, logical, assignment, and membership operators. It explains their functionality with examples and addresses control flow statements such as if-elif-else and looping constructs like while and for loops. Additionally, it discusses loop control statements like break, continue, and pass, along with the use of else in loops.
Py-Slides-2 (1).ppt
Py-Slides-2 (1).pptKalaiVani395886 The document discusses various operators and statements in the Python programming language. It covers arithmetic, comparison, logical, assignment, membership, and bitwise operators. It also explains control flow statements like if-else, while, for, break, continue, and pass in Python. Key operators and statements are defined with examples to illustrate their usage.
Py-Slides-2.ppt
Py-Slides-2.pptTejaValmiki This document discusses various operators and statements in the Python programming language. It covers arithmetic, comparison, logical, assignment, membership, and bitwise operators. It also explains control flow statements like if/elif/else, while loops, for loops, and the break, continue, and pass statements. Key points include:
- Python supports operators for arithmetic, comparison, assignment, logical/relational, conditional, and bitwise operations
- Control structures include if/elif/else conditional execution, while and for iterative loops, and break, continue, and pass statements to control loop behavior
- Loops like while and for allow iterating over sequences with optional else blocks to execute after normal termination
Py-Slides-2.ppt
Py-Slides-2.pptAllanGuevarra1 The document discusses various operators and statements in Python. It covers arithmetic, comparison, logical, assignment, membership, and bitwise operators. It also discusses control flow statements like if-else, while, for, break, continue, else and pass statements. The key points are:
- Python supports operators like +, -, *, /, % for arithmetic. ==, !=, >, < for comparison. and, or, not for logical operations.
- if-else and nested if-elif-else statements allow conditional execution of code blocks.
- while and for loops iterate over blocks until a condition is met or a sequence is exhausted.
- break and continue can terminate or skip iterations in loops.
03 Operators and expressions
03 Operators and expressionsmaznabili The document discusses operators and expressions in C#. It describes different categories of operators like arithmetic, logical, comparison, assignment, and other operators. It explains operator precedence and associativity. It also covers implicit and explicit type conversions. Expressions are defined as sequences of operators and operands that are evaluated to a single value. Examples are provided to demonstrate the use of various operators and expressions.
Operators_in_Python_Simplified_languages
Operators_in_Python_Simplified_languagesAbhishekGupta692777 The document explains various types of operators in Python programming, including unary, binary, arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, identity, and membership operators. It provides definitions, examples, and expected outputs for each type of operator, illustrating their usage in problem-solving. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding operators within Python.
Operators in Python
Operators in PythonAnusuya123 The document discusses various operators in Python including arithmetic, comparison, bitwise, logical, and membership operators. It provides examples of using each operator and explains their functionality. The key types of operators covered are arithmetic (e.g. +, -, *, /), comparison (e.g. ==, !=, >, <), bitwise (e.g. &, |, ^), logical (e.g. and, or, not), and membership (e.g. in, not in) operators. It also discusses operator precedence and provides examples of expressions using different operators.
Coper in C
Coper in Cthirumalaikumar3 Operators are symbols that tell the compiler to perform mathematical or logical manipulations on operands. This document discusses the different types of operators in C language, including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment/decrement, conditional, and bitwise operators. It also covers operator precedence and type conversions.
Lecture 05.pptx
Lecture 05.pptxMohammad Hassan Operators are symbols that perform operations on values in Python. There are different types of operators such as arithmetic, assignment, comparison, and logical operators. The order that operators are evaluated depends on their priority and whether they have left-sided or right-sided binding. Parentheses can be used to change the natural order of evaluations in expressions. Floating point numbers may result in small rounding errors due to limitations in how computers store numeric values.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02Mauricio Alexandre Silva Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...Kweku Zurek This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Service PIN codes (LIST)
Vitamin and Nutritional Deficiencies.pptx
Vitamin and Nutritional Deficiencies.pptxVishal Chanalia Vitamin and nutritional deficiency occurs when the body does not receive enough essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, needed for proper functioning. This can lead to various health problems, including weakened immunity, stunted growth, fatigue, poor wound healing, cognitive issues, and increased susceptibility to infections and diseases. Long-term deficiencies can cause serious and sometimes irreversible health complications.
VCE Literature Section A Exam Response Guide
VCE Literature Section A Exam Response Guidejpinnuck This practical guide shows students of Unit 3&4 VCE Literature how to write responses to Section A of the exam. Including a range of examples writing about different types of texts, this guide:
*Breaks down and explains what Q1 and Q2 tasks involve and expect
*Breaks down example responses for each question
*Explains and scaffolds students to write responses for each question
*Includes a comprehensive range of sentence starters and vocabulary for responding to each question
*Includes critical theory vocabulary lists to support Q2 responses
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptx
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptxmansk2 2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. In this slide try to present the brief history of Chaulukyas of Gujrat up to Kumarpala To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
Chaulukya or Solanki was one of the Rajputs born from Agnikul. In the Vadnagar inscription, the origin of this dynasty is told from Brahma's Chauluk or Kamandalu. They ruled in Gujarat from the latter half of the tenth century to the beginning of the thirteenth century. Their capital was in Anahilwad. It is not certain whether it had any relation with the Chalukya dynasty of the south or not. It is worth mentioning that the name of the dynasty of the south was 'Chaluky' while the dynasty of Gujarat has been called 'Chaulukya'. The rulers of this dynasty were the supporters and patrons of Jainism.
Peer Teaching Observations During School Internship
Peer Teaching Observations During School InternshipAjayaMohanty7 FOR B.ED,M.ED,M.A.EDUCATION AND ANY STUDENT OF TEACHER EDUCATION
How payment terms are configured in Odoo 18
How payment terms are configured in Odoo 18Celine George Payment terms in Odoo 18 help define the conditions for when invoices are due. This feature can split payments into multiple parts and automate due dates based on specific rules.
Romanticism in Love and Sacrifice An Analysis of Oscar Wilde’s The Nightingal...
Romanticism in Love and Sacrifice An Analysis of Oscar Wilde’s The Nightingal...KaryanaTantri21 The story revolves around a college student who despairs not having a red rose as a condition for dancing with the girl he loves. The nightingale hears his complaint and offers to create the red rose at the cost of his life. He sang a love song all night with his chest stuck to the thorns of the rose tree. Finally, the red rose grew, but his sacrifice was in vain. The girl rejected the flower because it didn’t match her outfit and preferred a jewellery gift. The student threw the flower on the street and returned to studying philosophy
THE PSYCHOANALYTIC OF THE BLACK CAT BY EDGAR ALLAN POE (1).pdf
THE PSYCHOANALYTIC OF THE BLACK CAT BY EDGAR ALLAN POE (1).pdfnabilahk908 Psychoanalytic Analysis of The Black Cat by Edgar Allan Poe explores the deep psychological dimensions of the narrator’s disturbed mind through the lens of Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory. According to Freud (1923), the human psyche is structured into three components: the Id, which contains primitive and unconscious desires; the Ego, which operates on the reality principle and mediates between the Id and the external world; and the Superego, which reflects internalized moral standards.
In this story, Poe presents a narrator who experiences a psychological breakdown triggered by repressed guilt, aggression, and internal conflict. This analysis focuses not only on the gothic horror elements of the narrative but also on the narrator’s mental instability and emotional repression, demonstrating how the imbalance of these three psychic forces contributes to his downfall.
ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]
ECONOMICS, DISASTER MANAGEMENT, ROAD SAFETY - STUDY MATERIAL [10TH]SHERAZ AHMAD LONE This study material for Class 10th covers the core subjects of Economics, Disaster Management, and Road Safety Education, developed strictly in line with the JKBOSE textbook. It presents the content in a simplified, structured, and student-friendly format, ensuring clarity in concepts. The material includes reframed explanations, flowcharts, infographics, and key point summaries to support better understanding and retention. Designed for classroom teaching and exam preparation, it aims to enhance comprehension, critical thinking, and practical awareness among students.
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptx
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptxInternational Society of Service Innovation Professionals ---
June 25 ISSIP Event - slides in process
20250618 PPre-Event Presentation Summary - Progress Update with Board Series June 25
ISSIP Website Upcoming Events Description: https://issip.org/event/semi-annual-issip-progress-call/
Register here (even if you cannot attend live online, all who register will get link to recording and slides post-event): https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSdThrop1rafOCo4PQkYiS2XApclJuMjYONEHRMGBsceRdcQqg/viewform
This pre-event presentation: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/june-2025-progress-update-with-board-call_in-process-pptx/280718770
This pre-event recording: https://youtu.be/Shjgd5o488o
---
Sustainable Innovation with Immersive Learning
Sustainable Innovation with Immersive LearningLeonel Morgado Prof. Leonel and Prof. Dennis approached educational uses, practices, and strategies of using immersion as a lens to interpret, design, and planning educational activities in a sustainable way. Rather than one-off gimmicks, the intent is to enable instructors (and institutions) to be able to include them in their regular activities, including the ability to evaluate and redesign them.
Immersion as a phenomenon enables interpreting pedagogical activities in a learning-agnostic way: you take a stance on the learning theory to follow, and leverage immersion to envision and guide your practice.
OBSESSIVE COMPULSIVE DISORDER.pptx IN 5TH SEMESTER B.SC NURSING, 2ND YEAR GNM...
OBSESSIVE COMPULSIVE DISORDER.pptx IN 5TH SEMESTER B.SC NURSING, 2ND YEAR GNM...parmarjuli1412 OBSESSIVE COMPULSIVE DISORDER INCLUDED TOPICS ARE INTRODUCTION, DEFINITION OF OBSESSION, DEFINITION OF COMPULSION, MEANING OF OBSESSION AND COMPULSION, DEFINITION OF OBSESSIVE COMPULSIVE DISORDER, EPIDERMIOLOGY OF OCD, ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS OF OCD, CLINICAL SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF OBSESSION AND COMPULSION, MANAGEMENT INCLUDED PHARMACOTHERAPY(ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUG+ANXIOLYTIC DRUGS), PSYCHOTHERAPY, NURSING MANAGEMENT(ASSESSMENT+DIAGNOSIS+NURSING INTERVENTION+EVALUATION))
A Visual Introduction to the Prophet Jeremiah
A Visual Introduction to the Prophet JeremiahSteve Thomason These images will give you a visual guide to both the context and the flow of the story of the prophet Jeremiah. Feel free to use these in your study, preaching, and teaching.
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptx
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) BLUF:
The Texas outbreak has slowed down, but sporadic cases continue to emerge in Kansas, Oklahoma, and New Mexico.
Elsewhere in the US, we continue to see signs of acceleration due to outbreaks outside the Southwest (North Dakota, Montana, and Colorado) and travel-related cases. Measles exposures due to travel are expected to pose a significant challenge throughout the summer.
The U.S. is on track to exceed its 30-year high for measles cases (1,274) within the next two weeks.
Here is the latest update:
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 919
•Texas: 744 (+2) (55% of cases are in Gaines County).
•New Mexico: 81 (83% of cases are from Lea County).
•Oklahoma: 20 (+2)
•Kansas: 74 (+5) (38.89% of the cases are from Gray County).
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 104
• Texas: 96 (+2) – This accounts for 13% of all cases in Texas.
• New Mexico: 7 – This accounts for 9.47% of all cases in New Mexico.
• Kansas: 3 – This accounts for 5.08% of all cases in the state of Kansas.
DEATHS: 3
•Texas: 2 – This is 0.27% of all cases in Texas.
•New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.23% of all cases in New Mexico.
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 1,197
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD
•Mexico: 2337 (+257), 5 fatalities
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 2,179 (+239) cases, 4 fatalities, 7 currently hospitalized.
•Canada: 3,207 (+208), 1 fatality
‒Ontario Outbreak, Canada: 2,115 (+74) cases, 158 hospitalizations, 1 fatality.
‒Alberta, Canada: 879(+118) cases, 5 currently hospitalized.
HistoPathology Ppt. Arshita Gupta for Diploma
HistoPathology Ppt. Arshita Gupta for Diplomaarshitagupta674 Hello everyone please suggest your views and likes so that I uploaded more study materials
In this slide full HistoPathology according to diploma course available like fixation
Tissue processing , staining etc
IIT KGP Quiz Week 2024 Sports Quiz (Prelims + Finals)
IIT KGP Quiz Week 2024 Sports Quiz (Prelims + Finals)IIT Kharagpur Quiz Club The document outlines the format for the Sports Quiz at Quiz Week 2024, covering various sports & games and requiring participants to Answer without external sources. It includes specific details about question types, scoring, and examples of quiz questions. The document emphasizes fair play and enjoyment of the quiz experience.
Intellectual Property Right (Jurisprudence).pptx
Intellectual Property Right (Jurisprudence).pptxVishal Chanalia Intellectual property corresponds to ideas owned by a person or a firm and thus subjected to legal protection under the law.
The main purpose of intellectual property is to give encouragement to the innovators of new concepts by giving them the opportunity to make sufficient profits from their inventions and recover their manufacturing costs and efforts.
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptx
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptxInternational Society of Service Innovation Professionals
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptx
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 6-14-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
Ad
Operators in Python Arithmetic Operators
- 1. Operators in Python All the operators in Python are classified according to their nature and type and they are: • Arithmetic Operators • Relational Operators • Logical Operators • Assignment Operators • Bitwise Operators • Boolean Operators • Membership Operators • Identity Operators
- 2. Arithmetic Operators • These operators perform basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc. and these operators are binary operators that means these operators acts on two operands. And there are 7 binary arithmetic operators available in Python. Operator Meaning Example Result + Addition 10 + 7 12 - Subtraction 10.0 - 1.5 8.5 * Multiplication 30 * 3 900 / Float Division 5 / 2 2.5 // Integer Division 5 // 2 2 ** Exponentiation 3 ** 2 9 % Remainder 10 % 3 1 Operator Priority Parenthesis (( ), [ ]) First Exponentiation (**) Second Multiplication (*), Division (/, //), Modulus (%) Third Addition (+), Subtraction (-) Fourth Assignment Fifth
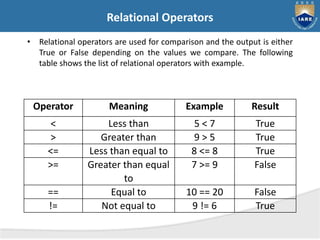
- 3. Relational Operators • Relational operators are used for comparison and the output is either True or False depending on the values we compare. The following table shows the list of relational operators with example. Operator Meaning Example Result < Less than 5 < 7 True > Greater than 9 > 5 True <= Less than equal to 8 <= 8 True >= Greater than equal to 7 >= 9 False == Equal to 10 == 20 False != Not equal to 9 != 6 True
- 4. Logical Operators • Logical operators are used to form compound conditions which are a combination of more than one simple condition. Each of the simple conditions are evaluated first and based on the result compound condition is evaluated. The result of the expression is either True or False based on the result of simple conditions. Operator Meaning Example Result and Logical AND (5 > 7) and (3 < 5) False or Logical OR (7 == 7) or (5 != 5) True not Logical NOT not(3 <= 2) True
- 5. Assignment Operators • These operators are used to store a value into a variable and also useful to perform simple arithmetic operations. Assignment operators are of two types: simple assignment operator and augmented assignment operator. Simple assignment operators are combined with arithmetic operators to form augmented assignment operators. The following table shows a list of assignment operators and its use. Operator Meaning Example Result = Simple assignment a = 10 10 += Addition assignment a = 5 a += 8 13 -= Subtraction assignment b = 5 b -= 8 -3 *= Multiplication assignment a =10 a *= 8 80 /= Float Division assignment a = 10 a /= 8 1.25 //= Integer Division assignment b = 10 b //= 10 1 **= Exponentiation assignment a = 10 a %= 5 0 %= Remainder assignment b = 10 b ** = 8 100000000
- 6. Bitwise Operators • Bitwise Operators acts on individual bits of the operands. These operators directly act on binary numbers. If we want to use these operators on integers then first these numbers are converted into binary numbers and then bitwise operators act on those bits. The following table shows the list of bitwise operators available in Python. Operator Meaning Example Result & Bitwise AND a = 10 = 0000 1010 b = 11 = 0000 1011 a & b = 0000 1010 = 10 a & b = 10 | Bitwise OR a = 10 = 0000 1010 b = 11 = 0000 1011 a | b = 0000 1011 = 11 a | b = 11 ^ Bitwise XOR a = 10 = 0000 1010 b = 11 = 0000 1011 a ^ b = 0000 0001 = 1 a ^ b = 1 ~ Bitwise Complement a = 10 = 0000 1010 ~a = 1111 0101 = -11 ~a = -11 << Bitwise Left Shift a = 10 a << 2 = 40 a << 2 = 40 >> Bitwise Right Shift a = 10 a >> 2 = 2 a >> 2 = 2
- 7. Boolean Operators • There are three boolean operators that act on bool type literals and provide bool type output. The result of the boolean operators are either True or False. Operator Meaning Example Result and Boolean AND a = True, b = False a and b = True and False a and b = False or Boolean OR a = True, b = False a or b = True or False a or b = True not Boolean NOT a = True not a = not True not a = False
- 8. Membership Operators There are two membership operators in Python that are useful to test for membership in a sequence. • in: This operator returns True if an element is found in the specified sequence, otherwise it returns False. • not in: This operator returns True if any element is not found in the sequence, otherwise it returns True.
- 9. Identity Operators These operators are used to compare the memory locations of two objects. Therefore it is possible to verify whether the two objects are same or not. In Python id() function gives the memory location of an object. Example id(a) returns the identity number or memory location of object a. There are two identity operators available in Python. They are • is: This operator is used to compare the memory location of two objects. If they are same then it returns True, otherwise returns False. • is not: This operator returns True if the memory locations of two objects are not same.If they are same then it returns False.
- 10. Operator Precedence and Associativity • An expression may contain several operators and the order in which these operators are executed in sequence is called operator precedence. The following table summarizes the operators in descending order of their precedence. Operator Name Precedence ( ) Parenthesis 1st ** Exponentiation 2nd -, ~ Unary minus, bitwise complement 3rd *, /, //, % Multiplication, Division, Floor Division, Modulus 4th +, - Addition, Subtraction 5th <<, >> Bitwise left shift, bitwise right shift 6th & Bitwise AND 7th ^ Bitwise XOR 8th | Bitwise OR 9th >, >=, <, <=, = =, != Relational Operators 10th =, %=, /=, //=, -=, +=, *=, **= Assignment Operators 11th is, is not Identity Operators 12th in, not in Membership Operators 13th not Logical NOT 14th or Logical OR 15th and Logical AND 16th
- 11. Single Line and Multiline Comments • There are two types of comments used in Python: • Single Line Comments: These are created simply by starting a line with the hash character (#), and they are automatically terminated by the end of line. If a line using the hash character (#) is written after the Python statement, then it is known as inline comment. • Multiline Comments: When multiple lines are used as comment lines, then writing hash character (#) in the beginning of every line is a tedious task. So instead of writing # character in the beginning of every line, we can enclose multiple comment lines within ''' (triple single quotes) or """ (triple double quotes). Multi line comments are also known as block comments.
- 12. INPUT AND OUTPUT • The purpose of a computer is to process data and return results.The data given to the computer is called input. The results returned by the computer are called output. So, we can say that a computer takes input, processes that input and produces the output.