Parallel programming concept dependency and loop parallelization
Download as pptx, pdf1 like1,458 views
The document discusses parallel programming concepts, focusing on dependency types and loop parallelization. It categorizes dependencies into data and control types, exploring their implications in loop iterations. Additionally, it highlights various methodologies for loop parallelization, including distributed loops and different parallelism strategies.
1 of 27
Downloaded 15 times












![LOOP CARRIED DEPENDENCY
• In loop-carried dependence, statements in an
iteration of a loop depend on statements in
another iteration of the loop.
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
S1: b[i]=8;
S2: a[i]=b[i-1] + 10;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-15-320.jpg)
![LOOP INDEPENDENT DEPENDENCY
• In loop-independent dependence, loops have
inter-iteration dependence, but do not have
dependence between iterations.
• Each iteration may be treated as a block and
performed in parallel without other
synchronization efforts.
for (i=0;i<4;i++)
{
S1: b[i] = 8;
S2: a[i] =b[i] + 10;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-16-320.jpg)
![for (i=1; i<4; i++)
for (j=1; j<4; j++)
S3: a[i][j] = a[i][j-1] + 1;
Node : Point in the iteration space
Directed Edge: Dependency
Node: Point in the iteration space
Directed Edge: next point that will
be encountered
after the current point is
traversed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-17-320.jpg)


![Examples of Loop
parallelization
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
S1: L[i] = L[i] + 10;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
S1: L[i] = L[i - 1] + 10;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-20-320.jpg)
![Can the following Loop be made
Parallel?
for (i=1;i<=100;i=i+1)
{
A[i+1] = A[i] + C[i]; /*S1*/
B[i+1] = B[i] + A[i+1]; /*S2*/
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-21-320.jpg)

![DISTRIBUTED LOOP
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
{
S1: a[i] = a[i -1] + b[i];
S2: c[i] = c[i] + d[i];
}
loop1: for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
{
S1: a[i] = a[i -1] + b[i];
}
loop2: for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
{
S2: c[i] = c[i] + d[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-23-320.jpg)
![DO ALL PARALLELISM
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
S1: a[i] = b[i] + c[i];
}
begin_parallelism();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
S1: a[i] = b[i] + c[i];
end_parallelism();
}
block();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-24-320.jpg)
![DO ACROSS PARALLELISM
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
a[i] = a[i - 1] + b[i] + 1;
}
S1: int tmp = b[i] + 1;
S2: a[i] = a[i - 1] + tmp;
post(0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
S1: int tmp = b[i] + 1;
wait(i - 1);
S2: a[i] = a[i - 1] + tmp;
post(i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-25-320.jpg)
![DO PIPE PARALLELISM
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
S1: a[i] = a[i - 1] + b[i];
S2: c[i] = c[i] + a[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
S1: a[i] = a[i - 1] + b[i];
post(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
wait(i);
S2: c[i] = c[i] + a[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelprogrammingconceptdependencyandloopparallelization-170415054536/85/Parallel-programming-concept-dependency-and-loop-parallelization-26-320.jpg)

Ad
Recommended
Hardware multithreading
Hardware multithreadingFraboni Ec This document discusses three types of hardware multithreading: coarse-grained, fine-grained, and simultaneous multithreading (SMT). Coarse-grained multithreading allows another thread to run during long stalls of the first thread. Fine-grained multithreading interleaves instructions from multiple threads in a round-robin fashion to hide stalls. SMT issues instructions from multiple threads in the same cycle by using register renaming and dynamic scheduling to maximize utilization.
Routing protocols for ad hoc wireless networks
Routing protocols for ad hoc wireless networks Divya Tiwari The document discusses routing protocols for ad hoc wireless networks. It outlines several key challenges for these protocols, including mobility, bandwidth constraints, error-prone shared wireless channels, and hidden/exposed terminal problems. It also categorizes routing protocols based on how routing information is updated (proactively, reactively, or through a hybrid approach), whether they use past or future temporal network information, the type of network topology supported (flat or hierarchical), and how they account for specific resources like power.
Application layer in network system
Application layer in network systemSalauddin Rubel The application layer is the topmost layer of the OSI model. It provides services to software applications and users including email, file transfer, web access, and directory services. Domain Name Service (DNS) translates human-friendly domain names to IP addresses, allowing applications and users to access resources by name. Electronic mail systems use SMTP for message transfer between mail servers and access protocols like POP and IMAP for users to retrieve messages from their mailboxes on servers. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) underlies the World Wide Web, with clients making requests from and servers responding with web pages and other objects. While the application layer enables useful services, special client software or proxy servers may be required, and intensive processing is needed for applications
Digital Hierarchy
Digital Hierarchypaul4g This document discusses digital telecommunications hierarchies and transmission modes. It describes:
- Digital signal hierarchies including DS0, T1, E1, OC-1, STS-1, and STM-1.
- Transmission modes like parallel, serial, synchronous, and asynchronous.
- How digital voice is encoded by sampling at 8 kHz and using 8 bits per sample.
- The framing structures of T1 and E1 interfaces, including how they are composed of DS0 channels and use timeslots like TS0 for framing and TS16 for signaling.
Dependencies
DependenciesMuhammad Ishaq This document discusses different types of dependencies that can occur in programs:
- Data dependencies occur when an instruction refers to data from a previous instruction. There are three types: true data dependencies where an instruction depends on a previous result; output dependencies where two instructions write to the same register; and anti-dependencies where an instruction depends on data that could be overwritten.
- Control dependencies occur when the execution of one instruction depends on the outcome of another instruction, such as in an if-then statement.
- Resource conflicts occur when two instructions need the same hardware resource at the same time, such as a functional unit or register, stalling execution even if the instructions do not have a data or control dependency.
Presentation of the IEEE 802.11a MAC Layer
Presentation of the IEEE 802.11a MAC LayerMahdi Ahmed Jama The document provides an overview of the IEEE 802.11 MAC protocol through a presentation. It discusses topics such as IEEE 802.11 layers, channels, infrastructure networks, ad hoc networks, joining a network, synchronization, communication approaches, MAC functionality including PCF and DCF, encryption, fragmentation, management functions, and MAC frame formats. The presentation was given on May 9th, 2001 by Mahdi Ahmed Jama to provide an introduction to the IEEE 802.11a MAC protocol.
Arithmetic and RISC pipeline
Arithmetic and RISC pipelineManviGautam2 The document discusses arithmetic pipelines used in computers. It describes how pipelines divide sequential processes into sub-processes that execute concurrently. As an example, it explains the 4-part floating point addition and subtraction process, including comparing exponents, aligning mantissas, adding or subtracting mantissas, and producing the result. Registers are used to store intermediate results between operations. The document also briefly mentions that RISC pipelines typically have 2-3 segments - one to fetch instructions, one for ALU execution, and optionally one for storing results.
Unit 2 ppt 3.ppt
Unit 2 ppt 3.pptSelvakanmani S This document provides an overview of the data link layer and media access control. It discusses topics like link-layer addressing, data link layer protocols, framing, error control, flow control, and common data link layer protocols. It provides examples of finite state machines to illustrate the simple protocol and stop-and-wait protocol. Key points covered include how framing separates messages, the use of bit stuffing to avoid flag patterns in data, flow control using buffers, and acknowledgments for error control.
Multithreading Presentation
Multithreading PresentationNeeraj Kaushik Threads allow multiple tasks to run concurrently by sharing memory and resources within a process. Context switching between threads is typically faster than between processes. Threads can be created and started in different ways and use synchronization techniques like locks, monitors, mutexes, semaphores, and wait handles to coordinate access to resources. The thread pool optimizes thread usage by maintaining pooled threads that can be assigned tasks to run asynchronously. Exceptions on worker threads must be handled manually.
Program and Network Properties
Program and Network PropertiesBeekrum Duwal The document discusses the fundamentals of parallel programming, focusing on conditions for parallelism, program partitioning, scheduling, and interconnect architecture. It highlights the importance of understanding data and resource dependencies, compiler optimizations, and the trade-offs of granularity and latency in maximizing performance. Key concepts include the analysis of dependence graphs, the nature of hardware and software parallelism, and the role of system interconnects in efficient parallel processing.
Operating system 31 multiple processor scheduling
Operating system 31 multiple processor schedulingVaibhav Khanna The document discusses multiple-processor scheduling in operating systems, outlining key concepts such as symmetric and asymmetric multiprocessing, processor affinity, and load balancing strategies. It also covers real-time CPU scheduling criteria, including soft and hard real-time systems, along with various scheduling algorithms like rate monotonic and earliest deadline first scheduling. Additionally, it highlights the impact of virtualization on scheduling efficiency and response times.
Security in distributed systems
Security in distributed systems Haitham Ahmed The document outlines the importance of security in distributed systems, highlighting key concepts such as cryptography, secure channels, and access control. It discusses potential threats and attacks, including various types of attacks on integrity and authenticity, along with mechanisms to defend against these threats. Additionally, it covers cryptographic approaches, specifically symmetric and asymmetric systems, as well as secure communication protocols, emphasizing the significance of user authentication and data integrity.
Distributed Mutual exclusion algorithms
Distributed Mutual exclusion algorithmsMNM Jain Engineering College 1. There are two main approaches to distributed mutual exclusion - token-based and non-token based. Token based approaches use a shared token to allow only one process access at a time, while non-token approaches use message passing to determine access order.
2. A common token based algorithm uses a centralized coordinator process that grants access to the requesting process. Ring-based algorithms pass a token around a logical ring, allowing the process holding it to enter the critical section.
3. Lamport's non-token algorithm uses message passing of requests and timestamps to build identical request queues at each process, allowing the process at the head of the queue to enter the critical section. The Ricart-Agrawala
Concept of Pipelining
Concept of PipeliningSHAKOOR AB This document discusses instruction pipelining as a technique to improve computer performance. It explains that pipelining allows multiple instructions to be processed simultaneously by splitting instruction execution into stages like fetch, decode, execute, and write. While pipelining does not reduce the time to complete individual instructions, it improves throughput by allowing new instructions to begin processing before previous instructions have finished. The document outlines some challenges to achieving peak performance from pipelining, such as pipeline stalls from hazards like data dependencies between instructions. It provides examples of how data hazards can occur if the results of one instruction are needed by a subsequent instruction before they are available.
Local multipoint distribution service(lmds)
Local multipoint distribution service(lmds)Vivek Kumar The document discusses a seminar on Local Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS). LMDS is a wireless technology that provides high-capacity point-to-multipoint data access using low-powered signals in the 25-31 GHz range. The seminar covers the introduction, architecture, equipment, design issues, applications, and benefits of LMDS networks. Key topics include the cellular design of LMDS cells spaced 4-5 km apart, the use of highly directional antennas, and LMDS providing applications such as wireless LAN, broadband local loop, and transmission of voice, video, and data services.
WSN presentation
WSN presentationBraj Raj Singh The document presents a graduate project on efficient data aggregation from polling points in wireless sensor networks. The proposed system called Mobi-Cluster aims to minimize overall network overhead and energy expenditure associated with multi-hop data retrieval while ensuring balanced energy consumption and prolonged network lifetime. This is achieved through building cluster structures consisting of member nodes that route data to assigned cluster heads, and selecting appropriate polling points to act as intermediaries between clusters and a mobile collector. The key stages of the Mobi-Cluster protocol are described as cluster head selection, polling point selection, cluster head attachment to polling points, data aggregation and forwarding to polling points, and communication between polling points and the mobile collector.
Operating System: Deadlock
Operating System: DeadlockInteX Research Lab The document discusses the concept of deadlock in operating systems, providing definitions and examples, including a real-world analogy with trains. It outlines methods for deadlock prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery, as well as the use of the Banker's algorithm for safe resource allocation. Various examples are presented to illustrate safe and unsafe states in resource allocation scenarios.
memory Interleaving and low order interleaving and high interleaving
memory Interleaving and low order interleaving and high interleavingJawwad Rafiq Memory interleaving splits memory into independent banks that can process read/write requests in parallel to increase throughput. It interleaves the address space so consecutive addresses are assigned to different banks. Low order interleaving uses the low order bits of an address to identify the memory module and high order bits for the word address within each module, allowing block access in a pipelined fashion. This improves the effective memory bandwidth.
Email HTTP And FTP
Email HTTP And FTP Shishpal Vishnoi The birth of electronic mail occurred in 1965 at MIT. Ray Tomlinson sent the first message between two computers in 1971 using the "@" symbol to denote sending from one computer to another. Email was further developed to allow organization into folders and offline reading. Common email protocols include SMTP, POP3, and IMAP. Email is important as it saves time and money while allowing instant communication. HTTPS encrypts messages sent over HTTP for secure transmission. FTP allows two computers to connect over the internet and transfer files by converting them to binary for transmission.
Overview on NUMA
Overview on NUMAAbed Maatalla This document provides an overview of Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architecture, which allows processors to access their own local memory faster than remote memory, promoting scalability in large symmetric multiprocessing systems. It discusses historical developments in processor technology, technical details of NUMA architecture, barriers, solutions, and existing simulators for performance evaluation. The implications of NUMA on memory access efficiency and its role in addressing the challenges of scaling SMP CPUs are highlighted.
Tcp Udp Icmp And The Transport Layer
Tcp Udp Icmp And The Transport Layertmavroidis This document summarizes several internet protocols including IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP. It describes key aspects of each protocol such as their purpose, packet structure, error handling mechanisms, and how they interact to enable communication over the internet. IP is a connectionless protocol that forwards packets based on destination addresses. TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols, with TCP providing reliable connections and UDP being connectionless. ICMP provides error reporting and control for IP. Port numbers and sockets are used to direct communication to specific applications.
Embedded Systems (18EC62) - ARM Cortex-M3 Instruction Set and Programming (Mo...
Embedded Systems (18EC62) - ARM Cortex-M3 Instruction Set and Programming (Mo...Shrishail Bhat The document discusses the ARM Cortex-M3 instruction set and programming for embedded systems, specifically focusing on the syntax and operation of assembler language. It covers basic syntax, data movement, memory access, and various instruction formats, including both 16-bit and 32-bit operations. Additionally, it highlights the unified assembler language (UAL) that allows easier code portability between ARM and Thumb instruction sets.
multiplexing
multiplexingSrinivasa Rao This document discusses multiplexing techniques for transmitting multiple communication signals over a single transmission medium. It covers frequency division multiplexing (FDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), and statistical TDM. FDM involves splitting the transmission bandwidth into multiple frequency bands, one for each signal. TDM involves splitting time into intervals and assigning each signal to a time slot. Statistical TDM dynamically allocates time slots based on demand. Examples of technologies that use these techniques include analog carrier systems, SONET/SDH digital networks, cable modems, ADSL internet, and various xDSL technologies.
11. dfs
11. dfsDr Sandeep Kumar Poonia The document discusses distributed file systems (DFS), which enable multiple machines to share files transparently and provide services such as storage, naming, and caching. It highlights the advantages of user mobility, fault tolerance, and scalability while addressing concerns about cache consistency and performance. Various file accessing models, implementation techniques, and examples like Sun NFS and the Andrew File System are also described, illustrating the complexities of maintaining consistency and reliability in distributed environments.
Chapter 3: Data & Signals
Chapter 3: Data & SignalsShafaan Khaliq Bhatti This document discusses analog and digital signals. It begins by explaining that data can be either analog or digital. Analog data are continuous and take on continuous values, while digital data have discrete states and take discrete values. Signals can also be analog or digital. Analog signals can have an infinite number of values within a range, while digital signals can have only a limited number of discrete values. Periodic analog signals such as sine waves are discussed, along with their properties including frequency, period, amplitude, phase, and wavelength. Composite signals made up of multiple sine waves are also covered. The document then discusses digital signals and how they can be represented by analog signals.
Deadlock avoidance (Safe State, Resource Allocation Graph Algorithm)
Deadlock avoidance (Safe State, Resource Allocation Graph Algorithm)Shayek Parvez This document summarizes key concepts related to deadlock avoidance in operating systems. It discusses the four conditions for deadlock, describes the concept of a safe state for resource allocation, and provides an example of modeling resource allocation using a resource allocation graph. The document is presented as part of a course on operating systems, covering topics such as deadlock avoidance, safe state determination, and modeling resource allocation through graphs.
Multi-Hopping
Multi-HoppingAditya Pandey The document discusses multi-hopping in wireless networks. Multi-hopping occurs when there is no direct communication link between the source and target, so the signal passes through one or more intermediate nodes. It describes the working of multi-hop networks using an example. There are two main types - mobile ad hoc networks which do not require fixed infrastructure, and multi-hop cellular networks which use relays to improve coverage and throughput. Some applications of multi-hop networks mentioned are battlefield communication, emergency response systems, and cellular networks.
Types and Functions of DDBMS
Types and Functions of DDBMSAdeel Rasheed This document discusses types and functions of distributed database management systems (DDBMS). There are two main types of DDBMS: homogeneous and heterogeneous. A homogeneous DDBMS uses similar software across sites, while a heterogeneous DDBMS uses different schemas and software. Basic functions of a DDBMS include data storage, security, multi-user access control, and data integrity. Additional functions are extended communication services, distributed query processing, extended concurrency control, and extended recovery services.
Optimization Techniques
Optimization TechniquesJoud Khattab This document discusses various optimization techniques used in computer architecture, including instruction level parallelism, loop optimization, software pipelining, and out-of-order execution. It provides examples of how scheduling, loop transformations like unrolling and parallelization, and hiding instruction latencies through techniques like software pipelining can improve performance. Additionally, it contrasts in-order versus out-of-order execution, noting that out-of-order allows independent instructions to execute around stalled instructions for better throughput.
Loop Unroll_ACA_CS505.ppt
Loop Unroll_ACA_CS505.pptHassanJavaid48 The document discusses instruction level parallelism (ILP) and how to exploit it through static loop unrolling. ILP refers to the inherent parallelism in a sequence of instructions that allows some to execute concurrently. Static loop unrolling makes copies of the loop body to reduce loop overhead and expose more parallelism by scheduling instructions from different iterations together. While this can improve performance, loop unrolling increases code size and register pressure and is difficult to apply when the number of iterations is unknown.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Multithreading Presentation
Multithreading PresentationNeeraj Kaushik Threads allow multiple tasks to run concurrently by sharing memory and resources within a process. Context switching between threads is typically faster than between processes. Threads can be created and started in different ways and use synchronization techniques like locks, monitors, mutexes, semaphores, and wait handles to coordinate access to resources. The thread pool optimizes thread usage by maintaining pooled threads that can be assigned tasks to run asynchronously. Exceptions on worker threads must be handled manually.
Program and Network Properties
Program and Network PropertiesBeekrum Duwal The document discusses the fundamentals of parallel programming, focusing on conditions for parallelism, program partitioning, scheduling, and interconnect architecture. It highlights the importance of understanding data and resource dependencies, compiler optimizations, and the trade-offs of granularity and latency in maximizing performance. Key concepts include the analysis of dependence graphs, the nature of hardware and software parallelism, and the role of system interconnects in efficient parallel processing.
Operating system 31 multiple processor scheduling
Operating system 31 multiple processor schedulingVaibhav Khanna The document discusses multiple-processor scheduling in operating systems, outlining key concepts such as symmetric and asymmetric multiprocessing, processor affinity, and load balancing strategies. It also covers real-time CPU scheduling criteria, including soft and hard real-time systems, along with various scheduling algorithms like rate monotonic and earliest deadline first scheduling. Additionally, it highlights the impact of virtualization on scheduling efficiency and response times.
Security in distributed systems
Security in distributed systems Haitham Ahmed The document outlines the importance of security in distributed systems, highlighting key concepts such as cryptography, secure channels, and access control. It discusses potential threats and attacks, including various types of attacks on integrity and authenticity, along with mechanisms to defend against these threats. Additionally, it covers cryptographic approaches, specifically symmetric and asymmetric systems, as well as secure communication protocols, emphasizing the significance of user authentication and data integrity.
Distributed Mutual exclusion algorithms
Distributed Mutual exclusion algorithmsMNM Jain Engineering College 1. There are two main approaches to distributed mutual exclusion - token-based and non-token based. Token based approaches use a shared token to allow only one process access at a time, while non-token approaches use message passing to determine access order.
2. A common token based algorithm uses a centralized coordinator process that grants access to the requesting process. Ring-based algorithms pass a token around a logical ring, allowing the process holding it to enter the critical section.
3. Lamport's non-token algorithm uses message passing of requests and timestamps to build identical request queues at each process, allowing the process at the head of the queue to enter the critical section. The Ricart-Agrawala
Concept of Pipelining
Concept of PipeliningSHAKOOR AB This document discusses instruction pipelining as a technique to improve computer performance. It explains that pipelining allows multiple instructions to be processed simultaneously by splitting instruction execution into stages like fetch, decode, execute, and write. While pipelining does not reduce the time to complete individual instructions, it improves throughput by allowing new instructions to begin processing before previous instructions have finished. The document outlines some challenges to achieving peak performance from pipelining, such as pipeline stalls from hazards like data dependencies between instructions. It provides examples of how data hazards can occur if the results of one instruction are needed by a subsequent instruction before they are available.
Local multipoint distribution service(lmds)
Local multipoint distribution service(lmds)Vivek Kumar The document discusses a seminar on Local Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS). LMDS is a wireless technology that provides high-capacity point-to-multipoint data access using low-powered signals in the 25-31 GHz range. The seminar covers the introduction, architecture, equipment, design issues, applications, and benefits of LMDS networks. Key topics include the cellular design of LMDS cells spaced 4-5 km apart, the use of highly directional antennas, and LMDS providing applications such as wireless LAN, broadband local loop, and transmission of voice, video, and data services.
WSN presentation
WSN presentationBraj Raj Singh The document presents a graduate project on efficient data aggregation from polling points in wireless sensor networks. The proposed system called Mobi-Cluster aims to minimize overall network overhead and energy expenditure associated with multi-hop data retrieval while ensuring balanced energy consumption and prolonged network lifetime. This is achieved through building cluster structures consisting of member nodes that route data to assigned cluster heads, and selecting appropriate polling points to act as intermediaries between clusters and a mobile collector. The key stages of the Mobi-Cluster protocol are described as cluster head selection, polling point selection, cluster head attachment to polling points, data aggregation and forwarding to polling points, and communication between polling points and the mobile collector.
Operating System: Deadlock
Operating System: DeadlockInteX Research Lab The document discusses the concept of deadlock in operating systems, providing definitions and examples, including a real-world analogy with trains. It outlines methods for deadlock prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery, as well as the use of the Banker's algorithm for safe resource allocation. Various examples are presented to illustrate safe and unsafe states in resource allocation scenarios.
memory Interleaving and low order interleaving and high interleaving
memory Interleaving and low order interleaving and high interleavingJawwad Rafiq Memory interleaving splits memory into independent banks that can process read/write requests in parallel to increase throughput. It interleaves the address space so consecutive addresses are assigned to different banks. Low order interleaving uses the low order bits of an address to identify the memory module and high order bits for the word address within each module, allowing block access in a pipelined fashion. This improves the effective memory bandwidth.
Email HTTP And FTP
Email HTTP And FTP Shishpal Vishnoi The birth of electronic mail occurred in 1965 at MIT. Ray Tomlinson sent the first message between two computers in 1971 using the "@" symbol to denote sending from one computer to another. Email was further developed to allow organization into folders and offline reading. Common email protocols include SMTP, POP3, and IMAP. Email is important as it saves time and money while allowing instant communication. HTTPS encrypts messages sent over HTTP for secure transmission. FTP allows two computers to connect over the internet and transfer files by converting them to binary for transmission.
Overview on NUMA
Overview on NUMAAbed Maatalla This document provides an overview of Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architecture, which allows processors to access their own local memory faster than remote memory, promoting scalability in large symmetric multiprocessing systems. It discusses historical developments in processor technology, technical details of NUMA architecture, barriers, solutions, and existing simulators for performance evaluation. The implications of NUMA on memory access efficiency and its role in addressing the challenges of scaling SMP CPUs are highlighted.
Tcp Udp Icmp And The Transport Layer
Tcp Udp Icmp And The Transport Layertmavroidis This document summarizes several internet protocols including IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP. It describes key aspects of each protocol such as their purpose, packet structure, error handling mechanisms, and how they interact to enable communication over the internet. IP is a connectionless protocol that forwards packets based on destination addresses. TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols, with TCP providing reliable connections and UDP being connectionless. ICMP provides error reporting and control for IP. Port numbers and sockets are used to direct communication to specific applications.
Embedded Systems (18EC62) - ARM Cortex-M3 Instruction Set and Programming (Mo...
Embedded Systems (18EC62) - ARM Cortex-M3 Instruction Set and Programming (Mo...Shrishail Bhat The document discusses the ARM Cortex-M3 instruction set and programming for embedded systems, specifically focusing on the syntax and operation of assembler language. It covers basic syntax, data movement, memory access, and various instruction formats, including both 16-bit and 32-bit operations. Additionally, it highlights the unified assembler language (UAL) that allows easier code portability between ARM and Thumb instruction sets.
multiplexing
multiplexingSrinivasa Rao This document discusses multiplexing techniques for transmitting multiple communication signals over a single transmission medium. It covers frequency division multiplexing (FDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), and statistical TDM. FDM involves splitting the transmission bandwidth into multiple frequency bands, one for each signal. TDM involves splitting time into intervals and assigning each signal to a time slot. Statistical TDM dynamically allocates time slots based on demand. Examples of technologies that use these techniques include analog carrier systems, SONET/SDH digital networks, cable modems, ADSL internet, and various xDSL technologies.
11. dfs
11. dfsDr Sandeep Kumar Poonia The document discusses distributed file systems (DFS), which enable multiple machines to share files transparently and provide services such as storage, naming, and caching. It highlights the advantages of user mobility, fault tolerance, and scalability while addressing concerns about cache consistency and performance. Various file accessing models, implementation techniques, and examples like Sun NFS and the Andrew File System are also described, illustrating the complexities of maintaining consistency and reliability in distributed environments.
Chapter 3: Data & Signals
Chapter 3: Data & SignalsShafaan Khaliq Bhatti This document discusses analog and digital signals. It begins by explaining that data can be either analog or digital. Analog data are continuous and take on continuous values, while digital data have discrete states and take discrete values. Signals can also be analog or digital. Analog signals can have an infinite number of values within a range, while digital signals can have only a limited number of discrete values. Periodic analog signals such as sine waves are discussed, along with their properties including frequency, period, amplitude, phase, and wavelength. Composite signals made up of multiple sine waves are also covered. The document then discusses digital signals and how they can be represented by analog signals.
Deadlock avoidance (Safe State, Resource Allocation Graph Algorithm)
Deadlock avoidance (Safe State, Resource Allocation Graph Algorithm)Shayek Parvez This document summarizes key concepts related to deadlock avoidance in operating systems. It discusses the four conditions for deadlock, describes the concept of a safe state for resource allocation, and provides an example of modeling resource allocation using a resource allocation graph. The document is presented as part of a course on operating systems, covering topics such as deadlock avoidance, safe state determination, and modeling resource allocation through graphs.
Multi-Hopping
Multi-HoppingAditya Pandey The document discusses multi-hopping in wireless networks. Multi-hopping occurs when there is no direct communication link between the source and target, so the signal passes through one or more intermediate nodes. It describes the working of multi-hop networks using an example. There are two main types - mobile ad hoc networks which do not require fixed infrastructure, and multi-hop cellular networks which use relays to improve coverage and throughput. Some applications of multi-hop networks mentioned are battlefield communication, emergency response systems, and cellular networks.
Types and Functions of DDBMS
Types and Functions of DDBMSAdeel Rasheed This document discusses types and functions of distributed database management systems (DDBMS). There are two main types of DDBMS: homogeneous and heterogeneous. A homogeneous DDBMS uses similar software across sites, while a heterogeneous DDBMS uses different schemas and software. Basic functions of a DDBMS include data storage, security, multi-user access control, and data integrity. Additional functions are extended communication services, distributed query processing, extended concurrency control, and extended recovery services.
Similar to Parallel programming concept dependency and loop parallelization (20)
Optimization Techniques
Optimization TechniquesJoud Khattab This document discusses various optimization techniques used in computer architecture, including instruction level parallelism, loop optimization, software pipelining, and out-of-order execution. It provides examples of how scheduling, loop transformations like unrolling and parallelization, and hiding instruction latencies through techniques like software pipelining can improve performance. Additionally, it contrasts in-order versus out-of-order execution, noting that out-of-order allows independent instructions to execute around stalled instructions for better throughput.
Loop Unroll_ACA_CS505.ppt
Loop Unroll_ACA_CS505.pptHassanJavaid48 The document discusses instruction level parallelism (ILP) and how to exploit it through static loop unrolling. ILP refers to the inherent parallelism in a sequence of instructions that allows some to execute concurrently. Static loop unrolling makes copies of the loop body to reduce loop overhead and expose more parallelism by scheduling instructions from different iterations together. While this can improve performance, loop unrolling increases code size and register pressure and is difficult to apply when the number of iterations is unknown.
Parallel Computing with SolrCloud: Presented by Joel Bernstein, Alfresco
Parallel Computing with SolrCloud: Presented by Joel Bernstein, AlfrescoLucidworks This document summarizes Joel Bernstein's presentation on parallel SQL in Solr 6.0. The key points are:
1. SQL provides an optimizer to choose the best query plan for complex queries in Solr, avoiding the need for users to determine optimal faceting APIs or parameters.
2. SQL queries in Solr 6.0 can perform distributed joins, aggregations, sorting, and filtering using Solr search predicates. Aggregations can be performed using either map-reduce or facets.
3. Under the hood, SQL queries are compiled to TupleStreams which are serialized to Streaming Expressions and executed in parallel across worker collections using Solr's streaming API framework.
Parallel SQL for SolrCloud
Parallel SQL for SolrCloudJoel Bernstein This document summarizes Joel Bernstein's presentation on parallel SQL in Solr. The key points are:
1. SQL provides an easier way for users to query Solr compared to its other complex APIs, and SQL queries can be optimized.
2. Solr 6.0 introduces a SQL interface that supports high-cardinality aggregations, distributed joins, and Solr search predicates.
3. Under the hood, SQL queries are compiled into TupleStreams and executed in parallel across worker collections using a streaming API and expressions. This allows massive throughput for queries.
Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra (part 2)
Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra (part 2)Frankie Jones The document discusses Boolean algebra and logic gates. It defines logic gates, explains their operations, and provides their logic symbols and truth tables. The types of logic gates covered are AND, OR, NOT, NOR, NAND, XOR, and XNOR. It also discusses sequential logic circuits like flip-flops, providing details on SR, JK, T, and D flip-flops including how to build them using logic gates. Additional topics covered include the difference between combinational and sequential logic circuits, Boolean theorems, sum-of-products and product-of-sums expressions, and the Karnaugh map method for simplifying logic expressions.
LOOP STATEMENTS AND TYPES OF LOOP IN C LANGUAGE BY RIZWAN
LOOP STATEMENTS AND TYPES OF LOOP IN C LANGUAGE BY RIZWANMD RIZWAN MOLLA The document provides an extensive overview of loop structures in C programming, including definitions, types, syntax, and control statements such as break and continue. It explains three main types of loops— for, while, and do-while—along with their use cases and practical applications in real-world scenarios like data processing and game development. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of mastering loops for efficient coding and outlines best practices for implementing them.
Data Flow Modeling
Data Flow ModelingPadmanaban Kalyanaraman The document describes data flow modeling in VHDL. It discusses how data flow style architecture models hardware in terms of the movement of data over continuous time between combinational logic components. It also describes how concurrent signal assignment statements can be used to model simple combinational logic. Examples provided include half adder, full adder, comparator, multiplexer, decoder, and arithmetic logic unit designs modeled using data flow style and concurrent signal assignments.
Dzanan_Bajgoric_C2CUDA_MscThesis_Present
Dzanan_Bajgoric_C2CUDA_MscThesis_PresentDžanan Bajgorić The document is a master's thesis titled "Automatic Program Parallelization for GPU Environment". It discusses using a compiler called C2CUDA to automatically parallelize sequential C programs for execution on a GPU. The thesis presents techniques for data dependence analysis and loop transformations to expose parallelism. It also provides results of experiments parallelizing matrix operations and magnetic resonance imaging algorithms using C2CUDA. Speedups of up to 58x were achieved for the parallelized applications compared to sequential execution.
Cursor
CursorJay Patel Cursors in SQL procedures allow defining a result set that can be iterated through row by row. A cursor acts as a pointer to each row in the result set. To use a cursor, it must be declared to define the result set, opened to establish the result set, rows must be fetched from the cursor one at a time into variables, and the cursor closed once complete. The example demonstrates declaring a cursor for a SELECT statement, fetching rows and summing a value, and closing the cursor to return the result.
Cursor
CursorJay Patel Cursors in SQL procedures allow defining a result set that can be iterated through row by row. A cursor acts as a pointer to each row in turn. To use a cursor, it must be declared to define the result set, opened to establish the set, individual rows can then be fetched and processed one at a time using variables, and the cursor is closed once complete. Basic cursor usage involves the DECLARE, OPEN, FETCH and CLOSE statements. An example demonstrates summing the salaries from an employee table by declaring a cursor over it, fetching rows into a variable and accumulating the sum in a loop.
parallel programming.ppt
parallel programming.pptnazimsattar The document discusses parallel programming concepts like synchronization and data parallelism. It provides examples of regularly parallelizable problems like matrix multiplication and SOR that can divide the data among processors. Irregular problems like molecular dynamics also have parallelizable loops but require more sophisticated partitioning due to load balancing issues from varying neighbor counts per molecule. Synchronization is needed between loops to ensure correct parallel execution.
VLSI Lab manual PDF
VLSI Lab manual PDFUR11EC098 The document describes the design and simulation of half adders, full adders, multiplexers, and demultiplexers using VHDL. It includes block diagrams, truth tables, and VHDL code for implementing these circuits using dataflow, behavioral, and structural modeling in Xilinx ISE. Code examples and output waveforms are provided for half adders, full adders, 4-to-1 multiplexers, and 1-to-4 demultiplexers. The aim is to learn how to design and simulate basic digital circuits using different VHDL modeling approaches.
Pavlo Zhdanov "Mastering solid and base principles for software design"
Pavlo Zhdanov "Mastering solid and base principles for software design"LogeekNightUkraine The document discusses SOLID principles and other principles of software design including single responsibility, open/closed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, and dependency inversion. It provides definitions and examples of each. The SOLID principles aim to create simple, modular, and understandable code by establishing best practices for class design. Additional design principles discussed ensure reusable, cohesive components with stable dependencies and abstractions.
Algorithms of graph
Algorithms of graphgetacew The document discusses connected components and directed graphs, explaining how to determine if vertices are connected or if a graph is acyclic and connected (defining trees). It introduces algorithms such as BFS and DFS to check connectivity, and it details the process of topological sorting for directed acyclic graphs. Additionally, it covers concepts like indegree, outdegree, and their significance in representing task dependencies in directed graphs.
Lab9 processos
Lab9 processosEduardo Bezerra This document describes digital systems and processes in VHDL. It includes sections on implicit and explicit processes, comparison and selection in explicit processes, and a case study on using an explicit process to implement an asynchronous reset register with a clock and enable signal. Examples are provided of implicit process assignments, explicit processes using if/else statements and case statements, and shift registers with asynchronous reset. Templates for common constructs like registers and counters using explicit processes are also shown from Quartus II.
Realtime Analytics
Realtime AnalyticseXascale Infolab The document discusses the challenges and strategies in real-time analytics on big data, emphasizing the importance of velocity and volume. It highlights the limitations of current computational architectures and the failure of Moore's Law, proposing incrementalization, small data approaches, and parallelization as potential paths to improve performance. Additionally, it introduces concepts like ripple joins and incremental view maintenance for efficient data processing in dynamic environments.
Number_Systems_and_Boolean_Algebra.ppt
Number_Systems_and_Boolean_Algebra.pptVEERA BOOPATHY E The document provides an overview of number systems, arithmetic operations, binary codes, and Boolean algebra, along with their properties and theorems. It covers conversions between various numeral systems, including binary, octal, and hexadecimal, as well as logic gates and circuits used in digital electronics. Additionally, it discusses Karnaugh maps for simplifying Boolean expressions.
Compiling openCypher graph queries with Spark Catalyst
Compiling openCypher graph queries with Spark CatalystGábor Szárnyas The document discusses the development of a scalable graph query engine utilizing OpenCypher and Spark Catalyst, focusing on incrementally maintaining views of large graphs with complex queries. It explains the use of a cache for efficient evaluation and highlights various research objectives, including support for incremental views and pattern matching in graph databases. Key research initiatives and benchmarks, such as the LDBC social network benchmark, are also addressed, showcasing the framework and tools supporting graph data management and analytics.
m4_VHDL_ED.pdf
m4_VHDL_ED.pdfJonGarciario This document provides an overview of VHDL including libraries and types, conditional statements like WHEN ELSE and WITH SELECT, processes, components, testbenches and simulation. It discusses libraries, entity-architecture structure, data types, operators, objects like signals and variables. It also covers various VHDL constructs like if-then-else, case, for loops, processes, and how to describe combinational circuits.
Digital System Design Lab Report - VHDL ECE
Digital System Design Lab Report - VHDL ECERamesh Naik Bhukya The document describes the implementation of 16-bit and 64-bit shift registers using VHDL in data flow modeling. It includes the VHDL code, test bench, and simulation results for shift registers that shift the values in the input register right by 1 bit position on the positive edge of the clock. The 16-bit shift register outputs the shifted value on q1 and the 64-bit shift register outputs the shifted value on q2. The design and functionality of both shift registers are verified through simulation.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
LDMMIA GRAD Student Check-in Orientation Sampler
LDMMIA GRAD Student Check-in Orientation SamplerLDM & Mia eStudios Completed Tuesday June 10th.
An Orientation Sampler of 8 pages.
It helps to understand the text behind anything. This improves our performance and confidence.
Your training will be mixed media. Includes Rehab Intro and Meditation vods, all sold separately.
Editing our Vods & New Shop.
Retail under $30 per item. Store Fees will apply. Digital Should be low cost.
I am still editing the package. I wont be done until probably July? However; Orientation and Lecture 1 (Videos) will be available soon. Media will vary between PDF and Instruction Videos.
Thank you for attending our free workshops. Those can be used with any Reiki Yoga training package. Traditional Reiki does host rules and ethics. Its silent and within the JP Culture/Area/Training/Word of Mouth. It allows remote healing but there’s limits for practitioners and masters. We are not allowed to share certain secrets/tools. Some content is designed only for “Masters”. Some yoga are similar like the Kriya Yoga-Church (Vowed Lessons). We will review both Reiki and Yoga (Master symbols) later on. Sounds Simple but these things host Energy Power/Protection.
Imagine This package will be a supplement or upgrade for professional Reiki. You can create any style you need.
♥♥♥
•* ́ ̈ ̧.•
(Job) Tech for students: In short, high speed is essential. (Space, External Drives, virtual clouds)
Fast devices and desktops are important. Please upgrade your technology and office as needed and timely. - MIA J. Tech Dept (Timeless)
♥♥♥
•* ́ ̈ ̧.•
Copyright Disclaimer 2007-2025+: These lessons are not to be copied or revised without the
Author’s permission. These Lessons are designed Rev. Moore to instruct and guide students on the path to holistic health and wellness.
It’s about expanding your Nature Talents, gifts, even Favorite Hobbies.
♥♥♥
•* ́ ̈ ̧.•
First, Society is still stuck in the matrix. Many of the spiritual collective, say the matrix crashed. Its now collapsing. This means anything lower, darker realms, astral, and matrix are below 5D. 5D is thee trend. It’s our New Dimensional plane. However; this plane takes work ethic,
integration, and self discovery. ♥♥♥
•* ́ ̈ ̧.•
We don’t need to slave, mule, or work double shifts to fuse Reiki lol. It should blend naturally within our lifestyles. Same with Yoga. There’s no
need to use all the poses/asanas. For under a decade, my fav exercises are not asanas but Pilates. It’s all about Yoga-meditation when using Reiki. (Breaking old myths.)
Thank You for reading our Orientation Sampler. The Workshop is 14 pages on introduction. These are a joy and effortless to produce/make.
Webcrawler_Mule_AIChain_MuleSoft_Meetup_Hyderabad
Webcrawler_Mule_AIChain_MuleSoft_Meetup_HyderabadVeera Pallapu 1. MuleSoft AI Chain Concept Introduction
2. Demo on Mule AI Chain Connector
3. Q/A
4. Wrap up
Unit- 4 Biostatistics & Research Methodology.pdf
Unit- 4 Biostatistics & Research Methodology.pdfKRUTIKA CHANNE Blocking and confounding (when a third variable, or confounder, influences both the exposure and the outcome) system for Two-level factorials (a type of experimental design where each factor (independent variable) is investigated at only two levels, typically denoted as "high" and "low" or "+1" and "-1")
Regression modeling (statistical model that estimates the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables using a line): Hypothesis testing in Simple and Multiple regression models
Introduction to Practical components of Industrial and Clinical Trials Problems: Statistical Analysis Using Excel, SPSS, MINITAB®️, DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS, R - Online Statistical Software to Industrial and Clinical trial approach
Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptx
Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptxbobby205207 Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptx
Introduction to Generative AI and Copilot.pdf
Introduction to Generative AI and Copilot.pdfTechSoup In this engaging and insightful two-part webinar series, where we will dive into the essentials of generative AI, address key AI concerns, and demonstrate how nonprofits can benefit from using Microsoft’s AI assistant, Copilot, to achieve their goals.
This event series to help nonprofits obtain Copilot skills is made possible by generous support from Microsoft.
How to Configure Vendor Management in Lunch App of Odoo 18
How to Configure Vendor Management in Lunch App of Odoo 18Celine George The Vendor management in the Lunch app of Odoo 18 is the central hub for managing all aspects of the restaurants or caterers that provide food for your employees.
THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION included definition, characteristics, nurse patient...
THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION included definition, characteristics, nurse patient...parmarjuli1412 The document provides an overview of therapeutic communication, emphasizing its importance in nursing to address patient needs and establish effective relationships. THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION included some topics like introduction of COMMUNICATION, definition, types, process of communication, definition therapeutic communication, goal, techniques of therapeutic communication, non-therapeutic communication, few ways to improved therapeutic communication, characteristics of therapeutic communication, barrier of THERAPEUTIC RELATIONSHIP, introduction of interpersonal relationship, types of IPR, elements/ dynamics of IPR, introduction of therapeutic nurse patient relationship, definition, purpose, elements/characteristics , and phases of therapeutic communication, definition of Johari window, uses, what actually model represent and its areas, THERAPEUTIC IMPASSES and its management in 5th semester Bsc. nursing and 2nd GNM students
LDMMIA Spring Ending Guest Grad Student News
LDMMIA Spring Ending Guest Grad Student NewsLDM & Mia eStudios Available Sun June 8th, for Weekend June 14th/15th.
Timeless for Summer 25.
Our libraries do host classes for a year plus in most shops. Timelines do vary.
See also our Workshops 8, 9, and 2 Grad/Guest Updates.
Workshop 9 was uploaded early also for Weekend June 14th/15th.
Reiki Yoga Level 1 - Practitioner Studies. For our June Schedules
I luv the concept of effortless learning. My Background includes traditional & Distant Education. My Fav classes were online. A few on Campus recent years.
So, for LDMMIA I believe in Self-Help, Self-Care, Self-Serve lol. “How can my followers/readers privately attend courses?” So this season, I do want to expand our new Merch Shop. This includes digital production like no other - Wow. More Updates this Mo lol.
Merch Host: teespring.com
PEST OF WHEAT SORGHUM BAJRA and MINOR MILLETS.pptx
PEST OF WHEAT SORGHUM BAJRA and MINOR MILLETS.pptxArshad Shaikh Wheat, sorghum, and bajra (pearl millet) are susceptible to various pests that can significantly impact crop yields. Common pests include aphids, stem borers, shoot flies, and armyworms. Aphids feed on plant sap, weakening the plants, while stem borers and shoot flies damage the stems and shoots, leading to dead hearts and reduced growth. Armyworms, on the other hand, are voracious feeders that can cause extensive defoliation and grain damage. Effective management strategies, including resistant varieties, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide applications, are essential to mitigate pest damage and ensure healthy crop production.
Paper 108 | Thoreau’s Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil Disobedience
Paper 108 | Thoreau’s Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil DisobedienceRajdeep Bavaliya Dive into the powerful journey from Thoreau’s 19th‑century essay to Gandhi’s mass movement, and discover how one man’s moral stand became the backbone of nonviolent resistance worldwide. Learn how conscience met strategy to spark revolutions, and why their legacy still inspires today’s social justice warriors. Uncover the evolution of civil disobedience. Don’t forget to like, share, and follow for more deep dives into the ideas that changed the world.
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 108: The American Literature
Submitted Date: April 2, 2025
Paper Name: The American Literature
Topic: Thoreau’s Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil Disobedience
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/HXeq6utg7iQ
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/thoreau-s-influence-on-gandhi-the-evolution-of-civil-disobedience.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#CivilDisobedience #ThoreauToGandhi #NonviolentResistance #Satyagraha #Transcendentalism #SocialJustice #HistoryUncovered #GandhiLegacy #ThoreauInfluence #PeacefulProtest
Keyword Tags:
civil disobedience, Thoreau, Gandhi, Satyagraha, nonviolent protest, transcendentalism, moral resistance, Gandhi Thoreau connection, social change, political philosophy
Overview of Employee in Odoo 18 - Odoo Slides
Overview of Employee in Odoo 18 - Odoo SlidesCeline George The employee module is a core component of the HR workspace that helps the business to get the employee activities and details. This would also allow you to get the employee details by acting as a centralized system and accessing, updating, and managing all the other employee data.
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big Cycle
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big CycleDadang Solihin A complete and practical understanding of the Big Debt Cycle. A much more practical understanding of how supply and demand really work compared to the conventional economic thinking. A complete and practical understanding of the Overall Big Cycle, which is driven by the Big Debt Cycle and the other major cycles, including the big political cycle within countries that changes political orders and the big geopolitical cycle that changes world orders.
How to Create an Event in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 Slides
How to Create an Event in Odoo 18 - Odoo 18 SlidesCeline George Creating an event in Odoo 18 is a straightforward process that allows you to manage various aspects of your event efficiently.
Odoo 18 Events Module is a powerful tool for organizing and managing events of all sizes, from conferences and workshops to webinars and meetups.
Exploring Ocean Floor Features for Middle School
Exploring Ocean Floor Features for Middle SchoolMarie This 16 slide science reader is all about ocean floor features. It was made to use with middle school students.
You can download the PDF at thehomeschooldaily.com
Thanks! Marie
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecdrazelitouali Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Ad
Parallel programming concept dependency and loop parallelization
- 1. PARALLEL PROGRAMMING CONCEPT DEPENDENCY AND LOOP PARALLELIZATION •Parallel programming concept and their examples •Dependency and their two types with examples •Loop parallelism and their types with examples R.AISHWARYA
- 4. • Simultaneous use of multiple compute resources to solve a computational problem • Compute resources • Primary reasons • Best practices • Goals • Steps
- 8. Statement 2: b=a+2; “5” Statement 1: a=5;
- 9. •Find dependencies within iterations of a loop •Goal of determining different relationships between statements. •To allow multiple processors to work on different portions of the loop in parallel •First analyze the dependencies within individual loops. •It help determine which statements in the loop need to be completed before other statements can start. •Two general categories of dependencies: Data and Control dependency
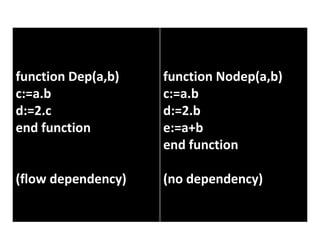
- 10. function Dep(a,b) c:=a.b d:=2.c end function (flow dependency) function Nodep(a,b) c:=a.b d:=2.b e:=a+b end function (no dependency)
- 11. DATA DEPENDENCY TYPE NOTATION DESCRIPTION True (Flow) Dependence S1 ->T S2 A true dependence between S1 and S2 means that S1 writes to a location later read from by S2 Anti Dependence S1 ->A S2 An anti-dependence between S1 and S2 means that S1 reads from a location later written to by S2.(before) Output Dependence S1 ->I S2 An input dependence between S1 and S2 means that S1 and S2 read from the same location.
- 12. EXAMPLES True dependence S0: int a, b; S1: a = 2; S2: b = a + 40; S1 ->T S2, meaning that S1 has a true dependence on S2 because S1writes to the variable a, which S2 reads from. Anti-dependence S0: int a, b = 40; S1: a = b - 38; S2: b = -1; S1 ->A S2, meaning that S1 has an anti-dependence on S2 because S1reads from the variable b before S2 writes to it. Output-dependence S0: int a, b = 40; S1: a = b - 38; S2: a = 2; S1 ->O S2, meaning that S1 has an output dependence on S2 because both write to the variable a.
- 13. CONTROL DEPENDENCY if(a == b) then { c = “controlled”; } d=“not controlled”; if(a == b) then { } c = “controlled”; d=“not controlled”; if(a == b) then { c = “controlled”; d=“not controlled”; }
- 14. DEPENDENCY IN LOOP Loops can have two types of dependence: •Loop-carried dependency •Loop-independent dependency
- 15. LOOP CARRIED DEPENDENCY • In loop-carried dependence, statements in an iteration of a loop depend on statements in another iteration of the loop. for(i=0;i<4;i++) { S1: b[i]=8; S2: a[i]=b[i-1] + 10; }
- 16. LOOP INDEPENDENT DEPENDENCY • In loop-independent dependence, loops have inter-iteration dependence, but do not have dependence between iterations. • Each iteration may be treated as a block and performed in parallel without other synchronization efforts. for (i=0;i<4;i++) { S1: b[i] = 8; S2: a[i] =b[i] + 10; }
- 17. for (i=1; i<4; i++) for (j=1; j<4; j++) S3: a[i][j] = a[i][j-1] + 1; Node : Point in the iteration space Directed Edge: Dependency Node: Point in the iteration space Directed Edge: next point that will be encountered after the current point is traversed
- 19. •Extraction parallel tasks from loops •Data is stored in random access data structures •A program exploiting loop-level parallelism will use multiple threads or processes which operate on same time •It provides speedup •Amdhal’s law
- 20. Examples of Loop parallelization for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { S1: L[i] = L[i] + 10; } for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { S1: L[i] = L[i - 1] + 10; }
- 21. Can the following Loop be made Parallel? for (i=1;i<=100;i=i+1) { A[i+1] = A[i] + C[i]; /*S1*/ B[i+1] = B[i] + A[i+1]; /*S2*/ }
- 22. METHODOLOGIES FOR PARALLELIZING LOOPS • DISTRIBUTED Loop • DOALL Parallelism • DOACROSS Parallelism • HELIX • DOPIPE Parallelism
- 23. DISTRIBUTED LOOP for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) { S1: a[i] = a[i -1] + b[i]; S2: c[i] = c[i] + d[i]; } loop1: for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) { S1: a[i] = a[i -1] + b[i]; } loop2: for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) { S2: c[i] = c[i] + d[i]; }
- 24. DO ALL PARALLELISM for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { S1: a[i] = b[i] + c[i]; } begin_parallelism(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { S1: a[i] = b[i] + c[i]; end_parallelism(); } block();
- 25. DO ACROSS PARALLELISM for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { a[i] = a[i - 1] + b[i] + 1; } S1: int tmp = b[i] + 1; S2: a[i] = a[i - 1] + tmp; post(0); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { S1: int tmp = b[i] + 1; wait(i - 1); S2: a[i] = a[i - 1] + tmp; post(i); }
- 26. DO PIPE PARALLELISM for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { S1: a[i] = a[i - 1] + b[i]; S2: c[i] = c[i] + a[i]; } for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { S1: a[i] = a[i - 1] + b[i]; post(i); } for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { wait(i); S2: c[i] = c[i] + a[i]; }