PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction to Object Oriented Programming Using Java.pdf
- 1. Introduction to Object Oriented Programming using Java Chapter 1.1
- 2. To provide students with the basics of Object Oriented Programming using Java.. Aim
- 3. After completing this chapter, you should be able to: • Explain the Object Oriented features in Java • Describe the role of JVM • Illustrate keywords, variables and data types in Java • Demonstrate common lexical issues in Java • Illustrate Java type conversion and casting • Describe arrays in Java Instructional Objectives
- 4. Learning Outcomes At the end of this chapter, you are expected to: • Differentiate between the features of C++ and Java. • Apply various data types, keywords and variables in a simple Java program. • Demonstrate common lexical issues by creating a program in Java to count the number of spaces, identifiers and comments. • Describe the types of type conversion with examples. • Create a program to illustrate the concept of passing an array to method. • Demonstrate the applications of multidimensional array with an example.
- 5. Introduction to Object Oriented Programming in Java
- 6. I. Object Oriented Programming in Java Introduction One of the most important concepts of programming language is its reliability. Object Oriented Programming concept helps keeping a programming language to utmost reliable and dependable. Let’s look down upon history of Java and how does it come to existence as a programming language after C and C++.
- 7. Object Oriented Programming in Java Evolution of Java Researchers were thinking of a programming language which could be securable, reusable and support all platforms and also acts as a class-based, object-oriented with specifically designed dependencies to fix the drawbacks of existing languages like C and C++. Where C is not secured, and C++ does not have the advanced characteristic. It intended to develop an application program which can be "write once and run anywhere" (WORA), which means the compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java.
- 8. Object Oriented Programming in Java History of Java The most popular programming languages are C, C++, C#, and Java. Where Java is an advanced programming language and facilitates advanced technical features when compared with each other. A revolutionary task to develop a program for digital devices such as set top boxes and television was an interesting fact which made Java programming to come into existence. It was an advance concept at that time for Green team members (developers of Java programmers) but it satisfied the demands of internet programming. Later, Netscape incorporated Java programming. Java is a propertied language which has its best elements to inherit and combine with any innovative concept which can build its own unique mission. Java is a technically blended language which has a rich elements that can address any changing expectations and technical innovations. At present, Java is one of the most popular programming in use, particularly in client-server architecture, internet programming, mobile devices, games, e-business solutions etc.
- 9. Object Oriented Programming in Java Object Oriented Programming Concepts Java is an Object Oriented language. It provides the feature to implement an Object Oriented model, where it is organised around objects and logic rather than data. It is used in the beginning of software lifecycle and also used to develop other applications. Object Oriented Programming is a technique in which programs are written on the basis of objects e.g. (Java) where it adopts a concept that views everything as an object and implements a logic in relation to it. Let’s see the concepts of Object Oriented Programming in detail with an real time example.
- 11. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Object An object is nothing but a matter of thing what we find in everyday life. Technically, Java is a software bundle of related state and behaviour. Example: Car, box, mountain, computer etc.
- 12. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Object and its components
- 13. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Object with Its Attributes
- 14. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Class In Java programming, class is defined as a blueprint from which objects are created. It models and describes the state and behaviour of an object. Example: Consider a car with several properties like clutch, steering, break, etc.
- 15. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Inheritance Inheritance is a property by which state and behaviour of one class (super class) can be inherited to its sub-class. It is a powerful and a natural mechanism for organising and structuring a software. Example: Human heredity
- 16. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Abstraction Hiding the implementation details from the user is called as abstraction. Here, only the functionality will be provided. In Java, abstraction can be achieved by abstract class, and Interface. A class with an abstract keyword is called as abstraction. Interface – blueprint of a class. Full abstraction can be achieved using this mechanism. Example: Invention of flight is based on the flying mechanism learnt from birds. So flights are derived form base class birds.
- 17. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Encapsulation Encapsulation is one of the fundamental concept of OOP. Mechanism of binding the data and function together in a single unit is called as encapsulation.
- 18. Object Oriented Programming Concepts Polymorphism Polymorphism is an ability of an object to take many forms. It reacts differently in different situation. In Java, polymorphism is used to reduce code complexities. Methods or function of a class implies the behaviour of polymorphism. In Java, all Java objects are polymorphic.
- 20. Components of Java Java Compiler Compiler is used to systemize the program and check against language syntax rules. It converts the source code to byte code and then compiles them. The Java compiler generates an architecture-neutral object file format (the compiled code – source code and byte code) to be executable on many processors. Source code - collection of computer instructions written in human readable format. Writes the output in java file Byte code - computer object code, also called as instruction set of Java Virtual Machine. Writes the output in class file
- 21. Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Java Virtual Machine – enables the computer to run Java program. It reads and interprets class files and executes the program’s instruction into native hardware platform. JVM is platform independent (obtainable for many hardware and software platforms). In the Java virtual machine specification, the behaviour of a virtual machine instance is described in terms of subsystems, memory areas, data types, and instructions. These components describe an abstract inner architecture for the abstract Java virtual machine. The purpose of these components is not so much to dictate an inner architecture for implementations. It is more to provide a way to strictly define the external behaviour of implementations. The specification defines the required behaviour of any Java virtual machine implementation in terms of these abstract components and their interactions.
- 22. Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Let’s discuss what does JVM performs? It is used to load the code It Verifies and executes the code And it provides run time environment
- 23. Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- 24. Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Components of JVM: Following are the components of JVM: • Stack • Heap • Constant Pool • Code segment • Program counter
- 25. Components Of JVM 1. Stack Temporary values are stored in frames of a stack. It contains the state of Java method invocation. While invoking a method, JVM pushes a new frame onto that thread’s Java stack. After completion of a single method, the virtual machine pops and discards the frame for that method.
- 26. Components Of JVM Heap Heap consists of objects. The JVM has a heap that is the runtime data area from which memory for all class instances and arrays are allocated. It is created at the JVM start-up. • Heap Memory – store Java objects • Non-heap memory – Store Meta data and other loaded classes.
- 27. Components Of JVM Constant Pool Constant pool consist of all constant data. They comprise of • Numbers • Strings • Symbolic names of classes, interfaces and fields
- 28. Components Of JVM Program Counter Tracking of current instruction execution at any moment is done by Program Counter (PC) register. It is similar to that of pointer which keeps in track of current instruction in sequence. Every time a new thread is created, a PC register is also created simultaneously. PC keeps a pointer to the current statement that is being executed in its thread.
- 29. 29 Simple Java Program • Java is a general-purpose programming language. Like any programming language, Java also has its own syntax, structure and programming paradigm to build a robust, reusable and maintainable applications programs. • Java programs are executed in its development environment such as Java Development Kit (JDK) and Eclipse IDE. • Programmatically, Java is a derivative of C++language. Syntax of Java looks similar like C. Code blocks are modularised into methods and delimited by braces ({ }) and variables are declared before they are used. • Java program starts with a package where the package can be defined as a namespace mechanism. It helps to maintain the hierarchical file system, manage file system and class system.
- 30. Hierarchy of Java Program Components
- 31. Java Program Example : A simple java program is illustrated below : public class FirstProgram { Public static void main (string [ ]args) { Sytem.out.println(“ First Java Program”); } //end of main } //end of First Program class
- 32. Self – Assessment Questions 1) Java is an architectural dependent programming language. a) True b) False 2) ______________ is an instance of class. a) Package b) Object c) Class d) None of these 3) By default, all Java Objects are Polymorphic. a) True b) False
- 33. Data types, Keywords and Variables
- 34. II. Data Types, Keyword and Variables Variables are memory locations to store values. When a user creates a variable, a memory space is reserved for that the variable. Based on the type of the variable, the operating system allocates memory and decides what can be stored in that reserved space. A user can store integers, decimals, character, etc. by assigning different data types to the variables. Datatype is a keyword used to allocate sufficient memory space for the data. Pictorial representation of datatypes and its classifications are given below:
- 35. Classification of Data types
- 36. Classification of Data types Let’s see the list of datatypes and its description in the following. The types are: • Integer • Floating point • Character • Boolean • Type conversion and Casting • Automatic Type promotion in expression
- 37. Integers
- 38. Integers Java defines four integer types: Byte short int long All of these are signed, positive and negative values. Java does not support unsigned datatypes. Whereas signed and unsigned integers are supported by many other computer languages. Java designers felt that unsigned integers are unnecessary because they are mostly used to specify behavior of the higher order bit, which defines the sign of an integer value. The width of an integer type should not be thought of as the amount of storage it consumes, but rather as the behavior it defines for variables and expressions of that type. The Java run- time environment is free to use whatever size it wants, as long as the types behave as you declared them.
- 39. Integers Integers and its types Name Width Range Long 64 -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 Int 32 -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 Short 16 -32,768 to 32,768 Byte 8 -128 to 127
- 40. Bytes • The smallest integer type is byte. • This is a signed 8-bit type that has a range from -128 to 127. • Variables of type byte are especially useful when you’re working with a stream of data from a network or file. It can be represented as: Byte b, c;
- 41. Short • Short is a signed 16-bit type. • It has a range from –32,768 to 32,767. • It is probably the least-used Java type. Here are some examples of short variable declarations: short s; short t;
- 42. Int • The most commonly used integer type is int. • It is a signed 32-bit type that has a range from –2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. • In addition to other uses, variables of type int are commonly employed to control loops and to index arrays.
- 43. Long • Long is a signed 64-bit type and is useful for those occasions where an int type is not large enough to hold the desired value. • The range of a long is quite large. This makes it useful when big, whole numbers are needed.
- 44. Floating – Point • Floating-point numbers, also known as real numbers • There are two kinds of floating-point types : Float Double which represent single- and double-precision numbers, respectively.
- 45. Floating Point
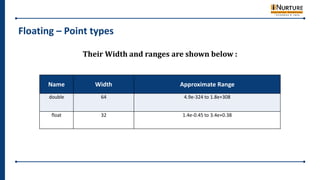
- 46. Floating – Point types Their Width and ranges are shown below : Name Width Approximate Range double 64 4.9e-324 to 1.8e+308 float 32 1.4e-0.45 to 3.4e+0.38
- 47. Floating – Point types Float • Float is specified as a single-precision value that uses 32 bits of storage. • Single precision is faster and takes half as much space as double precision, , but will become imprecise when the values are either very large or very small. Here are some example float variable declarations: float hightemp, lowtemp;
- 48. Floating – Point types Double • Double is denoted by the keyword ‘double’ which is used to store a value of 64 bit. It is faster than single precision on modern processor that have been optimized for high- speed mathematical calculations. Some importance of double are: • All transcendental math functions, such as sin( ) cos( ) sqrt( ) • return double values. • Double is best choice, when you need to maintain accuracy over many iterative calculations, or are manipulating large-valued numbers.
- 49. Example Programs
- 50. Integer Public class DataType_int { int a=100; int b=-150; void add( ) { Int c=a + b; Sysytem.out.println (“The int value is:” +c); } } Class Demo { public static void main(String args[ ] ) { Datatype_Int obj =new DataType_Int ( ); Obj.add(); } } Output: The int value is -50
- 51. Double Integer // Compute the area of a circle. class Area { public static void main(String args[]) {double pi, r, a; r = 10.8; // radius of circle pi = 3.1416; // pi, approximately a = pi * r * r; // compute area System.out.println("Area of circle is " + a); } } Output: Area of circle is 366.435
- 52. Characters
- 53. Characters • char in Java is not the same as char in C or C++. • Java uses Unicode to represent characters. • Unicode defines a fully international character set that can represent all of the characters found in all human languages. • It is a unification of dozens of character sets, such as Latin Greek Arabic Cyrillic Hebrew
- 54. Characters • In Java, char is 16 bit and ranges from 0 to 65,536. • There are no negative chars. • The standard set of characters known as ASCII still ranges from 0 to 127 as always, and the extended 8-bit character set, ISO-Latin-1, ranges from 0 to 255.
- 55. Characters Example Program : Demonstrates char variables class CharDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { char ch1, ch2; ch1 = 88; // code for X ch2 = 'Y'; System.out.print("ch1 and ch2: "); System.out.println(ch1 + " " + ch2); } } This program displays the following output: ch1 and ch2: X Y
- 56. Boolean
- 57. Boolean The Boolean logical operators are: | , & , ^ , ! , || , && , == , != . • Java supplies a primitive data type called Boolean, instances of which can take the value true or false only, and have the default value false. • The major use of Boolean facilities is to implement the expressions which control if decisions and while loops.
- 58. Boolean Example program: class Boolean { public static void main(String args[]) { // these are boolean variables boolean A = true; boolean B = false; System.out.println ("A|B = "+(A|B)); System.out.println ("A&B = "+(A&B)); // program execution using boolean System.out.println ("!A = "+(!A)); System.out.println ("A^B = "+(A^B)); System.out.println ("(A|B)&A = "+((A|B)&A)); } } Syntax: booleanValue(); // returns the value of Boolean object
- 59. Type Casting and Conversion
- 60. Type conversion and Casting • Type casting is used to assign value of one type of a variable to another type. Casting in other words is an instruction to the compiler to convert one type to another. • It helps Java not only to perform only arithmetic operations on pairs of values of same type but performs operations on mixed type too. • For example the value of the right side is automatically converted to the type of the left side in compatible types. • In Java, Boolean and int are not compatible. • When the above said conditions are met, a widening conversion takes place.
- 61. Type conversion and Casting Types : There are two types Types Casting Widening casting Narrowing Casting
- 62. Type conversion and Casting 1) Widening casting In widening casting, the value types are not directly expressed. Here, integer and floating are compatible with each other. Integer literal can be assigned to char. Widening Byte Short Int Long Float Double
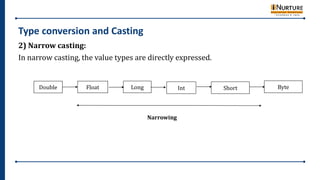
- 63. Type conversion and Casting 2) Narrow casting: In narrow casting, the value types are directly expressed. Narrowing Double Float Long Int Short Byte
- 64. Type conversion and Casting Difference between Widening and Narrowing Widening Casting Narrowing Casting Used to access new methods of child class or while referring super class to child class Used to access redefined class of parent class in the child class
- 65. Type conversion and Casting Sample Program: Package conversion; Public class main { Public Static Void main(string [ ] args) { int var1=12; double var2=15.2; double result = var1+var2; System.Out.Println (“The sum is” + result) } }
- 66. Self – Assessment Questions 1) Boolean is used to control the decisional statement in a program a) True b) False 2) Java supplies a primitive data type called_________________. a) Integer b) Float c) Boolean d) Character 3) Any size of an integer is handled by Java. a) True b) False
- 67. Lexical Issues
- 68. Lexical Issues • Java programs are the collection of whitespace, identifiers, literals, comments and separators. • Lexical issues are very common in programming, which is used to analysis, operate and implement the program in a sequential order.
- 69. Lexical Issues Let us see the detail description of lexical issues in the following. i. Whitespace • As word by itself, a whitespace is nothing but a space, tab, or a new line. • Java is a case sensitive free-form language which means a user need not follow any special rules. • For example, there is no format to be followed to write a Java program. • A program can be written even in a single line or any number of lines can be used, whatever user wishes. • By default, single whitespace is required between each character.
- 70. Lexical Issues Identifiers • An identifier can be described as any descriptive sequence of uppercase, lowercase letters, underscore or a dollar -sign character. • Identifiers are used for specifying class name, method name and variable name. Since Java is case-sensitive language any letter of a word will be different from the other form of the similar word. • Let us say in Java, a word max is different from MAX.
- 71. Lexical Issues Literals Literals are used to specify a default value or to declare a constant value. It can be a: • Boolean – True or False • Numeric – floating, decimal, integer or a fixed point • Character based – single character or a string
- 72. Lexical Issues Comments Three types of comments are supported by Java. They are Comment Description /*text*/ Compiler ignores everything from /* to */ //text Compiler ignores everything from // to the end of the line //**documentation*/ Called as doc comment (documentation comment) – used by automatically generated document
- 73. Lexical Issues Separators Separators are characters used to terminate statements. Commonly used separators are semicolon (;). Following are few separators used in Java programs Symbol Name Purpose ( ) Parenthesis Control the order of operation { } Braces Used to group statements and declaration [ ] Brackets Used to declare array types and dereferencing array values ; semicolon Terminates statement , comma Separates consecutive identifiers in a variable decalaration
- 74. Self – Assessment Questions 1) ____________line space is required to separate each statement. a) Single b) Double c) More than one d) Not required 2) Java is a case-sensitive programming language. a) True b) False 3) _______ is used to store values specified by a data type. a) Variables b) Identifiers c) Literals d) Separators
- 75. Arrays
- 76. Arrays Array is a collection of similar types of elements that have contiguous memory location. It is a container object that holds values of homogeneous type. Java array is container object that contains elements of similar data type. It can have : Only fixed set of elements which can be stored in it. Also have label as static data structure because during the time of declaration only the size of the array is specified. An array containing number of variables and it can even start from zero – which is called as an empty, instead they are referenced by array access expressions that use non-negative integer index values. Syntax: datatype[ ] identifier; Or datatype identifier;
- 77. Arrays Initialization of an array: [ ] - Int operator is used to initialize an array. Example program: Int [] arr = new int [15]; // 15 is the size of an array
- 78. Array Array Type : Array types are used in declarations and in cast expression. An array type is written as the name of an element type followed by some number of empty pairs of square brackets []. The number of bracket pairs indicates the depth of array nesting. An array's length is not part of its type. It may be of any type, whether primitive or reference. • Arrays with an interface type as the element type are allowed. An element of such an array may have as its value a null reference or an instance of any type that implements the interface. • An array with an abstract class type as the element type are allowed. An element of such an array may have as its value a null reference or an instance of any subclass of the abstract class that is not itself abstract.
- 79. Array Array Variable: A variable of an array type enfolds a reference to an object. It is used to create a variable and does not create any space to that specified variable. Some of the variable declarations are listed below. They are: Declaration Comment Int [ ] Array of int Short [ ] [ ] Array of short Object [ ] Array of object Collection<?> Array of collection of unknown types
- 80. Array Single Dimensional Array: A one-dimensional array consist of a list of like-typed variables. The general form of a one-dimensional array declaration is The general form of new as it applies to one- dimensional arrays, appears as follows: arrayRefVar =new dataType[arraySize]; type var-name[ ]; // syntax
- 81. Array The above statement does two things: 1. It creates an array using new dataType[arraySize]; 2. It assigns the reference of the newly created array to the variable arrayRefVar. The example below allocates a 12-element array of integers and links them to month_days. month_days = new int[12]; After this statement executes, month_days will refer to an array of 12 integers. Further, all elements in the array will be initialized to zero.
- 82. Array You can access a specific element in the array, once after you allocate an array by Specifying its index within square brackets. All array indexes start at zero. For example, this statement assigns the value 28 to the second element of month_days. month_days[1] = 28; The next line displays the value stored at index 3. System.out.println(month_days[3]);
- 83. Array Putting together all the pieces, here is a program that creates an array of the number of days in each month. // Demonstrate a one-dimensional array. class Array { public static void main(String args[]) { int month_days[]; month_days = new int[12]; month_days [0] = 31; month_days [1] = 28; month_days [2] = 31; month_days [3] = 30; month_days [4] = 31; month_days [5] = 30; month_days [6] = 31; month_days [7] = 31; month_days [8] = 30; month_days [9] = 31; month_days [10] = 30; month_days [11] = 31; System.out.println ("April has " + month_days[3] + " days."); } }
- 84. Array When you run this program, it prints the number of days in April. As mentioned, Java array indexes start with zero, so the number of days in April is month_days[3] or 30. It is possible to combine the declaration of the array variable with the allocation of the array itself, as shown here:
- 85. Array Multidimensional Array Java does not support multidimensional arrays. However, you can declare and create an array of arrays However, as you will see, there are a couple of subtle differences. To declare a multidimensional array variable, specify each additional index using another set of square brackets. For example, the following declares a two dimensional array variable called twoD. int twoD [ ] [ ] = new int[4][5];
- 86. // Demonstrate a two-dimensional array. class TwoDArray { public static void main(String args[]) { int twoD[ ] [ ]= new int[4][5]; int i, j, k = 0; for(i=0; i<4; i++) for(j=0; j<5; j++) { twoD[i][j] = k; k++; } for(i=0; i<4; i++) { for(j=0; j<5; j++) System.out.print(twoD[i][j] + " "); System.out.println(); }}} This program generates the following output: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 The following program numbers each element in the array from left to right, top to bottom, and then displays these values:
- 87. Summary Java is an Object Oriented Programming Language. Java is a technically blended language which has a rich elements that can address any changing expectations. Java adopts a concept that views very thing as an object and places an extra ordinary demands on the programs. Variables are memory locations to store values. A class is defined as blueprint from which objects are created. Casting is an instruction to the compiler to convert one type to another. Separators are characters used to terminate statements. Array is a collection of similar types of elements that have contiguous memory location. Java does not support multi-dimensional array
- 88. Subjective Questions 1. Explain various data types, keywords and variables with an example Java program 2. What is an array in Java? Explain its types with an example. 3. What are lexical issues and explain how does it help in program implementation?
- 89. • Brief description of activity Activity • Do an online study and prepare a presentation of 10-15 slides which describes the evolution of Java from C++. • You are required to: • Differentiate between C++ and Java and list down the secure features of Java when compared to C++. • Pen down the strategies used in Java to make it reliable and robust with a real time example. Online Activity (30 min)
- 90. • The complete reference Java-2: Herbert Schildt-5th edition- McGraw Hill professional • SAMS teach yourself Java-2- Rogers Cedenhead and Leura Lemay- 3rd edition – Pearson e-References






























![Java Program
Example : A simple java program is illustrated below :
public class FirstProgram
{
Public static void main (string [ ]args)
{
Sytem.out.println(“ First Java Program”);
} //end of main
} //end of First Program class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-31-320.jpg)

















![Integer
Public class DataType_int
{
int a=100;
int b=-150;
void add( )
{
Int c=a + b;
Sysytem.out.println (“The int
value is:” +c);
}
}
Class Demo
{
public static void main(String
args[ ] )
{
Datatype_Int obj =new
DataType_Int ( );
Obj.add();
}
}
Output:
The int value is -50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-50-320.jpg)
![Double Integer
// Compute the area of a circle.
class Area {
public static void main(String args[])
{double pi, r, a;
r = 10.8; // radius of circle
pi = 3.1416; // pi, approximately
a = pi * r * r; // compute area
System.out.println("Area of circle is " + a);
}
}
Output:
Area of circle is 366.435](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-51-320.jpg)



![Characters
Example Program : Demonstrates char variables
class CharDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
char ch1, ch2;
ch1 = 88; // code for X
ch2 = 'Y';
System.out.print("ch1 and ch2: ");
System.out.println(ch1 + " " + ch2);
}
}
This program displays the following output:
ch1 and ch2: X Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-55-320.jpg)


![Boolean
Example program:
class Boolean
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// these are boolean variables
boolean A = true;
boolean B = false;
System.out.println ("A|B = "+(A|B));
System.out.println ("A&B = "+(A&B)); // program execution using boolean
System.out.println ("!A = "+(!A));
System.out.println ("A^B = "+(A^B));
System.out.println ("(A|B)&A = "+((A|B)&A));
}
}
Syntax:
booleanValue(); // returns the value of Boolean object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-58-320.jpg)





![Type conversion and Casting
Sample Program:
Package conversion;
Public class main
{
Public Static Void main(string [ ] args)
{
int var1=12;
double var2=15.2;
double result = var1+var2;
System.Out.Println (“The sum is” + result)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-65-320.jpg)







![Lexical Issues
Separators
Separators are characters used to terminate statements. Commonly used separators
are semicolon (;). Following are few separators used in Java programs
Symbol Name Purpose
( ) Parenthesis Control the order of operation
{ } Braces Used to group statements and
declaration
[ ] Brackets Used to declare array types and
dereferencing array values
; semicolon Terminates statement
, comma Separates consecutive identifiers in a
variable decalaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-73-320.jpg)


![Arrays
Array is a collection of similar types of elements that have contiguous memory location.
It is a container object that holds values of homogeneous type. Java array is container object that
contains elements of similar data type.
It can have : Only fixed set of elements which can be stored in it.
Also have label as static data structure because during the time of declaration only the size of the
array is specified. An array containing number of variables and it can even start from zero – which is
called as an empty, instead they are referenced by array access expressions that use non-negative
integer index values.
Syntax:
datatype[ ] identifier; Or datatype identifier;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-76-320.jpg)
![Arrays
Initialization of an array:
[ ] - Int operator is used to initialize an array.
Example program:
Int [] arr = new int [15]; // 15 is the size of an array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-77-320.jpg)
![Array
Array Type :
Array types are used in declarations and in cast expression. An array type is written as the name of
an element type followed by some number of empty pairs of square brackets []. The number of
bracket pairs indicates the depth of array nesting.
An array's length is not part of its type. It may be of any type, whether primitive or reference.
• Arrays with an interface type as the element type are allowed. An element of such an array
may have as its value a null reference or an instance of any type that implements the interface.
• An array with an abstract class type as the element type are allowed. An element of such an
array may have as its value a null reference or an instance of any subclass of the abstract class
that is not itself abstract.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-78-320.jpg)
![Array
Array Variable:
A variable of an array type enfolds a reference to an object. It is used to create a
variable and does not create any space to that specified variable. Some of the
variable declarations are listed below. They are:
Declaration Comment
Int [ ] Array of int
Short [ ] [ ] Array of short
Object [ ] Array of object
Collection<?> Array of collection of unknown types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-79-320.jpg)
![Array
Single Dimensional Array:
A one-dimensional array consist of a list of like-typed variables.
The general form of a one-dimensional array declaration is
The general form of new as it applies to one- dimensional arrays, appears as
follows:
arrayRefVar =new dataType[arraySize];
type var-name[ ]; // syntax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-80-320.jpg)
![Array
The above statement does two things:
1. It creates an array using new dataType[arraySize];
2. It assigns the reference of the newly created array to the variable arrayRefVar.
The example below allocates a 12-element array of integers and links them to
month_days.
month_days = new int[12];
After this statement executes, month_days will refer to an array of 12 integers.
Further, all elements in the array will be initialized to zero.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-81-320.jpg)
![Array
You can access a specific element in the array, once after you allocate an array by
Specifying its index within square brackets. All array indexes start at zero.
For example, this statement assigns the value 28 to the second element of
month_days.
month_days[1] = 28;
The next line displays the value stored at index 3.
System.out.println(month_days[3]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-82-320.jpg)
![Array
Putting together all the pieces, here is a program that creates an array of the
number of days in each month.
// Demonstrate a one-dimensional
array.
class Array {
public static void main(String
args[]) {
int month_days[];
month_days = new int[12];
month_days [0] = 31;
month_days [1] = 28;
month_days [2] = 31;
month_days [3] = 30;
month_days [4] = 31;
month_days [5] = 30;
month_days [6] = 31;
month_days [7] = 31;
month_days [8] = 30;
month_days [9] = 31;
month_days [10] = 30;
month_days [11] = 31;
System.out.println ("April has " +
month_days[3] + " days.");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-83-320.jpg)
![Array
When you run this program, it prints the number of days in April. As mentioned,
Java array indexes start with zero, so the number of days in April is
month_days[3] or 30.
It is possible to combine the declaration of the array variable with the allocation
of the array itself, as shown here:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-84-320.jpg)
![Array
Multidimensional Array
Java does not support multidimensional arrays. However, you can declare and
create an array of arrays
However, as you will see, there are a couple of subtle differences. To declare a
multidimensional array variable, specify each additional index using another set of
square brackets. For example, the following declares a two dimensional array
variable called twoD.
int twoD [ ] [ ] = new int[4][5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-85-320.jpg)
![// Demonstrate a two-dimensional array.
class TwoDArray {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int twoD[ ] [ ]= new int[4][5];
int i, j, k = 0;
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
for(j=0; j<5; j++) {
twoD[i][j] = k;
k++;
}
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
for(j=0; j<5; j++)
System.out.print(twoD[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}}}
This program generates the
following output:
0 1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19
The following program numbers each element in the array from left to right, top to
bottom, and then displays these values:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjm01c01pptintroductiontoobjectorientedprogrammingusingjava-241018051710-64805ca5/85/PJ_M01_C01_PPT_Introduction-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-Using-Java-pdf-86-320.jpg)













































![Présentation_gestion[1] [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/prsentationgestion1autosaved-250608153959-37fabfd3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)





