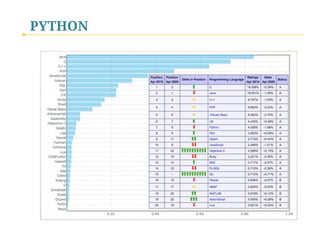
Python Programming - I. Introduction
6 likes4,626 views
Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
1 of 61
Downloaded 602 times






































Ad
Recommended
What is Python? An overview of Python for science.



What is Python? An overview of Python for science.Nicholas Pringle Python is a general purpose, high-level, free and open-source programming language that is readable and intuitive. It has strong scientific computing packages like NumPy, SciPy, and Matplotlib that allow it to be used for tasks like MATLAB. Python emphasizes code readability and reusability through standards like PEP8 and version control, making it well-suited for collaboration between individual, institutional, and developer users in its large, diverse community.
Python final ppt



Python final pptRipal Ranpara The document provides an introduction and overview of the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language that is easy to learn and read. It also covers Python features such as portability, extensive standard libraries, and support for functional, structured, and object-oriented programming. The document then discusses Python data types including numbers, strings, and various Python syntax elements before concluding with the history and evolution of the Python language through various versions.
Python Programming - III. Controlling the Flow



Python Programming - III. Controlling the FlowRanel Padon This document discusses controlling program flow in Python programming. It covers sequence, selection, and repetition control structures including if/else statements, while loops, for loops, and nested control structures. Examples of pseudocode and Python code are provided to illustrate different control structures. The document also discusses logical operators, augmented assignment operators, and practice exercises for readers to test their understanding of controlling program flow.
Python Seminar PPT



Python Seminar PPTShivam Gupta Best Python PPT
i Was create for my College Seminar And i hope you can also use at your college Seminar.
Python Crash Course



Python Crash CourseHaim Michael These are the slides I was using when delivering the Python Crash Course (https://www.meetup.com/life-michael/events/247984087/). The crash course was delivered in Hebrew. More info about the Python Programming course I deliver can be found at python.course.lifemichael.com.
Python programming



Python programmingProf. Dr. K. Adisesha This document provides an introduction and overview of the Python programming language. It discusses that Python was created by Guido Van Rossum in 1991 and named after Monty Python. Python can be used for both procedural and object-oriented programming approaches. It is an interpreted language that is free to use, easy to learn, and has a simple syntax. Python is popular for web development, data analysis, science/engineering, and more. The document then covers Python syntax and provides examples of using variables, data types, and the interactive mode versus script mode of writing Python code.
PYTHON CURRENT TREND APPLICATIONS- AN OVERVIEW



PYTHON CURRENT TREND APPLICATIONS- AN OVERVIEWEditorIJAERD Python is a powerful high-level, interpreted, interactive, and object-oriented scripting language created by
Guido Van Rossum in late 1980’s. Python is a very suitable language for the beginner level programmers and supports
the development of a wide range of applications from simple text processing to www browsers to games developments.
One of the biggest reasons for Python’s rapid growth is the simplicity of its syntax. The language reads almost like plain
English, making it easy to write complex programs. In this paper we first analyze you to Python programming language
popularity and features. Moreover, this paper specifying applications areas where python can be applied and specially
analyzing web application frameworks which are using in Python programming language
Introduction to Python Programing



Introduction to Python Programingsameer patil Python was developed by Guido Van Rossum in 1991. It is a simple, easy to learn, open source, high-level, dynamically typed, platform independent language that supports both procedural and object-oriented programming. Python's memory allocation and deallocation is handled automatically by its memory manager and garbage collector during runtime.
About Python Programming Language | Benefit of Python



About Python Programming Language | Benefit of PythonInformation Technology Boost your career with Python Programming Language at SSDN Technologies in Gurgaon. In this training you learn about Python basic to advance concept by industry expert. Register Now !!
Python - An Introduction



Python - An IntroductionSwarit Wadhe Python An Introduction, A presentation Developed by Swarit Wadhe. This Slide Will Give you basic information about python (Origin, Codes and difference from other languages).
I hope you'll find this helpfull and if you do please share it with your fellows.
Python presentation by Monu Sharma



Python presentation by Monu SharmaMayank Sharma This presentation provides an overview of Python, including:
- Python is an interpreted, high-level and object-oriented programming language.
- It has a simple syntax and is used for web, enterprise, and scientific applications by companies like Google, Facebook, and NASA.
- Popular reasons for using Python include its readability, large standard library, cross-platform capabilities, and emphasis on code legibility with indentation.
Introduction to python programming



Introduction to python programmingSrinivas Narasegouda If you want to learn the basics of Python programming language here it is in the simplest way. Enjoy learning.
Python tutorial



Python tutorialVijay Chaitanya (1) Python uses indentation rather than braces to indicate blocks of code for functions and control flow. All statements within a block must be indented the same amount.
(2) Python identifiers can consist of letters, numbers, and underscores but must start with a letter or underscore. Identifiers are case-sensitive.
(3) There are reserved words in Python that cannot be used as identifiers such as def, if, else, and, or, not, etc.
Python Tutorial Part 2



Python Tutorial Part 2Haitham El-Ghareeb This document provides an overview of key Python concepts:
1. Modules allow organizing Python code into files and namespaces. The file name is the module name with a .py extension.
2. Python code is compiled into bytecode cache files (.pyc) for improved performance. These files are platform independent.
3. Advanced optimizations can be applied to bytecode with command line flags, but may affect program functionality in rare cases.
4. Standard modules provide useful functions like dir() to inspect modules and packages for organizing code. Input/output, strings, files and exceptions are also covered.
Python Programming Language



Python Programming LanguageLaxman Puri Python is a widely used general purpose programming language that was created in the late 1980s by Guido van Rossum. It emphasizes code readability and has a large standard library. It supports multiple programming paradigms like object oriented, imperative, and functional programming. Compared to other languages, Python programs are typically shorter than equivalent programs in languages like Java due to features like dynamic typing.
Python programming introduction



Python programming introductionSiddique Ibrahim This document provides an overview of basic Python programming concepts including programming languages, compilers, interpreters, linkers, loaders, Python syntax checking, Python virtual machine, commenting in Python, Python character sets, tokens, literals, variables, keywords, operators, delimiters, and the print function. It explains key elements like machine language uses 0s and 1s, high level languages are easier for humans, compilers translate to machine code while interpreters convert line by line, and linkers combine program modules into a single executable.
Python quick guide1



Python quick guide1Kanchilug This document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses Python's history, key features such as being easy to use, scalable, high-level, object-oriented, interpreted, and having a rich core library. It also covers Python's uses in areas like web development, databases, GUI programming, and more. The document is intended to introduce readers to Python and provide context for a book on making use of the language.
Programming



Programmingmonishagoyal4 This document discusses key concepts in Python programming including data types, operators, strings, modules, object-oriented programming, and connecting to SQLite databases. It provides examples of numeric, boolean, and sequence data types. It also demonstrates various math operators, string operators like concatenation and multiplication, and how to import and use modules. Object-oriented concepts like classes, attributes, and behaviors are explained using a parrot example. Finally, it mentions how to connect a SQLite database to Python code using the MySQLdb interface.
Presentation on python



Presentation on pythonwilliam john The document discusses Bram Cohen's view that Python is a good language for maintainability as it has clean syntax, object encapsulation, good library support, and optional parameters, and then provides details about the history and features of the Python programming language such as being dynamically typed, having a large standard library, and being cross-platform.
Why learn python in 2017?



Why learn python in 2017?Karolis Ramanauskas Semi-motivational talk about why today is a great time to learn Python. Slides include a brief overview of the current state of the language, its application areas, and Python's future.
PYTHON NOTES



PYTHON NOTESNi This document provides an overview of Python programming concepts including what Python is, variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, loops, functions, exceptions, lists, dictionaries, tuples and more. Some key points covered include:
- Python is an interpreted, object-oriented programming language that can be used for many different application types.
- Variables, constants, operators, and control flow structures like conditionals and loops are introduced as the basic building blocks of Python programs.
- Common data types like strings, lists, dictionaries and tuples are described along with their characteristics and functions.
- Other concepts explained are functions, exceptions, formatting, modules and more.
Python Book/Notes For Python Book/Notes For S.Y.B.Sc. I.T.



Python Book/Notes For Python Book/Notes For S.Y.B.Sc. I.T.Niraj Bharambe This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is a high-level language that is easier for humans to write and understand compared to low-level languages. It can be compiled into byte code or interpreted. The document then discusses the history and origins of Python, its key features like being easy to learn and maintain, and how to install Python on different operating systems. It also covers running Python programs, debugging techniques, and setting the Python environment path and variables.
Python basics



Python basicsRANAALIMAJEEDRAJPUT The document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is an easy to learn, high-level, open-source programming language. It describes Python's design philosophy of code readability and how it allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code compared to languages like C++ and Java. The document also discusses Python's powerful libraries, wide use across industries, and how to get started with Python programming using the IDLE integrated development environment.
Chapter 0 Python Overview (Python Programming Lecture)



Chapter 0 Python Overview (Python Programming Lecture)IoT Code Lab Python Programming Course Lecture by IoT Code Lab Training.
Discussed Topic:
Chapter 0: Python Overview
0. Python Introduction
1. What is Python?
2. Story of Python
3. Why Python
4. Use of Python
5. Python Download + Installation
6. How to Use? + Online Course Resource
1. Variable, Data Type, Expression
1. Create First Python Program File
2. First Program - Hello World
3. Comment
4. Variable + Data Type + Example
5. Variable Naming Convention
6. Practice 0.1
2. Input/ Output
1. Input/ Output (String)
1. A String Input & Output
2. Display A Message in Print & Input function
3. Check Data Type
4. Practice 0.2
2. Input/ Output (Number)
1. An Integer Number Input & Output + Check Data Type
2. Type Conversion
3. A Float Number Input & Output + Check Data Type
4. Built-in Function with Example
5. Practice 0.3
3. Formatted Input Output
Introduction about Python by JanBask Training



Introduction about Python by JanBask TrainingJanBask Training Introduction about Python by JanBask Training, we are offering Online Pyton Training. You should visit: http://www.janbasktraining.com/python/ for Pyton Training.
Python Programming Language



Python Programming LanguageDr.YNM Python is a general purpose programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991. It is an interpreted, interactive, object-oriented language with a simple syntax. Python supports cross-platform development and is widely used for scripting, game development, and building desktop and mobile applications. To use Python, developers must download the Python interpreter and can write and run code using the interactive shell or integrated development environments like IDLE. The document then discusses Python's multi-paradigm programming style, advantages like rapid development, and how to install Python and write basic programs using variables, operators, and data types.
Python and its Applications



Python and its ApplicationsAbhijeet Singh This document provides an overview of the Python programming language and its applications. It begins by defining Python as a clear and powerful object-oriented language. It then lists some of Python's key features, such as its elegant syntax, large standard library, ability to run on multiple platforms, and being free and open source. The document provides a simple "Hello World" example in Python. It also compares short code samples in Python, C++ and Java. The remainder of the document discusses some common applications of Python, including web development, science/engineering, robotics, GUI development, data science, machine learning, computer vision and more. It provides examples of using Python for tasks like web crawling, games development, file management and automation
Python basics



Python basicsHoang Nguyen A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and optionally returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python Programming - VIII. Inheritance and Polymorphism



Python Programming - VIII. Inheritance and PolymorphismRanel Padon The document discusses inheritance and polymorphism in Python programming. It provides background on object-oriented programming principles like inheritance, base and derived classes. It gives examples of inheritance with classes like Magulang (parent) and Anak (child), Rectangle and Square. It also explains polymorphism through examples of objects from different classes like Tatsulok and Bilog that can be treated the same due to a common superclass. Finally, it discusses abstract classes and gives an example with the abstract MgaTauhan class and derived classes.
Python Programming - V. Sequences (List and Tuples) and Dictionaries



Python Programming - V. Sequences (List and Tuples) and DictionariesRanel Padon Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
More Related Content
What's hot (19)
About Python Programming Language | Benefit of Python



About Python Programming Language | Benefit of PythonInformation Technology Boost your career with Python Programming Language at SSDN Technologies in Gurgaon. In this training you learn about Python basic to advance concept by industry expert. Register Now !!
Python - An Introduction



Python - An IntroductionSwarit Wadhe Python An Introduction, A presentation Developed by Swarit Wadhe. This Slide Will Give you basic information about python (Origin, Codes and difference from other languages).
I hope you'll find this helpfull and if you do please share it with your fellows.
Python presentation by Monu Sharma



Python presentation by Monu SharmaMayank Sharma This presentation provides an overview of Python, including:
- Python is an interpreted, high-level and object-oriented programming language.
- It has a simple syntax and is used for web, enterprise, and scientific applications by companies like Google, Facebook, and NASA.
- Popular reasons for using Python include its readability, large standard library, cross-platform capabilities, and emphasis on code legibility with indentation.
Introduction to python programming



Introduction to python programmingSrinivas Narasegouda If you want to learn the basics of Python programming language here it is in the simplest way. Enjoy learning.
Python tutorial



Python tutorialVijay Chaitanya (1) Python uses indentation rather than braces to indicate blocks of code for functions and control flow. All statements within a block must be indented the same amount.
(2) Python identifiers can consist of letters, numbers, and underscores but must start with a letter or underscore. Identifiers are case-sensitive.
(3) There are reserved words in Python that cannot be used as identifiers such as def, if, else, and, or, not, etc.
Python Tutorial Part 2



Python Tutorial Part 2Haitham El-Ghareeb This document provides an overview of key Python concepts:
1. Modules allow organizing Python code into files and namespaces. The file name is the module name with a .py extension.
2. Python code is compiled into bytecode cache files (.pyc) for improved performance. These files are platform independent.
3. Advanced optimizations can be applied to bytecode with command line flags, but may affect program functionality in rare cases.
4. Standard modules provide useful functions like dir() to inspect modules and packages for organizing code. Input/output, strings, files and exceptions are also covered.
Python Programming Language



Python Programming LanguageLaxman Puri Python is a widely used general purpose programming language that was created in the late 1980s by Guido van Rossum. It emphasizes code readability and has a large standard library. It supports multiple programming paradigms like object oriented, imperative, and functional programming. Compared to other languages, Python programs are typically shorter than equivalent programs in languages like Java due to features like dynamic typing.
Python programming introduction



Python programming introductionSiddique Ibrahim This document provides an overview of basic Python programming concepts including programming languages, compilers, interpreters, linkers, loaders, Python syntax checking, Python virtual machine, commenting in Python, Python character sets, tokens, literals, variables, keywords, operators, delimiters, and the print function. It explains key elements like machine language uses 0s and 1s, high level languages are easier for humans, compilers translate to machine code while interpreters convert line by line, and linkers combine program modules into a single executable.
Python quick guide1



Python quick guide1Kanchilug This document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses Python's history, key features such as being easy to use, scalable, high-level, object-oriented, interpreted, and having a rich core library. It also covers Python's uses in areas like web development, databases, GUI programming, and more. The document is intended to introduce readers to Python and provide context for a book on making use of the language.
Programming



Programmingmonishagoyal4 This document discusses key concepts in Python programming including data types, operators, strings, modules, object-oriented programming, and connecting to SQLite databases. It provides examples of numeric, boolean, and sequence data types. It also demonstrates various math operators, string operators like concatenation and multiplication, and how to import and use modules. Object-oriented concepts like classes, attributes, and behaviors are explained using a parrot example. Finally, it mentions how to connect a SQLite database to Python code using the MySQLdb interface.
Presentation on python



Presentation on pythonwilliam john The document discusses Bram Cohen's view that Python is a good language for maintainability as it has clean syntax, object encapsulation, good library support, and optional parameters, and then provides details about the history and features of the Python programming language such as being dynamically typed, having a large standard library, and being cross-platform.
Why learn python in 2017?



Why learn python in 2017?Karolis Ramanauskas Semi-motivational talk about why today is a great time to learn Python. Slides include a brief overview of the current state of the language, its application areas, and Python's future.
PYTHON NOTES



PYTHON NOTESNi This document provides an overview of Python programming concepts including what Python is, variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, loops, functions, exceptions, lists, dictionaries, tuples and more. Some key points covered include:
- Python is an interpreted, object-oriented programming language that can be used for many different application types.
- Variables, constants, operators, and control flow structures like conditionals and loops are introduced as the basic building blocks of Python programs.
- Common data types like strings, lists, dictionaries and tuples are described along with their characteristics and functions.
- Other concepts explained are functions, exceptions, formatting, modules and more.
Python Book/Notes For Python Book/Notes For S.Y.B.Sc. I.T.



Python Book/Notes For Python Book/Notes For S.Y.B.Sc. I.T.Niraj Bharambe This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is a high-level language that is easier for humans to write and understand compared to low-level languages. It can be compiled into byte code or interpreted. The document then discusses the history and origins of Python, its key features like being easy to learn and maintain, and how to install Python on different operating systems. It also covers running Python programs, debugging techniques, and setting the Python environment path and variables.
Python basics



Python basicsRANAALIMAJEEDRAJPUT The document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is an easy to learn, high-level, open-source programming language. It describes Python's design philosophy of code readability and how it allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code compared to languages like C++ and Java. The document also discusses Python's powerful libraries, wide use across industries, and how to get started with Python programming using the IDLE integrated development environment.
Chapter 0 Python Overview (Python Programming Lecture)



Chapter 0 Python Overview (Python Programming Lecture)IoT Code Lab Python Programming Course Lecture by IoT Code Lab Training.
Discussed Topic:
Chapter 0: Python Overview
0. Python Introduction
1. What is Python?
2. Story of Python
3. Why Python
4. Use of Python
5. Python Download + Installation
6. How to Use? + Online Course Resource
1. Variable, Data Type, Expression
1. Create First Python Program File
2. First Program - Hello World
3. Comment
4. Variable + Data Type + Example
5. Variable Naming Convention
6. Practice 0.1
2. Input/ Output
1. Input/ Output (String)
1. A String Input & Output
2. Display A Message in Print & Input function
3. Check Data Type
4. Practice 0.2
2. Input/ Output (Number)
1. An Integer Number Input & Output + Check Data Type
2. Type Conversion
3. A Float Number Input & Output + Check Data Type
4. Built-in Function with Example
5. Practice 0.3
3. Formatted Input Output
Introduction about Python by JanBask Training



Introduction about Python by JanBask TrainingJanBask Training Introduction about Python by JanBask Training, we are offering Online Pyton Training. You should visit: http://www.janbasktraining.com/python/ for Pyton Training.
Python Programming Language



Python Programming LanguageDr.YNM Python is a general purpose programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991. It is an interpreted, interactive, object-oriented language with a simple syntax. Python supports cross-platform development and is widely used for scripting, game development, and building desktop and mobile applications. To use Python, developers must download the Python interpreter and can write and run code using the interactive shell or integrated development environments like IDLE. The document then discusses Python's multi-paradigm programming style, advantages like rapid development, and how to install Python and write basic programs using variables, operators, and data types.
Python and its Applications



Python and its ApplicationsAbhijeet Singh This document provides an overview of the Python programming language and its applications. It begins by defining Python as a clear and powerful object-oriented language. It then lists some of Python's key features, such as its elegant syntax, large standard library, ability to run on multiple platforms, and being free and open source. The document provides a simple "Hello World" example in Python. It also compares short code samples in Python, C++ and Java. The remainder of the document discusses some common applications of Python, including web development, science/engineering, robotics, GUI development, data science, machine learning, computer vision and more. It provides examples of using Python for tasks like web crawling, games development, file management and automation
Viewers also liked (16)
Python basics



Python basicsHoang Nguyen A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and optionally returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python Programming - VIII. Inheritance and Polymorphism



Python Programming - VIII. Inheritance and PolymorphismRanel Padon The document discusses inheritance and polymorphism in Python programming. It provides background on object-oriented programming principles like inheritance, base and derived classes. It gives examples of inheritance with classes like Magulang (parent) and Anak (child), Rectangle and Square. It also explains polymorphism through examples of objects from different classes like Tatsulok and Bilog that can be treated the same due to a common superclass. Finally, it discusses abstract classes and gives an example with the abstract MgaTauhan class and derived classes.
Python Programming - V. Sequences (List and Tuples) and Dictionaries



Python Programming - V. Sequences (List and Tuples) and DictionariesRanel Padon Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
Python Programming - VII. Customizing Classes and Operator Overloading



Python Programming - VII. Customizing Classes and Operator OverloadingRanel Padon The document discusses customizing classes in Python through operator overloading. It defines operator overloading as allowing programmers to define special methods that are called when operators are used on user-defined classes. This allows operators to work with class objects in a natural way. The document provides examples of overloading operators like + and - for a Rational number class. It also discusses string representation using __str__, attribute access, type conversion, and summarizes with a case study of a Rational class that overloads various operators and functions.
Python Programming - II. The Basics



Python Programming - II. The BasicsRanel Padon Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
Python Programming - XI. String Manipulation and Regular Expressions



Python Programming - XI. String Manipulation and Regular ExpressionsRanel Padon The document discusses string manipulation and regular expressions in Python programming. It covers topics like string methods, regular expression concepts including alternatives, grouping, quantification, anchors, meta-characters and character classes. Examples are provided to demonstrate matching patterns in text using regular expressions. The re module is introduced as the core module for using regular expressions in Python.
Python Programming - IX. On Randomness



Python Programming - IX. On RandomnessRanel Padon The document discusses various randomization algorithms used in Python programming including pseudorandom number generators (PRNGs) like the Mersenne Twister and Linear Congruential Generator (LCG). It provides details on how these algorithms work, their statistical properties, and examples of using LCG to simulate coin tosses and compare results to Python's random number generator.
Python Programming - X. Exception Handling and Assertions



Python Programming - X. Exception Handling and AssertionsRanel Padon The document discusses exception handling in Python programming. It defines an exception as an event that occurs during program execution that indicates an error. It describes how Python uses try and except blocks to handle exceptions. The try block contains code that may raise exceptions, and except blocks handle specific exceptions. Finally blocks always execute to cleanup resources, even if no exception occurs. User-defined exceptions should inherit from the built-in Exception class. The raise statement throws exceptions, and assertions act like raise-if statements to validate program logic.
Python Programming - VI. Classes and Objects



Python Programming - VI. Classes and ObjectsRanel Padon This document discusses classes and objects in Python programming. It covers key concepts like class attributes, instantiating classes to create objects, using constructors and destructors, composition where objects have other objects as attributes, and referencing objects. The document uses examples like a Time class to demonstrate class syntax and how to define attributes and behaviors for classes.
Switchable Map APIs with Drupal



Switchable Map APIs with DrupalRanel Padon The document discusses using the Strategy Design Pattern to create a modular maps system for CNN Travel that allows switching between different map APIs. It presents the Mapstraction library as an existing approach but notes issues. The Strategy pattern is applied to create a custom Drupal module that isolates map logic from specific APIs (Google, HERE, Mapbox), enabling flexible switching. The system provides map widgets and services info for partner sites via a common interface regardless of the underlying API in use.
Python Programming - XII. File Processing



Python Programming - XII. File ProcessingRanel Padon The document discusses file handling and processing in Python. It covers opening and closing files, different file open modes like read, write and append, parsing files, buffering, and random access files. Common file operations like reading, writing, splitting and stripping file contents are demonstrated. The document also provides examples of parsing HTML and CSV files, using files with classes, and serializing objects for efficient storage and transfer.
Python Programming - XIII. GUI Programming



Python Programming - XIII. GUI ProgrammingRanel Padon The document discusses Tkinter, the Python GUI programming interface. Tkinter provides a wrapper for the Tk GUI toolkit. Tk was originally created for Tcl but has bindings for other languages like Python through Tkinter. Tkinter allows Python programs to create graphical user interfaces by providing classes and methods that interface with the Tk GUI toolkit. Some key Tkinter widgets discussed include Frame, Label, Button, Entry, Radiobutton and Checkbutton. Pros of Tkinter include brevity, cross-platform support, maturity and extensibility. Potential cons are that it relies on Tcl/Tk which some consider unnecessary and it may have a theoretical speed disadvantage due to the multiple layers of interpretation.
Instagram PowerPoint



Instagram PowerPointVerna Abante new media presentation on Instagram for CSUF's COMM352 Advertising Media Planning Course.
verna abante
spring 2012
Introduction to python for Beginners 



Introduction to python for Beginners Sujith Kumar Python is a general purpose programming language that can be used for both programming and scripting. It was created in the 1990s by Guido van Rossum who named it after the Monty Python comedy troupe. People use Python for a variety of tasks due to its readability, object-oriented capabilities, extensive libraries, and ability to integrate with other languages. To run Python code, it must first be compiled into bytecode which is then interpreted by the Python virtual machine.
Instagram presentation 



Instagram presentation Gee Ekachai The document discusses different ways that various groups use Instagram. It mentions that media companies, brands, non-profits, celebrities, public figures, and Instagram communities all utilize Instagram. It also lists some photo apps and books related to Instagram. Additionally, it provides some websites where you can view Instagram photos on the web and names some Instagram related apps.
Introduction to Python



Introduction to PythonNowell Strite This document provides an introduction and overview of the Python programming language. It covers Python's history and key features such as being object-oriented, dynamically typed, batteries included, and focusing on readability. It also discusses Python's syntax, types, operators, control flow, functions, classes, imports, error handling, documentation tools, and popular frameworks/IDEs. The document is intended to give readers a high-level understanding of Python.
Ad
Similar to Python Programming - I. Introduction (20)
DEMO On PYTHON WEB Development.pptx



DEMO On PYTHON WEB Development.pptxSHAIKIRFAN715544 This document provides information about a demo on Python web development presented by Shaik Irfan. It includes details about the presenter's qualifications and experience. It then discusses front-end and back-end web development. The rest of the document outlines the course contents which cover Python fundamentals, databases, GUI development, APIs, front-end technologies and the Django framework. It also lists some common career paths that involve Python like data analysis, cyber security, machine learning and database administration.
An Introduction To Python - Python, Print()



An Introduction To Python - Python, Print()Blue Elephant Consulting This presentation is a part of the COP2271C college level course taught at the Florida Polytechnic University located in Lakeland Florida. The purpose of this course is to introduce Freshmen students to both the process of software development and to the Python language.
The course is one semester in length and meets for 2 hours twice a week. The Instructor is Dr. Jim Anderson.
A video of Dr. Anderson using these slides is available on YouTube at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=_LxfIQuFALY
Python Intro For Managers



Python Intro For ManagersAtul Shridhar This document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses that Python is an easy to use, open-source scripting language (3 sentences or less).
Programming Languages and Development Tools: State of the Art and (Hopefully)...



Programming Languages and Development Tools: State of the Art and (Hopefully)...Bambang Purnomosidi D. P. This document discusses programming languages and development tools. It covers various programming paradigms like imperative, functional, declarative, and object-oriented programming. It also discusses programming environments and factors like software development methodologies, distributed computing, testing, and project management tools. The document notes trends in popular languages like JavaScript and Rust and domains like backend distributed systems, big data, and artificial intelligence. It concludes by suggesting areas of future focus like distributed systems, big data, and cross-platform frameworks.
Specification Of The Programming Language Of Java



Specification Of The Programming Language Of JavaKim Moore - First generation languages are machine languages that use binary code directly, requiring programmers to manipulate toggle switches to program computers in the 1940s-1950s. This allowed for very efficient execution but made programs difficult to write and fix errors in.
- Programming languages have evolved through 5 generations, with each generation bringing programming to a higher level of abstraction and easier use for humans. Early generations used machine language directly while later ones introduced assembly languages, high-level languages, and object-oriented languages.
- The passage discusses first generation machine languages as the lowest level, directly using binary for computation on early computers without compilers or assemblers yet. This allowed for
STARTING A CAREER IN PROGRAMMING



STARTING A CAREER IN PROGRAMMINGActonRoy UNDERSTANDING COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
A programming language is used for instructing a computer to act according to the user’s wish. It provides us with a medium of communication between humans and machine. Humans provide input and computer provides an output based on the input.
A computer is a hardware machine, and it can’t interpret the human language to store and process data. It only uses binary language to understand commands.
https://lset.uk/
Navigating the Tech Landscape of Software Development



Navigating the Tech Landscape of Software DevelopmentAbelPhilipJoseph An introduction to different domain in software development.
Python Programming Unit1_Aditya College of Engg & Tech



Python Programming Unit1_Aditya College of Engg & TechRamanamurthy Banda Python was created in the late 1980s by Guido van Rossum at CWI in the Netherlands as a successor to the ABC language. It is an interpreted, object-oriented programming language that is easy to read and maintain. Python code is portable and can be used for web development, desktop GUIs, games, data science, and more due to its large standard library and extensive third party libraries. Some limitations are that performance is not as fast as lower-level compiled languages and it is not well-suited for mobile applications.
Why Python in required in Civil Engineering



Why Python in required in Civil EngineeringRushikesh Kolhe Python is a general purpose, dynamic, high level and interpreted programming language that is easy to learn yet powerful and versatile, making it attractive for application development. It supports multiple programming paradigms including object oriented, imperative and functional programming. Python is widely used for tasks like web development, machine learning, scientific computing, and more due to its large standard library and being cross-platform, free/open source, and having a simple syntax. People use Python because it is easy to learn and use, expressive, interpreted, cross-platform, free/open source, supports object oriented programming, is extensible, and has a large standard library and GUI programming support.
MODULE 1.pptx



MODULE 1.pptxKPDDRAVIDIAN The type of a value refers to the kind of data it represents. In Python, the main types are:
- int - integer numbers like 1, 2, 100
- float - floating point numbers like 1.5, 3.14159
- str - strings, sequences of characters like 'hello'
- bool - boolean values True or False
When you write code, Python assigns a type to each value. The type determines how it can be used and what operations are valid on it. For example, you can add two integers but not add an integer to a string. Checking and understanding types is important for writing correct Python code.
C Programming for Beginners – Master the C Language.pdf



C Programming for Beginners – Master the C Language.pdfJava Assignment Learn the fundamentals of C programming, its features, real-world applications, and how to write your first C program. Master the C language with ease!
Module 1 Review of Python Basics An Introduction



Module 1 Review of Python Basics An Introductionpercivalfernandez2 Introduction to Python Programming
Fantasy cricket game using python(intershala project)



Fantasy cricket game using python(intershala project)Rr This document describes a 6-week summer training project on developing a fantasy cricket game using Python. It includes an introduction to Python, the training contents on Python basics, OOP, databases and GUI development. It outlines the problem of creating the fantasy game, database design, and screenshots of the game interface. The coding and testing of the game are discussed. Finally, it concludes the potential of using Python for teaching programming concepts.
Welcome To CNC Web World.pdf



Welcome To CNC Web World.pdfCNC Web world Power Point Presentation for CNC Web World, Why you Should join CNC Web World what are the advantages.
Pyhton-1a-Basics.pdf



Pyhton-1a-Basics.pdfMattupallipardhu This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses what Python is, why it was created, its basic features and uses. Python is an interpreted, object-oriented programming language that is designed to be readable. It can be used for tasks such as web development, scientific computing, and scripting. The document also covers Python basics like variables, data types, operators, and input/output functions. It provides examples of Python code and discusses best practices for writing and running Python programs.
C-Programming-Language an overview.pptxx



C-Programming-Language an overview.pptxxTpoint Tech Blog The C programming language is a powerful, high-performance, general-purpose language that has played a foundational role in the evolution of modern computing. Developed by Dennis Ritchie in the early 1970s at Bell Labs, C was designed to create system software and operating systems, particularly UNIX. It is widely respected for its efficiency, speed, and direct access to memory, which makes it ideal for system-level programming, embedded systems, and hardware-related applications.
C follows a procedural programming paradigm, enabling developers to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable functions. It provides a rich set of operators, control statements, and data types that give programmers a high degree of control over system resources. One of the defining features of C is its portability — code written in C can often be compiled and run on various hardware platforms with minimal modifications.
Despite the rise of modern high-level languages, C remains relevant due to its simplicity, minimalism, and role in teaching fundamental programming concepts. It also serves as the foundation for many other languages, including C++, Java, and Python. Whether you're a student, systems developer, or embedded programmer, learning C equips you with essential skills for understanding how computers truly work.
For more information and interview questions, you can also visit Tpoint Tech, where you can find many related topics.
Contact Information:
• Address : G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India
• Mobile: +91-9599086977
• Email: [email protected]
• Website: https://www.tpointtech.com/
Programming Languages and Development Tools: State of the Art and (Hopefully)...



Programming Languages and Development Tools: State of the Art and (Hopefully)...Bambang Purnomosidi D. P.
Ad
More from Ranel Padon (9)
The Synergy of Drupal Hooks/APIs (Custom Module Development with ChartJS)



The Synergy of Drupal Hooks/APIs (Custom Module Development with ChartJS)Ranel Padon Showcases the most useful Drupal hooks and functions. Demonstrates their powerful and beautiful interactions. Uses a custom chart block to illustrate the synergy of functions.
CKEditor Widgets with Drupal



CKEditor Widgets with DrupalRanel Padon Discusses how to configure and implement custom CKEditor widgets in Drupal. Includes numerous examples of custom widgets and actual widgets that we use in CNN Travel site.
Note that you could also download the PDF copy of this presentation by clicking the Save/Download button. The PDF copy has far better quality than the one rendered here online.
Views Unlimited: Unleashing the Power of Drupal's Views Module



Views Unlimited: Unleashing the Power of Drupal's Views ModuleRanel Padon Unleashing the power of Views Drupal module. Discusses Display Formats (Map, Chart, Slideshow, Data Export), Fields, Basic Filters, Exposed Filters, Contextual Filters, Relationships, Attachment, and so on. Includes numerous sample use cases and recommendations.
Batch Scripting with Drupal (Featuring the EntityFieldQuery API)



Batch Scripting with Drupal (Featuring the EntityFieldQuery API)Ranel Padon The document discusses using batch scripting with Drupal and the EntityFieldQuery API. It explains why batch processing is useful, such as avoiding PHP timeouts and integrating with installation profiles. The EntityFieldQuery API allows querying entity properties and fields across entity types in a database-agnostic way. The document also provides details on implementing a custom batch module, including using the Form and Batch APIs, and defining callbacks. Two use cases are presented: updating user profile field formats in batches, and setting preview images for taxonomy terms. The summary recommends links for additional resources on batch processing and the EntityFieldQuery API.
PyCon PH 2014 - GeoComputation



PyCon PH 2014 - GeoComputationRanel Padon This document discusses using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and Python for rapid mass valuation of lots along Pasig River tributaries in the Philippines. It describes using AHP to determine the weights of factors like land use, accessibility and lot size that influence land value. Survey data is analyzed in SPSS and preference matrices are computed in Python. ArcPy is used to perform geoprocessing and create a market value map. The project demonstrates applying AHP and open source tools for automated, GIS-integrated valuation at large scales.
Power and Elegance - Leaflet + jQuery



Power and Elegance - Leaflet + jQueryRanel Padon Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
Python Programming - IV. Program Components (Functions, Classes, Modules, Pac...



Python Programming - IV. Program Components (Functions, Classes, Modules, Pac...Ranel Padon Feel free to download the material for offline viewing later, better images' resolutions, and crispier fonts.
Of Nodes and Maps (Web Mapping with Drupal - Part II)



Of Nodes and Maps (Web Mapping with Drupal - Part II)Ranel Padon Discusses the input, storage, and display mechanisms of spatial fields on nodes: how to utilize Geofield's input widgets and output formatters, how to integrate Geofield with Leaflet and OpenLayers, and how to integrate them with Views.
Web Mapping with Drupal



Web Mapping with DrupalRanel Padon The document discusses various modules in Drupal that enable web mapping capabilities. It describes the Geofield module, which stores and displays geospatial data as fields that can then be used in Views to show the data on a map. It also covers the Leaflet and OpenLayers modules, with Leaflet being newer and lighter than OpenLayers. The OpenLayers module allows for more customizations but requires two Views to implement - one for the data and one for the map. The document provides an overview of how these modules can be used to build web maps with Drupal.
Recently uploaded (20)
Agentic AI: Beyond the Buzz- LangGraph Studio V2



Agentic AI: Beyond the Buzz- LangGraph Studio V2Shashikant Jagtap Presentation given at the LangChain community meetup London
https://lu.ma/9d5fntgj
Coveres
Agentic AI: Beyond the Buzz
Introduction to AI Agent and Agentic AI
Agent Use case and stats
Introduction to LangGraph
Build agent with LangGraph Studio V2
June Patch Tuesday



June Patch TuesdayIvanti Ivanti’s Patch Tuesday breakdown goes beyond patching your applications and brings you the intelligence and guidance needed to prioritize where to focus your attention first. Catch early analysis on our Ivanti blog, then join industry expert Chris Goettl for the Patch Tuesday Webinar Event. There we’ll do a deep dive into each of the bulletins and give guidance on the risks associated with the newly-identified vulnerabilities.
AI Agents in Logistics and Supply Chain Applications Benefits and Implementation



AI Agents in Logistics and Supply Chain Applications Benefits and ImplementationChristine Shepherd AI agents are reshaping logistics and supply chain operations by enabling automation, predictive insights, and real-time decision-making across key functions such as demand forecasting, inventory management, procurement, transportation, and warehouse operations. Powered by technologies like machine learning, NLP, computer vision, and robotic process automation, these agents deliver significant benefits including cost reduction, improved efficiency, greater visibility, and enhanced adaptability to market changes. While practical use cases show measurable gains in areas like dynamic routing and real-time inventory tracking, successful implementation requires careful integration with existing systems, quality data, and strategic scaling. Despite challenges such as data integration and change management, AI agents offer a strong competitive edge, with widespread industry adoption expected by 2025.
Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account J...



Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account J...angelo60207 Prevent infrastructure costs from becoming a significant line item on your startup’s budget! Serial entrepreneur and software architect Angelo Mandato will share his experience with AWS Activate (startup credits from AWS) and knowledge on how to architect a lean and mean AWS account ideal for budget minded and bootstrapped startups. In this session you will learn how to manage a production ready AWS account capable of scaling as your startup grows for less than $100/month before credits. We will discuss AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, architect priorities, and the importance of having flexible, optimized Infrastructure as Code. We will wrap everything up discussing opportunities where to save with AWS services such as S3, EC2, Load Balancers, Lambda Functions, RDS, and many others.
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...



Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL?
(POSETTE: An Event for Postgres 2025)
June 11, 2025
Shinya Kato
NTT DATA Japan Corporation
Domino IQ – Was Sie erwartet, erste Schritte und Anwendungsfälle



Domino IQ – Was Sie erwartet, erste Schritte und Anwendungsfällepanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/domino-iq-was-sie-erwartet-erste-schritte-und-anwendungsfalle/
HCL Domino iQ Server – Vom Ideenportal zur implementierten Funktion. Entdecken Sie, was es ist, was es nicht ist, und erkunden Sie die Chancen und Herausforderungen, die es bietet.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse
- Was sind Large Language Models (LLMs) und wie stehen sie im Zusammenhang mit Domino iQ
- Wesentliche Voraussetzungen für die Bereitstellung des Domino iQ Servers
- Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitung zur Einrichtung Ihres Domino iQ Servers
- Teilen und diskutieren Sie Gedanken und Ideen, um das Potenzial von Domino iQ zu maximieren
TimeSeries Machine Learning - PyData London 2025



TimeSeries Machine Learning - PyData London 2025Suyash Joshi Timeseries Machine Learning - forecasting and anomaly detection with InfluxDB
vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdf



vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdfAmirStern2 מכונות CNC קידוח אנכיות הן הבחירה הנכונה והטובה ביותר לקידוח ארונות וארגזים לייצור רהיטים. החלק נוסע לאורך ציר ה-x באמצעות ציר דיגיטלי מדויק, ותפוס ע"י צבת מכנית, כך שאין צורך לבצע setup (התאמות) לגדלים שונים של חלקים.
No-Code Workflows for CAD & 3D Data: Scaling AI-Driven Infrastructure



No-Code Workflows for CAD & 3D Data: Scaling AI-Driven InfrastructureSafe Software When projects depend on fast, reliable spatial data, every minute counts.
AI Clearing needed a faster way to handle complex spatial data from drone surveys, CAD designs and 3D project models across construction sites. With FME Form, they built no-code workflows to clean, convert, integrate, and validate dozens of data formats – cutting analysis time from 5 hours to just 30 minutes.
Join us, our partner Globema, and customer AI Clearing to see how they:
-Automate processing of 2D, 3D, drone, spatial, and non-spatial data
-Analyze construction progress 10x faster and with fewer errors
-Handle diverse formats like DWG, KML, SHP, and PDF with ease
-Scale their workflows for international projects in solar, roads, and pipelines
If you work with complex data, join us to learn how to optimize your own processes and transform your results with FME.
Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too Late



Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too LateMichael Furman In today's cloud-native landscape, Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for orchestrating containerized applications, but its inherent complexity introduces unique security challenges. Are you one YAML away from disaster?
This presentation, "Kubernetes Security: Act Now Before It’s Too Late," is your essential guide to understanding and mitigating the critical security risks within your Kubernetes environments. This presentation dives deep into the OWASP Kubernetes Top Ten, providing actionable insights to harden your clusters.
We will cover:
The fundamental architecture of Kubernetes and why its security is paramount.
In-depth strategies for protecting your Kubernetes Control Plane, including kube-apiserver and etcd.
Crucial best practices for securing your workloads and nodes, covering topics like privileged containers, root filesystem security, and the essential role of Pod Security Admission.
Don't wait for a breach. Learn how to identify, prevent, and respond to Kubernetes security threats effectively.
It's time to act now before it's too late!
TrustArc Webinar - 2025 Global Privacy Survey



TrustArc Webinar - 2025 Global Privacy SurveyTrustArc How does your privacy program compare to your peers? What challenges are privacy teams tackling and prioritizing in 2025?
In the sixth annual Global Privacy Benchmarks Survey, we asked global privacy professionals and business executives to share their perspectives on privacy inside and outside their organizations. The annual report provides a 360-degree view of various industries' priorities, attitudes, and trends. See how organizational priorities and strategic approaches to data security and privacy are evolving around the globe.
This webinar features an expert panel discussion and data-driven insights to help you navigate the shifting privacy landscape. Whether you are a privacy officer, legal professional, compliance specialist, or security expert, this session will provide actionable takeaways to strengthen your privacy strategy.
This webinar will review:
- The emerging trends in data protection, compliance, and risk
- The top challenges for privacy leaders, practitioners, and organizations in 2025
- The impact of evolving regulations and the crossroads with new technology, like AI
Predictions for the future of privacy in 2025 and beyond
Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account



Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean accountangelo60207 Prevent infrastructure costs from becoming a significant line item on your startup’s budget! Serial entrepreneur and software architect Angelo Mandato will share his experience with AWS Activate (startup credits from AWS) and knowledge on how to architect a lean and mean AWS account ideal for budget minded and bootstrapped startups. In this session you will learn how to manage a production ready AWS account capable of scaling as your startup grows for less than $100/month before credits. We will discuss AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, architect priorities, and the importance of having flexible, optimized Infrastructure as Code. We will wrap everything up discussing opportunities where to save with AWS services such as S3, EC2, Load Balancers, Lambda Functions, RDS, and many others.
PyData - Graph Theory for Multi-Agent Integration



PyData - Graph Theory for Multi-Agent Integrationbarqawicloud Graph theory is a well-known concept for algorithms and can be used to orchestrate the building of multi-model pipelines. By translating tasks and dependencies into a Directed Acyclic Graph, we can orchestrate diverse AI models, including NLP, vision, and recommendation capabilities. This tutorial provides a step-by-step approach to designing graph-based AI model pipelines, focusing on clinical use cases from the field.
“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...



“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/state-space-models-vs-transformers-for-ultra-low-power-edge-ai-a-presentation-from-brainchip/
Tony Lewis, Chief Technology Officer at BrainChip, presents the “State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
At the embedded edge, choices of language model architectures have profound implications on the ability to meet demanding performance, latency and energy efficiency requirements. In this presentation, Lewis contrasts state-space models (SSMs) with transformers for use in this constrained regime. While transformers rely on a read-write key-value cache, SSMs can be constructed as read-only architectures, enabling the use of novel memory types and reducing power consumption. Furthermore, SSMs require significantly fewer multiply-accumulate units—drastically reducing compute energy and chip area.
New techniques enable distillation-based migration from transformer models such as Llama to SSMs without major performance loss. In latency-sensitive applications, techniques such as precomputing input sequences allow SSMs to achieve sub-100 ms time-to-first-token, enabling real-time interactivity. Lewis presents a detailed side-by-side comparison of these architectures, outlining their trade-offs and opportunities at the extreme edge.
Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Cases



Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Casespanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/domino-iq-what-to-expect-first-steps-and-use-cases/
HCL Domino iQ Server – From Ideas Portal to implemented Feature. Discover what it is, what it isn’t, and explore the opportunities and challenges it presents.
Key Takeaways
- What are Large Language Models (LLMs) and how do they relate to Domino iQ
- Essential prerequisites for deploying Domino iQ Server
- Step-by-step instructions on setting up your Domino iQ Server
- Share and discuss thoughts and ideas to maximize the potential of Domino iQ
Down the Rabbit Hole – Solving 5 Training Roadblocks



Down the Rabbit Hole – Solving 5 Training RoadblocksRustici Software Feeling stuck in the Matrix of your training technologies? You’re not alone. Managing your training catalog, wrangling LMSs and delivering content across different tools and audiences can feel like dodging digital bullets. At some point, you hit a fork in the road: Keep patching things up as issues pop up… or follow the rabbit hole to the root of the problems.
Good news, we’ve already been down that rabbit hole. Peter Overton and Cameron Gray of Rustici Software are here to share what we found. In this webinar, we’ll break down 5 training roadblocks in delivery and management and show you how they’re easier to fix than you might think.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI Professional



Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI ProfessionalVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI Professional
Enabling BIM / GIS integrations with Other Systems with FME



Enabling BIM / GIS integrations with Other Systems with FMESafe Software Jacobs has successfully utilized FME to tackle the complexities of integrating diverse data sources in a confidential $1 billion campus improvement project. The project aimed to create a comprehensive digital twin by merging Building Information Modeling (BIM) data, Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie) data, and various other data sources into a unified Geographic Information System (GIS) platform. The challenge lay in the disparate nature of these data sources, which were siloed and incompatible with each other, hindering efficient data management and decision-making processes.
To address this, Jacobs leveraged FME to automate the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data between ArcGIS Indoors and IBM Maximo. This process ensured accurate transfer of maintainable asset and work order data, creating a comprehensive 2D and 3D representation of the campus for Facility Management. FME's server capabilities enabled real-time updates and synchronization between ArcGIS Indoors and Maximo, facilitating automatic updates of asset information and work orders. Additionally, Survey123 forms allowed field personnel to capture and submit data directly from their mobile devices, triggering FME workflows via webhooks for real-time data updates. This seamless integration has significantly enhanced data management, improved decision-making processes, and ensured data consistency across the project lifecycle.
Artificial Intelligence in the Nonprofit Boardroom.pdf



Artificial Intelligence in the Nonprofit Boardroom.pdfOnBoard OnBoard recently partnered with Microsoft Tech for Social Impact on the AI in the Nonprofit Boardroom Survey, an initiative designed to uncover the current and future role of artificial intelligence in nonprofit governance.
Ben Blair - Operating Safely in a Vibe Coding World



Ben Blair - Operating Safely in a Vibe Coding WorldAWS Chicago AWS Community Day Midwest 2025
Ben Blair
Operating Safely in a Vibe Coding World
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...



Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...



“State-space Models vs. Transformers for Ultra-low-power Edge AI,” a Presenta...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
Python Programming - I. Introduction
- 1. PYTHON PROGRAMMING: I. INTRODUCTION Engr. Ranel O. Padon
- 2. ABOUT ME My Programming Love Story BS Geodetic Engineering (Undergraduate Course): C UP ITDC (Special Training Courses): PHP & MySQL, Java MS Computer Science (Graduate Course): C, Perl, Java DGE Projects: MAPD (Java), GeoValuation (Python) Freelance Project: Lead Web Developer q LGIS -> http://www.iesmanila.com/lgis (Drupal) Corporate Work: Senior Software Engineer at Kite Systems, Ltd. q CNN Travel -> http://travel.cnn.com (formerly in Drupal) q CNN Arabic -> http://arabic.cnn.com (Drupal)
- 3. PYTHON PROGRAMMING TOPICS I • Introduction to Python Programming II • Python Basics III • Controlling the Program Flow IV • Program Components: Functions, Classes, Modules, and Packages V • Sequences (List and Tuples), and Dictionaries VI • Object-Based Programming: Classes and Objects VII • Customizing Classes and Operator Overloading VIII • Object-Oriented Programming: Inheritance and Polymorphism IX • Randomization Algorithms X • Exception Handling and Assertions XI • String Manipulation and Regular Expressions XII • File Handling and Processing XIII • GUI Programming Using Tkinter
- 4. WHAT IS A COMPUTER?
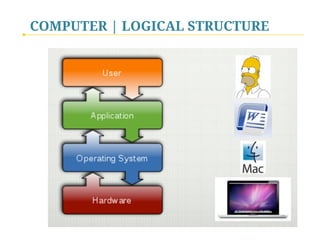
- 7. COMPUTER | LOGICAL STRUCTURE
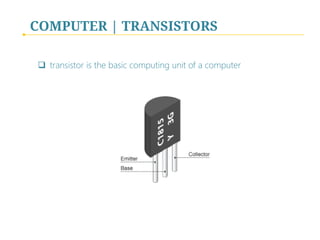
- 8. COMPUTER | TRANSISTORS q transistor is the basic computing unit of a computer
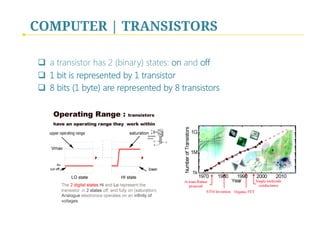
- 9. COMPUTER | TRANSISTORS q a transistor has 2 (binary) states: on and off q 1 bit is represented by 1 transistor q 8 bits (1 byte) are represented by 8 transistors
- 10. COMPUTER | TRANSISTORS q thousands/millions of tiny transistors are then embedded in microchips/integrated circuits (along with resistors and capacitors)
- 11. COMPUTER | NATIVE TONGUE because of transistors, computer uses the binary system/language
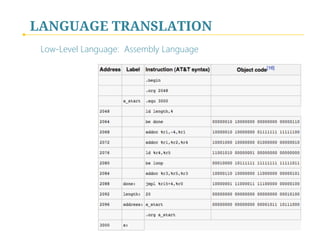
- 12. LANGUAGE TRANSLATION Low-Level Language: Assembly Language
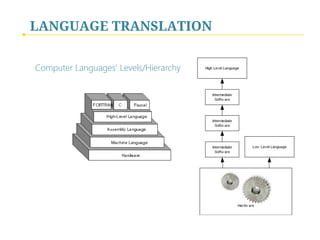
- 13. LANGUAGE TRANSLATION Computer Languages’ Levels/Hierarchy
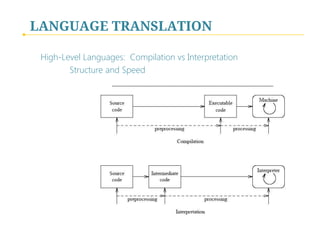
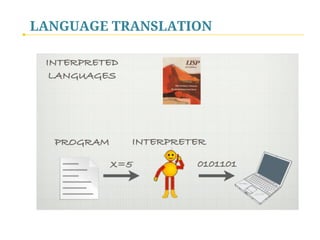
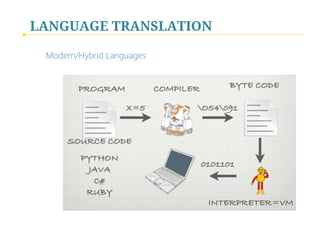
- 14. LANGUAGE TRANSLATION High-Level Languages: Compilation vs Interpretation Structure and Speed
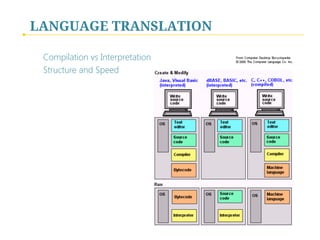
- 15. LANGUAGE TRANSLATION Compilation vs Interpretation Structure and Speed
- 20. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING The process of designing, writing, testing, debugging, and maintaining the source code of computer programs. This source code is written in one or more programming languages (such as Java, C++, C#, Python, etc.)
- 21. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING The purpose is to create a set of instructions that computers use to perform specific operations or to exhibit desired behaviors. Requires expertise in many different subjects, including knowledge of the application domain, specialized algorithms and formal logic.
- 22. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Application programmers write programs to handle a specific job, such as a program to track inventory within an organization. They also may revise existing packaged software or customize generic applications which are frequently purchased from independent software vendors.
- 23. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Systems programmers write programs to maintain and control computer systems software, such as operating systems and database management systems. These workers make changes in the instructions that determine how the network, workstations, and CPU of the system handle the various jobs they have been given and how they communicate with peripheral equipment such as printers and disk drives.
- 24. Systems programmers write programs to maintain and control computer systems software, such as operating systems and database management systems. These workers make changes in the instructions that determine how the network, workstations, and CPU of the system handle the various jobs they have been given and how they communicate with peripheral equipment such as printers and disk drives. PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
- 25. PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES Systems programmers write programs to maintain and control computer systems software, such as operating systems and database management systems. These workers make changes in the instructions that determine how the network, workstations, and CPU of the system handle the various jobs they have been given and how they communicate with peripheral equipment such as printers and disk drives.
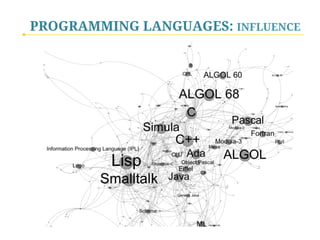
- 27. Programming languages used in most famous websites PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
- 28. Systems programmers write programs to maintain and control computer systems software, such as operating systems and database management systems. These workers make changes in the instructions that determine how the network, workstations, and CPU of the system handle the various jobs they have been given and how they communicate with peripheral equipment such as printers and disk drives. PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES: INFLUENCE
- 29. q Basic Programmers q Computer Software Engineers q Web designers and Developers q Computer System Analyst q Freelancing Consultant q . . . JOB OPPORTUNITIES
- 30. PYTHON
- 31. PYTHON
- 32. Guido Van Rossum (The Creator) PYTHON: THE MAN
- 39. PYTHON
- 40. PYTHON
- 41. PYTHON
- 42. PYTHON
- 43. PYTHON
- 44. PYTHON
- 45. PYTHON
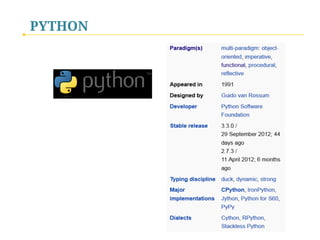
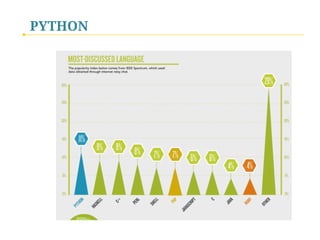
- 46. PYTHON Top 10 Popular Languages
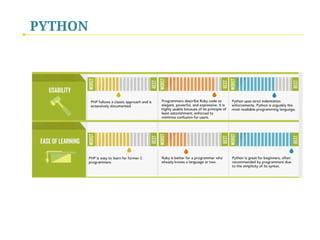
- 47. PYTHON Python is simple & accessible. q Good compromise language q Easy to learn q Widely-used q Flexible
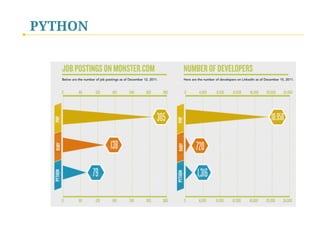
- 49. PYTHON widely-used in the Industry (Dropbox uses Python!)
- 50. PYTHON used by the Government
- 52. PYTHON works with Java and C#
- 53. PYTHON ... is Flexible q Scripting q Procedural Programming q Object-Oriented Programming q Functional Programming
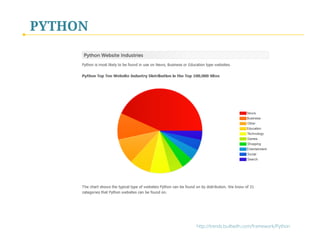
- 54. PYTHON Common Python Application Domains
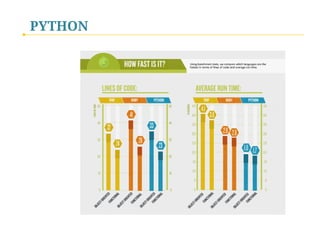
- 55. PYTHON Python: Handy, Powerful & Versatile
- 56. PYTHON Read & Practice. To be an expert at something, you need 10,000 hours!
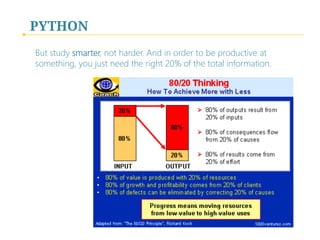
- 57. PYTHON But study smarter, not harder. And in order to be productive at something, you just need the right 20% of the total information.
- 58. PYTHON Find the essentials/most important building blocks
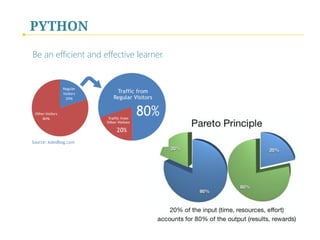
- 59. PYTHON Be an efficient and effective learner.
- 60. PYTHON | END NOTES q Python is readable, maintainable, beautiful, and elegant. q There are many reusable Python libraries out there. q Not all things are important: q you don’t have to study all the intricacies of a programming language to be productive. q EQ is very important in programming in general: q patience/persistence (never say die attitude) q attention to details (spotting anomalies to the lowest level) q belief/positive thinking (having confidence and an upbeat attitude) q resourcefulness/creativity (combining basic language constructs) q determination (especially when debugging)
- 61. REFERENCES q Deitel, Deitel, Liperi, & Wiedermann - Python: How to Program (2001). q Disclaimer: Most of the images/information used here have no proper source citation, and I do not claim ownership of these either. I don’t want to reinvent the wheel, and I just want to reuse and reintegrate materials that I think are useful or cool, then present them in another light, form, or perspective. Moreover, the images/information here are mainly used for illustration/educational purposes only, in the spirit of openness of data, spreading light, and empowering people with knowledge. J




