Python_Programming_PPT Basics of python programming language
- 1. •PYTHO N AS A PRO G RAM MI NG LANG UAG E •PYTHO N DATA TYPE S •STR IN GS: BASI C O PER ATIO N, O PER ATOR S, PR ECEDE NCE AND ASSO CIATI VI TY •I NDE XI NG AND SL ICI N G •STR IN G ME THO DS, STRI N G FO R MATTI NG EXPR ESSI O NS, STR I NG F OR MATTI NG M ETHO D CAL LS •CO MM ENTS •EXPR ESSI O NS •VAR IAB LE S,ASSI G NM ENTS •CO NTRO L STRU CTUR ES •LO OPI NG AND BR ANCHI N G STATEME NTS PYTHON PROGRAMMING UNIT-I:
- 2. Python Introduction • Python is a dynamic, high level, free open source and interpreted programming language. It supports object-oriented programming as well as procedural oriented programming. • Python is a programming language that includes features of C and Java. It provides the style of writing an elegant code like C, and for object-oriented programming, it offers classes and objects like Java. • It was created by Guido van Rossum, and released in 1991. • Python is commonly used for developing websites and software, game development, data analysis, and data visualization. 2
- 3. Python Interpreter • Machines only understand machine code or machine language, a language represented by strings of bits — 1s and 0s. • A python interpreter is a computer program that converts each high-level program statement into machine code. • An interpreter translates the command that you write out into code that the computer can understand. • Python is the most famous example of a high-level language. 3
- 4. Features of Python 1. Free and Open Source: • Python language is freely available at the official website and you can download it. Since it is open-source, this means that source code is also available to the public. So you can download it, use it as well as share it. 2. Easy to code: • Python is a high-level programming language. Python is very easy to learn the language as compared to other languages like C, C#, Javascript, Java, etc. It is very easy to code in the Python language and anybody can learn Python basics in a few hours or days. It is also a developer-friendly language. 4
- 5. Features of Python 3. Easy to Read: • Python’s syntax is straightforward. The code block is defined by the indentations rather than by semicolons or brackets. 4. Object-Oriented Language: • One of the key features of Python is Object-Oriented programming. Python supports object-oriented language and concepts of classes, object encapsulation, etc. 5. GUI Programming Support: • Graphical User interfaces can be made using a module such as PyQt5, PyQt4, wxPython, or Tk in Python. PyQt5 is the most popular option for creating graphical apps with Python. 5
- 6. Features of Python 6. High-Level Language: • Python is a high-level language. When we write programs in Python, we do not need to remember the system architecture, nor do we need to manage the memory. 7. Large Community Support: • Python has gained popularity over the years. Our questions are constantly answered by the enormous StackOverflow community. 8. Easy to Debug: • Excellent information for mistake tracing. You will be able to quickly identify and correct the majority of your program’s issues once you understand how to interpret Python’s error traces. 6
- 7. Features of Python 9. Python is a Portable language: • If we have Python code for Windows and if we want to run this code on other platforms such as Linux, Unix, and Mac then we do not need to change it, we can run this code on any platform. 10. Python is an Integrated language: • Python is also an Integrated language because we can easily integrate Python with other languages like C, C++, etc. 11. Interpreted Language: • Python is an Interpreted Language because Python code is executed line by line at a time. like other languages C, C++, Java, etc. there is no need to compile Python code this makes it easier to debug our code. The source code of Python is converted into an immediate form called bytecode. 7
- 8. Features of Python 12. Large Standard Library: • Python has a large standard library that provides a rich set of modules and functions so you do not have to write your own code for every single thing. There are many libraries present in Python such as regular expressions, unit-testing, web browsers, etc. 13. Dynamically Typed Language: • Python is a dynamically-typed language. That means the type for a variable is decided at run time not in advance because of this feature we don’t need to specify the type of variable. 15. Allocating Memory Dynamically: • In Python, the variable data type does not need to be specified. The memory is automatically allocated to a variable at runtime when it is given a value. 8
- 9. Python Installation • Download Python Executable Installer from www.python.org 9
- 10. First Python Program Execution 1) Interactive Mode Programming • Invoking the interpreter without passing a script file as a parameter brings up the following prompt 10
- 11. First Python Program Execution 2) Script Mode Programming • Invoking the interpreter with a script parameter begins execution of the script and continues until the script is finished. When the script is finished, the interpreter is no longer active. • Let us write a simple Python program in a script. Python files have extension .py. Type the following source code in a test.py file − • print ("Hello, Python!“) 11
- 12. Python Indentation • Indentation refers to the spaces at the beginning of a code line. • Where in other programming languages the indentation in code is for readability only, the indentation in Python is very important. • Python uses indentation to indicate a block of code. • Example • if 5>2: print("Five is greater than two!") 12
- 13. Python Comment • Comments can be used to explain Python code. • Comments can be used to make the code more readable. • Comments can be used to prevent execution when testing code. • Creating a Comment: Comments starts with a #, and Python will ignore them. • Example • #This is a comment print("Hello, World!") 13
- 14. Python Multi Line Comment • To add a multiline comment: 1. insert a # for each line. 2. you can add a multiline string (triple quotes) in your code, and place your comment inside it • Example • """ This is a comment written in more than just one line """ print("Hello, World!") 14
- 15. Python Variables • Variables are containers for storing data values. • Unlike other programming languages, Python has no command for declaring a variable. • A variable is created the moment you first assign a value to it. • Variables do not need to be declared with any particular type and can even change type after they have been set. • Example: Assign Value to Variable • x = 5 y = "John" print(x) print(y) 15
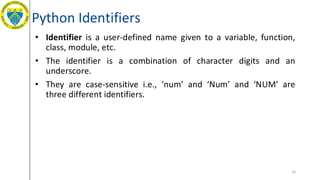
- 16. Python Identifiers • Identifier is a user-defined name given to a variable, function, class, module, etc. • The identifier is a combination of character digits and an underscore. • They are case-sensitive i.e., ‘num’ and ‘Num’ and ‘NUM’ are three different identifiers. 16
- 17. Python Identifiers • Rules for Naming Python Identifiers 1. It cannot be a reserved python keyword. 2. It should not contain white space. 3. It can be a combination of A-Z, a-z, 0-9, or underscore. 4. It should start with an alphabet character or an underscore ( _ ). 5. It should not contain any special character other than an underscore ( _ ). 17
- 18. Python Examples of Python Identifiers • Example • #Legal names: myvar = "John" my_var = "John" _my_var = "John" myVar = "John" MYVAR = "John" myvar2 = "John“ • #Illegal names: 2myvar = "John" my-var = "John" my var = "John" 18
- 19. Python Operators • Operators in general are used to perform operations on values and variables. These are standard symbols used for the purpose of logical and arithmetic operations. • OPERATORS: These are the special symbols. Eg- + , * , /, etc. • OPERAND: It is the value on which the operator is applied. • Types of Operators in Python 1. Arithmetic Operators 2. Comparison Operators 3. Logical Operators 4. Bitwise Operators 5. Assignment Operators 6. Identity Operators and Membership Operators 19
- 20. Python Arithmetic Operators 20 Operator Description Syntax + Addition: adds two operands x + y – Subtraction: subtracts two operands x – y * Multiplication: multiplies two operands x * y / Division (float): divides the first operand by the second x / y // Division (floor): divides the first operand by the second x // y % Modulus: returns the remainder when the first operand is divided by the second x % y ** Power: Returns first raised to power second x ** y
- 21. Python Comparison Operators 21 Operator Description Syntax > Greater than: True if the left operand is greater than the right x > y < Less than: True if the left operand is less than the right x < y == Equal to: True if both operands are equal x == y != Not equal to – True if operands are not equal x != y >= Greater than or equal to True if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right x >= y <= Less than or equal to True if the left operand is less than or equal to the right x <= y
- 22. Python Logical Operators 22 Operator Description Syntax and Logical AND: True if both the operands are true x and y Or Logical OR: True if either of the operands is true x or y not Logical NOT: True if the operand is false not x
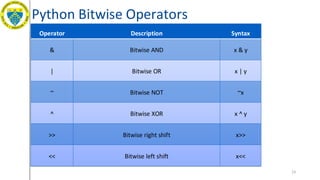
- 23. Python Bitwise Operators 23 Operator Description Syntax & Bitwise AND x & y | Bitwise OR x | y ~ Bitwise NOT ~x ^ Bitwise XOR x ^ y >> Bitwise right shift x>> << Bitwise left shift x<<
- 24. Python Assignment Operators 24 Operator Description Syntax = Assign the value of the right side of the expression to the left side operand x = y + z += Add AND: Add right-side operand with left-side operand and then assign to left operand a+=b a=a+b -= Subtract AND: Subtract right operand from left operand and then assign to left operand a-=b a=a-b *= Multiply AND: Multiply right operand with left operand and then assign to left operand a*=b a=a*b /= Divide AND: Divide left operand with right operand and then assign to left operand a/=b a=a/b %= Modulus AND: Takes modulus using left and right operands and assign the result to left operand a%=b a=a%b //= Divide(floor) AND: Divide left operand with right operand and then assign the value(floor) to left operand a//=b a=a//b **= Exponent AND: Calculate exponent(raise power) value using operands and assign value to left operand a**=b a=a**b
- 25. Python Identity Operators • In Python, is and is not are the identity operators both are used to check if two values are located on the same part of the memory. • Two variables that are equal do not imply that they are identical. • is : True if the operands are identical • is not: True if the operands are not identical 25
- 26. Python Membership Operators • In Python, in and not in are the membership operators that are used to test whether a value or variable is in a sequence. • in :True if value is found in the sequence • not in :True if value is not found in the sequence 26
- 27. Python Operator Precedence 27 Operator Description Operator Description ** Exponentiation I Bitwise OR +x, -x Positive, negative <, , >=, !=, == Comparison operators *, /, //, % Multiplication, division, floor division, modulo is, is not Identity operators +, – Addition, subtraction in, not in Membership operators <> Bitwise shift operators not Logical NOT & Bitwise AND and Logical AND ^ Bitwise XOR or Logical OR
- 28. Python Operator Precedence 1) x = 7 + 3 * 2 Ans: 13 2) x = 5 + 3 * 2 ** 2 // 4 Ans: 8 3) x = 6 + 3 * 2 – 1 Ans:? 28
- 29. Python Data Types • Variables can store data of different types, and different types can do different things. • Python has the following data types built-in by default, in these categories: 1. Text Type: str 2. Numeric Types: int, float, complex 3. Sequence Types: list, tuple, range 4. Mapping Type: dict 5. Set Types: set, frozenset 6. Boolean Type: bool 29
- 30. Python Data Types • Getting the Data Type: • You can get the data type of any object by using the type() function: • Example: Print the data type of the variable x: x = 5 print(type(x)) Output: <class 'int'> 30
- 31. Python Data Types 31 Example Data Types x = "Hello World" str x = 20 int x = 20.5 float x = 1j complex x = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] list x = ("apple", "banana", "cherry") tuple x = range(6) range x = {"name" : "John", "age" : 36} dict x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"} set x = frozenset({"apple", "banana", "cherry"}) frozenset x = True bool
- 32. Python Strings • A String is a data structure in Python that represents a sequence of characters. • It is an immutable data type, meaning that once you have created a string, you cannot change it. • Strings are used widely in many different applications, such as storing and manipulating text data, representing names, addresses, and other types of data that can be represented as text. • Python does not have a character data type, a single character is simply a string with a length of 1. 32
- 33. Python Strings Creating a String in Python: • Strings in Python can be created using single quotes or double quotes or even triple quotes. Let us see how we can define a string in Python. Example: String1 = 'Welcome to DSU‘ print(String1) Output: Welcome to DSU 33
- 34. Python String Indexing • Accessing characters in Python String (String Indexing) • In Python, individual characters of a String can be accessed by using the method of Indexing. • Indexing allows negative address references to access characters from the back of the String, e.g. -1 refers to the last character, -2 refers to the second last character, and so on. • While accessing an index out of the range will cause an IndexError. • Only Integers are allowed to be passed as an index, float or other types that will cause a TypeError. 34
- 36. Python String Indexing 36 Example: String1 = "GeeksForGeeks" print("Initial String: ") print(String1) print("nFirst character of String is: ") print(String1[0]) print("nLast character of String is: ") print(String1[-1]) Output: Initial String: GeeksForGeeks First character of String is: G Last character of String is: s
- 37. Python String Indexing • Reversing a Python String: • By accessing characters from a string, we can also reverse strings in Python. • We can Reverse a string by using String slicing method. 37 Example: str = "geeksforgeeks" print(str[::-1]) Output: skeegrofskeeg
- 38. Python String Slicing • String Slicing: • In Python, the String Slicing method is used to access a range of characters in the String. • Slicing in a String is done by using a Slicing operator, i.e., a colon (:). • String returned after slicing includes the character at the start index but not the character at the last index. • In this example, we will use the string-slicing method to extract a substring of the original string. The [3:12] indicates that the string slicing will start from the 3rd index of the string to the 12th index, (12th character not including). We can also use negative indexing in string slicing. 38
- 39. Python String Slicing 39 Example: String1 = "GeeksForGeeks" print("Initial String: ") print(String1) print("nSlicing characters from 3-12: ") print(String1[3:12]) print("nSlicing characters between " + "3rd and 2nd last character: ") print(String1[3:-2]) Output: Initial String: GeeksForGeeks Slicing characters from 3-12: ksForGeek Slicing characters between 3rd and 2nd last character: ksForGee
- 40. Python String • Deleting from a String: • In Python, the Updation or deletion of characters from a String is not allowed. • This will cause an error because item assignment or item deletion from a String is not supported. • Although deletion of the entire String is possible with the use of a built-in del keyword. • This is because Strings are immutable, hence elements of a String cannot be changed once assigned. Only new strings can be reassigned to the same name. 40
- 41. Python String • Updating a character • A character of a string can be updated in Python by first converting the string into a Python List and then updating the element in the list. • As lists are mutable in nature, we can update the character and then convert the list back into the String. • Another method is using the string slicing method. Slice the string before the character you want to update, then add the new character and finally add the other part of the string again by string slicing. 41
- 42. Python String 42 # Python Program to Update character of a String String1 = "Hello, I'm a Geek" print("Initial String: ") print(String1) list1 = list(String1) list1[2] = 'p' String2 = ''.join(list1) print("nUpdating character at 2nd Index: ") print(String2) String3 = String1[0:2] + 'p' + String1[3:] print(String3) Output: Initial String: Hello, I'm a Geek Updating character at 2nd Index: Heplo, I'm a Geek Heplo, I'm a Geek
- 43. Python String • Updating Entire String: • As Python strings are immutable in nature, we cannot update the existing string. We can only assign a completely new value to the variable with the same name. 43 String1 = "Hello, I'm a Geek" print("Initial String: ") print(String1) String1 = "Welcome to the Geek World" print("nUpdated String: ") print(String1) Output: Initial String: Hello, I'm a Geek Updated String: Welcome to the Geek World
- 44. Python String • Deleting a character • Python strings are immutable, that means we cannot delete a character from it. When we try to delete the character using the del keyword, it will generate an error. • So we will first slice the string up to the character that we want to delete and then concatenate the remaining string next from the deleted character. 44
- 45. Python String 45 Example: String1 = "Hello, I'm a Geek" print("Initial String: ") print(String1) String2 = String1[0:2] + String1[3:] print("nDeleting character at 2nd Index: ") print(String2) Output: Initial String: Hello, I'm a Geek Deleting character at 2nd Index: Helo, I'm a Geek
- 46. Python String Escape Sequences • Escape Sequencing in Python: • While printing Strings with single and double quotes in it causes SyntaxError because String already contains Single and Double Quotes and hence cannot be printed with the use of either of these. • Hence, to print such a String either Triple Quotes are used or Escape sequences are used to print Strings. • Escape sequences start with a backslash and can be interpreted differently. • If single quotes are used to represent a string, then all the single quotes present in the string must be escaped and the same is done for Double Quotes. 46
- 47. Python String Escape Sequences 47 String1 = '''I'm a "Geek"''' print("Initial String with use of Triple Quotes: ") print(String1) # Escaping Single Quote String1 = 'I'm a "Geek"' print("nEscaping Single Quote: ") print(String1) # Escaping Double Quotes String1 = "I'm a "Geek"" print("nEscaping Double Quotes: ") print(String1) # Printing Paths with the use of Escape Sequences String1 = "C:PythonGeeks" print("nEscaping Backslashes: ") print(String1) # Printing Paths with the use of Tab String1 = "HitGeeks" print("nTab: ") print(String1) # Printing Paths with the use of New Line String1 = "PythonnGeeks" print("nNew Line: ") print(String1) Output: Initial String with use of Triple Quotes: I'm a "Geek" Escaping Single Quote: I'm a "Geek" Escaping Double Quotes: I'm a "Geek" Escaping Backslashes: C:PythonGeeks Tab: Hi Geeks New Line: Python Geeks
- 48. Python String Escape Sequences 48 String1 = '''I'm a "Geek"''' print("Initial String with use of Triple Quotes: ") print(String1) # Escaping Single Quote String1 = 'I'm a "Geek"' print("nEscaping Single Quote: ") print(String1) # Escaping Double Quotes String1 = "I'm a "Geek"" print("nEscaping Double Quotes: ") print(String1) # Printing Paths with the use of Escape Sequences String1 = "C:PythonGeeks" print("nEscaping Backslashes: ") print(String1) # Printing Paths with the use of Tab String1 = "HitGeeks" print("nTab: ") print(String1) # Printing Paths with the use of New Line String1 = "PythonnGeeks" print("nNew Line: ") print(String1) Output: Initial String with use of Triple Quotes: I'm a "Geek" Escaping Single Quote: I'm a "Geek" Escaping Double Quotes: I'm a "Geek" Escaping Backslashes: C:PythonGeeks Tab: Hi Geeks New Line: Python Geeks
- 49. Python Conditionals • Python supports the usual logical conditions from mathematics : These conditions can be used in several ways, most commonly in "if statements" and loops. • Equals: a == b • Not Equals: a != b • Less than: a < b • Less than or equal to: a <= b • Greater than: a > b • Greater than or equal to: a >= b 49
- 50. Python If Condition • An "if statement" is written by using the if keyword. • Example of If statement: • a = 33 b = 200 if b > a: print("b is greater than a") • Output: • b is greater than a 50
- 51. Python Elif Condition • The elif keyword is Python's way of saying "if the previous conditions were not true, then try this condition". • Example • a = 33 b = 33 if b > a: print("b is greater than a") elif a == b: print("a and b are equal") 51
- 52. Python Else Condition • The else keyword catches anything which isn't caught by the preceding conditions. • Example • a = 200 b = 33 if b > a: print("b is greater than a") elif a == b: print("a and b are equal") else: print("a is greater than b") 52
- 53. Python And Condition • The and keyword is a logical operator, and is used to combine conditional statements: • Example • Test if a is greater than b, AND if c is greater than a: • a = 200 b = 33 c = 500 if a > b and c > a: print("Both conditions are True") • Output: • Both conditions are True 53
- 54. Python Or Condition • The or keyword is a logical operator, and is used to combine conditional statements: • Example • Test if a is greater than b, OR if a is greater than c: • a = 200 b = 33 c = 500 if a > b or a > c: print("At least one of the conditions is True") • Output: • At least one of the conditions is True 54
- 55. Python not Condition • The not keyword is a logical operator, and is used to reverse the result of the conditional statement: • Example • Test if a is NOT greater than b: • a = 33 b = 200 if not a > b: print("a is NOT greater than b") • Output: • a is NOT greater than b 55
- 56. Python Nested if Condition • You can have if statements inside if statements, this is called nested if statements. • Example • x = 41 if x > 10: print("Above ten,") if x > 20: print("and also above 20!") else: print("but not above 20.") • Output: • Above ten, and also above 20! 56
- 57. Python Loops • A loop is an instruction that repeats multiple times as long as some condition is met. • Types of Python Loops: • While Loop • For Loop • Break Statement 57
- 58. While Loop • The while loop is used to execute a set of statements as long as a condition is true. 58
- 59. While Loop • While Loop Syntax: while expression: statement(s) 59 Example: count = 0 while (count < 3): count = count + 1 print("Hello GM") Output: Hello GM Hello GM Hello GM
- 60. For Loop • A for loop in Python is used to iterate over a sequence (list, tuple, set, dictionary, and string). 60
- 61. For Loop • For Loop Syntax: for iterator_var in sequence: statements(s) 61 Example: n = 4 for i in range(0, n): print(i) Output: 0 1 2 3
- 62. Nested Loop • Python programming language allows to use one loop inside another loop which is called nested loop. • Nested Loops Syntax: for iterator_var in sequence: for iterator_var in sequence: statements(s) statements(s) 62
- 63. Nested Loop 63 Example: #outer loop for i in range(1, 11): # nested loop # to iterate from 1 to 10 for j in range(1, 11): # print multiplication print(i * j, end=' ') print() Output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80 9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81 90 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
- 64. Continue Statement • The continue statement in Python returns the control to the beginning of the loop. 64 Example: for letter in 'geeksfor': if letter == 'e' or letter == 's': continue print('Current Letter :', letter) Output: Current Letter : g Current Letter : k Current Letter : f Current Letter : o Current Letter : r
- 65. Break Statement • The break statement in Python brings control out of the loop. 65 Example: for letter in 'geeksforgeeks': if letter == 'e' or letter == 's': break print('Current Letter :', letter) Output: Current Letter : e
- 66. Pass Statement • We use pass statement in Python to write empty loops. Pass is also used for empty control statements, functions and classes. • Example: This Python code iterates through the characters of the string ‘geeksforgeeks’ using a ‘for' loop. However, it doesn’t perform any specific action within the loop, and the ‘pass' statement is used. After the loop, it prints “Last Letter :” followed by the last character in the string, which is ‘s’. 66 Example: for letter in 'geeksforgeeks': pass print('Last Letter :', letter) Output: Last Letter : s
- 67. Questions From Unit-1 1) Explain Features of Python Programming Language. 2) Explain different types of comments in Python. 3) What is Variable? How to assign Value to variable in python? 4) What is Python identifier? Write rules for naming the identifiers. Give some examples of legal names of identifiers. 5) What are Python Operators? Explain Types of operators in detail with example. 6) What is difference between == and ‘is’ operator in python? 7) Explain Built-in data types of python. 8) What is string in python? Explain String Indexing and slicing with example. 9) Explain Escape Sequences in python. 10)Explain if, elif and else with example. 11)Explain while loop and for loop with syntax and example. 12)Explain usage of continue, break and pass keyword in python. 67
- 68. 68 The End



























![Python Data Types
31
Example Data Types
x = "Hello World" str
x = 20 int
x = 20.5 float
x = 1j complex
x = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] list
x = ("apple", "banana", "cherry") tuple
x = range(6) range
x = {"name" : "John", "age" : 36} dict
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"} set
x = frozenset({"apple", "banana", "cherry"}) frozenset
x = True bool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-31-320.jpg)




![Python String Indexing
36
Example:
String1 = "GeeksForGeeks"
print("Initial String: ")
print(String1)
print("nFirst character of String is: ")
print(String1[0])
print("nLast character of String is: ")
print(String1[-1])
Output:
Initial String:
GeeksForGeeks
First character of String is:
G
Last character of String is:
s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-36-320.jpg)
![Python String Indexing
• Reversing a Python String:
• By accessing characters from a string, we can also reverse strings in
Python.
• We can Reverse a string by using String slicing method.
37
Example:
str = "geeksforgeeks"
print(str[::-1])
Output:
skeegrofskeeg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-37-320.jpg)
![Python String Slicing
• String Slicing:
• In Python, the String Slicing method is used to access a range of
characters in the String.
• Slicing in a String is done by using a Slicing operator, i.e., a colon (:).
• String returned after slicing includes the character at the start index
but not the character at the last index.
• In this example, we will use the string-slicing method to extract a
substring of the original string. The [3:12] indicates that the string
slicing will start from the 3rd index of the string to the 12th index,
(12th character not including). We can also use negative indexing in
string slicing.
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-38-320.jpg)
![Python String Slicing
39
Example:
String1 = "GeeksForGeeks"
print("Initial String: ")
print(String1)
print("nSlicing characters from 3-12: ")
print(String1[3:12])
print("nSlicing characters between " +
"3rd and 2nd last character: ")
print(String1[3:-2])
Output:
Initial String:
GeeksForGeeks
Slicing characters from 3-12:
ksForGeek
Slicing characters between 3rd and 2nd
last character:
ksForGee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-39-320.jpg)


![Python String
42
# Python Program to Update character of a String
String1 = "Hello, I'm a Geek"
print("Initial String: ")
print(String1)
list1 = list(String1)
list1[2] = 'p'
String2 = ''.join(list1)
print("nUpdating character at 2nd Index: ")
print(String2)
String3 = String1[0:2] + 'p' + String1[3:]
print(String3)
Output:
Initial String:
Hello, I'm a Geek
Updating character at 2nd Index:
Heplo, I'm a Geek
Heplo, I'm a Geek](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-42-320.jpg)


![Python String
45
Example:
String1 = "Hello, I'm a Geek"
print("Initial String: ")
print(String1)
String2 = String1[0:2] + String1[3:]
print("nDeleting character at 2nd
Index: ")
print(String2)
Output:
Initial String:
Hello, I'm a Geek
Deleting character at 2nd Index:
Helo, I'm a Geek](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonunit-11-240913132017-1248e94b/85/Python_Programming_PPT-Basics-of-python-programming-language-45-320.jpg)


















































![kddprocess-[1].pptx DAta Mining Seminar KDD process](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/kddprocess-1-241112064254-4d5d2007-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

























