Session 07 - Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes77 views
In this session, you will learn: 1. Object-Oriented Concepts 2. Introduction to OO Analysis and Design
1 of 38
Downloaded 11 times





![Page 5Classification: Restricted
5
What kind of language can alleviate difficulties with
communication & complexity hopefully well?
Why Object-Oriented?
“The "software crises" came about when people realized the major
problems in software development were … caused by communication
difficulties and the management of complexity” [Budd]
The Whorfian Hypothesis:
Human beings … are very much at the mercy of the particular language
which has become the medium of expression for their society … the 'real
world' is … built upon the language habits …
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session07-introtoobjectorientedprogrammingwithjava-slides-180607171625/85/Session-07-Intro-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-with-Java-6-320.jpg)

























![Page 34Classification: Restricted
Object and Class in Java - Demo
A basic example of a class:
class Student1{
int id;//data member (also instance variable)
String name;//data member(also instance variable)
public static void main(String args[]){
Student1 s1=new Student1();//creating an object of Student
System.out.println(s1.id);
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session07-introtoobjectorientedprogrammingwithjava-slides-180607171625/85/Session-07-Intro-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-with-Java-35-320.jpg)
![Page 35Classification: Restricted
Another Example of Objects and Classes in Java
class Student2{
int rollno;
String name;
void insertRecord(int r, String n){ //method
rollno=r;
name=n;
}
void displayInformation(){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name);}//method
public static void main(String args[]){
Student2 s1=new Student2();
Student2 s2=new Student2();
s1.insertRecord(111,"Karan");
s2.insertRecord(222,"Aryan");
s1.displayInformation();
s2.displayInformation();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session07-introtoobjectorientedprogrammingwithjava-slides-180607171625/85/Session-07-Intro-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-with-Java-36-320.jpg)


Ad
Recommended
Session 18 - Review Session and Attending Java Interviews



Session 18 - Review Session and Attending Java InterviewsPawanMM This document provides an overview of topics to be covered in a Java interview preparation session, including common Java interview questions, OOP concepts, exceptions, collections, and maps. Sample questions cover Java fundamentals like object-oriented programming principles, inheritance, polymorphism, abstract classes versus interfaces, exception handling, and collections like lists versus sets versus maps. The session aims to help candidates understand commonly asked interview questions and prepare for a Java programming interview.
Session 16 - Collections - Sorting, Comparing Basics



Session 16 - Collections - Sorting, Comparing BasicsPawanMM In this session you will learn:
1. Recap of Arrays, ArrayLists
2. Basically, there can be 2 operations that you would want to perform on Arrays/ArrayLists.. (and maybe, other collections)
3. Search: Override equals() and hashCode().
4. Sort: provide comparison logic – Two ways
4.1 Comparable interface
4.2 Comparator interface
Session 14 - Object Class



Session 14 - Object ClassPawanMM This document provides an overview of the Object class in Java. It discusses the toString(), equals(), and hashCode() methods. The toString() method returns a string representation of an object. The equals() method tests for equality between two objects. The hashCode() method generates a hash value for an object used in hash tables. It is important to override these methods in subclasses to define object equality and hashing behavior. The document also covers concepts like hashing, hash tables, and hash functions.
Session 19 - Review Session



Session 19 - Review SessionPawanMM This document summarizes the content covered in a Java training session on review questions. It includes questions on Java access modifiers, autoboxing, overriding methods, static vs non-static contexts, differences between Lists and Sets in Java, and topics to be covered in the next session including Maps, HashMaps, TreeMaps and Map methods.
OOP with Java - Continued 



OOP with Java - Continued Hitesh-Java In this core java training session, you will learn OOP with Java Contd. Topics covered in this session are:
• Review of last class concepts
• Types of Inheritance and a look at Aggregation
• Polymorphism
• Method overloading
• Method overriding
For more information about this course visit on this link: https://www.mindsmapped.com/courses/software-development/learn-java-fundamentals-hands-on-training-on-core-java-concepts/
Object Oriented Programming Concepts



Object Oriented Programming ConceptsAbhigyan Singh Yadav Basic Concepts of Object Oriented Programming (OOP) explained in layman's terms. For having a better understanding of building blocks of OOPs Language. Explanantion of Class, Objects & Methods followed by explanation of Message Passing, Inheritance, Abstraction, Encapsulation, & Polymorphism with examples.
Objected-Oriented Programming with Java



Objected-Oriented Programming with JavaOum Saokosal This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in Java, including classes, objects, constructors, and accessing object data and methods. It defines a class as a template for creating objects, with data fields and behaviors like constructors and methods. Constructors are used to construct (create) objects from a class by initializing their data fields. Objects are then accessed by calling their methods, such as a toString() method to return the object's data as a string. The document also notes that Java is a pure object-oriented programming language and many other languages also use OOP.
Object Oriented Programming_Lecture 2



Object Oriented Programming_Lecture 2Mahmoud Alfarra chapter 1: Lecture 2
Let’s think on concept of Class and Object
- Concept of Objects and classes
- UML Class Diagram
الكلية الجامعية للعلوم والتكنولوجيا - خان يونس
University college of science & technology
OOPS Characteristics



OOPS Characteristicsbaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers This document discusses the key concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP) including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It defines objects as instances of classes that have data fields and methods. Classes contain both data and functions and can have private, public, or protected members. Encapsulation binds data and functions into a class. Inheritance allows deriving new classes from existing ones. Polymorphism enables classes to provide different implementations of methods with the same name. Abstraction simplifies complexity by modeling appropriate classes for a problem.
Object oriented programming With C#



Object oriented programming With C#Youssef Mohammed Abohaty This document introduces object-oriented programming concepts including classes, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. It discusses how OOP allows for more organized and flexible code through the use of classes, objects, and methods. Key aspects of classes like constructors, destructors, and access modifiers are explained. Other concepts covered include static vs non-static classes, method overloading, enumerations, structures, abstract classes, interfaces, and abstract methods. The document aims to provide an overview of fundamental OOP principles.
Object oriented programming concepts



Object oriented programming conceptsrahuld115 This presentation provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP). It discusses key OOP concepts including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and message passing. Objects are instances of classes that contain both data and behaviors. Classes define common properties and methods for objects. Encapsulation binds data and functions together, while inheritance allows classes to inherit properties from parent classes. Polymorphism allows the same message to be interpreted differently. Message passing facilitates communication between objects.
Chapter2 array of objects



Chapter2 array of objectsMahmoud Alfarra This document discusses arrays of objects in object-oriented programming. It outlines that a class can be used as a new data type, and arrays can be defined to hold multiple objects of that class. Methods can be used to manage arrays of objects, such as adding, deleting, and searching for objects. The document also explains that objects are passed by reference to methods rather than by value. An immutable class is defined as one that does not allow changes to its private data fields once an object is created. The document provides a full example of a contact book program that uses a Contact class and ManagArray class to store contact objects in an array and perform operations on them.
04. Review OOP with Java



04. Review OOP with JavaOum Saokosal This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in Java including arrays, classes and objects, inheritance, abstract classes, overridden methods, interfaces, and polymorphism. It defines each concept and provides examples in Java code to illustrate how each concept works in practice.
4 pillars of OOPS CONCEPT



4 pillars of OOPS CONCEPTAjay Chimmani it describes the main concepts of object oriented programming
For more posts : http://comsciguide.blogspot.com/
For full playlist of Interview puzzles videos : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3v9ipJOEEPfI4zt4ExamGJwndkvg0SFc
24 standard interview puzzles: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3v9ipJOEEPefIF4nscYOobim1iRBJTjw
Aptitude training playlist link : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3v9ipJOEEPfumKHa02HWjCfPvGQiPZiG
for C and C++ questions, that are asked in the interviews, go through the posts in the link : http://comsciguide.blogspot.com/
for more videos, my youtube channel : https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCvMy2V7gYW7VR2WgyvLj3-A
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming



Introduction to Object Oriented ProgrammingMoutaz Haddara An Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Download the presentation to view it correctly, as it has some animations that won't show here.
If you have any questions, please contact me. You are free to use it this presentation, but it would be nice at least to give me some credit :)
Content:
1- History of Programming
2. Objects and Classes
3- Abstraction, Inheritance, Encapsulation, and Polymorphism
Characteristics of oop



Characteristics of oopRasim Izhar Ali This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts. It defines OOP as a programming technique that uses objects and classes. Key concepts discussed include classes and objects, inheritance, data abstraction, encapsulation, and polymorphism. Benefits of OOP include reusability, extensibility, understandability and security. Inheritance allows reuse of existing classes, and can be single, multiple, public, protected or private. Data abstraction hides background details and provides essential information. Encapsulation binds data and functions that manipulate the data. Polymorphism enables different object types to respond to the same function name.
Classes And Objects



Classes And Objectsrahulsahay19 This document provides an overview of classes and objects in C#, covering key concepts like constructors, inheritance, access modifiers, abstract classes, static classes, sealed classes, and partial classes. It compares classes to objects, discusses how constructors are used to create objects, and explains features like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism that C# supports for object-oriented programming. The summary reiterates that C# provides everything needed for OOP and additionally discusses static classes, sealed classes, and partial classes.
Lecture 2



Lecture 2emailharmeet The document discusses key concepts in object-oriented programming (OOP) including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and message passing. It provides examples of a simple class named "item" that includes variables and methods. It also discusses how objects are composed of data and functions, and how classes are used to organize data and functions through principles like private/public access and data abstraction.
Introduction to object oriented programming



Introduction to object oriented programmingAbzetdin Adamov This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming concepts including abstraction, encapsulation, and inheritance. It defines abstraction as identifying an object's crucial behavior while eliminating irrelevant details. Encapsulation ties an object's state and behavior together, keeping them hidden from external code. Inheritance allows a new class to inherit behaviors from an existing parent class, expressing "is-a" relationships. Real-world objects have state represented by fields and behavior exposed through methods.
Oops concept on c#



Oops concept on c#baabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in C#, including classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. It defines key terms like class and object, and explains how C# supports OOP principles such as defining classes with methods and properties, extending classes through inheritance, hiding implementation through encapsulation, and allowing polymorphic behavior through function overloading and overriding. Abstract classes and sealed modifiers are also covered. The document is intended to help explain basic OOP concepts in C# to readers.
البرمجة الهدفية بلغة جافا - مفاهيم أساسية 



البرمجة الهدفية بلغة جافا - مفاهيم أساسية Mahmoud Alfarra ملفات مساق البرمجة الهدفية (الشيئية) التي يتم تدريسها لطلبة بكالوريوس تكنولوجيا المعلومات وبكالوريوس تطوير نظم الحاسوب في الكلية الجامعية للعلوم والتكنولوجيا.
الملف يضم مفاهيم:
Class
Object
إعدادي وتدريسي
Java Programming - Polymorphism



Java Programming - PolymorphismOum Saokosal This document discusses polymorphism and inheritance in object-oriented programming. It begins with defining polymorphism and how it relates to inheritance and class encapsulation. An example is provided to demonstrate how a reference variable can refer to objects from different classes that inherit from the same parent class. The document also discusses specific uses of polymorphism in methods and arrays, as well as notes about overriding and adding new methods. It covers casting objects and using the instanceof operator to check the type before casting. Key concepts of polymorphism, inheritance, overriding, and casting are summarized.
Object oriented programming



Object oriented programmingSandeep Karthikeyan Object oriented programming is based on the concepts of classes and objects, where a class defines attributes and methods that objects follow as real-world instances of the class. For example, the human being class could define attributes like name and methods like walk(), and John would be an object instance of that class. Popular object oriented programming languages include C++, C#, Python, Java, and JavaScript. OOP aims to simplify complex processes, promote modularity for code reusability and efficiency, group similar things together and separate dissimilar things, and protect data through encapsulation.
Session 13 - Exception handling - continued



Session 13 - Exception handling - continuedPawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Throw and Throws keywords
2. Exception propagation – the cases of Checked and Unchecked Exceptions
3. Defining your own custom Exception
Ruby OOP: Objects over Classes



Ruby OOP: Objects over ClassesAman King A talk presented in RubyConf India 2010 at Bangalore, India. It revisits the role of objects and classes in Ruby OOP, and encourages programmers to discover a new approach to OOP.
Object oriented programming concept- Saurabh Upadhyay



Object oriented programming concept- Saurabh UpadhyaySaurabh Upadhyay On this Presentation, we will learn about the basics of OOPs. Object-Oriented Programming is a paradigm that provides many concepts, such as inheritance, data binding, polymorphism, etc.
Simula is considered the first object-oriented programming language. The programming paradigm where everything is represented as an object is known as a truly object-oriented programming language.
Smalltalk is considered the first truly object-oriented programming language.
Inner Classes & Multi Threading in JAVA



Inner Classes & Multi Threading in JAVATech_MX The document discusses inner classes, static classes, and multithreading in Java. It defines inner classes as classes defined within other classes. There are four types of inner classes: non-static, static, local, and anonymous. Static inner classes are similar to top-level classes but are declared within another class. They can be accessed without creating an instance of the outer class. Multithreading allows multiple parts of a program to run concurrently by using threads.
Lecture 4



Lecture 4emailharmeet Object oriented programming involves creating classes that define objects and their behaviors, and then creating objects from those classes that can communicate by sending messages. The key aspects are:
1. Creating classes that define abstract data types with attributes and methods.
2. Instantiating objects from those classes that have unique identities and states.
3. Sending messages to objects by calling their methods using dot notation.
Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java 



Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java Hitesh-Java In this core java training session, you will learn Object Oriented Programming. Topics covered in this session are:
• Object Oriented Programming Concepts
• Introduction to OO Analysis and Design
For more information about this course visit on this link: https://www.mindsmapped.com/courses/software-development/learn-java-fundamentals-hands-on-training-on-core-java-concepts/
Core Java for Selenium



Core Java for SeleniumRajathi-QA In this quality assurance training session, you will learn Core Java for Selenium. Topics covered in this course are:
• Java Fundamentals
• Introduction to Java
• Programming Language fundamentals
• Key Java Concepts
• Strings and collections
TO know more, visit this link: https://www.mindsmapped.com/courses/quality-assurance/get-practical-training-on-software-testing-quality-assurance-qa/
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
OOPS Characteristics



OOPS Characteristicsbaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers This document discusses the key concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP) including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It defines objects as instances of classes that have data fields and methods. Classes contain both data and functions and can have private, public, or protected members. Encapsulation binds data and functions into a class. Inheritance allows deriving new classes from existing ones. Polymorphism enables classes to provide different implementations of methods with the same name. Abstraction simplifies complexity by modeling appropriate classes for a problem.
Object oriented programming With C#



Object oriented programming With C#Youssef Mohammed Abohaty This document introduces object-oriented programming concepts including classes, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. It discusses how OOP allows for more organized and flexible code through the use of classes, objects, and methods. Key aspects of classes like constructors, destructors, and access modifiers are explained. Other concepts covered include static vs non-static classes, method overloading, enumerations, structures, abstract classes, interfaces, and abstract methods. The document aims to provide an overview of fundamental OOP principles.
Object oriented programming concepts



Object oriented programming conceptsrahuld115 This presentation provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP). It discusses key OOP concepts including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and message passing. Objects are instances of classes that contain both data and behaviors. Classes define common properties and methods for objects. Encapsulation binds data and functions together, while inheritance allows classes to inherit properties from parent classes. Polymorphism allows the same message to be interpreted differently. Message passing facilitates communication between objects.
Chapter2 array of objects



Chapter2 array of objectsMahmoud Alfarra This document discusses arrays of objects in object-oriented programming. It outlines that a class can be used as a new data type, and arrays can be defined to hold multiple objects of that class. Methods can be used to manage arrays of objects, such as adding, deleting, and searching for objects. The document also explains that objects are passed by reference to methods rather than by value. An immutable class is defined as one that does not allow changes to its private data fields once an object is created. The document provides a full example of a contact book program that uses a Contact class and ManagArray class to store contact objects in an array and perform operations on them.
04. Review OOP with Java



04. Review OOP with JavaOum Saokosal This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in Java including arrays, classes and objects, inheritance, abstract classes, overridden methods, interfaces, and polymorphism. It defines each concept and provides examples in Java code to illustrate how each concept works in practice.
4 pillars of OOPS CONCEPT



4 pillars of OOPS CONCEPTAjay Chimmani it describes the main concepts of object oriented programming
For more posts : http://comsciguide.blogspot.com/
For full playlist of Interview puzzles videos : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3v9ipJOEEPfI4zt4ExamGJwndkvg0SFc
24 standard interview puzzles: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3v9ipJOEEPefIF4nscYOobim1iRBJTjw
Aptitude training playlist link : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL3v9ipJOEEPfumKHa02HWjCfPvGQiPZiG
for C and C++ questions, that are asked in the interviews, go through the posts in the link : http://comsciguide.blogspot.com/
for more videos, my youtube channel : https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCvMy2V7gYW7VR2WgyvLj3-A
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming



Introduction to Object Oriented ProgrammingMoutaz Haddara An Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Download the presentation to view it correctly, as it has some animations that won't show here.
If you have any questions, please contact me. You are free to use it this presentation, but it would be nice at least to give me some credit :)
Content:
1- History of Programming
2. Objects and Classes
3- Abstraction, Inheritance, Encapsulation, and Polymorphism
Characteristics of oop



Characteristics of oopRasim Izhar Ali This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts. It defines OOP as a programming technique that uses objects and classes. Key concepts discussed include classes and objects, inheritance, data abstraction, encapsulation, and polymorphism. Benefits of OOP include reusability, extensibility, understandability and security. Inheritance allows reuse of existing classes, and can be single, multiple, public, protected or private. Data abstraction hides background details and provides essential information. Encapsulation binds data and functions that manipulate the data. Polymorphism enables different object types to respond to the same function name.
Classes And Objects



Classes And Objectsrahulsahay19 This document provides an overview of classes and objects in C#, covering key concepts like constructors, inheritance, access modifiers, abstract classes, static classes, sealed classes, and partial classes. It compares classes to objects, discusses how constructors are used to create objects, and explains features like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism that C# supports for object-oriented programming. The summary reiterates that C# provides everything needed for OOP and additionally discusses static classes, sealed classes, and partial classes.
Lecture 2



Lecture 2emailharmeet The document discusses key concepts in object-oriented programming (OOP) including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and message passing. It provides examples of a simple class named "item" that includes variables and methods. It also discusses how objects are composed of data and functions, and how classes are used to organize data and functions through principles like private/public access and data abstraction.
Introduction to object oriented programming



Introduction to object oriented programmingAbzetdin Adamov This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming concepts including abstraction, encapsulation, and inheritance. It defines abstraction as identifying an object's crucial behavior while eliminating irrelevant details. Encapsulation ties an object's state and behavior together, keeping them hidden from external code. Inheritance allows a new class to inherit behaviors from an existing parent class, expressing "is-a" relationships. Real-world objects have state represented by fields and behavior exposed through methods.
Oops concept on c#



Oops concept on c#baabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in C#, including classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. It defines key terms like class and object, and explains how C# supports OOP principles such as defining classes with methods and properties, extending classes through inheritance, hiding implementation through encapsulation, and allowing polymorphic behavior through function overloading and overriding. Abstract classes and sealed modifiers are also covered. The document is intended to help explain basic OOP concepts in C# to readers.
البرمجة الهدفية بلغة جافا - مفاهيم أساسية 



البرمجة الهدفية بلغة جافا - مفاهيم أساسية Mahmoud Alfarra ملفات مساق البرمجة الهدفية (الشيئية) التي يتم تدريسها لطلبة بكالوريوس تكنولوجيا المعلومات وبكالوريوس تطوير نظم الحاسوب في الكلية الجامعية للعلوم والتكنولوجيا.
الملف يضم مفاهيم:
Class
Object
إعدادي وتدريسي
Java Programming - Polymorphism



Java Programming - PolymorphismOum Saokosal This document discusses polymorphism and inheritance in object-oriented programming. It begins with defining polymorphism and how it relates to inheritance and class encapsulation. An example is provided to demonstrate how a reference variable can refer to objects from different classes that inherit from the same parent class. The document also discusses specific uses of polymorphism in methods and arrays, as well as notes about overriding and adding new methods. It covers casting objects and using the instanceof operator to check the type before casting. Key concepts of polymorphism, inheritance, overriding, and casting are summarized.
Object oriented programming



Object oriented programmingSandeep Karthikeyan Object oriented programming is based on the concepts of classes and objects, where a class defines attributes and methods that objects follow as real-world instances of the class. For example, the human being class could define attributes like name and methods like walk(), and John would be an object instance of that class. Popular object oriented programming languages include C++, C#, Python, Java, and JavaScript. OOP aims to simplify complex processes, promote modularity for code reusability and efficiency, group similar things together and separate dissimilar things, and protect data through encapsulation.
Session 13 - Exception handling - continued



Session 13 - Exception handling - continuedPawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Throw and Throws keywords
2. Exception propagation – the cases of Checked and Unchecked Exceptions
3. Defining your own custom Exception
Ruby OOP: Objects over Classes



Ruby OOP: Objects over ClassesAman King A talk presented in RubyConf India 2010 at Bangalore, India. It revisits the role of objects and classes in Ruby OOP, and encourages programmers to discover a new approach to OOP.
Object oriented programming concept- Saurabh Upadhyay



Object oriented programming concept- Saurabh UpadhyaySaurabh Upadhyay On this Presentation, we will learn about the basics of OOPs. Object-Oriented Programming is a paradigm that provides many concepts, such as inheritance, data binding, polymorphism, etc.
Simula is considered the first object-oriented programming language. The programming paradigm where everything is represented as an object is known as a truly object-oriented programming language.
Smalltalk is considered the first truly object-oriented programming language.
Inner Classes & Multi Threading in JAVA



Inner Classes & Multi Threading in JAVATech_MX The document discusses inner classes, static classes, and multithreading in Java. It defines inner classes as classes defined within other classes. There are four types of inner classes: non-static, static, local, and anonymous. Static inner classes are similar to top-level classes but are declared within another class. They can be accessed without creating an instance of the outer class. Multithreading allows multiple parts of a program to run concurrently by using threads.
Lecture 4



Lecture 4emailharmeet Object oriented programming involves creating classes that define objects and their behaviors, and then creating objects from those classes that can communicate by sending messages. The key aspects are:
1. Creating classes that define abstract data types with attributes and methods.
2. Instantiating objects from those classes that have unique identities and states.
3. Sending messages to objects by calling their methods using dot notation.
Similar to Session 07 - Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java (20)
Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java 



Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java Hitesh-Java In this core java training session, you will learn Object Oriented Programming. Topics covered in this session are:
• Object Oriented Programming Concepts
• Introduction to OO Analysis and Design
For more information about this course visit on this link: https://www.mindsmapped.com/courses/software-development/learn-java-fundamentals-hands-on-training-on-core-java-concepts/
Core Java for Selenium



Core Java for SeleniumRajathi-QA In this quality assurance training session, you will learn Core Java for Selenium. Topics covered in this course are:
• Java Fundamentals
• Introduction to Java
• Programming Language fundamentals
• Key Java Concepts
• Strings and collections
TO know more, visit this link: https://www.mindsmapped.com/courses/quality-assurance/get-practical-training-on-software-testing-quality-assurance-qa/
PHP OOP Lecture - 01.pptx



PHP OOP Lecture - 01.pptxAtikur Rahman This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP). It discusses procedural programming and how it differs from OOP. The main features/principles of OOP are data abstraction, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. Advantages of OOP include promoting code reuse and flexibility through polymorphism. Key terms are defined, including class, object, properties, and methods. A class defines the blueprint for an object, while an object is an instance of a class that occupies memory.
Introduction to OOP concepts



Introduction to OOP conceptsAhmed Farag Introduction to OOP concepts:
- encapsulation
- inheritance
- polymorphism
- abstraction
Menofia University
Object oriented vs. object based programming



Object oriented vs. object based programmingMohammad Kamrul Hasan this slides describe similarities and difference between object based programming and object oriented programming
Class and Object.
Object- oriented Programming
Object based Programming
Object based vs. object-oriented programming
C# by Zaheer Abbas Aghani



C# by Zaheer Abbas AghaniInformation Technology Center C# is an object-oriented programming language created by Microsoft that can be used to create a variety of applications. The key steps in executing a C# program are compilation, where source code is converted to bytecode, and execution, where the bytecode is converted to machine code and run. C# supports important object-oriented concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction and encapsulation. Classes define the attributes and behaviors of objects, and objects are instantiated from classes. Constructors initialize new objects.
C# by Zaheer Abbas Aghani



C# by Zaheer Abbas AghaniInformation Technology Center C# is an object-oriented programming language created by Microsoft. It was created by a team led by Anders Hejlsberg with the goal of combining the best aspects of existing languages and improving upon them. C# code is compiled into an intermediate language called IL, which is then executed by the Common Language Runtime (CLR). Key concepts of object-oriented programming in C# include classes, objects, abstraction, encapsulation, polymorphism, and inheritance. Classes define the attributes and behaviors of objects, and objects are instances of classes.
Overview of Object Oriented Programming using C++



Overview of Object Oriented Programming using C++jayanthi699330 Basic Concepts of Object Oriented Programming
PPT_Object Oriented Programming (2).pptx



PPT_Object Oriented Programming (2).pptxfaizus786 This is a ppt about oops in which we can learn about coding , more specifically about Object Orientated Programming in different languages and th basic concepts of it sjskksjsjsjsjwnsnnsmamamammssmsmmsmsmsmsmammamamamamammamamamammamamamamammamamamamamskakkama
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that organizes software design around objects rather than functions or logic. Objects represent entities in the real world, containing data (attributes) and behavior (methods). This paradigm simplifies complex software design by focusing on reusability, modularity, and maintainability. Below is an in-depth discussion of OOP concepts, principles, and their applications.
Core Concepts of OOP
1. Objects
An object is an instance of a class. It encapsulates data (attributes) and methods (functions) that operate on the data. For example, a Car object may have attributes like color and speed and methods like accelerate() or brake().
2. Classes
A class is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines the structure (attributes) and behavior (methods) that the objects of that class will have. For example:
class Car:
def __init__(self, color, speed):
self.color = color
self.speed = speed
def accelerate(self):
self.speed += 10
Here, the Car class provides a template, and we can create multiple car objects with different attributes.
3. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is the process of bundling data and methods that operate on
Object Oriented Programming



Object Oriented ProgrammingRatnaJava In this session you will learn:
Implement classes and objects in Java
Create class constructors
Overload constructors
Inherit classes and create sub-classes
Implement abstract classes and methods
Use static keyword
For more information: https://www.mindsmapped.com/courses/software-development/become-a-java-developer-hands-on-training/
Introduction to Java Object Oiented Concepts and Basic terminologies



Introduction to Java Object Oiented Concepts and Basic terminologiesTabassumMaktum The document discusses the basic concepts of object-oriented programming including objects, classes, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It defines objects as entities with attributes and behaviors. Classes are templates that describe common properties and behaviors of objects. Abstraction hides unnecessary details and focuses on important attributes. Encapsulation binds code and data together and restricts access. Inheritance creates a parent-child relationship between classes where subclasses inherit attributes of base classes. Polymorphism allows the same operation to be applied to different types.
javaopps concepts



javaopps conceptsNikhil Agrawal The document discusses key concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP) in Java, including objects, classes, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It provides examples of classes like Student and Rectangle to demonstrate how objects are instantiated from classes and how methods can access and modify object attributes.
OOP.pptx



OOP.pptxashmitsen2005 Object-oriented programming (OOP) organizes software design around objects rather than functions and logic. An object can be defined as a data field with unique attributes and behavior. OOP uses classes as templates that describe an object's behaviors and states, with objects being instances of classes. Key concepts of OOP include inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, encapsulation, and classes.
power poitnt of oops



power poitnt of oopsDhiraj Kumar 1. The document discusses key concepts in object-oriented programming including classes, objects, state, methods, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
2. A class defines an object type and its attributes and behaviors, while an object is an instance of a class that exists in memory.
3. Objects communicate by passing messages and have state represented by attribute values and behaviors defined as methods.
Object -oriented analysis and design.ppt



Object -oriented analysis and design.pptpierrerj05 This document contain class diagram, object diagram and the principles of object oriented programming
Chapter 1- Introduction.ppt



Chapter 1- Introduction.pptTigistTilahun1 The document discusses object-oriented programming and the Java programming language. It begins by describing the different types of computer languages, including machine languages, assembly languages, and high-level languages. It then provides an overview of the Java programming language, noting that it is a high-level, compiled and interpreted language. The document also discusses key concepts of object-oriented programming like objects, classes, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It provides examples of objects, classes, and how to initialize objects in Java.
Oops concepts



Oops conceptsACCESS Health Digital This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts. It begins by defining a programming language and different levels of abstraction in languages. It then defines object-oriented programming as relying on classes and objects, with classes acting as blueprints for objects. The basic building blocks of OOP - objects, classes, attributes, and methods - are introduced. Each concept is then defined in more detail, including objects, classes, inheritance, encapsulation, abstraction, and polymorphism. The document concludes by outlining some advantages of using an object-oriented programming approach.
Introduction to oop and java fundamentals



Introduction to oop and java fundamentalsAnsgarMary This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming concepts in Java, including classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It then discusses the Java programming environment, fundamental programming structures in Java like data types, variables, operators, control flow statements, and arrays. Key characteristics of the Java language are also summarized.
Ad
More from PawanMM (20)
Session 48 - JS, JSON and AJAX



Session 48 - JS, JSON and AJAXPawanMM This document provides an agenda for a training session on frontend development fundamentals including HTML for content, JavaScript for user interaction, and CSS for styling and layout. It also includes an example login form with fields for a user ID and password, and instructions and reset options. The training aims to cover basic concepts for building interfaces and handling user input.
Session 46 - Spring - Part 4 - Spring MVC



Session 46 - Spring - Part 4 - Spring MVCPawanMM In this session you will learn:
1. Spring framework
2. Inversion of Control
3. Dependency Injection – Two types
4. Defining beans using XML
5. Inheriting beans
6. Auto-wiring
7. Annotations based on a configuration
8. Java-based configuration
9. Spring AOP
Session 45 - Spring - Part 3 - AOP



Session 45 - Spring - Part 3 - AOPPawanMM This document provides an overview of Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP) using Spring. It defines key AOP concepts like join points, pointcuts, advice, and aspects. It discusses how AOP can be used to separate cross-cutting concerns from core application logic. It also presents examples of implementing different types of advice like before, after, after-returning and around advice using Spring AOP annotations. Finally, it provides examples of configuring AOP using XML and the jars required to implement AOP with AspectJ.
Session 44 - Spring - Part 2 - Autowiring, Annotations, Java based Configuration



Session 44 - Spring - Part 2 - Autowiring, Annotations, Java based ConfigurationPawanMM In this session you will learn:
1. Auto-wiring
2. Annotations based on the configuration
3. Java-based configuration
Session 43 - Spring - Part 1 - IoC DI Beans



Session 43 - Spring - Part 1 - IoC DI BeansPawanMM In this session you will learn:
1.Spring Framework
2. Core Container
3. Data Access/Integration
4. Web Layer
5. Spring Setup
6. Key features
7. Spring Bean
8. Dependency Injection
9. Relation between DI and IoC
10. Spring IoC Containers
11. Spring DI
Session 42 - Struts 2 Hibernate Integration



Session 42 - Struts 2 Hibernate IntegrationPawanMM In this session you will learn:
1. Struts 2
2. Struts Action Class
3. Validation
4. Control Tags
5. Data Tags
Session 41 - Struts 2 Introduction



Session 41 - Struts 2 IntroductionPawanMM In this session you will learn:
1. Introduction to Struts Framework
2. Features
3. Evolution
4. Struts Demo
5. Declarative validation
6. Architecture
7. Validators
8. Interceptors
Session 40 - Hibernate - Part 2



Session 40 - Hibernate - Part 2PawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Generator Class in Hibernate
2. SQL Dialects
3. Collection Mapping
4. One-to-one Mapping
5. Cascade Types
6. Many to one / One to many
7. Hibernate Lazy Loading
8. Transaction Management
9. HQL – Hibernate Query Language
10. HCQL – Hibernate Criteria Query Language
11. Hibernate Caching
Session 39 - Hibernate - Part 1



Session 39 - Hibernate - Part 1PawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Hibernate
2. Advantages of Hibernate
3. Hibernate Architecture – High Level
4. Hibernate – Detailed Architecture
5. Hibernate Architecture – Important Levels
6. Hibernate jar files
7. Hibernate tools download
8. CRUD Operations
9. Hibernate with Annotations
10. Design Patterns in Java
Session 38 - Core Java (New Features) - Part 1



Session 38 - Core Java (New Features) - Part 1PawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Core Java features with Examples
2. Assertions
3. Varargs
4. Static import
5. Autoboxing and Unboxing
6. Enum
7. Covariant
8. Annotations
9. Generics
10. Instrumentation
11. Catch Multiple Exceptions
Session 37 - JSP - Part 2 (final)



Session 37 - JSP - Part 2 (final)PawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. JSP vs Servlet
2. LifeCycle of Servlet
3. JSP Elements
4. JSP Page directive
5. Directives vs Action tags
Session 36 - JSP - Part 1



Session 36 - JSP - Part 1PawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. JSP (Java Server Pages Technology)
2. JSP vs Servlet
3. MVC Architecture
4. Scriplet
Session 35 - Design Patterns



Session 35 - Design PatternsPawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Design Patterns
2. Flow of the Demo App
3. Value objects
4. Data Access object
5. Factory pattern
Session 34 - JDBC Best Practices, Introduction to Design Patterns



Session 34 - JDBC Best Practices, Introduction to Design PatternsPawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Deployment Descriptor
2. Configuring and Mapping a Servlet
3. The flow of the demo web apps
4. JDBC Best practices
5. Design Patterns
Session 33 - Session Management using other Techniques



Session 33 - Session Management using other TechniquesPawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Session Management
2. Servlets
3. Hidden fields
4. URL rewriting
5. HTTPSession
Session 32 - Session Management using Cookies



Session 32 - Session Management using CookiesPawanMM This document discusses session management in Java servlets using various techniques like cookies, hidden form fields, URL rewriting, and HTTPSession. It begins with an overview of session tracking in servlets and why it is needed given the stateless nature of HTTP. It then demonstrates how to use cookies to maintain session state by creating, reading, and deleting cookies. The next session will cover session management in more detail using servlets, hidden fields, URL rewriting, and HTTPSession.
Session 31 - Session Management, Best Practices, Design Patterns in Web Apps



Session 31 - Session Management, Best Practices, Design Patterns in Web AppsPawanMM In this session, you will learn:
1. Session Management and Tracking
2. Best Practices
3. Design Patterns
4. Cookies
Session 30 - Servlets - Part 6



Session 30 - Servlets - Part 6PawanMM The document provides an overview of servlet scopes including request, session, application, and page scope. Request scope lasts for the duration of a single request, session scope spans multiple requests from the same client, application scope lasts for the entire duration the web application is running, and page scope is only applicable to JSP and lasts on a single page. The document also discusses the differences between servlet parameters and attributes, with parameters being read-only strings and attributes being read-write objects that can be added to different scopes.
Session 29 - Servlets - Part 5



Session 29 - Servlets - Part 5PawanMM This document provides an overview of servlets and Java EE concepts like request scopes, session scopes, and request dispatching. It discusses validating web applications, redirecting requests, and the differences between parameters and attributes. Code examples are provided for redirecting requests, using request dispatchers, and getting the servlet context. The different scopes - request, session, application - are explained in terms of their lifetime and how to store data within each scope.
Session 28 - Servlets - Part 4



Session 28 - Servlets - Part 4PawanMM This document summarizes key points from a Java & JEE training session on servlets. It discusses SQL injection exercises and form validation. It demonstrates validating forms using JavaScript on the client-side and Java on the server-side. Examples are given for JavaScript form validation, including checking for non-empty fields and restricting input length. The document also covers redirecting requests to other resources using response.sendRedirect() and includes code examples of redirecting. Finally, it previews topics for the next session, which will cover validation, redirection, and request scope in web applications.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Trends Artificial Intelligence - Mary Meeker



Trends Artificial Intelligence - Mary MeekerClive Dickens Mary Meeker’s 2024 AI report highlights a seismic shift in productivity, creativity, and business value driven by generative AI. She charts the rapid adoption of tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney, likening today’s moment to the dawn of the internet. The report emphasizes AI’s impact on knowledge work, software development, and personalized services—while also cautioning about data quality, ethical use, and the human-AI partnership. In short, Meeker sees AI as a transformative force accelerating innovation and redefining how we live and work.
Crypto Super 500 - 14th Report - June2025.pdf



Crypto Super 500 - 14th Report - June2025.pdfStephen Perrenod This OrionX's 14th semi-annual report on the state of the cryptocurrency mining market. The report focuses on Proof-of-Work cryptocurrencies since those use substantial supercomputer power to mint new coins and encode transactions on their blockchains. Only two make the cut this time, Bitcoin with $18 billion of annual economic value produced and Dogecoin with $1 billion. Bitcoin has now reached the Zettascale with typical hash rates of 0.9 Zettahashes per second. Bitcoin is powered by the world's largest decentralized supercomputer in a continuous winner take all lottery incentive network.
Establish Visibility and Manage Risk in the Supply Chain with Anchore SBOM



Establish Visibility and Manage Risk in the Supply Chain with Anchore SBOMAnchore Over 70% of any given software application consumes open source software (most likely not even from the original source) and only 15% of organizations feel confident in their risk management practices.
With the newly announced Anchore SBOM feature, teams can start safely consuming OSS while mitigating security and compliance risks. Learn how to import SBOMs in industry-standard formats (SPDX, CycloneDX, Syft), validate their integrity, and proactively address vulnerabilities within your software ecosystem.
June Patch Tuesday



June Patch TuesdayIvanti Ivanti’s Patch Tuesday breakdown goes beyond patching your applications and brings you the intelligence and guidance needed to prioritize where to focus your attention first. Catch early analysis on our Ivanti blog, then join industry expert Chris Goettl for the Patch Tuesday Webinar Event. There we’ll do a deep dive into each of the bulletins and give guidance on the risks associated with the newly-identified vulnerabilities.
Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account J...



Your startup on AWS - How to architect and maintain a Lean and Mean account J...angelo60207 Prevent infrastructure costs from becoming a significant line item on your startup’s budget! Serial entrepreneur and software architect Angelo Mandato will share his experience with AWS Activate (startup credits from AWS) and knowledge on how to architect a lean and mean AWS account ideal for budget minded and bootstrapped startups. In this session you will learn how to manage a production ready AWS account capable of scaling as your startup grows for less than $100/month before credits. We will discuss AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, architect priorities, and the importance of having flexible, optimized Infrastructure as Code. We will wrap everything up discussing opportunities where to save with AWS services such as S3, EC2, Load Balancers, Lambda Functions, RDS, and many others.
Cisco ISE Performance, Scalability and Best Practices.pdf



Cisco ISE Performance, Scalability and Best Practices.pdfsuperdpz Cisco ISE Performance, Scalability and Best Practices
cnc-drilling-dowel-inserting-machine-drillteq-d-510-english.pdf



cnc-drilling-dowel-inserting-machine-drillteq-d-510-english.pdfAmirStern2 CNC מכונות קידוח drillteq d-510
Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too Late



Kubernetes Security Act Now Before It’s Too LateMichael Furman In today's cloud-native landscape, Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for orchestrating containerized applications, but its inherent complexity introduces unique security challenges. Are you one YAML away from disaster?
This presentation, "Kubernetes Security: Act Now Before It’s Too Late," is your essential guide to understanding and mitigating the critical security risks within your Kubernetes environments. This presentation dives deep into the OWASP Kubernetes Top Ten, providing actionable insights to harden your clusters.
We will cover:
The fundamental architecture of Kubernetes and why its security is paramount.
In-depth strategies for protecting your Kubernetes Control Plane, including kube-apiserver and etcd.
Crucial best practices for securing your workloads and nodes, covering topics like privileged containers, root filesystem security, and the essential role of Pod Security Admission.
Don't wait for a breach. Learn how to identify, prevent, and respond to Kubernetes security threats effectively.
It's time to act now before it's too late!
Developing Schemas with FME and Excel - Peak of Data & AI 2025



Developing Schemas with FME and Excel - Peak of Data & AI 2025Safe Software When working with other team members who may not know the Esri GIS platform or may not be database professionals; discussing schema development or changes can be difficult. I have been using Excel to help illustrate and discuss schema design/changes during meetings and it has proven a useful tool to help illustrate how a schema will be built. With just a few extra columns, that Excel file can be sent to FME to create new feature classes/tables. This presentation will go thru the steps needed to accomplish this task and provide some lessons learned and tips/tricks that I use to speed the process.
Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME Flow



Providing an OGC API Processes REST Interface for FME FlowSafe Software This presentation will showcase an adapter for FME Flow that provides REST endpoints for FME Workspaces following the OGC API Processes specification. The implementation delivers robust, user-friendly API endpoints, including standardized methods for parameter provision. Additionally, it enhances security and user management by supporting OAuth2 authentication. Join us to discover how these advancements can elevate your enterprise integration workflows and ensure seamless, secure interactions with FME Flow.
Agentic AI: Beyond the Buzz- LangGraph Studio V2



Agentic AI: Beyond the Buzz- LangGraph Studio V2Shashikant Jagtap Presentation given at the LangChain community meetup London
https://lu.ma/9d5fntgj
Coveres
Agentic AI: Beyond the Buzz
Introduction to AI Agent and Agentic AI
Agent Use case and stats
Introduction to LangGraph
Build agent with LangGraph Studio V2
AI Agents in Logistics and Supply Chain Applications Benefits and Implementation



AI Agents in Logistics and Supply Chain Applications Benefits and ImplementationChristine Shepherd AI agents are reshaping logistics and supply chain operations by enabling automation, predictive insights, and real-time decision-making across key functions such as demand forecasting, inventory management, procurement, transportation, and warehouse operations. Powered by technologies like machine learning, NLP, computer vision, and robotic process automation, these agents deliver significant benefits including cost reduction, improved efficiency, greater visibility, and enhanced adaptability to market changes. While practical use cases show measurable gains in areas like dynamic routing and real-time inventory tracking, successful implementation requires careful integration with existing systems, quality data, and strategic scaling. Despite challenges such as data integration and change management, AI agents offer a strong competitive edge, with widespread industry adoption expected by 2025.
vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdf



vertical-cnc-processing-centers-drillteq-v-200-en.pdfAmirStern2 מכונות CNC קידוח אנכיות הן הבחירה הנכונה והטובה ביותר לקידוח ארונות וארגזים לייצור רהיטים. החלק נוסע לאורך ציר ה-x באמצעות ציר דיגיטלי מדויק, ותפוס ע"י צבת מכנית, כך שאין צורך לבצע setup (התאמות) לגדלים שונים של חלקים.
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...



Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL?
(POSETTE: An Event for Postgres 2025)
June 11, 2025
Shinya Kato
NTT DATA Japan Corporation
Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Cases



Domino IQ – What to Expect, First Steps and Use Casespanagenda Webinar Recording: https://www.panagenda.com/webinars/domino-iq-what-to-expect-first-steps-and-use-cases/
HCL Domino iQ Server – From Ideas Portal to implemented Feature. Discover what it is, what it isn’t, and explore the opportunities and challenges it presents.
Key Takeaways
- What are Large Language Models (LLMs) and how do they relate to Domino iQ
- Essential prerequisites for deploying Domino iQ Server
- Step-by-step instructions on setting up your Domino iQ Server
- Share and discuss thoughts and ideas to maximize the potential of Domino iQ
“Solving Tomorrow’s AI Problems Today with Cadence’s Newest Processor,” a Pre...



“Solving Tomorrow’s AI Problems Today with Cadence’s Newest Processor,” a Pre...Edge AI and Vision Alliance For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/06/solving-tomorrows-ai-problems-today-with-cadences-newest-processor-a-presentation-from-cadence/
Amol Borkar, Product Marketing Director at Cadence, presents the “Solving Tomorrow’s AI Problems Today with Cadence’s Newest Processor” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly integrating into every aspect of technology. While the neural processing unit (NPU) often receives the majority of the spotlight as the ultimate AI problem solver, it is essential to recognize that not all AI workloads can be efficiently executed on an NPU and that neural network architectures are evolving rapidly. To create efficient chips and systems with market longevity, designers must plan for diverse AI workloads that include networks yet to be invented.
In this presentation, Borkar introduces a new processor from Cadence Tensilica. This new solution is designed to complement any NPU, creating the perfect synergy between the two processing engines and establishing a robust AI subsystem able to efficiently support workloads yet to be encountered. This combination allows developers to achieve efficiency and performance on the AI workloads of today and tomorrow, paving the way for future innovations in AI-powered devices.
TimeSeries Machine Learning - PyData London 2025



TimeSeries Machine Learning - PyData London 2025Suyash Joshi Timeseries Machine Learning - forecasting and anomaly detection with InfluxDB
Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...



Can We Use Rust to Develop Extensions for PostgreSQL? (POSETTE: An Event for ...NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
“Solving Tomorrow’s AI Problems Today with Cadence’s Newest Processor,” a Pre...



“Solving Tomorrow’s AI Problems Today with Cadence’s Newest Processor,” a Pre...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
Session 07 - Intro to Object Oriented Programming with Java
- 1. Java & JEE Training Session 7 – Object Oriented Analysis and Design with Java
- 2. Page 1Classification: Restricted Agenda • Object Oriented Programming Concepts • Introduction to OO Analysis and Design
- 3. Java & JEE Training Object Oriented Programming
- 4. Page 3Classification: Restricted Object Oriented Programming • Why OO programming? • What is OOAD? Why?
- 5. Page 4Classification: Restricted Why Object Oriented?
- 6. Page 5Classification: Restricted 5 What kind of language can alleviate difficulties with communication & complexity hopefully well? Why Object-Oriented? “The "software crises" came about when people realized the major problems in software development were … caused by communication difficulties and the management of complexity” [Budd] The Whorfian Hypothesis: Human beings … are very much at the mercy of the particular language which has become the medium of expression for their society … the 'real world' is … built upon the language habits …
- 7. Page 6Classification: Restricted Why Object-Oriented? For conceptual.. Modelling reasons… What kind of language can be used to create this concept diagram, or Harry’s mental image? Harry’s mental image
- 8. Page 7Classification: Restricted Why Object-Oriented? For conceptual.. Modelling reasons… What kind of language can be used to create this concept diagram, or Harry’s mental image? Harry’s mental image Model with Procedural language
- 9. Page 8Classification: Restricted Why Object-Oriented? For conceptual.. Modelling reasons… What kind of language can be used to create this concept diagram, or Harry’s mental image? Water Rivers Oceans Fish Penguins Crocodiles Fresh water Salt water have have have live in have have Harry’s mental image Model with Object Oriented
- 10. Page 9Classification: Restricted Why Object-Oriented? Why Model? • To understand why a software system is needed, what it should do, and how it should do it. • To communicate our understanding of why, what and how. • To detect commonalities and differences in your perception, my perception, his perception and her perception of reality. • To detect misunderstandings and miscommunications.
- 11. Page 10Classification: Restricted Object Oriented Programming • Consists of classes and object. • Object communicates with each other by passing messages What is an object????
- 12. Page 11Classification: Restricted Object States An Object has State and Behavior
- 13. Page 12Classification: Restricted Objects • Objects have state and behavior State: What an object knows about itself Behavior :What an object can do. Object Name State = charecter stics Behaviou r: Dog State: Name Breed Height Weight Behavi our: eat() run() walk()
- 14. Page 13Classification: Restricted Class • Class is Blue Print • Logical structure • Set of instructions given to JVM , how to create instance ( object ) out of it.
- 15. Page 14Classification: Restricted Class • Class consists of • Member variables and member methods. • State/ characteristics is represented via member variables • Member methods defines the responsibility of the class • Data within object represents its state. • State - Member Variables • To: • Text: • Behavior – Member functions • sendSms • Forward • delete
- 16. Page 15Classification: Restricted Messages To Text sendSms Forward cancel Messages1: Tom To : 123-456- 7896 Text : Hi Tom, sendSms Forward cancel Messages2: Jack To : 478-963- 7896 Text : Hi Jack sendSms Save Delete Class Object Tom Object Jack
- 17. Page 16Classification: Restricted Contacts Name: Number email createContact updateContact deleteContact Contacts1: Tom Name: Tom Number : 456-789- 7895 Email :[email protected] createContact updateContact Contacts2: Jack Name: Jack Number 789-896- 8965 Email: [email protected] createContact updateContact
- 18. Page 17Classification: Restricted Features of OOP: 4 pillars • Inheritance: When one object acquires all the properties and behaviours of parent object i.e. known as inheritance. It provides code reusability. • Polymorphism: When one task is performed by different ways i.e. known as polymorphism. For example: to convince the customer differently, to draw something, shape or rectangle etc. In Java, we use method overloading and method overriding to achieve polymorphism. • Abstraction: Hiding internal details and showing functionality. In Java, we use abstract class and interface to achieve abstraction. • Encapsulation: Binding (or wrapping) code and data together into a single unit is known as encapsulation. For example: capsule, it is wrapped with different medicines. A Java class is the example of encapsulation. Java bean is the fully encapsulated class because all the data members are private here.
- 19. Page 18Classification: Restricted 18 Encapsulation a.k.a. information hiding Objects encapsulate: property behavior as a collection of methods invoked by messages …state as a collection of instance variables Abstraction Focus on the essential Omits tremendous amount of details …Focus on what an object “is and does” What is Object-Orientation - Abstraction and Encapsulation
- 20. Page 19Classification: Restricted What is Object-Orientation - Subclass vs. Superclass / Inheritance • Specialization: The act of defining one class as a refinement of another. • Subclass: A class defined in terms of a specialization of a superclass using inheritance. • Superclass: A class serving as a base for inheritance in a class hierarchy • Inheritance: Automatic duplication of superclass attribute and behavior definitions in subclass. multiple inheritance? Person name SSN Student std-id level Employee emp-id age
- 21. Page 20Classification: Restricted What is Object-Orientation - Polymorphism Objects of different classes respond to the same message differently.
- 22. Page 21Classification: Restricted Advantages of Object Oriented Approach • Realistic Modelling
- 23. Page 22Classification: Restricted Advantages of Object Oriented Programing • Realistic Modelling Bike String color; String model; Integer speed; Accelerate() Decelerate() Break()
- 24. Page 23Classification: Restricted Advantages of Object Oriented Approach • Code Reusability Contacts1: Tom Name: Tom Number : 456- 789-7895 Email :[email protected] createContact updateContact deleteContact
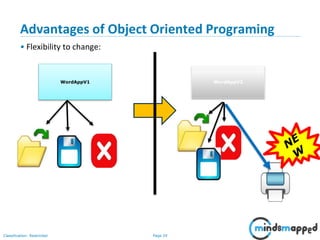
- 25. Page 24Classification: Restricted Advantages of Object Oriented Programing • Flexibility to change: WordAppV1 WordAppV2
- 26. Page 25Classification: Restricted Advantages of Object Oriented • Modularity
- 27. Java & JEE Training Object Oriented Analysis and Design
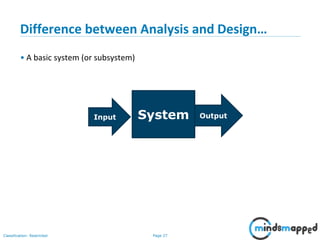
- 28. Page 27Classification: Restricted Difference between Analysis and Design… • A basic system (or subsystem) SystemInput Output
- 29. Page 28Classification: Restricted Difference between Analysis and Design… • Analysis • Design SystemInput ???? ????Input Output
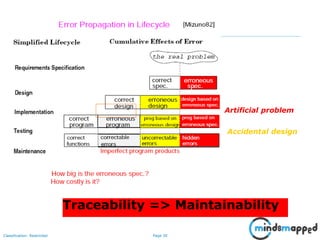
- 30. Page 29Classification: Restricted 29 What is OOAD? • Analysis — understanding, finding and describing concepts in the problem domain. • Design — understanding and defining software solution/objects that represent the analysis concepts and will eventually be implemented in code. • OOAD — Analysis is object-oriented and design is object-oriented. A software development approach that emphasizes a logical solution based on objects. Maintainability through Traceability!
- 31. Page 30Classification: Restricted 30 Traceability => Maintainability Artificial problem Accidental design
- 32. Page 31Classification: Restricted More later… • More practical examples of OOAD in later sessions… • Now let us start looking at Object Oriented Programming concepts using Java
- 33. Java & JEE Training Object Oriented Programming with Java - Basic Class Demo
- 34. Page 33Classification: Restricted Naming Conventions Name Convention class name should start with uppercase letter and be a noun e.g. String, Color, Button, System, Thread etc. interface name should start with uppercase letter and be an adjective e.g. Runnable, Remote, ActionListener etc. method name should start with lowercase letter and be a verb e.g. actionPerformed(), main(), print(), println() etc. variable name should start with lowercase letter e.g. firstName, orderNumber etc. package name should be in lowercase letter e.g. java, lang, sql, util etc. constants name should be in uppercase letter. e.g. RED, YELLOW, MAX_PRIORITY etc.
- 35. Page 34Classification: Restricted Object and Class in Java - Demo A basic example of a class: class Student1{ int id;//data member (also instance variable) String name;//data member(also instance variable) public static void main(String args[]){ Student1 s1=new Student1();//creating an object of Student System.out.println(s1.id); System.out.println(s1.name); } }
- 36. Page 35Classification: Restricted Another Example of Objects and Classes in Java class Student2{ int rollno; String name; void insertRecord(int r, String n){ //method rollno=r; name=n; } void displayInformation(){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name);}//method public static void main(String args[]){ Student2 s1=new Student2(); Student2 s2=new Student2(); s1.insertRecord(111,"Karan"); s2.insertRecord(222,"Aryan"); s1.displayInformation(); s2.displayInformation(); } }
- 37. Page 36Classification: Restricted Topics to be covered in next session • Deep dive into coding OOP with Java… with practical examples. • How to create a class • How to create objects • How to create instance variables • How to create class variables • Constructors




