Software coding and testing
- 1. E-Content on Software Engineering UNIT III: Software Coding and Different Types of Testing Lesson One: Software Coding Standard Lesson Two: Software Testing Strategy and Principles Lesson Three: Software Testing Approaches and Types Lesson Four: Alpha &Beta Testing and Black Box & White Box Testing Developed by Dr. Sandeep Kumar Nayak
- 2. Lesson One : Software Coding Standard
- 3. Introduction When you convert a design document into source code, one of your primary goals should be to write the source code and internal documentation in such a way so that it is easy to verify that the source code conforms to the design, and so that it is easy to debug, test, and maintain the source code. The coding standard below is designed to assist you in achieving this goal. Coding standards define a programming style. It is simply a set of rules and guidelines for the formatting of source code. Coding standards, also known as programming styles or coding conventions.
- 4. Coding Standards Coding standards define a programming style. Coding Standards give the program a common look and feel to understand it easily. Coding Standards are guidelines for documentation and code style for the programmer. It is simply a set of rules and guidelines for the formatting of source code. A coding standard does not usually concern itself with wrong or right in a more abstract sense.
- 5. Why have Coding Standards? Reduce the cost of software maintains is the most often cited reason to follow coding standards. 80% of the lifetime cost of a piece of software goes to maintenance. Coding Standards increases readability substantially Any member of a development should be able to read the code of another member.
- 6. Why Coding Standards Are Important? Coding Standards are important for safety, security, and reliability. Every development team should use a coding standard. Even the most experienced developer could introduce a coding defect without realizing it. And that one defect could lead to a minor glitch. Or worse, a serious security breach. There are four main drivers for using a coding standard: Compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO). Consistent code quality — no matter who writes the code. Software security from the start. Reduced development costs and accelerated time to market.
- 7. Benefits of Coding Standards Code Integration Team Member Integration Uniform Problem Solving Minimizes Communication Minimizes Performance Pitfalls Saves Money Due to Less Man Hours In professional environments, the benefits of coding standards are readability, maintainability & compatibility. In addition, today’s enterprise solutions are so complex for that some other benefits are -
- 8. Coding Rules and Guidelines Coding rules and guidelines ensure that software is: Safe: It can be used without causing harm. Secure: It can’t be hacked. Reliable: It functions as it should, every time. Testable: It can be tested at the code level. Maintainable: It can be maintained, even as your codebase grows. Portable: It works the same in every environment.
- 9. Common Aspects of Coding Standards Here are the some common aspect of coding standards- Naming Conventions File Naming and Organization Formatting and Indentation Comments and Documentation Classes, Functions and Interfaces Pointer and Reference Usage Testing of code
- 10. Types of Coding Standards Use of comments Variable names Function names Maximum length of a routine (lines of code) Maximum number of routines within a class Degree of complexity allowed (nested loops, compound Boolean testing, etc.) Naming convention of source code files
- 11. Source code directory structure for developer machines, build machines and source code control tools Source code file contents (i.e. one C++ class per file) Ways to indicate incomplete code in source. Types of Coding Standards
- 12. Conclusion The purpose of coding standard is that any developer familiar with the guidelines can work on any code that followed them. We need to write code that minimizes the time it would take someone else to understand it – even if that someone else is you. Sometimes a coding standard is an accepted practice for a particular language. For instance, programmers generally accept that when writing C# source code they will write parameters and private and protected fields using Camel casing. They will write all other identifiers using Pascal casing.
- 13. Lesson Two : Software Testing Strategy and Principles
- 14. It is very important to achieve optimum test results while conducting software testing without differing from the goal. Introduction Software Testing refers to the process of evaluating attributes like correctness, completeness, security, consistency, unambiguousness, quality etc. If you were to test the entire possible combinations project execution time and costs would rise exponentially. We need certain strategies and principles to optimize the testing effort.
- 15. Software test strategy is a blue print, that describes the testing approach of the software development cycle. It is formed to inform project managers, testers, and developers about some major issues of the testing process. Software Testing Strategy The strategy is a plan for defining the testing approach, what you want to accomplish and how you are going to do it. A number of software testing strategies are developed in the testing process. All these strategies provide the tester a template, which is used for testing.
- 16. For every stage of development design, a corresponding test strategy should be created to test the new feature sets. Testing strategy is not a part of testing. It’s the reflection of whole quality assurance in SDLC. The design and architecture of the software are also useful in choosing testing strategy. Testing strategies are describe how the software risks of the stakeholders are moderated at the test-level, which types of testing are to be performed, and which entry and exit criteria apply.
- 18. 1.Analytic testing strategy: This uses formal and informal techniques to access and prioritize risks that arise during software testing. It takes a complete overview of requirements, design, and implementation of objects to determine the motive of testing. In addition, it gathers complete information about the software, targets to be achieved, and the data required for testing the software. 2.Model-based testing strategy: This strategy tests the functionality of the software according to the real world scenario (like software functioning in an organization). It recognizes the domain of data and selects suitable test cases according to the probability of errors in that domain.
- 19. 3.Methodical testing strategy: It tests the functions and status of software according to the checklist, which is based on user requirements. This strategy is also used to test the functionality, reliability, usability, and performance of the software. 4.Process-oriented testing strategy: It tests the software according to already existing standards such as the IEEE standards. In addition, it checks the functionality of the software by using automated testing tools.
- 20. 5.Dynamic testing strategy: This tests the software after having a collective decision of the testing team. Along with testing, this strategy provides information about the software such as test cases used for testing the errors present in it. 6.Philosophical testing strategy: It tests the software assuming that any component of the software can stop functioning anytime. It takes help from software developers, users and systems analysts to test the software.
- 21. Test Principles will help you create an effective test strategy and draft error catching test cases. For that, you need to know some basic testing principles. Software Testing Principle 1.Testing shows presence of defects 2.Exhaustive testing is impossible 3.Early testing 4.Defect clustering 5.Pesticide paradox 6.Testing is context dependent 7.Absence of error – fallacy Here are the common seven testing principles that are widely practiced in the software industry.
- 22. 1. Testing Shows Presence of Defects: The goal of testing is to make the software fail. Sufficient testing reduces the presence of defects. In case testers are unable to find defects after repeated regression testing doesn’t mean that the software is bug-free. 2. Exhaustive Testing is Impossible: Testing all the functionalities using all valid and invalid inputs and preconditions is known as Exhaustive testing. 3. Early Testing: Defects detected in early phases of SDLC are less expensive to fix. So conducting early testing reduces the cost of fixing defects.
- 23. 4. Defect Clustering: Defect Clustering in software testing means that a small module or functionality contains most of the bugs or it has the most operational failures. 5. Pesticide Paradox: Pesticide Paradox in software testing is the process of repeating the same test cases again and again, eventually, the same test cases will no longer find new bugs. So to overcome this Pesticide Paradox, it is necessary to review the test cases regularly and add or update them to find more defects.
- 24. 6. Testing is Context Dependent: Testing approach depends on the context of the software we develop. We do test the software differently in different contexts. For example, online banking application requires a different approach of testing compared to an e-commerce site.
- 25. 7. Absence of Error – Fallacy: It is possible that software which is 99% bug-free is still unusable. This can be the case if the system is tested thoroughly for the wrong requirement. Software testing is not mere finding defects, but also to check that software addresses the business needs. The absence of Error is a Fallacy i.e. To solve this problem, the next principle of testing states that Early Testing.
- 26. Lesson Three : Software Testing Approaches and Types
- 27. Software Testing is a process, used to identify the correctness, completeness and quality of developed computer software. It is the process of executing a program/application under a positive or negative condition by manual or automated means. It Checks for the- Specification Functionality Performance Introduction
- 28. Software Testing Approach A test approach is the test strategy implementation of a project, defines how testing would be carried out. Test approach has two techniques: Proactive - An approach in which the test design process is initiated as early as possible in order to find and fix the defects before the build is created. Reactive - An approach in which the testing is not started until after design and coding are completed.
- 29. Different Test Approaches There are many strategies that a project can adopt depending on the context and some of them are: Dynamic and heuristic approaches Consultative approaches Model-based approach that uses statistical information about failure rates. Approaches based on risk-based testing where the entire development takes place based on the risk Methodical approach, which is based on failures. Standard-compliant approach specified by industry-specific standards.
- 30. Software Testing Types Software Testing Methodology is defined as strategies and testing types used to certify that, the application under testing meets the client expectations. Each testing methodology has a defined test objective, test strategy and deliverables. Software Testing has static and dynamic testing to validate the software product.
- 32. Static Testing, a software testing technique in which the software is tested without executing the code. It has two parts analysis and review. Static Testing Analysis - The code written by developers are analyzed (usually by tools) for structural defects that may lead to bugs. Review - Typically used to find and eliminate errors or ambiguities in documents such as requirements, design, etc.
- 33. Dynamic Testing, is a kind of software testing in witch the software should be compiled & executed. Dynamic Testing Dynamic Testing is further classified in two main categories, on the basis of software functionality. Functional Testing Non-Functional Testing Parameters such as Memory Usage, CPU Usage, Response Time and Overall Performance of the software are analyzed.
- 34. Functional Testing, is a type of software testing where the system is tested against the functional requirements and specifications. Functional Testing Functional Testing is divided in two type of testing- White Box Testing Black Box Testing It ensures that the requirements are properly satisfied the software application or not. Functional Testing are tested by feeding the input and examining the output.
- 35. Testing directly related to the faults remains' in earlier stage or introduced at coding level. So, each level of testing aim to test the different aspect of the system. Unit Testing Integration Testing System Testing & Acceptance Testing There are four different level of testing used in testing process. Levels of Functional Testing
- 36. Non-Functional Testing, is a type of software testing which checks the non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, reliability, etc. of a software application. Non-Functional Testing It is designed to test the readiness of a system as per nonfunctional parameters which are never addressed by functional testing.
- 37. Non-functional testing should increase usability, efficiency, maintainability, and portability of the product. Helps to reduce production risk and cost associated with non- functional aspects of the product. Optimize the way product is installed, setup, executes, managed and monitored. Collect and produce measurements, and metrics for internal research and development. Improve and enhance knowledge of the product behavior and technologies in use. Objectives Non-Functional Testing
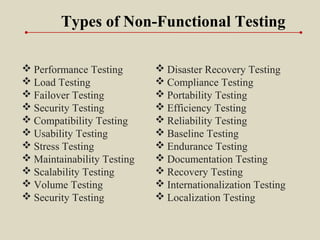
- 38. Types of Non-Functional Testing Performance Testing Load Testing Failover Testing Security Testing Compatibility Testing Usability Testing Stress Testing Maintainability Testing Scalability Testing Volume Testing Security Testing Disaster Recovery Testing Compliance Testing Portability Testing Efficiency Testing Reliability Testing Baseline Testing Endurance Testing Documentation Testing Recovery Testing Internationalization Testing Localization Testing
- 39. In order to be cost effective, testing must be concentrated on areas where it will be most effective. Conclusion Testing usually related to the faults remaining from earlier stage, that can lead to a heavy distraction. Testing is just a process in order to make your software application defect free.
- 40. Lesson Four : Alpha &Beta Testing and Black Box & White Box Testing
- 41. Alpha Testing Alpha Testing is a type of acceptance testing, performed to identify all possible issues/bugs before releasing the product to everyday users or the public. Alpha Testing is carried out in a “Lab Environment” by the “Testers or Internal Employees” of the organization. The focus of this testing is to simulate real users by using a black box and white box techniques. The aim is to carry out the tasks that a typical user might perform.
- 42. Beta Testing of a product is performed by “Real Users” of the software application in a “Real Environment” and can be considered as a form of external User Acceptance Testing. Beta Testing This is a testing stage followed by the internal full alpha test cycle. This is the final testing phase where the companies release the software to few external user groups outside the company test teams or employees. This initial software version is known as the beta version. Most companies gather user feedback in this release.
- 43. Following are the differences between Alpha and Beta Testing: Alpha Testing Vs Beta Testing Alpha Testing Beta Testing It is performed by Testers who are usually internal employees of the organization It is performed by Clients or End Users who are not employees of the organization Alpha Testing performed at developer's site It is performed at a client location or end user Reliability and Security Testing are not performed in-depth Alpha Testing Reliability, Security, Robustness are checked during Beta Testing Alpha testing involves both the white box and black box techniques Beta Testing typically uses Black Box Testing
- 44. Alpha Testing Beta Testing Alpha testing requires a lab environment or testing environment Beta testing doesn't require any lab environment or testing environment. The software is made available to the public and is said to be real time environment Long execution cycle may be required for Alpha testing Only a few weeks of execution are required for Beta testing Critical issues or fixes can be addressed by developers immediately in Alpha testing Most of the issues or feedback is collected from Beta testing will be implemented in future versions of the product Alpha testing is to ensure the quality of the product before moving to Beta testing Beta testing also concentrates on the quality of the product, but gathers users input on the product and ensures that the product is ready for real time users.
- 45. White Box Testing It is also called Glass Box/Clear Box/Structural testing. White Box testing based on internal prospective of the system, and programming skills are used to design test case for testing. Testing is based on internal code structure of the application. Testing usually done at Unit Level Testing.
- 46. Unit Level Testing Unit Testing, is a level of software testing where individual units/components of a software are tested. Code Coverage Statement Coverage Branch Coverage Path Coverage Unit Level Testing Techniques
- 47. Black Box Testing It is also called Behavior/ Specification/ Input-Output testing. It is software testing method in which testing evaluates the functionality of the software under the test without looking at the internal code structure.
- 48. Equivalence Partitioning Boundary Value Analysis Decision Table State Transition Black Box Testing Techniques No knowledge of internal design or code is required. Test are based on requirement and functionality. Black Box Testing can be applied at every level (Unit, Integration, System & Acceptance) of software testing.
- 49. Differences Between Black Box Testing and White Box Testing Black Box Testing White Box Testing Black Box Testing is a software testing method in which the internal structure/ design/ implementation of the item being tested is NOT known to the tester White Box Testing is a software testing method in which the internal structure/ design/ implementation of the item being tested is known to the tester.
- 50. Black Box Testing White Box Testing Mainly applicable to higher levels of testing : Acceptance Testing System Testing Mainly applicable to lower levels of testing : Unit Testing Integration Testing Generally, independent Software Testers Generally, Software Developers Not Required Required Not Required Required Requirement Specifications Detail Design
- 51. Thank You