Source coding
- 1. DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS Part I: Source Encoding
- 2. Why digital? • Ease of signal generation • Regenerative repeating capability • Increased noise immunity • Lower hardware cost • Ease of computer/communication integration ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 2
- 3. Basic block diagram Info Source Channel Digital source encoder encoder modulation channel CH Output Source Channel Digital transducer decoder decoder demod ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 3
- 4. Some definitions • Information source – Raw data:voice, audio – Source encoder:converts analog info to a binary bitstream – Channel encoder:map bitstream to a pulse pattern – Digital modulator: RF carrier modulation of bits or bauds ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 4
- 5. A bit of history • Foundation of digital communication is the work of Nyquist(1924) • Problem:how to telegraph fastest on a channel of bandwidth W? • Ironically, the original model for communications was digital! (Morse code) • First telegraph link was established between Baltimore and Washington in 1844 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 5
- 6. Nyquist theorem • Nyquist theorem, still standing today, says that over a channel of bandwidth W, we can signal fastest with no interference at a rate no more than 2W • Any faster and we will get intersymbol interference • He further proved that the pulse shape that achieves this rate is a sinc ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 6
- 7. Signaling too fast • Here is what might happen when signaling exceeds Nyquist’s rate Transmittted bitstream Received bitstream Pulse smearing could have been avoided if pulses had more separation, I.e. bitrate reduced ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 7
- 8. Shannon channel capacity • Claude Shannon, a Bell Labs Mathematician, proved in 1948 that a communication channel is fundamentally speed-limited. This limit is given by C=Wlog2(1+P/NoW) bits/sec • Where W is channel’s bandwidth, P signal power and No is noise spectral density ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 8
- 9. Implications of channel capacity • If data rate is kept below channel capacity, R<C, then t is theoretically possible to achieve error-free transmission • If data rate exceeds channel capacity, error- free transmission is no longer possible ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 9
- 10. First step toward digital comm: sampling theorem • Main question: can a finite number of samples of a continuous wave be enough to represent the information? OR • Can you tell what the original signal was below? ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 10
- 11. How to fill in the blanks? • Could you have guessed this? Is there a unique signal connecting the samples? ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 11
- 12. Sampling schemes • There are at least 3 sampling schemes – Ideal – Flat-top – Sample and hold ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 12
- 13. Ideal sampling • Ideal sampling refers to the type of samples taken. Here, we are talking about impulse like(zero width) samples. Ts ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 13
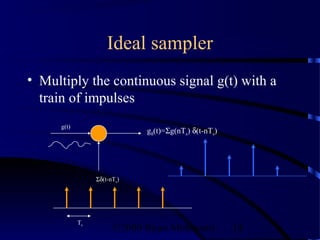
- 14. Ideal sampler • Multiply the continuous signal g(t) with a train of impulses g(t) gδ(t)=Σg(nTs) δ(t-nTs) Σδ(t-nTs) Ts ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 14
- 15. Key question • What is the proper sampling rate to allow for a perfect reconstruction of the signal from its samples? • To answer this question, we need to know how g(t) and gδ(t) are related? ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 15
- 16. Spectrum of gδ(t) • gδ(t) is given by the following product gδ(t)=g(t)Σδ(t-nTs) • Taking Fourier transform Gδ(f)= G(f)*{fsΣδ(f-nfs) • Graphical rendition of this convolution follows next ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 16
- 17. Expanding the convolution • We can exchange convolution and summation Gδ(f)=G(f)*{fsΣδ(f-nfs)= fs Σ {G(f)* δ (f-nfs)} • Each convolution shifts G(f) to f= nfs G(f) G(f)* δ (f-nfs)} nfs ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 17
- 18. Gδ(f):final result • Spectrum of the sampled signal is then given by Gδ (f)=fs Σ {G(f-nfs) • This is simply the replication of the original continuous signal at multiples of sampling rate ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 18
- 19. Showing the spectrum of gδ(t) • Each term of the convolution is the original spectrum shifted to a multiple of sampling frequency G(f) Gδ(f) fs fs 2fs ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 19
- 20. Recovering the original signal • It is possible to recover the original spectrum by lowpass filtering the sampled signal Gδ(f) fs W fs 2fs LPF -W W ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 20
- 21. Nyquist sampling rate • In order to cleanly extract baseband (original) spectrum, we need sufficient separation with the adjacent sidebands • Min. separation can be found as follows Gδ(f) fs fs-w>W fs>2W W fs ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 21
- 22. Sampling below Nyquist: aliasing • If signal is sampled below its Nyquist rate, spectral folding, or aliasing, occurs. Lowpass filtering will not recover the baseband spectrum intact as a result of spectral folding fs<2W ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 22
- 23. Sample-and-hold • A practical way of sampling a signal is sample-and-hold operation. Here is the idea:signal is sampled and its value held until the next sample ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 23
- 24. Issues • Here are the questions we need to answer: – What is the sampling rate now? – Can the message be recovered? – What price do we pay for going with a practical approach? ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 24
- 25. Modeling sample-and-hold • The result of sample-and-hold can be simulated by writing the sampled signal as s(t)=Σm(nTs)h(t-nTs) • Where h(t) is a basic square pulse and m(t) is the baseband message This is a square pulse h(t) scaled by signal Sample at that point, ie m(nTs)h(t-nTs) Ts ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 25
- 26. A system’s view • It is possible to come up with a system that does sample-and-hold. h(t) X h(t) Ts Ideal sampling Each impulse generates a square pulse,h(t), at the output. Outputs are also spaced by Ts this we have a sample-and- hold signal Ts ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 26
- 27. Message reconstruction • Key question: can we go back to the original signal after sample-and-hold ? • This question can be answered in the frequency domain ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 27
- 28. Spectrum of the sample-and-hold signal • Sample-and-hold signal is generated by passing an ideally sampled signal, mδ(t), through a filter h(t). Therefore, we can write s(t)= mδ(t)*h(t) or S(f)= Mδ(f)H(f) what we have available Contains message M(f) Known( it is a sinc) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 28
- 29. Is message recoverable? • Let’s look at the individual components of S(f). From ideal sampling results Mδ(f)=fsΣM(f-kfs) Mδ(f) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 29
- 30. Problems with message recovery • The problem here is we don’t have access to Mδ(f). If we did, it would be like ideal sampling • What we do have access to is S(f) S(f)= Mδ(f)H(f) • We therefore have a distorted version of an ideally sampled signal ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 30
- 31. Example message • Let’s show what is happening. Assume a message spectrum that is flat as follows M(f) -W W Mδ(f) fs 2fs ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 31
- 32. Sample-and-hold spectrum • We don’t see Mδ(f). We see Mδ(f)H(f). Since h(t) was a square pulse of width Ts, H(f) is sinc(fTs) . M (f). δ W f H(f) 1/Ts=fs f ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 32
- 33. Distortion potential • The original analog message is in the lowpass term of Mδ(f) • H(f) through the product Mδ(f)H(f) causes a distortion of this term. • Lowpass filtering of the sample-and-hold signal will only recover a distorted message ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 33
- 34. Illustrating distortion Mδ(f) W fs 2fs want to recover this H(f) 1/Ts=fs f Sample and hold signal. If lowpass filtered, the original What is actually recovered Message is not recovered ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 34
- 35. How to control distortion? • In order to minimize the effect of H(f) on reconstruction, we must make H(f) as flat as possible in the message bandwidth(-W,W) • What does it mean? It means move the first zero crossing to the right by increasing the sampling rate, or decreasing pulse width ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 35
- 36. Does it make sense? • The narrower the pulse, hence higher sampling rate, the more accurate you can capture signal variations ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 36
- 37. Variation on sample-and-hold • Contrast the two following arrangements Ts τ sample period and pulse width are not the same ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 37
- 38. How does this affect reconstruction? • The only thing that will change is h(t) and hence H(f) Mδ(f) W f want to recover this H(f) different zero crossing 1/τ f Sample and hold signal. What is actually recovered If lowpass filtered, the original Message is not recovered ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 38
- 39. How to improve reconstruction? • Again, we need to flatten out H(f) within (- W,W). and the way to do it is to use narrower pulses (smaller τ) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 39
- 40. Sample-and-hold converges to ideal sampling • If reducing the pulse width of h(t) is a good idea, why not take it to the limit and make them zero? • We can do that in which case sample-and- hold collapses to ideal sampling(impulses are zero width pulses) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 40
- 41. Pulse Code Modulation Filtering, Sampling, Quantization and Encoding
- 42. Elements of PCM Transmitter • Encoder consists of 5 pieces Continuous LPF Sampler Quantizer Encoder message • Transmission path Regenerative Regenerative repeater repeater ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 42
- 43. Quantization • Quantization is the process of taking continuous samples and converting them to a finite set of discrete levels 1.52 1.2 .86 ? -0.41 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 43
- 44. Defining a quantizer • Quantizer is defined by its input/output characteristics; continuous values in, discrete values out out out in in Output remains constant Even as input varies over a range Midtread type Midrise type ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 44
- 45. Quantization noise/error • Quantizer clearly discards some information. Question is how much error is committed? Message(m) Quantized message (v) q(m) Error=q=m-v ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 45
- 46. Illustrating quantization error Sampled quantized v3 ∆ v2 Quantization error v1 ∆ quantizer step size ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 46
- 47. More on ∆ ∀ ∆ Controls how fine samples are quantized. Equivalently, ∆ controls quantization error. • To determine ∆ we need to know two parameters – Number of quantization levels – Dynamic range of the signal ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 47
- 48. ∆ for a uniform quantizer • Let sample values lie in the range ( -mmax, +mmax). We also want to have exactly L levels at the output of the quantizer. Simple math tells us max L levels ∆=2mmax/L min ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 48
- 49. Quantization error bounds • Quantization error is bounded by half the step size Level 2 ∆ Error q Error q Level 1 |q|<∆/2 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 49
- 50. Statistics of q • Quantization error is random. It can be positive or negative with equal probability. • This is an example of a uniformly distributed random variable. Density function f(q) 1/∆ q -∆/2 ∆/2 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 50
- 51. Quantization noise power • Any uniformly distributed random variable in the range (-a/2 to a/2) has an average power(variance) given by a2/12. • Here, quantization noise range is ∆, therefore σ2q= ∆2/12 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 51
- 52. Signal-to-quantization noise • Leaving aside random noise, there is always a finite quantization noise. • Let the original continuous signal have power P=<m2(t)> and quantization noise variance(power) σ2q (SNR)q=P/ σ2q=12P/ ∆2 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 52
- 53. Substituting for ∆ • We have related step size to signal dynamic range and number of quantization levels ∆=2mmax/L • Therefore, signal to quantization noise(sqnr) sqnr=(SNR)q=[3P/m2max]L2 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 53
- 54. Example • Let m(t)=cos(2πfmt). What is the signal to quantization noise ratio(sqnr) for a 256- level quantizer • Average message power P is 0.5, therefore sqnr=(3x0.5/1)2562=98304~50dB ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 54
- 55. Nonuniform quantizer • Uniform quantization is a fantasy. Reason is that signal amplitude is not equally spread out. It occupies mostly low amplitude levels ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 55
- 56. Solution:nonuniform intervals • Quantize fine where amplitudes spend most of their time ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 56
- 57. Implementing nonuniform quantization:companding • Signal is first processed through a nonlinear device that stretches low amplitudes and compresses large amplitudes Large amplitudes pressed output Low amplitudes stretched input ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 57
- 58. A-law and µ-law • There are two companding curves, A-law and µ-law. Both are very similar • Each has an adjustment parameter that controls the degree of companding (slope of the curve) • Following companding, a uniform quantization is used ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 58
- 59. Encoder • Quantizer outputs are merely levels. We need to convert them to a bitstream to finish the A/D operation • There are many ways of doing this – Natural coding – Gray coding ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 59
- 60. Natural coding • How many bits does it take to represent L- levels? The answer is n=log2L bits/sample • Natural coding is a simple decimal to binary conversion 0…000 1…001 Quantizer levels(8) 2…010 Encoder output(3 bits per sample 3…011 ………. 7…111 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 60
- 61. Gray coding • Here is the problem with natural coding: if levels 2(010) and 1(001) are mistaken, then we suffer two bit errors • We want an encoding scheme that assigns code words to adjacent levels that differ in at most one bit location ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 61
- 62. Gray coding example • Take a 4-bit quantizer (16 levels). Adjacent levels differ by juts one bit 0…0001 1…0000 2…0100 3…0101 4…1101 …………. ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 62
- 63. Quantizer word size • Knowing n, we can refer to n-bit quantizers • For example, if L=256 with n=8bits/sample • We are then looking at an 8-bit quantizer ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 63
- 64. Interaction between sqnr and bit/sample • Converting sqnr to dB provides a different insight. Take 10log10(sqnr) • sqnr=kL2 where k=[3P/m2max] • In dB (sqnr)dB=α+20logL= α+20log2n (sqnr)dB= α+6n dB ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 64
- 65. sqnr varies linearly with bits/sample • What we just saw says higher sqnr is achieved by increasing n(bits/sample). • Question then is, what keeps us from doing that for ever thus getting arbitrarily large sqnr’s? ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 65
- 66. Cost factor • We can increase number of bits/sample hence quantization levels but at a cost • The cost is in increased bandwidth but why? • One clue is that as we go to finer quantization, levels become tightly packed and difficult to discern at the receiver hence higher error rates. There is also a bandwidth cost ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 66
- 67. Basis for finding PCM bandwidth • Nyquist said in a channel with transmission bandwidth BT, we can transmit at most 2BT pulses per second: R(pulses/second)<2BT(Hz) Or BT(Hz)>R/2(pulses/second) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 67
- 68. Transmission over phone lines • Analog phone lines are limited to 4KHz in bandwidth, what is the fastest pulse rate possible? R<2BT=2x4000=8000 pulses/sec • That’s it? Modems do a bit faster than this! • One way to raise this rate is to stuff each pulse with multiple bits. More on that later ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 68
- 69. Accomodating a digital source • A source is generating a million bits/sec. What is the minimum required transmission bandwidth. BT>R/2=106/2=500 KHz ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 69
- 70. PCM bit rate • The bit rate at the output of encoder is simply the following product • R(bits/sec)=n(bits/sample)xfs(samples/sec) R=nfs bits/sec quantized 101101 Encoded at 5 bits/sample ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 70
- 71. PCM bandwidth • But we know sampling frequency is 2W. Substituting fs=2W in R=n fs R=2nW (bits/sec) • We also had BT>R/2. Replacing R we get BT>nW ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 71
- 72. Comments on PCM bandwidth • We have established a lower bound(min) on the required bandwidth. • The cost of doing PCM is the large required bandwidth. The way we can measure it is • Bandwidth expansion quantified by BT/W>n (bits/sample) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 72
- 73. Bandwidth expansion factor • Similar to FM, there is a bandwidth expansion factor relative to baseband, i.e. β=BT/W>n • Let’s say we have 8 bits/sample meaning it takes , at a minimum, 8 times more than baseband bandwidth to do PCM ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 73
- 74. PCM bandwidth example • Want to transmit voice (~4KHz ) using an 8-bit PCM. How much bandwidth is needed? • We know W=4KHz, fs=8 KHz and n=8. BT>nW=8x4000=32KHz • This is the minimum PCM bandwidth under “ideal” conditions. Ideal has to do with pulse shape used ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 74
- 75. Bandwidth-power exchange • We said using finer quantization (more bits/sample) enhances sqnr because (sqnr)dB= α+6n dB • At the same time we showed bandwidth increases linearly with n. So we have a trade-off ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 75
- 76. sqnr improvement • Let’s say we increase n by 1 from 8 to 9 bits/sample. As result, sqnr increases by 6 dB sqnr= α+6x8= α+48 +6dB sqnr= α+6x9= α+54 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 76
- 77. Bandwidth increase • Going from n= 8 bits/sample, to 9 bits/sample, min. bandwidth rises from 8W to 9W. • If message bandwidth is 4 KHz, then BT=32 KHz for n=8 +4 KHz or 12.5% increase BT=36 KHz for n=9 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 77
- 78. Is it worth it? • Let’s look at the trade-off: – Cost in increased bandwidth:12.5% – Benefit in increased sqnr: 6dB • Every 3 dB means a doubling of the sqnr ratio. So we have quadrupled sqnr by paying 12.5% more in bandwidth ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 78
- 79. Another way to look at the exchange • We provided 12.5% more bandwidth and ended up with 6 dB more sqnr. • If we are satisfied with the sqnr we have, we can dial back transmitted power by 6 dB and suffer no loss in sqnr • In other words, we have exchanged bandwidth for lower power ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 79
- 80. Similarity with FM • PCM and FM are examples of wideband modulation. All such modulations provide bandwidth-power exchange but at different rates. Recall β=BT/W 2 • FM…….SNR~β • PCM…..SNR~22β Much more sensitive to beta, Better exchnage ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 80
- 81. Complete PCM system design • Want to transmit voice with average power of 1/2 watt and peak amplitude 1 volt using 256 level quantizer. Find – sqnr – Bit rate – PCM bandwidth ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 81
- 82. Signal to quantization noise • We had sqnr=[3P/m2max]L2 We have L=256, P=1/2 and mmax=1. sqnr=98304~50 dB ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 82
- 83. PCM bitrate • Bit rate is given by R=2nW (bits/sec)=2x8x4000=64 Kb/sec • This rate is a standard PCM voice channel • This is why we can have 56K transmission over the digital portion of telephone network which can accomodating 64 Kb/sec. ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 83
- 84. PCM bandwidth • We can really talk about minimum bandwidth given by BT|min=nW=8x4000=32 KHz • In other words, we need a minimum of 32 KHz bandwidth to transmit 64 KB/sec of data. ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 84
- 85. Realistic PCM bandwidth • Rule of thumb to find the required bandwidth for digital data is that bandwidth=bit rate BT=R • So for 64 KB/sec we need 64 KHz of bandwidth One hertz per bit ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 85
- 86. Differential PCM • Concept of differential encoding is of great importance in communications • The underlying idea is not to look at samples individually but to look at past values as well. • Often, samples change very little thus a substantial compression can be achieved ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 86
- 87. Why differential? • Let’s say we have a DC signal and blindly go about PCM-encoding it. Is it smart? • Clearly not. What we have failed to realize is that samples don’t change. We can send the first sample and tell the receiver that the rest are the same ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 87
- 88. Definition of differential encoding • We can therefore say that in differential encoding, what is recorded and ultimately transmitted is the change in sample amplitudes not their absolute values • We should send only what is NEW. ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 88
- 89. Where is the saving? • Consider the following two situations 2 0 -0.4 2 2 2 2 0.4 -0.8 -0.4 1.6 0.8 0.4 1.6 1.6 0.8 • The right samples are adjacent sample differences with much smaller dynamic range requiring fewer quantization levels ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 89
- 90. Implementation of DPCM:prediction • At the heart of DPCM is the idea of prediction • Based on n-1 previous samples, encoder generates an estimate of the nth sample. Since the nth sample is known, prediction error can be found. This error is then transmitted ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 90
- 91. Illustrating prediction • Here is what is happening at the transmitter To be trasmited Prediction error Past samples(already sent) Prediction of the Current sample Only Prediction error is sent ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 91
- 92. What does the receiver do? • Receiver has the identical prediction algorithm available to it. It has also received all previous samples so it can make a prediction of its own • Transmitter helps out by supplying the prediction error which is then used by the receiver to update the predicted value ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 92
- 93. Interesting speculation • What if our power of prediction was perfect? In other words, what if we could predict the next sample with no error?. What kind of communication system would be looking at? ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 93
- 94. Prediction error • Let m(t) be the message and Ts sample interval, then prediction error is given ˆ e(nTs ) = m(nTs ) − m (nTs ) Prediction error ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 94
- 95. Prediction filter • Prediction is normally done using a weighted sum of N previous samples N m (nTs ) = ∑ wi m(( n − i )Ts ) ˆ i =1 • The quality of prediction depends on the good choice of weights wi ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 95
- 96. Finding the optimum filter • How do you find the “best” weights? • Obviously, we need to minimize the prediction error. This is done statistically Min { e 2 ( nTs )} over w • Choose a set of weights that gives the lowest (on average) prediction error ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 96
- 97. Prediction gain • Prediction provides an SNR improvement by a factor called prediction gain σ2 M message power Gp = 2 = σe prediction error power ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 97
- 98. How much gain? • On average, this gain is about 4-11 dB. • Recall that 6 dB of SNR gain can be exchanged for 1 bit per sample • At 8000 samples/sec(for speech) we can save 1 to 2 bits per sample thus saving 8-16 Kb/sec. ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 98
- 99. DPCM encoder Input sample + Prediction error + quantizer encoder Prediction - error Prediction + Updated prediction N-tap prediction • Prediction error is used to correct the estimate in time for the next round of prediction ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 99
- 100. Delta modulation (DM) • DM is actually a very simplified form of DPCM • In DM, prediction of the next sample is simply the previous sample Prediction error Estimate of ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 100
- 101. DM encoder-diagram out ∆ in -∆ Input sample + + 1-bit Prediction error(±∆) Prediction quantizer - error Prediction + Updated prediction Delay Ts ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 101
- 102. DM encoder operation • Prediction error generates ±∆ at the output of quantizer • If error is positive, it means prediction is below sample value in which case the estimate is updated by + ∆ for the next step ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 102
- 103. Slope overload effect • Signal rises faster than prediction: ∆ too small samples Ts ∆ predictions initial estimate ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 103
- 104. Steady state: granular noise • Prediction can track the signal; prediction error small Two drops to reach the signal ∆ ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 104
- 105. Shortcomings of DM • It is clearly the prediction stage that is lacking • Samples must be closely taken to insure that “previous-sample” prediction algorithm is reasonably accurate • This means higher sample rates ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 105
- 106. Multiplexing • Concurrent communications calls for some form of multiplexing. There are 3 categories – FDMA(frequency division multiple access) – TDMA(time division multiple access) – CDMA(code division multiple access) • All 3 enjoy a healthy presence in the communications market ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 106
- 107. FDMA • In FDM, multiple users can be on at the same time by placing them in orthogonal frequency bands guardband user 1 user 2 user N TOTAL BANDWIDTH ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 107
- 108. FDMA example:AMPS • AMPS, wireless analog standard, is a good example – Reverse link(mobile-to-base): 824-849MHz – Forward link: 869-894 MHz – channel bandwidth:30 KHz – total # channels: 833 – Modulation: FM, peak deviation 12.5 KHz ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 108
- 109. TDMA • Where FDMA is primarily an analog standard, TDMA and CDMA are for digital communication • In TDMA, each user is assigned a time “slot”, as opposed to a frequency slot in FDMA ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 109
- 110. Basic idea behind TDMA • Take the following 3 digital lines frame ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 110
- 111. TDM-PCM TDM-PAM TDM-PCM(bits) quantizer and quantizer and encoder encoder channel lpf decoder lpf ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 111
- 112. Parameters of TDM-PCM • A TDM-PCM line multiplexing M users is characterized by the following parameters – data rate(bit or pulse rate) – bandwidth ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 112
- 113. TDM-PCM Data rate • Here is what we have – M users – Each sampled at Nyquist rate – Each sample PCM’d into n bit words • Total bit rate then is R=M(users)xfs(samples /sec/user)xn(bits/sec) =nMfs bits sec ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 113
- 114. TDM-PCM bandwidth • Recall Nyquist bandwidth. Given R pulses per second, we need at least R/2 Hz. • In reality we need more (depending on the pulse shape) so BT=R=nMfs Hz ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 114
- 115. T1 line • Best known of all TDM schemes is AT&T’s T1 line • T1 line multiplexes 24 voice channels(4KHz) into one single bitstream running at the rate of 1.544 Mb/sec. Let’s see how ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 115
- 116. T1 line facts • Each of the 24 voice lines are sampled at 8 KHz • Each sample is then encoded into 8 bits • A frame consists of 24 samples, one from each line • Some data bits are preempted for control and supervisory signaling ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 116
- 117. T1 line structure: all frames except 1,7,13,19... channel 1 channel 2 channel 24 1234567812345678 12345678 information bits (8-bits per sample) FRAME(repeats) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 117
- 118. Inserting non-data bits • In addition to data, we need slots for signaling bits (on-hook/off hook, charging) • Every 6th frame (1,7,13,19..) is selected and the least significant bit per channel is replaced by a signaling bit channel 1 channel 2 channel 24 1234567 1234567 1234567 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 118
- 119. Framing bit • Timing is of utmost significance in T1. We MUST be able to know where the beginning of each frame is • At the end of each frame a single bit is added to help with frame identification channel 1 channel 2 channel 24 1234567812345678 12345678F information bits (8-bits per sample) ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 119
- 120. T1 frame length • How long is one frame?One revolution generates frame sampled at 8KHz rotates at 8000 revs/sec. 24 frame length=1/8000= 125 microseconds ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 120
- 121. T1 bit rate per frame • Data rate – 8x24=192 bits per frame • Framing bit rate – 1 bit per frame • Total per frame – 193 bits/frame ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 121
- 122. Total T1 bit rate • We know there are 8000 frames a sec. and there are 193 bits per frame. Therefore T1 rate=193x8000=1.544 Mb/sec ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 122
- 123. Signaling rate component • Not all 1.544 Mb/sec is data. In every 6th frame, we replace 24 data bits by signaling bits. Therefore signaling rate= (8000 frames/sec)(1/6)(24 bits)=32 Kbits/sec ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 123
- 124. TDM hierarchy • It is possible to build upon T1 as follows 64 kb/sec DS-2 DS-1 DS-3 1st level 2nd level 3rd level 24 multiplexer multiplexer multiplexer DS-0 DS-2: 7 lines DS-3: DS-1: 44.736 Mb/sec 6.312 Mb/sec 1.544 MB/sec ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 124
- 125. Recommended problems • 6.2 • 6.15 • 6.17 ©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 125




















































![Substituting for ∆
• We have related step size to signal dynamic
range and number of quantization levels
∆=2mmax/L
• Therefore, signal to quantization
noise(sqnr)
sqnr=(SNR)q=[3P/m2max]L2
©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sourcecoding-121110054738-phpapp01/85/Source-coding-53-320.jpg)










![Interaction between sqnr and
bit/sample
• Converting sqnr to dB provides a different
insight. Take 10log10(sqnr)
• sqnr=kL2 where k=[3P/m2max]
• In dB
(sqnr)dB=α+20logL= α+20log2n
(sqnr)dB= α+6n dB
©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sourcecoding-121110054738-phpapp01/85/Source-coding-64-320.jpg)

















![Signal to quantization noise
• We had
sqnr=[3P/m2max]L2
We have L=256, P=1/2 and mmax=1.
sqnr=98304~50 dB
©2000 Bijan Mobasseri 82](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sourcecoding-121110054738-phpapp01/85/Source-coding-82-320.jpg)










































