String Matching algorithm String Matching algorithm String Matching algorithm
- 2. WHAT IS STRING MATCHING ? • In computer science, String searching algorithms, sometimes called string matching algorithms, that try to be find place where one or several string (also called pattern) are found within a larger string or text.
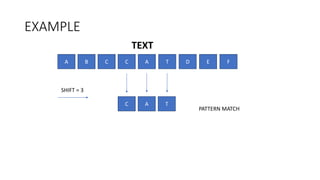
- 3. EXAMPLE A B C C A T D E F SHIFT = 3 C A T PATTERN MATCH TEXT
- 4. STRING MATCHING ALGORITHM • There are many types of String Matching Algorithm like:- 1. The Naive string-matching algorithm. 2. The Rabin-Karp algorithm. 3. String matching with finite automata 4. The Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm
- 5. Naïve String Matching Algorithm Input: The algorithm takes two strings as input - the text (longer string) and the pattern (shorter string). Initialization: Let n be the length of the text and m be the length of the pattern. Loop through the text: For each starting position i from 0 to n - m: •Initialize a variable j to 0 to track the index in the pattern. •While j is less than the length of the pattern m and the character at position i + j in the text matches the character at position j in the pattern: •Increment j. •If j equals m, it means the entire pattern has been matched starting at position i. •Output the position i as the starting index of the pattern in the text. Repeat: Continue this process for all possible starting positions in the text. Output: The algorithm outputs the starting positions in the text where the pattern is found.
- 6. PSEUDO-CODE • NaiveStringMatch(Text, Pattern): • n = length(Text) • m = length(Pattern) • for i = 0 to n - m • j = 0 • while j < m and Pattern[j] = Text[i + j] • j = j + 1 • if j = m • print "Pattern found at position", i
- 7. Rabin-Karp Algorithm Input: The algorithm takes two strings as input - the text (longer string) and the pattern (shorter string). Initialization: • Let n be the length of the text and m be the length of the pattern. • Choose two constants: d, the number of characters in the alphabet, and q, a prime number. Preprocessing: • Compute the hash value of the pattern P and the hash value of the first substring of the text t0. • Iterate over the pattern and the first substring of the text: • Compute the hash value of the pattern using a rolling hash function: P = (d * P + ASCII value of character) mod q. • Compute the hash value of the first substring of the text similarly: t0 = (d * t0 + ASCII value of character) mod q. Matching: • Slide a window of length m over the text from left to right. • For each position s in the text: • Check if the hash value of the pattern matches the hash value of the current substring of the text. • If the hash values match, perform a character-by-character comparison to confirm the match. • If a match is found, output the starting position s as the index where the pattern occurs in the text. • Update the hash value for the next substring using a rolling hash function: • ts+1 = (d * (ts - ASCII value of character at position s * h) + ASCII value of character at position s+m) mod q. • Repeat this process until all positions in the text have been examined. Output: The algorithm outputs the starting positions in the text where the pattern is found.
- 8. PSEUDO-CODE In this pseudo-code: • T is the text • P is the pattern • d is the number of characters in the input set. • q is a prime number used as modulus • n = length[T] • m = length[P] • h = pow(d, m-1) mod q • P = 0 • t0 = 0 • # Preprocessing: Compute the hash value of the pattern and the first substring of T • for i = 1 to m • P = (d*P + P[i]) mod q • t0 = (d*t0 + T[i]) mod q • # Matching: Slide the window through T and compare hash values • for s = 0 to n-m • if P = ts • if P[1.....m] = T[s+1.....s+m] if s < n-m • ts+1 = (d*(ts - T[s+1]*h) + T[s+m+1]) mod q




![PSEUDO-CODE
• NaiveStringMatch(Text, Pattern):
• n = length(Text)
• m = length(Pattern)
• for i = 0 to n - m
• j = 0
• while j < m and Pattern[j] = Text[i + j]
• j = j + 1
• if j = m
• print "Pattern found at position", i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringmatchingalgorithm-1-240318035616-5e667b51/85/String-Matching-algorithm-String-Matching-algorithm-String-Matching-algorithm-6-320.jpg)

![PSEUDO-CODE In this pseudo-code:
• T is the text
• P is the pattern
• d is the number of
characters in the input set.
• q is a prime number used as
modulus
• n = length[T]
• m = length[P]
• h = pow(d, m-1) mod q
• P = 0
• t0 = 0
• # Preprocessing: Compute the hash value of the pattern and the first substring of T
• for i = 1 to m
• P = (d*P + P[i]) mod q
• t0 = (d*t0 + T[i]) mod q
• # Matching: Slide the window through T and compare hash values
• for s = 0 to n-m
• if P = ts
• if P[1.....m] = T[s+1.....s+m] if s < n-m
• ts+1 = (d*(ts - T[s+1]*h) + T[s+m+1]) mod q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringmatchingalgorithm-1-240318035616-5e667b51/85/String-Matching-algorithm-String-Matching-algorithm-String-Matching-algorithm-8-320.jpg)