strings in php how to use different data types in string
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes13 views
OPEN SOURCE WEB APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT stringg and variables
1 of 38
Download to read offline




































![What is the following is the output of the following PHP code?
• <?php
• $str = "Hello, world!";
• echo $str[0];
• ?>
• H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strings-250328042212-6391a33b/85/strings-in-php-how-to-use-different-data-types-in-string-38-320.jpg)
Ad
Recommended
PHP Web Programming



PHP Web ProgrammingMuthuselvam RS This chapter discusses working with text and numbers in PHP. It covers defining and manipulating strings, including validating, formatting, and changing case. Functions for selecting, replacing, and exploding parts of strings are described. Working with numbers, math operators, variables, and number formatting functions are also summarized. Key string functions include substr(), str_replace(), printf(), and number functions include rand(), round(), pow(), and abs().
String handling and arrays by Dr.C.R.Dhivyaa Kongu Engineering College



String handling and arrays by Dr.C.R.Dhivyaa Kongu Engineering CollegeDhivyaa C.R This document discusses strings and arrays in PHP. It covers:
- Defining strings using quotes, concatenation, and heredoc syntax
- Common string functions like length, position, comparison, replacement
- Creating arrays using assignment, array() constructor, and functions
- Retrieving array values by index and with list()
- Multidimensional arrays containing other arrays
- The document provides examples of each PHP string and array concept.
UNIT II (7).pptx



UNIT II (7).pptxDrDhivyaaCRAssistant This document discusses strings and arrays in PHP. It covers string functions like strlen(), strpos(), and substr() for inspecting, comparing, and manipulating strings. It also covers creating, accessing, and iterating through arrays, including multidimensional arrays. Functions like count(), current(), next(), reset(), and foreach are described for working with arrays. The document also introduces numerical types in PHP like integers and floats.
UNIT II (7).pptx



UNIT II (7).pptxDrDhivyaaCRAssistant Open Source Systems Array and String , by Dr.C.R.Dhivyaa, Assistant Professor, Kongu Engineering College
Tokens in php (php: Hypertext Preprocessor).pptx



Tokens in php (php: Hypertext Preprocessor).pptxBINJAD1 In PHP a token is considered an individual component of a program. The keywords, variables, constants, operators and strings used in a program are tokens in PHP.
0-Slot21-22-Strings.pdf



0-Slot21-22-Strings.pdfssusere19c741 The document discusses strings in C including how to declare, initialize, input, output, and manipulate strings using standard library functions as well as how to manage arrays of strings. It provides examples of declaring and initializing strings, using scanf and gets to input strings, common string manipulation functions like strlen and strcpy, and demonstrates how to work with arrays of strings such as storing and sorting a list of names.
Functions, List and String methods



Functions, List and String methodsPranavSB This document contains notes from a Python class covering functions, lists, strings, and their methods. It discusses built-in functions like len(), range(), and type conversions. It also covers control flow structures like if/else, for loops, exceptions, modules, and functions in more detail including defining functions, parameters, arguments, returning values, docstring, and variable scopes. Assignments include writing functions to process lists and check for palindromes in strings.
Text and Numbers (Data Types)in PHP



Text and Numbers (Data Types)in PHPKamal Acharya This document discusses text and numbers in programming. It covers defining and manipulating text strings using single or double quotes. Escape characters can be used inside strings. Text can be validated and formatted using various string functions like trim(), strlen(), strtoupper(), substr(), and str_replace(). Numbers can be integers or floats. Variables hold data and can be operated on with arithmetic and assignment operators like +, -, *, /, %, and .=. Variables can also be incremented, decremented, and placed inside strings.
9780538745840 ppt ch03



9780538745840 ppt ch03Terry Yoast This chapter discusses string manipulation functions in PHP. It covers constructing strings, working with single strings through functions like strlen() and strtoupper(), working with multiple strings by parsing and splitting them with functions like explode() and strtok(), comparing strings, and using regular expressions. The chapter provides examples of encoding/decoding strings and manipulating case, as well as counting characters, words, and searching/extracting substrings.
Strings



StringsSaranya saran The document discusses strings in C programming. It defines strings as arrays of characters terminated by a null character. It explains that string handling functions are declared in the string.h header file and are used to perform operations on strings like getting the length, concatenating, comparing, and manipulating case. Several functions are described like strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), strcmp(), strrev(), strlwr(), strupr(). Examples are given showing how to use these functions to work with strings.
introduction to server-side scripting



introduction to server-side scriptingAmirul Shafeeq This document provides an introduction to server-side scripting and PHP. It discusses how server-side pages work by having the web server run scripts and send HTML to users' browsers. It then lists several common server-side scripting languages like PHP, ASP, and Python. The document proceeds to introduce PHP in more detail, covering its basics like syntax, variables, strings, arithmetic operators, and functions. It provides examples of conditional statements like if/else and looping with for and while loops.
characters_strings.pdf



characters_strings.pdfHoPeTaylor7 This document provides an outline and overview of functions for handling characters and strings in C from several standard libraries. It discusses fundamentals of characters and strings, the character handling library ctype.h, string conversion functions in stdlib.h, I/O functions in stdio.h, and string processing functions in string.h, including searching, comparing, tokenizing and memory functions. The goal is to introduce techniques for text processing using these standard libraries.
00012.PYTHON - STRING MANIPULATION SLIDES



00012.PYTHON - STRING MANIPULATION SLIDESPanavGupta3 This pdf gives an overview on how strong manipulation works in Python
Introduction to Python for Bioinformatics



Introduction to Python for BioinformaticsJosé Héctor Gálvez A very basic introduction to the main concepts of python and scripting languages in general, with a focus on the skills required for bioinformatics.
All_About_Strings.pptxxbsnsnsmsmsmmmsmsmsm



All_About_Strings.pptxxbsnsnsmsmsmmmsmsmsmkumarsahil80682 Okdbxndndmldlslslsksksbsbbdbdbdndmmdkdldkmdbdbdbbnbbbbbbsnsnskdkkdkdndbdcbdmsnsvdbdndnndnbdvdhsmdbgdbdnmmdbbdbbbdndndndndndjdjdhdhdhdhdhbdbdndnndndndndndjdjdjdjsjdjdjsnsjsjsjdvdvdvdbdbdhdhfbhfjdnjdndjdjdjdnndndndndndndjddnsnnsnsnsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmammmmnznsnsnsnsnsnsnsnsnsnsnnsnsnnnnnnnjdjdjdjhfbfbbffnjdjdjjdjdjddjjdhfjfjfjfjfjfjfjfjfjfjdjfjffjfjjfjbdbdbvbhhsvgwehgehdjdhhdhdheh
BCSE101E_Python_Module5 (4).pdf



BCSE101E_Python_Module5 (4).pdfmukeshb0905 This document provides an overview of strings and regular expressions in Python. It discusses string comparison, formatting, slicing, splitting, and stripping. For regular expressions, it covers matching, search and replace, and patterns. Meta characters, special sequences, sets, search, and common patterns are explained.
Python basics



Python basicsHoang Nguyen A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and optionally returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python basics



Python basicsHarry Potter A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python basics



Python basicsFraboni Ec A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then tells the processor to execute the program. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations that take in arguments and return values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be accessed by index and manipulated with methods like upper() that return new strings.
Python basics



Python basicsJames Wong A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python basics



Python basicsTony Nguyen A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be accessed by index and manipulated with methods like upper() that return new strings.
Python basics



Python basicsLuis Goldster A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be accessed by index and manipulated with methods like upper() that return new strings.
Python basics



Python basicsYoung Alista A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Web Application Development using PHP Chapter 3



Web Application Development using PHP Chapter 3Mohd Harris Ahmad Jaal This document discusses PHP functions including:
- The syntax and advantages of functions
- Common string, numeric, and date/time functions
- Creating user-defined functions
- Passing arguments to functions
- Returning values from functions
The document provides examples of using built-in PHP functions like strlen(), rand(), date(), and creating user-defined functions that can accept arguments and return values. It also discusses concepts like default arguments and stopping function execution with return.
Advance topics of C language



Advance topics of C languageMehwish Mehmood The document discusses pointers in C programming. It defines a pointer as a variable that stores the memory address of another variable rather than the actual data. Pointers can be used to return multiple values from a function, pass arrays and strings to functions, and dynamically allocate and access memory. The key pointer operators are the address of (&) operator, which returns the address of its operand, and the dereferencing (*) operator, which refers to the object a pointer points to. Pointers can be passed to functions by value or by reference. The document also discusses structures, which allow grouping of different data types, and arrays, which can be passed to functions where only the array address is passed.
Pixel to Percentage conversion Convert left and right padding of a div to per...



Pixel to Percentage conversion Convert left and right padding of a div to per...vishal choudhary Pixel to Percentage conversion
esponsive web design means that your website (



esponsive web design means that your website (vishal choudhary To define responsive web design means that your website (and its pages) can adapt and deliver the best experience to users, whether they’re on their desktop, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. For that to happen, though, your website needs a responsive design.
More Related Content
Similar to strings in php how to use different data types in string (20)
9780538745840 ppt ch03



9780538745840 ppt ch03Terry Yoast This chapter discusses string manipulation functions in PHP. It covers constructing strings, working with single strings through functions like strlen() and strtoupper(), working with multiple strings by parsing and splitting them with functions like explode() and strtok(), comparing strings, and using regular expressions. The chapter provides examples of encoding/decoding strings and manipulating case, as well as counting characters, words, and searching/extracting substrings.
Strings



StringsSaranya saran The document discusses strings in C programming. It defines strings as arrays of characters terminated by a null character. It explains that string handling functions are declared in the string.h header file and are used to perform operations on strings like getting the length, concatenating, comparing, and manipulating case. Several functions are described like strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), strcmp(), strrev(), strlwr(), strupr(). Examples are given showing how to use these functions to work with strings.
introduction to server-side scripting



introduction to server-side scriptingAmirul Shafeeq This document provides an introduction to server-side scripting and PHP. It discusses how server-side pages work by having the web server run scripts and send HTML to users' browsers. It then lists several common server-side scripting languages like PHP, ASP, and Python. The document proceeds to introduce PHP in more detail, covering its basics like syntax, variables, strings, arithmetic operators, and functions. It provides examples of conditional statements like if/else and looping with for and while loops.
characters_strings.pdf



characters_strings.pdfHoPeTaylor7 This document provides an outline and overview of functions for handling characters and strings in C from several standard libraries. It discusses fundamentals of characters and strings, the character handling library ctype.h, string conversion functions in stdlib.h, I/O functions in stdio.h, and string processing functions in string.h, including searching, comparing, tokenizing and memory functions. The goal is to introduce techniques for text processing using these standard libraries.
00012.PYTHON - STRING MANIPULATION SLIDES



00012.PYTHON - STRING MANIPULATION SLIDESPanavGupta3 This pdf gives an overview on how strong manipulation works in Python
Introduction to Python for Bioinformatics



Introduction to Python for BioinformaticsJosé Héctor Gálvez A very basic introduction to the main concepts of python and scripting languages in general, with a focus on the skills required for bioinformatics.
All_About_Strings.pptxxbsnsnsmsmsmmmsmsmsm



All_About_Strings.pptxxbsnsnsmsmsmmmsmsmsmkumarsahil80682 Okdbxndndmldlslslsksksbsbbdbdbdndmmdkdldkmdbdbdbbnbbbbbbsnsnskdkkdkdndbdcbdmsnsvdbdndnndnbdvdhsmdbgdbdnmmdbbdbbbdndndndndndjdjdhdhdhdhdhbdbdndnndndndndndjdjdjdjsjdjdjsnsjsjsjdvdvdvdbdbdhdhfbhfjdnjdndjdjdjdnndndndndndndjddnsnnsnsnsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmsmammmmnznsnsnsnsnsnsnsnsnsnsnnsnsnnnnnnnjdjdjdjhfbfbbffnjdjdjjdjdjddjjdhfjfjfjfjfjfjfjfjfjfjdjfjffjfjjfjbdbdbvbhhsvgwehgehdjdhhdhdheh
BCSE101E_Python_Module5 (4).pdf



BCSE101E_Python_Module5 (4).pdfmukeshb0905 This document provides an overview of strings and regular expressions in Python. It discusses string comparison, formatting, slicing, splitting, and stripping. For regular expressions, it covers matching, search and replace, and patterns. Meta characters, special sequences, sets, search, and common patterns are explained.
Python basics



Python basicsHoang Nguyen A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and optionally returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python basics



Python basicsHarry Potter A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python basics



Python basicsFraboni Ec A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then tells the processor to execute the program. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations that take in arguments and return values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be accessed by index and manipulated with methods like upper() that return new strings.
Python basics



Python basicsJames Wong A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Python basics



Python basicsTony Nguyen A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be accessed by index and manipulated with methods like upper() that return new strings.
Python basics



Python basicsLuis Goldster A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be accessed by index and manipulated with methods like upper() that return new strings.
Python basics



Python basicsYoung Alista A program is a sequence of instructions that are run by the processor. To run a program, it must be compiled into binary code and given to the operating system. The OS then gives the code to the processor to execute. Functions allow code to be reused by defining operations and returning values. Strings are sequences of characters that can be manipulated using indexes and methods. Common string methods include upper() and concatenation using +.
Web Application Development using PHP Chapter 3



Web Application Development using PHP Chapter 3Mohd Harris Ahmad Jaal This document discusses PHP functions including:
- The syntax and advantages of functions
- Common string, numeric, and date/time functions
- Creating user-defined functions
- Passing arguments to functions
- Returning values from functions
The document provides examples of using built-in PHP functions like strlen(), rand(), date(), and creating user-defined functions that can accept arguments and return values. It also discusses concepts like default arguments and stopping function execution with return.
Advance topics of C language



Advance topics of C languageMehwish Mehmood The document discusses pointers in C programming. It defines a pointer as a variable that stores the memory address of another variable rather than the actual data. Pointers can be used to return multiple values from a function, pass arrays and strings to functions, and dynamically allocate and access memory. The key pointer operators are the address of (&) operator, which returns the address of its operand, and the dereferencing (*) operator, which refers to the object a pointer points to. Pointers can be passed to functions by value or by reference. The document also discusses structures, which allow grouping of different data types, and arrays, which can be passed to functions where only the array address is passed.
More from vishal choudhary (20)
Pixel to Percentage conversion Convert left and right padding of a div to per...



Pixel to Percentage conversion Convert left and right padding of a div to per...vishal choudhary Pixel to Percentage conversion
esponsive web design means that your website (



esponsive web design means that your website (vishal choudhary To define responsive web design means that your website (and its pages) can adapt and deliver the best experience to users, whether they’re on their desktop, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. For that to happen, though, your website needs a responsive design.
software evelopment life cycle model and example of water fall model



software evelopment life cycle model and example of water fall modelvishal choudhary studying the existing or obsolete system and software,
conducting interviews of users and developers,
referring to the database or
collecting answers from the questionnaires.
software Engineering lecture on development life cycle



software Engineering lecture on development life cyclevishal choudhary SDLC starts from the moment, when it’s made a decision to launch the project.
There is no one single SDLC model.
They are divided into groups,
Each with its features and weaknesses
SE-Lecture1.ppt



SE-Lecture1.pptvishal choudhary The document provides an introduction to software engineering. It defines software engineering as an engineering discipline concerned with all aspects of software production. It discusses why software engineering is important given that errors in complex software systems can have devastating consequences, as shown through examples of software failures in air traffic control, satellite launches, and ambulance dispatch systems. The document also covers fundamental software engineering concepts like the software process, process models, and costs.
SE-Testing.ppt



SE-Testing.pptvishal choudhary The document discusses software testing concepts like validation testing vs defect testing, system and component testing strategies, and test automation tools. It defines key terms like bugs, defects, errors, faults, and failures. It also describes techniques like equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis that are used to generate test cases that thoroughly test software. Component testing tests individual program parts while system testing tests integrated groups of components. Test cases specify conditions to determine if software works as intended.
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptx



june 10 2025 ppt for madden on art science is over.pptxroger malina art science is over -talk by roger malina for jack madden group
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd



Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecdrazelitouali Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Energy Balances Of Oecd Countries 2011 Iea Statistics 1st Edition Oecd
Module 4 Presentation - Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Y...



Module 4 Presentation - Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Y...GeorgeDiamandis11 Enhancing Competencies and Engagement Strategies in Youth Work
Adam Grant: Transforming Work Culture Through Organizational Psychology



Adam Grant: Transforming Work Culture Through Organizational PsychologyPrachi Shah This presentation explores the groundbreaking work of Adam Grant, renowned organizational psychologist and bestselling author. It highlights his key theories on giving, motivation, leadership, and workplace dynamics that have revolutionized how organizations think about productivity, collaboration, and employee well-being. Ideal for students, HR professionals, and leadership enthusiasts, this deck includes insights from his major works like Give and Take, Originals, and Think Again, along with interactive elements for enhanced engagement.
Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big Cycle



Ray Dalio How Countries go Broke the Big CycleDadang Solihin A complete and practical understanding of the Big Debt Cycle. A much more practical understanding of how supply and demand really work compared to the conventional economic thinking. A complete and practical understanding of the Overall Big Cycle, which is driven by the Big Debt Cycle and the other major cycles, including the big political cycle within countries that changes political orders and the big geopolitical cycle that changes world orders.
Final Sketch Designs for poster production.pptx



Final Sketch Designs for poster production.pptxbobby205207 Final Sketch Designs for poster production.
Respiratory System , Urinary System



Respiratory System , Urinary SystemRushiMandali Human Anatomy and Physiology II Unit 3 B pharm Sem 2
Respiratory system
Anatomy of respiratory system with special reference to anatomy
of lungs, mechanism of respiration, regulation of respiration
Lung Volumes and capacities transport of respiratory gases,
artificial respiration, and resuscitation methods
Urinary system
Anatomy of urinary tract with special reference to anatomy of
kidney and nephrons, functions of kidney and urinary tract,
physiology of urine formation, micturition reflex and role of
kidneys in acid base balance, role of RAS in kidney and
disorders of kidney
Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptx



Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptxbobby205207 Unit 3 Poster Sketches with annotations.pptx
How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18



How to Manage Maintenance Request in Odoo 18Celine George Efficient maintenance management is crucial for keeping equipment and work centers running smoothly in any business. Odoo 18 provides a Maintenance module that helps track, schedule, and manage maintenance requests efficiently.
Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...



Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...National Information Standards Organization (NISO) This presentation was provided by Nicole 'Nici" Pfeiffer of the Center for Open Science (COS), during the first session of our 2025 NISO training series "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communications." Session One was held June 5, 2025.
How to Manage & Create a New Department in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Manage & Create a New Department in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George In Odoo 18's Employee module, organizing your workforce into departments enhances management and reporting efficiency. Departments are a crucial organizational unit within the Employee module.
Hemiptera & Neuroptera: Insect Diversity.pptx



Hemiptera & Neuroptera: Insect Diversity.pptxArshad Shaikh *Order Hemiptera:*
Hemiptera, commonly known as true bugs, is a large and diverse order of insects that includes cicadas, aphids, leafhoppers, and shield bugs. Characterized by their piercing-sucking mouthparts, Hemiptera feed on plant sap, other insects, or small animals. Many species are significant pests, while others are beneficial predators.
*Order Neuroptera:*
Neuroptera, also known as net-winged insects, is an order of insects that includes lacewings, antlions, and owlflies. Characterized by their delicate, net-like wing venation and large, often prominent eyes, Neuroptera are predators that feed on other insects, playing an important role in biological control. Many species have aquatic larvae, adding to their ecological diversity.
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024



BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS BRINGS T0 YOU A FUN-FILLED, SEAT EDGE BUSINESS QUIZ
DIVE INTO THE PRELIMS OF BIZCOM 2024
QM: GOWTHAM S
BCom (2022-25)
THE QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS
SEXUALITY , UNWANTED PREGANCY AND SEXUAL ASSAULT .pptx



SEXUALITY , UNWANTED PREGANCY AND SEXUAL ASSAULT .pptxPoojaSen20 SEXUALITY AND ITS TYPES , UNWANTED PREGANCY AND SEXUAL ASSAULT
Exploring Ocean Floor Features for Middle School



Exploring Ocean Floor Features for Middle SchoolMarie This 16 slide science reader is all about ocean floor features. It was made to use with middle school students.
You can download the PDF at thehomeschooldaily.com
Thanks! Marie
Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...



Pfeiffer "Secrets to Changing Behavior in Scholarly Communication: A 2025 NIS...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024



BUSINESS QUIZ PRELIMS | QUIZ CLUB OF PSGCAS | 9 SEPTEMBER 2024Quiz Club of PSG College of Arts & Science
Ad
strings in php how to use different data types in string
- 1. Strings
- 4. Single Quoted • The simplest way to create a string is to enclose the string literal (i.e. string characters) in single quotation marks ('), like this:
- 5. Double-quote strings • Unlike single-quote strings, double-quote strings in PHP are capable of processing special characters.
- 9. We can perform several functions on string in PHP . The string manipulation functions are.
- 10. PHP Strings A string is a sequence of characters, like "Hello world!". we will look at some commonly used functions to manipulate strings. strlen() - Return the Length of a String The PHP strlen() function returns the length of a string.
- 11. str_word_count() - Count Words in a String The PHP str_word_count() function counts the number of words in a string.
- 12. strrev() - Reverse a String The PHP strrev() function reverses a string.
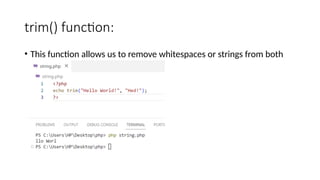
- 13. trim() function: • This function allows us to remove whitespaces or strings from both sides of a string.
- 15. str_replace() - Replace Text Within a String The PHP str_replace() function replaces some characters with some other characters in a string.
- 16. strtolower() function: • This function converts a string into the lowercase string.
- 17. strtoupper() function: • This function converts a string into the uppercase string.
- 18. Comparing Strings PHP strcmp() Function
- 19. Comparing Strings PHP strcmp() Function
- 20. Comparing Strings The strcmp() function compares two strings. The strcmp() function is binary-safe and case-sensitive.
- 21. Cleaning Strings The trim() function removes whitespace and other predefined characters from both sides of a string. Related functions: •ltrim() - Removes whitespace or other predefined characters from the left side of a string •rtrim() - Removes whitespace or other predefined characters from the right side of a string
- 22. Cleaning Strings
- 23. Cleaning Strings
- 24. chop() Function • The chop() function is used to remove whitespace or other predefined character from the right end of a string. • Syntax: chop(string,charlist); • Example <?php $str = "Hello World!"; echo "Your string is :".$str."<br>"; echo "By using 'chop()' Functions is your string is: ".chop($str,"World!"); ?> Parameter Description Required/Optional string the string to be check Required charlist charlist parameter is empty Optional Output: Your string is :Hello World! By using 'chop()' Functions is your string is: Hello
- 25. PHP chunk_split() Function • PHP chunk_split() function is used to splits a string into smaller parts or chunks. The function does not alter the original string. • Syntax: chunk_split(string,length,end) <?php $str = "Hello!; echo "Your string is:".$str; echo "By using 'chunk_split()' function your string is:".chunk_split($str,1,". .."); ?> Parameter Description Required/Optional string String to split Required Length Specify the length of the chunks. Default is 76 Optional end Specify what to place at the end each chunk. Optional Output: Your string is: Hello By using 'chunk_split()' function your string is: H…e...l...l...o...!...
- 26. PHP type casting • Type casting allows you to convert a value of one type to another. To cast a value, you use the following type casting operators:
- 27. Which of the following functions is used to find the first occurrence of a substring in a string? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_split()
- 28. Which of the following functions is used to find the first occurrence of a substring in a string? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_split()
- 29. Which of the following functions is used to replace all occurrences of a substring in a string with another substring? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_split()
- 30. Which of the following functions is used to replace all occurrences of a substring in a string with another substring? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_split()
- 31. Which of the following functions is used to count the number of words in a string? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_word_count()
- 32. Which of the following functions is used to count the number of words in a string? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_word_count()
- 33. Which of the following is not a built-in PHP function for working with strings? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_split() • strrev()
- 34. Which of the following is not a built-in PHP function for working with strings? • strlen() • strpos() • str_replace() • str_split() • strrev()
- 35. What is the following is the output of the following PHP code? • • $str = "Hello, world!"; • echo strlen($str); • 13
- 36. What is the following is the output of the following PHP code? • <?php • $str = "Hello, world!"; • echo strpos($str, "world"); • ?> • 7
- 37. What is the following is the output of the following PHP code? • <?php • $str = "Hello, world!"; • echo str_replace("world", "universe", $str); • ?> • Hello universe
- 38. What is the following is the output of the following PHP code? • <?php • $str = "Hello, world!"; • echo $str[0]; • ?> • H






















