Using R to Visualize Spatial Data: R as GIS - Guy Lansley
- 1. Guy Lansley Department of Geography, UCL [email protected] @GuyLansley GIS for Social Data and Crisis Mapping University of Kent, Canterbury 9th September 2016 Using R to Visualize Spatial Data: R as a GIS
- 2. What is a Geographic Information System? • Geographic – relates to a specific place on or in relation to the Earth’s surface • Information – is data to which some value or interpretation has been added. In GI, the information relates to measurements, maps, images, sounds etc. of the Earth’s surface • System – a system designed to perform a wide range of functions on and with GI • Although GISystems have developed greatly over the past fifty years, their underlying principles have remained the same GIS
- 3. How do we visualise spatial data? • Layers in a GIS Top Bottom
- 4. How do we visualise spatial data? • Layers Top Bottom
- 5. How do we visualise spatial data? • E.g. Top Bottom
- 6. Maps are models of reality • Models are generalisations of reality • Visualisations will determine what is represented • It is therefore easy to misrepresent Monmonier (1996) How to lie with maps
- 7. Popular Open Software • For analysing data – R - www.r-project.org and RStudio - www.rstudio.com – Python www.python.org and Jupyter - www.jupyter.org • Databases – PostgreSQL - www.postgresql.org & PostGIS - www.postgis.net • Geographic information systems – QGIS - www.qgis.org
- 8. QGIS • A fully functional open source GIS • Fantastical visualization capacities • An excellent alternative to ArcMap
- 9. R and Rstudio Advantages • It is fast • It is open source • It is a well developed, simple and effective programming language • Lots of people use it- New York Times, Google, Facebook, Ebay, University Researchers, etc…. • It can do anything you want it to (almost) • It interfaces to other software very easily • Can also call functions from other programming languages (including SQL, Python, Java and many more) • It now has a large user community with lots of support and documentation www.rstudio.com www.r-project.org
- 10. Features of R • Command line interface. • Object oriented. – You create things with names using the “<-” symbol. • Ten <- 5*2 • Two <- Ten/5 • Write a script of functions. • The standard installation has relatively few functions but more have been made available via open source downloadable packages R Scripts Workspace Console Multi-tab (includes plots) • Can also be run through Rstudio which provides a more user friendly GUI
- 11. Visualisations in R AverageHousePrice Distance from London % change in the last 12 months Data: www.hometrack.com/uk/insight/uk-cities-house-price-index & Google Maps • There are lots of options to improve the visualisation of data on a plot, such as proportional symbols, colouring, 3D plotting, trend lines. Size = Population (2011 Census) + -
- 12. Why should we make maps with code?
- 13. It’s Easy GIS packages make coding maps easier than ever before
- 14. Importing Data in R • Load a CSV of data • Load shapefile • Merge shapefile and CSV data, set projection Loading in spatial data is straight forward
- 15. Mapping in R • There are several different packages which provide good functionality for visualising spatial data in R • E.g. – ggplot2 – Graphing package implemented on top of the R statistical package. – tmap – This package offers a flexible, layer-based, and easy to use approach to create thematic maps, such as choropleths and bubble maps. – And many more…
- 16. The ggplot2 package • ggplot2 is a plotting system for R, based on the grammar of graphics, which uses base and lattice graphics. • Excellent for plots but also includes functionality for mapping Based on: Wilkinson, L., 2006. The grammar of graphics. Springer Science & Business Media.
- 17. The tmap package • A package which allows you to create and customise thematic maps quickly and clearly • The API broadly resembles that of ggplot2 but is a bit less fiddly. Based on: Wickham, H., 2010. A layered grammar of graphics. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 19(1), pp.3-28.
- 18. The tmap package Shapefile Variable
- 19. The tmap package Colour ramp
- 21. The tmap package Legend title
- 22. The tmap package Shapefile borders
- 24. The tmap package Layout options
- 25. Lots of packages for mapping • Maptools - Set of tools for manipulating and reading geographic data, in particular ESRI shapefiles • Maps - Display of maps. Projection code and larger maps are in separate packages • Sp - Classes and methods for spatial data; the classes document where the spatial location information resides, for 2D or 3D data. • Rgdal - Provides bindings to Frank Warmerdam's Geospatial Data Abstraction Library (GDAL) and access to projection/transformation operations from the PROJ.4 library R and Mapping Created by James Cheshire
- 26. Functionality Many packages in R allow you to utilise the spatial analysis functions of a standard GIS. It is also possible to apply several customisations to some functions
- 27. Functions • There are a range of specialised packages which provide spatial analysis functions in R • These include…
- 28. Using geometries • rgeos – opens up a range of functions which use geometries – including buffers, unions and distance calculation
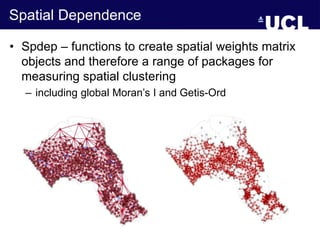
- 29. Spatial Dependence • Spdep – functions to create spatial weights matrix objects and therefore a range of packages for measuring spatial clustering – including global Moran’s I and Getis-Ord
- 30. Spatial Interpolation • Inverse Distance Weighting – gstat package - Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Geostatistical Modelling, Prediction and Simulation Data: People of the British Isles Project Courtesy Jens Kandt, UCL isonymy Data: People of the British Isles Project Courtesy Jens Kandt, UCL
- 31. 3D visualisaton • This example is interactive too!
- 32. Big Data Data is getting larger and more complex. Coding methods can take advantages of new database techniques
- 33. Big Datasets in R There are various techniques in R which can be used to handle very large data. Such as: • The ability to split and loop data and functions • Parallel processing • The ability to work via remote servers • Integration with higher performing programming languages or languages purposed for database management (i.e. SQL)
- 34. Mapping Flows in R Data from spatial.ly/2015/03/mapping-flows/
- 35. Complex data Chord Diagram, created using the circlize package
- 36. Consistency It is easy to replicate your styles, frames and projections once they have been developed the first time. This can save you hours of work in the long run and make the presentation of figures consistent.
- 37. Data source: Greater London Authority Facetted Maps in ggplot2 – Ggplot2 package - An implementation of the grammar of graphics in R
- 38. Reusing code You can reuse your saved map code if you are happy with the outputs You can run it again with any new data
- 39. Automation It is also possible to reduce man-hours spent making duplicate maps by automating code
- 40. 2011 Open Atlas Project • A manual map might typically take 5 minutes to create - thus: – 5 minutes X 134,567 maps = 672,835 minutes – Or 467.2 days (no breaks!) www.alex-singleton.com • Produced by Prof. Alex Singleton (CDRC, University of Liverpool) • R was used to automate the production of 134,567 into a collection of PDF atlases • This included downloading and formatting the data from the ONS websites
- 41. 2011 Open Atlas Project • Code available here: rpubs.com/alexsingleton/openatlas • E.g. Step 1: Download the data E.g. archive = http://www.nomisweb.co.uk/output/census/2011/ks101ew_2011_oa.zip
- 42. The Transport Map Book • Another automated output from Alex Singleton • Includes data on transport such as travel flows to work, accessibility to services, CO2 emissions, etc… • Stages • Data Import • Data Prep • Create Maps • Flow Maps • WZ Maps • OA Maps • LSOA Maps • LSOA CO2 Maps • Latex – output document • Code available from: github.com/alexsingleton/Transport-Map-Book
- 43. Interactive outputs Make sharing information easier through the creation of interactive widgets
- 44. Creating Webmaps with googleVis • Using UN data on child Labour http://data.un.org/Data.aspx?d=S OWC&f=inID%3A86 • A couple of short lines of code will create an interactive map in your internet browser
- 45. Shiny in R • Shiny combines the computational power of R with the interactivity of the modern web • Build useful web applications with only a few lines of code—no JavaScript required • Shiny user interfaces can be built entirely using R, or can be written directly in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for more flexibility. • Attractive default UI theme based on Twitter Bootstrap - twitter.github.com/bootstrap • Tutorial available here: http://rstudio.github.io/shiny/tutorial/ blog.snap.uaf.edu • For more examples visit: shiny.rstudio.com/gallery shiny.rstudio.com
- 46. A Basic Shiny App ui.R server.R
- 47. A Basic Shiny Map ui.R server.R Population density (2011 Census)
- 48. The Power of Shiny • Why Shiny? – All the power of R in the browser – Rapid development of applications – Limited requirement for new skills – With a bit of knowledge of HTML, widgets can be very easily embedded on websites There is also the leaflet package for creating interactive “slippy” web-maps. github.com/majerus/globe
- 49. Summary • Although it may entail a steep learning curve, there are some obvious advantages of handling spatial data in R • These include: – R’s advanced functionality, particularly due to the large range of bespoke packages which are now available – The relative simplicity of some functions with lots of customisations options – The ability to handle large volumes of data of many different formats – The possibility of using code to automate analysis and visualizations – The functionality to produce interactive outputs
- 50. Guy Lansley Department of Geography, UCL [email protected] @GuyLansley