web programming using html,css, JavaScript ,php etc
- 1. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 Web programming Henning Schulzrinne Dept. of Computer Science Columbia University
- 2. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 2 Web programming Web services vs. "classical" web programming Client vs. server programming client: JavaScript, Java HTML-centric vs. program-centric HTML-centric: PHP, ASP cgi, fast-cgi (Java) servlet data model: Java servlet, database
- 3. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 3 Web services vs. web programming web services = remote procedure call we saw SOAP structured data (XML) methods and responses generally, for machine consumption web programming generate HTML pages for humans often, database-driven replacement for IBM 3270 terminals ...
- 4. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 4 Client vs. server programming Execute code on client: download Java applet self-contained programming environment JavaScript (aka ECMAscript): modify and get values from HTML ("document object model" – DOM) Execute code on server generate document state maintenance (HTTP stateless) login, shopping cart, preferences
- 5. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 5 Taxonomy embedded in HTML separate server SSI, ASP, PHP, JSP, CFM server API (NSAPI), cgi, servlets client JavaScript Java applets, plug-in
- 6. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 6 Example: JavaScript – cookies var expires = new Date() var today = new Date() function setCookie(name, value, hours) { var expire = new Date(); expire.setTime (expire.getTime() + (1000 * 60 * 60 * hours)); document.cookie = name + "=" + escape(value) + ((expire == null) ? "" : ("; expires=" + expire.toGMTString())) } function unsetCookie(name) { var exp = new Date(); exp.setTime(today.getTime() - 10); document.cookie = name + "=" + "; expires=" + exp.toGMTString() } expires.setTime(today.getTime() + 86400*365)
- 7. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 7 JavaScript – DOM function tz (f,v) { var t = -1; switch (f[v].value) { case "US": t=128; break; case "CI": t=0; break; case "GH": t=1; break; .. } if (t != -1) { f.form.timezone.options[t].selected = true } }
- 8. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 8 Web as RPC request = HTTP GET, PUT response (result): headers + body object identifier ~ URL typed data (XML) vs. HTML from constant mostly constant completely on-demand
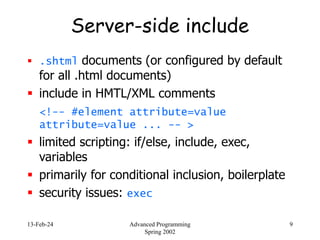
- 9. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 9 Server-side include .shtml documents (or configured by default for all .html documents) include in HMTL/XML comments <!-- #element attribute=value attribute=value ... -- > limited scripting: if/else, include, exec, variables primarily for conditional inclusion, boilerplate security issues: exec
- 10. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 10 SSI example Columbia CS home page <html> <head><TITLE>Computer Science: Welcome </TITLE> <script language=javascript> var section = "home"; var subsection = "home"; var subsectionID = "-1"; </script> </head> <!--#set var="SECTION" value="HOME" --> <!--#include file="top.inc" --> <!--#include file="home.txt" --> </tr> </table> <!--#include file="bottom.txt" --> </html>
- 11. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 11 SSI Example <body> <h1>SSI Test</h1> The document was last modified on <!-- #flastmod file="$DOCUMENT_NAME" and has <!-- #fsize file="$DOCUMENT_NAME" -- > bytes. <h2>Environment</h2> <!-- #printenv </pre>
- 12. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 12 Common gateway interface (cgi) Earliest attempt at dynamic web content language-independent passes HTTP request information via command line (ISINDEX) – rarely used environment variables: system info + query string (GET) request body (POST) standard input return HTML or XML via standard output non-parsed headers (NPH) return complete response
- 13. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 13 cgi arguments application/x-www-form-urlencoded format space characters "+" escape (%xx) reserved characters name=value pairs separated by & GET: foo.cgi?name=John+Doe&gender=male&family=5&city=kent &city=miami&other=abc%0D%0Adef&nickname=J%26D POST: include in body of message
- 14. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 14 cgi forms single form per submission <form action=scripturi method=GET|POST> form fields: <input type="text" name="text1" size=10 maxlength=15 value="Initial text"> <input type="hidden" name="state" value="secret"> <input type=radio name=radio value=WNYC checked> <input type=radio name=radio value=KQED> <input type=submit value="Submit">
- 15. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 15 Web state State: stateless state completely stored on client state referenced by client, stored on server (most common) Mechanisms: hidden form fields URL parameters cookies (HTTP headers)
- 16. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 16 cgi mechanics either called .cgi in HTML directory or stored in cgi-bin in CS, both /home/alice/html/foo.cgi or /home/alice/secure_html/foo.cgi work executable (script file) runs as nobody or as owning user (~user/mycgi.cgi) store secret data off the document tree!
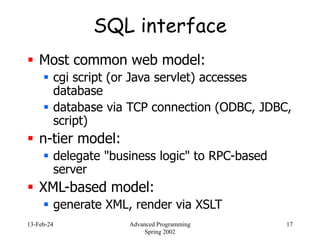
- 17. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 17 SQL interface Most common web model: cgi script (or Java servlet) accesses database database via TCP connection (ODBC, JDBC, script) n-tier model: delegate "business logic" to RPC-based server XML-based model: generate XML, render via XSLT
- 18. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 18 Tcl cgi example set env(LD_LIBRARY_PATH) /home/hgs/sun5/lib load $env(LD_LIBRARY_PATH)/libfbsql.so lappend auto_path /home/hgs/html/edas3 lappend auto_path /home/hgs/lib package require cgi cgi_debug –on cgi_eval { sql connect dbhost.columbia.edu dbuser secret cgi_body { ... } sql disconnect }
- 19. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 19 Tcl cgi cgi_body { h1 "Database view" set conflist [sql "SELECT conference,name,url,logo FROM conference WHERE conference=$c"] table { foreach conf $conflist { maplist $conf c name url logo table_row { td "$name" td "$url" } } } }
- 20. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 20 Python for cgi Handles processing cgi variables need to generate HTML by print but separate object-oriented routines #!/usr/local/bin/python #!/opt/CUCSpython/bin/python2.2 import os, string, sys from types import ListType print "Content-Type: text/html" # HTML is following print # blank line, EOH
- 21. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 21 cgi python print "<title>Python cgi script</title>" print "<body>" print "<h1>Python script</h1>" print "Before script" print sys.path try: import cgi except: print "error", sys.exc_info()[0] # only for Python 2.2! import cgitb; cgitb.enable()
- 22. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 22 cgi python form = cgi.FieldStorage() if not (form.has_key("name")): print "<form action=pcgi.cgi method=get>" print "<input type=text name=name size=10>" print "<input type=submit value=Submit>" print "</form>" else: print "<p>name:", form["name"].value print "</body>"
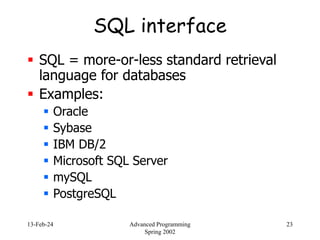
- 23. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 23 SQL interface SQL = more-or-less standard retrieval language for databases Examples: Oracle Sybase IBM DB/2 Microsoft SQL Server mySQL PostgreSQL
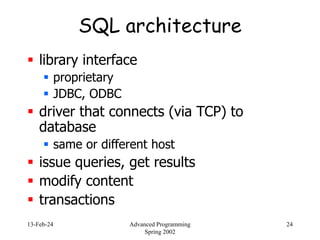
- 24. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 24 SQL architecture library interface proprietary JDBC, ODBC driver that connects (via TCP) to database same or different host issue queries, get results modify content transactions
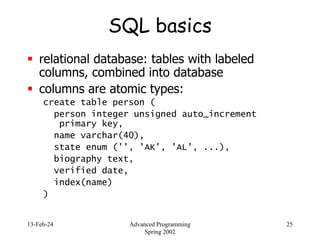
- 25. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 25 SQL basics relational database: tables with labeled columns, combined into database columns are atomic types: create table person ( person integer unsigned auto_increment primary key, name varchar(40), state enum ('', 'AK', 'AL', ...), biography text, verified date, index(name) )
- 26. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 26 SQL basics Integer: tinyint, smallint, mediumint, int(eger), bigint Floating point: float, double, real Decimal: decimal(m,d) (for $) Date: date, datetime, timestamp, time, year String: char(N), varchar(N), tinyblob, tinytext, blob, text, enum, set
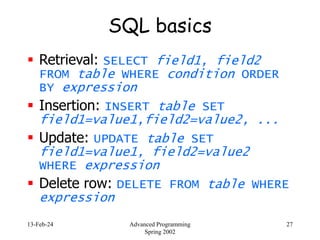
- 27. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 27 SQL basics Retrieval: SELECT field1, field2 FROM table WHERE condition ORDER BY expression Insertion: INSERT table SET field1=value1,field2=value2, ... Update: UPDATE table SET field1=value1, field2=value2 WHERE expression Delete row: DELETE FROM table WHERE expression
- 28. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 28 SQL basics: joins Join two tables that have a common value ("product") e.g., SELECT lastname,city.name FROM person,city WHERE city.zip=person.zip AND lastname='Jones'
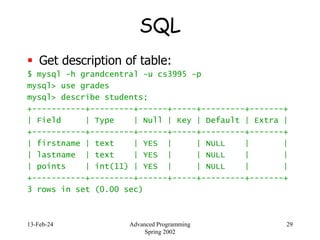
- 29. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 29 SQL Get description of table: $ mysql -h grandcentral -u cs3995 -p mysql> use grades mysql> describe students; +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | firstname | text | YES | | NULL | | | lastname | text | YES | | NULL | | | points | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 30. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 30 SQL Python interface import MySQLdb import MySQLdb.cursors try: db = connect(host='grandcentral', user='cs3995', passwd='cs3995', db='grades') except MySQLdb.Error, e: print "Error %d: %s" % (e.args[0], e.args[1]) sys.exit(1) c = db.cursor() c.execute("SELECT ... FROM ...") results = c.fetchall() # list of tuples c.close()
- 31. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 31 SQL Python interface Results are just tuples, with fields in order of table definition can also fetch one row at a time: c.execute("SELECT firstname,lastname FROM students ORDER BY lastname") print "<ul>" while (1): student = c.fetchone() if student == None: break print "<li>", student, student[0] print "</ul>"
- 32. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 32 Python SQL – dictionary cursor Map rows to dictionary elements instead of list elements: c.close() c = db.cursor(MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor) c.execute("SELECT firstname,lastname FROM students") results = c.fetchall() for row in results: print "%s, %s" % (row["firstname"], row["lastname"]) print "%d rows were returned" % c.rowcount
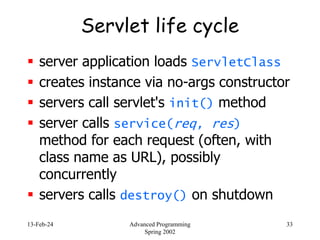
- 33. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 33 Servlet life cycle server application loads ServletClass creates instance via no-args constructor servers call servlet's init() method server calls service(req, res) method for each request (often, with class name as URL), possibly concurrently servers calls destroy() on shutdown
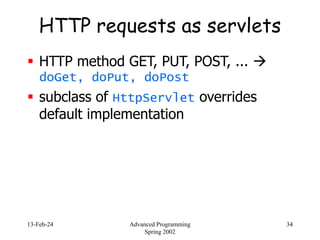
- 34. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 34 HTTP requests as servlets HTTP method GET, PUT, POST, ... doGet, doPut, doPost subclass of HttpServlet overrides default implementation
- 35. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 35 Servlet example import java.io.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; public class HelloClientServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { res.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = res.getWriter(); out.println("<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Hello Client!</TITLE>" + "<HEAD><BODY>Hello Client!</BODY><HTML>"); out.close(); } public String getServletInfo() { return "HelloClientServlet 1.0 by Stefan Zeiger"; } }
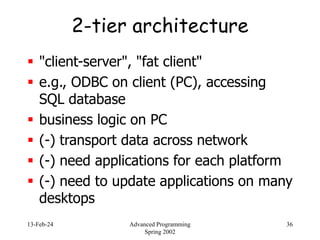
- 36. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 36 2-tier architecture "client-server", "fat client" e.g., ODBC on client (PC), accessing SQL database business logic on PC (-) transport data across network (-) need applications for each platform (-) need to update applications on many desktops
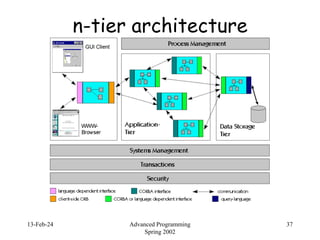
- 37. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 37 n-tier architecture
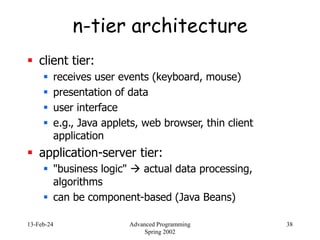
- 38. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 38 n-tier architecture client tier: receives user events (keyboard, mouse) presentation of data user interface e.g., Java applets, web browser, thin client application application-server tier: "business logic" actual data processing, algorithms can be component-based (Java Beans)
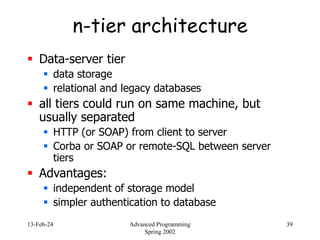
- 39. 13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming Spring 2002 39 n-tier architecture Data-server tier data storage relational and legacy databases all tiers could run on same machine, but usually separated HTTP (or SOAP) from client to server Corba or SOAP or remote-SQL between server tiers Advantages: independent of storage model simpler authentication to database




![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
7
JavaScript – DOM
function tz (f,v) {
var t = -1;
switch (f[v].value) {
case "US": t=128; break;
case "CI": t=0; break;
case "GH": t=1; break;
..
}
if (t != -1) {
f.form.timezone.options[t].selected = true
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-7-320.jpg)









![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
19
Tcl cgi
cgi_body {
h1 "Database view"
set conflist [sql "SELECT
conference,name,url,logo
FROM conference WHERE conference=$c"]
table {
foreach conf $conflist {
maplist $conf c name url logo
table_row {
td "$name"
td "$url"
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-19-320.jpg)

![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
21
cgi python
print "<title>Python cgi script</title>"
print "<body>"
print "<h1>Python script</h1>"
print "Before script"
print sys.path
try:
import cgi
except:
print "error", sys.exc_info()[0]
# only for Python 2.2!
import cgitb; cgitb.enable()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-21-320.jpg)
![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
22
cgi python
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
if not (form.has_key("name")):
print "<form action=pcgi.cgi method=get>"
print "<input type=text name=name size=10>"
print "<input type=submit value=Submit>"
print "</form>"
else:
print "<p>name:", form["name"].value
print "</body>"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-22-320.jpg)


![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
30
SQL Python interface
import MySQLdb
import MySQLdb.cursors
try:
db = connect(host='grandcentral',
user='cs3995', passwd='cs3995',
db='grades')
except MySQLdb.Error, e:
print "Error %d: %s" % (e.args[0], e.args[1])
sys.exit(1)
c = db.cursor()
c.execute("SELECT ... FROM ...")
results = c.fetchall() # list of tuples
c.close()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-30-320.jpg)
![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
31
SQL Python interface
Results are just tuples, with fields in
order of table definition
can also fetch one row at a time:
c.execute("SELECT firstname,lastname FROM
students ORDER BY lastname")
print "<ul>"
while (1):
student = c.fetchone()
if student == None: break
print "<li>", student, student[0]
print "</ul>"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-31-320.jpg)
![13-Feb-24 Advanced Programming
Spring 2002
32
Python SQL – dictionary
cursor
Map rows to dictionary elements instead of
list elements:
c.close()
c = db.cursor(MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor)
c.execute("SELECT firstname,lastname FROM
students")
results = c.fetchall()
for row in results:
print "%s, %s" % (row["firstname"],
row["lastname"])
print "%d rows were returned" % c.rowcount](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-240213063201-2690ae72/85/web-programming-using-html-css-JavaScript-php-etc-32-320.jpg)