02 java programming basic
- 1. IHS GIRLS TECH CLUB • JAVA PROGRAMMING BASICS IHS GIRLS TECH CLUB: JAVA PROGRAMMING BASICS
- 2. A PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE IS... • A language designed for programming computers • Consists of a combination of variables, functions, methods, and instructions for controlling actions in a computer system • Follows a specific syntax for controlling the behavior of a computer or machine • Thousands of different programming languages have been created, with many more being created every year • Description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning)
- 3. POPULAR PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 1. Java – 19.1% (Android) 2. C – 15.2% (iOS uses a version called Objective-C) 3. C++ – 10.1% 4. PHP – 8.7% 5. Visual Basic – 8.4% 6. Perl – 6.2% 7. Python – 3.8% 8. C# – 3.7% (Windows Mobile) 9. JavaScript – 3.1% 10. Ruby – 2.6% 11. Delphi – 2.1%
- 4. WHAT IS JAVA? • A trademark used for a programming language designed to develop applications, especially ones for the Internet, that can operate on different platforms • Created in 1991 by Sun Microsystems Popular programs built in Java
- 5. JAVA PROS AND CONS Pros • Free to use • Cross Platform (write once, run everywhere) • Smaller learning curve (get started faster) Cons • Performance in comparison with some other languages • History of security vulnerabilities
- 6. WHERE JAVA IS BEING USED e-Commerce Websites Computer Desktop Programs Mobile Applications Websites and Web games
- 7. TOOLS TO USE WITH JAVA Code Editor • A source code editor is a text editor program designed specifically for editing source code of computer programs by programmers. Popular Code Editors • Eclipse • Netbeans • Komodo • Notepad++ • Textmate
- 8. TOOLS TO USE WITH JAVA Java Virtual Machine (JVM) - Used for running Java code Java Development Kit (JDK) - is a program development environment for writing Java applets and applications. (USE THIS TO BUILD ANDROID APPS :DDD)
- 9. OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (OPP) Programming language based around real world objects (ie cars, people, etc). Code is grouped into objects so they can be easily reused. This avoids having to write the same code multiple times. Object Oriented Programming is often referred to by using OOP as the shortened version.
- 10. AN OBJECT HAS PROPERTIES Imagine an object that most people can relate to, a car. How can we describe a car?
- 11. Well, it has attributes such as: •Color •Make •Model •Year •Mileage •VIN Each of these attributes make every car what it is. In OOP, attributes, the features that describe an object, are called properties.
- 12. The next question is, what are the actions a car can do, or can be done to the car? Let’s take some of the obvious ones: • Turn the car on • Turn the car off • Accelerate • Brake In OOP, these actions are called methods. They allow the objects to do things. These methods also can provide a way to change the properties of the object. AN OBJECT HAS METHODS
- 13. THE CAR OBJECT In our example, the car is a grouping of properties and methods. Your car is different than your neighbors car. However, they both would share the same properties and methods. OOP allows these logical groupings to happen.
- 14. CREATING AN OBJECT In Java, to create an object you use a special method called a constructor. Once you have created an object, you now have an instance of that object. This process is known as instantiation. In our example, if you create a new car, that car is an instance of the car object. Your neighbor also has an instance of a car object. They both are similar things, but are completely different cars.
- 15. WHAT IS A CLASS? In Java, an object can also be called a class. In our example, our Car Class applies to all instances of cars that have already been created, as well as all cars that will be created in the future.
- 16. SUBCLASSES IN JAVA - A class can be broken down even further into a subclass. - This allows the better organization of objects. - In our example, we can have subclasses for Cars, Trucks, and Busses. - All of these are considered vehicles and share many of the same properties and methods. - This means we can use Vehicle, as the parent class. This makes Cars, Trucks, and Busses, subclasses.
- 18. SUBCLASSES CAN BE DIFFERENT - Not all subclasses are the same. - For example, a Bus may need to have methods for unloading and loading passengers. - A Truck may need properties to keep track of how much weight it can tow - Subclasses already have access to the properties and methods of the parent class. - As an example Cars, Trucks, and Busses can all use the same accelerate or brake methods that are defined in the Vehicle Class, but are given the flexiblity to add their own. - This concept is called inheritance
- 19. OOP SIMPLIFIED - In simple terms, OOP is just a method for building reusable objects (called classes). - Objects are everywhere in your daily life, vehicles, books, desks, computers, etc. - Java takes that approach when building programs. This allows you to write less code and reuse the objects you have already created.
- 20. OOP SUMMARY - Objects (classes) consist of properties and methods - Constructors are used to create objects - Subclassing and inheritance can help you save time by reusing and better organizing your code
- 21. JAVA SYNTAX In computer science, the syntax of a programming language is the set of rules that define the combinations of symbols that are considered to be correctly structured programs in that language.
- 22. SYNTAX BROKEN DOWN Syntax is broken down into four parts 1. Variable type a. Examples: Integer (number), string (letters) 2. Variable name a. Consist of any combination of letters and numbers b. The only special character allowed is an underscore (_) 3. Value a. Value the variable will hold b. Strings are defined by wrapping in quotes (" ") 4. Ending mark a. Marks the code as complete b. Denoted in Java with a semicolon (;)
- 23. SYNTAX EXAMPLE In this example, a variable type of string is used (strings are used to store letters). This variable is given the name helloVariable (this is determined by the developer). The equal sign states that the helloVariable will equal the value which is set to "Hello Everyone!". In other words when the helloVariable name is called, it will output the value of Hello Everyone! Finally, the semicolon closes out the code statement. Variable type - String Variable name - helloVariable Variable value - "Hello Everyone!" Ending mark - ; (semicolon)
- 24. SEMANTICS - What the code actually means - Different programming languages have different syntax, but the semantics (meaning) of the code is essentially the same
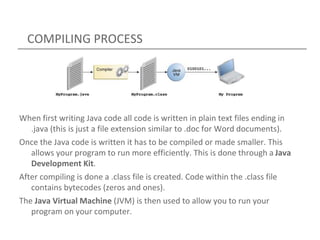
- 25. COMPILING PROCESS When first writing Java code all code is written in plain text files ending in .java (this is just a file extension similar to .doc for Word documents). Once the Java code is written it has to be compiled or made smaller. This allows your program to run more efficiently. This is done through a Java Development Kit. After compiling is done a .class file is created. Code within the .class file contains bytecodes (zeros and ones). The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is then used to allow you to run your program on your computer.
- 26. SUMMARY - Java is one of the most popular programming languages - Java is an Object Oriented Programming (OOP) language - Syntax is broken down into four parts; variable type, variable name, value, and ending mark. - After writing Java code, it is compiled and run through a Java Virtual Machine (JVM)